OCR A M4 core organic chemistry
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Hydrocarbons are made up of _____ and ______ only
carbon, hydrogen
Homologus series
A family of compounds with similar chemical properties, successive members differ by the addition of -CH2 group
functional group
Part of an organic molecule responsible for chemical properties
Some or all carbon atoms found in a benzene ring
aromatic
Carbon atoms form a ring with or without branches
alicyclic
A hydrocarbon with carbon atoms joined together in straight or branched chains.
aliphatic
Unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least 1 double carbon bond
alkene
Unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least 1 triple carbon bond
alkyne
saturated hydrocarbon containing single carbon bonds
alkane
a formula denoting the number of atoms in a molecule
molecular
simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound
empirical formula
The simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series
general
shows the relative positioning of atoms and bonds
displayed formular
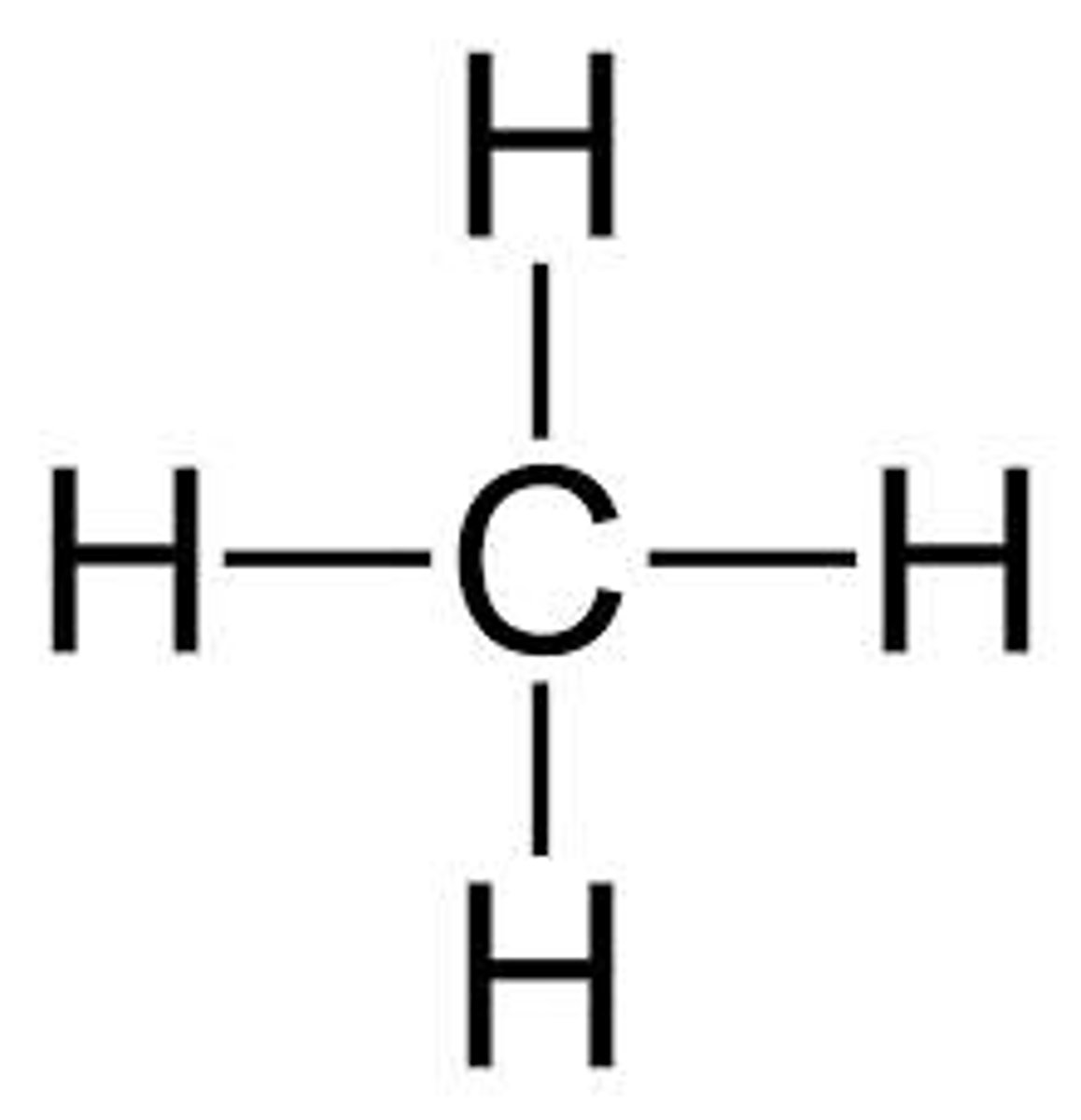
arrangement of atoms using the smallest level of detail
structural formula eg (CH3CH2CH3)
simplified organic formula
skeletal
same molecule formula but different structural formula
structural isomer
breaking covalent bonds process
bond fission
each atom has a single unpaired electron and 2 radicals are formed
homolytic fission
An atom takes both electrons, leaving one positive and one negative ion
heterolytic fission
A molecule is added to an unsaturated alkene
addition reaction
an atom/group of atoms is replaced by an atom/group of atoms
substitution reaction
the removal fo a small molecule from a larger one
elimination reaction
arrow representing the movement of a single, unpaired electric in mechanisms
curly arrow
an atom or groups of atoms with an unpaired electron
radical
are c-c bonds polar or non-polar
non-polar
alkanes produce carbon dioxide and water through what process
complete combustion
alkanes produce what in incomplete combustion?
CO, C, CO2 and H2O
alkanes react with ______ in the presence of UV (sunlight)
halogens
three stages of halogenation
initiation, propagation, termination
alkanes reacting with halogens is called
halogenation
mechanism for bromination of methane is called...
radical substitution
having the same structural formula but a different arrangement of the atoms in space
structural isomerism
E/Z isomerism only occurs in compounds which have a _______ bond
C=C double bond
rotation around a C=C bond is _____
restricted
conditions for hydrogenation of alkenes
- nickel catalyst
- 423 K
alkene mixed with hydrogen
hydrogenation
conditions for halogenation of alkenes
R.T.P
alkenes undergo a rapid reaction with halogens (Bromine or Chlorine)
halogenation
test for unsaturation
bromine water orange to colourless
addition reaction of alkenes and hydrogen halides conditions
gaseous hydrogen halide
If alkene is a gas for reaction with hydrogen halide, it is...
mixed with the hydrogen halide gas
If alkene is a liquid for reaction with hydrogen halide, the hydrogen halide is...
bubbled through the liquid
reaction of alkenes with steam
hydration reaction
conditions for a hydration reaction
- water must be in gaseous form
- phosphoric acid catalyst H3PO4
example of hydration reaction in industry
hydration of ethene to make ethanol
an atom or group of atoms which is attracted to a region of electron deficiency, where it donates an electron pair
nucleophile
an atom or group of atoms which is attracted to a region of electron density, where it accepts an electron pair.
electrophile
aldehyde suffix
-al
ketone suffix
-one
acyl chloride suffix
-oyl chloride
amine suffix
-amine
nitrile suffix
-nitrile
ester suffix
-oate
aldehyde functional group
-CHO
Ketone functional group
-C(CO)C-
ester functionalwhy group
C=O
acyl chloride functional group
-COCl
Amine functional group
-NH2
Nitrile functional group
-CN
a radical is different from an ion because a radical isn't necessarily ______
charged
C-H bonds are polar/non-polar
non-polar
C-C bonds are polar/non-polar
non-polar
alkanes are used as fuels because they are readily _____, easy to _____ and release _________ products in a plentiful supply of _____
available, transport, non-toxic, oxygen
stereoisomers which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other
optical isomers
propane is an example of an....
alkane
methylpropane is an examples of a ....
branched alkane
propene is an example of an....
alkene
chloroethane is an example of a...
haloalkane
ethanol is an example of an...
alcohol
ethanal is an example of an...
aldehyde
propanone is an example of a...
ketone
cyclohexane is an example of a...
cycloalkane
ethanoic acid is an example of a...
carboxylic acid
methyl propanoate is an example of an...
ester
unsaturated compounds can have carbon-carbon ____ bonds, ____ bonds, or _____ groups
double, triple, aromatic
an alkyl group is a ____ of a molecule with general formula _______
fragment, CnH2n+1
three different types of structural isomers
chain, positional, functional group
chain isomers have different _____ properties but similar _____ properties
physical, chemical
positional isomers have the ______ _____ positioned on different carbon atoms
functional group
positional isomers have different ____ properties and might have different _____ properties
physical, chemical
isomers with different chemical and physical properties
functional group isomers
isomers with different physical properties and similar chemical properties
chain isomers
isomers with different physical properties and might have different chemical properties
positional
_____ isomers have the same atoms but arranged into different functional groups
functional group
atoms can rotate as much as they like around a _____ bond
c-c single
bond angle in alkanes
109.5
bonding shape around carbon atoms in alkanes
tetrahedral
between alkanes, there are induced _____-______ interactions also called _____ forces which hold them together
dipole-dipole, london
a branched-chain alkanes has a _____ boiling point than its straight-chain isomer
lower
dipole-dipole interactions are________ in branched-chain isomers as there are smaller ________ surface areas
reduced, molecular
carbon monoxide is better at binding to ______ than oxygen which leads to oxygen _______
haemoglobin, deprivation
halogens react with alkanes in _______ reactions which are started by ultraviolet light to get going
photochemical
a hydrogen atom is substituted by chlorine or bromine in an _______ ________ reaction
free-radical substitution
how is a sigma bond made?
the direct overlapping of a sigma bond
How is a pi bond formed?
bond formed by the sideways overlap of two adjacent p orbitals
____ bonds are much weaker than ____ bonds because the electron density is spread out above and below the nuclei
pi, sigma
alkenes are much more reactive than _____ due to:
- bonds are ______-_____
- C-C and C-H bonds are _____ bonds
alkanes, non-polar, sigma
alkene double bond opens up and atoms are added to the carbon atoms
electrophilic addition
electrophiles include ______ charged ions and _____ molecules
positively, polar
Markovnikov's Rule
the major product from additional of a hydrogen halide to an unsymmetrical alkene is the one where hydrogen adds to the carbon with the most hydrogens already attached