physio - efferent division
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Q: What are the two divisions of the efferent nervous system?
A:
1. Somatic nervous system (SNS) – Controls voluntary skeletal muscle movements.
2. Autonomic nervous system (ANS) – Controls involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion.
Q: What is the main function of the efferent division?
A: To send motor commands from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands).
Q: What are the two branches of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
A:
1. Sympathetic division – “Fight or flight” response.
2. Parasympathetic division – “Rest and digest” response.
Q: How does the efferent division differ from the afferent division?
A:
• Efferent division: Sends motor signals from CNS to effectors.
• Afferent division: Sends sensory signals from receptors to CNS.
Q: How does the somatic nervous system (SNS) differ from the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
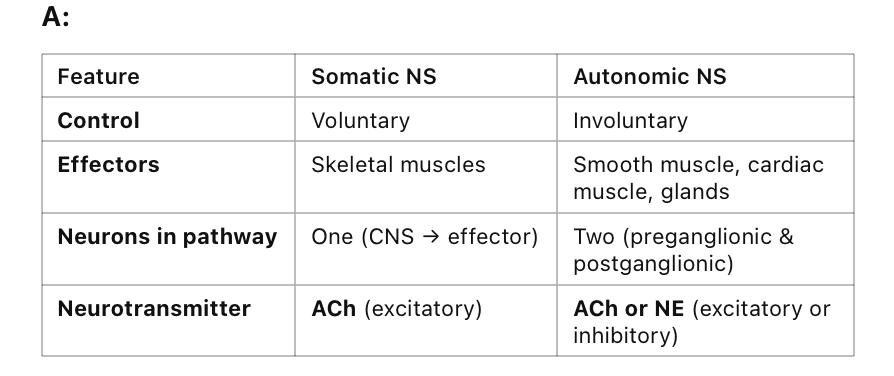
Q: What type of neurotransmitter does the somatic nervous system use?
A: Acetylcholine (ACh), which always excites skeletal muscle.
Q: What is a key difference in neural pathways between the SNS and ANS?
A:
• SNS: A single motor neuron directly innervates skeletal muscle.
• ANS: Uses two neurons (preganglionic & postganglionic) to reach effectors.
Q: What are the general functions of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS)?
A: “Fight or flight” – Prepares the body for emergency responses:
• ↑ Heart rate & blood pressure
• Bronchodilation (airway expansion)
• Increased glucose release
• Reduced digestion & urination
Q: What are the general functions of the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)?
A: “Rest and digest” – Promotes relaxation and energy conservation:
• ↓ Heart rate & blood pressure
• Bronchoconstriction (airway narrowing)
• Increased digestion & urination
• Energy storage
Q: Where do sympathetic preganglionic neurons originate?
A: In the thoracolumbar region (T1–L2 of the spinal cord).
Q: Where do parasympathetic preganglionic neurons originate?
A: In the brainstem and sacral spinal cord (craniosacral division).
Q: What are the two types of autonomic neurons in the ANS pathway?
A:
1. Preganglionic neurons – Originate in the CNS, release ACh, and synapse in autonomic ganglia.
2. Postganglionic neurons – Originate in ganglia, release either ACh or norepinephrine (NE) to target organs.
Q: What neurotransmitter is released by preganglionic neurons in both the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems?
A: Acetylcholine (ACh).
Q: What neurotransmitter is released by postganglionic neurons?
A:
• Sympathetic postganglionic neurons → Norepinephrine (NE).
• Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons → Acetylcholine (ACh).
Q: Where are autonomic ganglia located in the sympathetic vs. parasympathetic systems?
A:
• Sympathetic ganglia: Near the spinal cord.
• Parasympathetic ganglia: Near or inside the target organs.
Q: How is the adrenal medulla unique in the sympathetic nervous system?
A: Instead of a postganglionic neuron, it directly releases hormones (epinephrine & norepinephrine) into the bloodstream.
Q: What is the function of the adrenal medulla in stress responses?
A:
• Releases 80% epinephrine & 20% norepinephrine into circulation.
• Amplifies the fight-or-flight response.
• Prolongs sympathetic effects beyond synaptic transmission.
Q: What are the two main types of cholinergic receptors?
A:
1. Nicotinic (nAChR) – Found in autonomic ganglia & neuromuscular junctions (ionotropic, fast).
2. Muscarinic (mAChR) – Found in parasympathetic target organs (metabotropic, slower).
Q: What are the three types of adrenergic receptors, and their effects?
A:
1. α1 receptors → Vasoconstriction (increased blood pressure).
2. β1 receptors → ↑ Heart rate & contractility.
3. β2 receptors → Bronchodilation & skeletal muscle vasodilation.
Q: Which receptor is responsible for bronchodilation?
A: β2 adrenergic receptor.
Q: Which receptor increases heart rate and contractility?
A: β1 adrenergic receptor.
Q: Which receptor causes pupil constriction?
A: Muscarinic (mAChR) receptor.
Q: Which receptor causes vasoconstriction in the skin & mucosa?
A: α1 adrenergic receptor.
Q: Which receptor is found at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)?
A: Nicotinic (nAChR) receptor.
Q: What type of drugs block sympathetic activity?
A: Beta-blockers (e.g., propranolol) – Block β1 receptors, reducing heart rate & blood pressure.
Q: What type of drugs enhance parasympathetic activity?
A: Cholinergic agonists (e.g., pilocarpine) – Activate muscarinic receptors to increase digestion & urination.
Q: What type of drugs increase sympathetic effects?
A: Adrenergic agonists (e.g., albuterol) – Activate β2 receptors for bronchodilation.