Lab 4 Review: Bryophytes & Seedless Vascular
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Bryophytes include
mosses
liverworts
hornworts
Bryophyte adaptations for terrestrial life
1) cuticle: sterile jack layer around reproductive structures
2) antheridia/archegonia: embryo protected from desiccation (drying out)
3) Spores can go dormant
Do Bryophytes have vascular tissues (xylem/phloem)?
No
What do bryophytes have in place of leaves and stems?
rhizoids and a thallus
In haplodiplontic life cycles, what is the dominant 1N generation called?
Gametophyte
In haplodiplontic life cycles, what is the dominant 2N generation called?
Sporophyte
Liverworts adaptations
cutinized surface = reduced water loss
open pores (can NOT close) on thallus = gas exchange
Liverwort reproduction
Asexual
gemmae cups
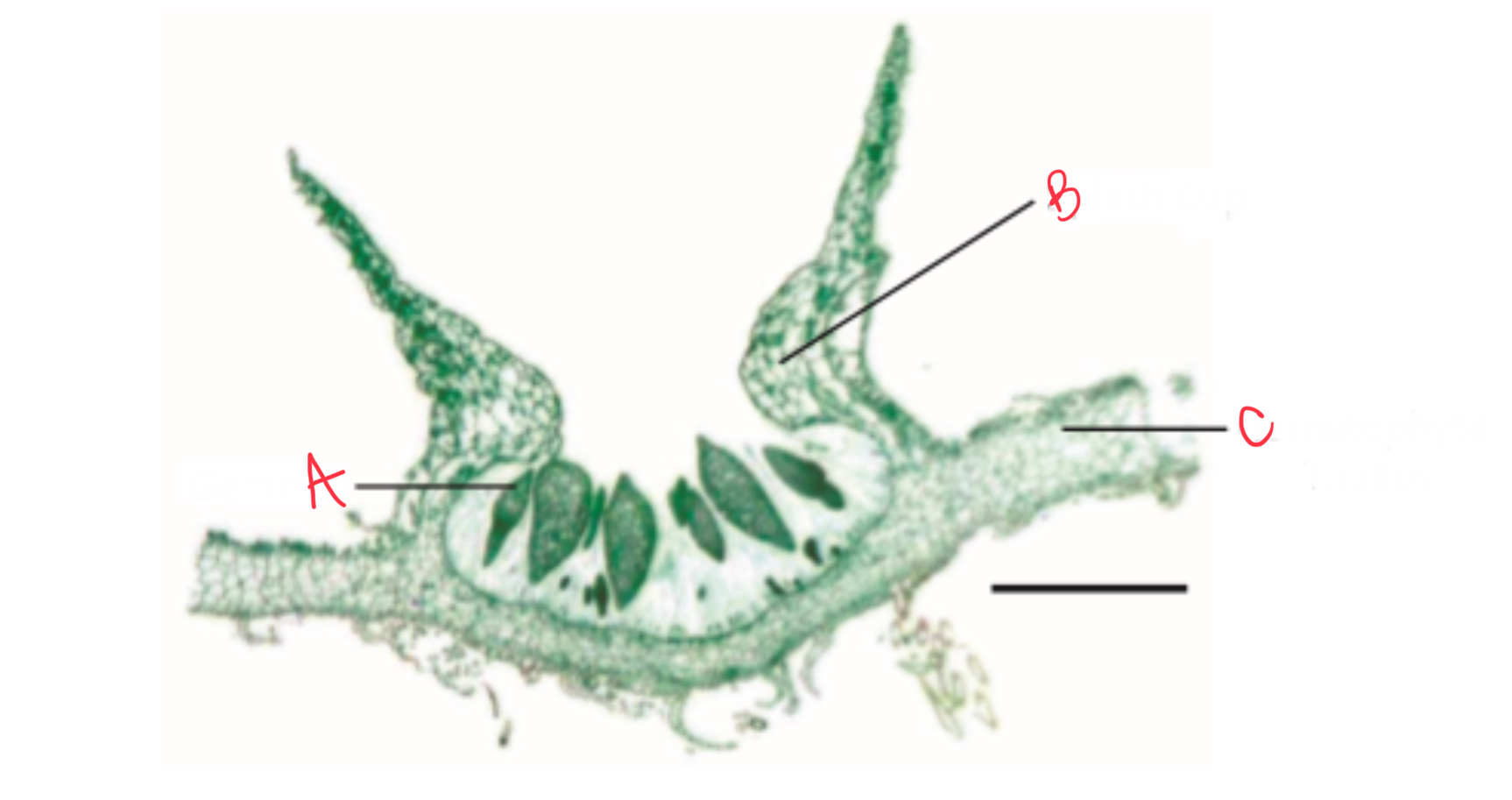
Identify the reproductions structures on liverwort
A) Gemma
B) Splash cup
C) Gametophyte thallus
Define dioecious
(“two houses”) Male and female parts exist on different plants
Archegonium
Female structure: contains 1 egg
Antheridium
Male reproductive structure: contain swimming sperm
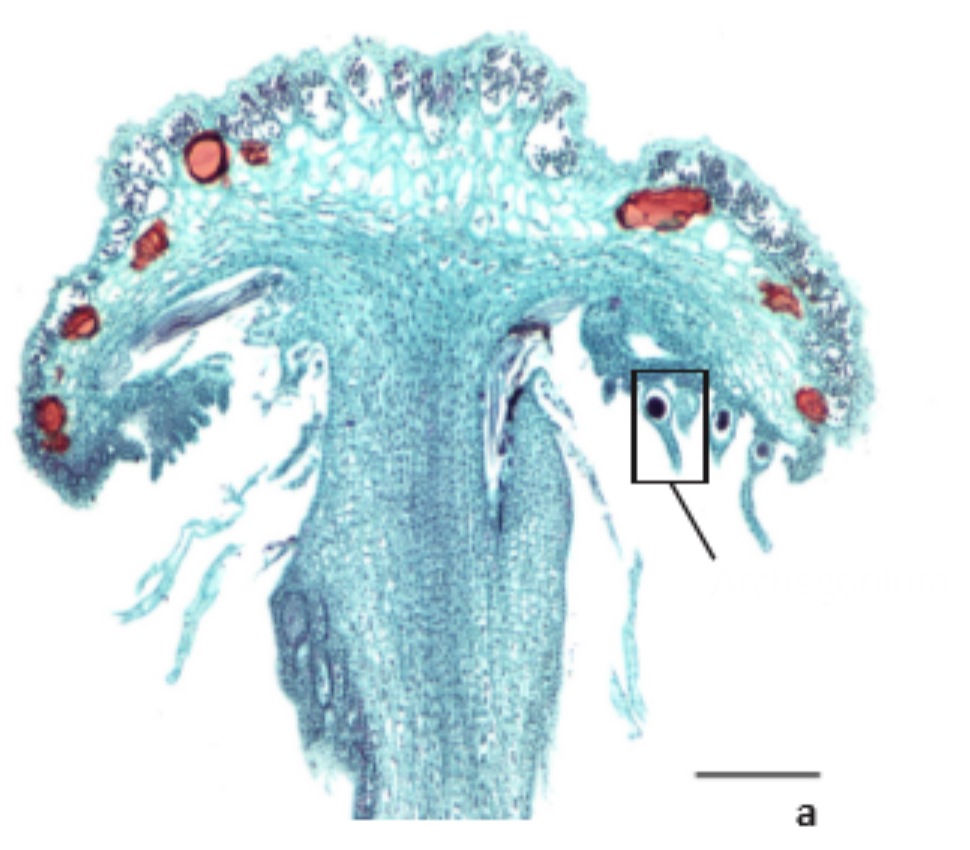
Identify the depicted structure
Archegonia
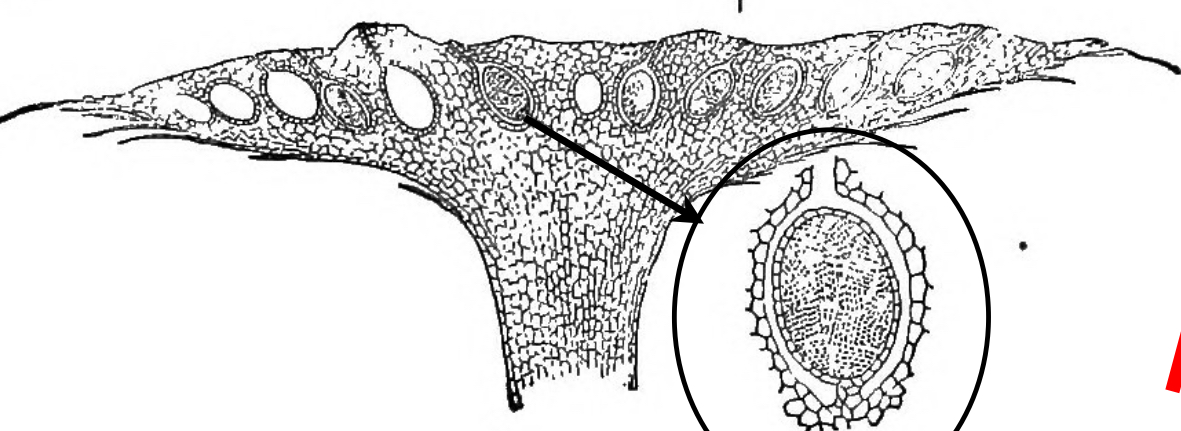
Identify the structure
Antheridia
True mosses adaptations
stomata on sporophyte (not gametophyte) = generally stay open
Conducting cells (growing vertically)
Which generation is dominant in true mosses
gametophyte
Ecological roles of Bryophyta
freezing and desiccation in harsh conditions
carbon sink - add living carbon to soil
pioneer species - stabilize soil and reduce erosion
some hornworts have:
stomata
cutin
nostoc
Hornworts dominant generation
sporophyte (2n)
Derived traits of seedless vascular plants
stems, roots, leaves
dominant sporophyte
vascular tissue
What kind of environment do seedless vascular plants thrive in?
Wet environment (swimming sperm)
Club mosses are NOT
true moss
Characteristics of club mosses
microphylls (“leaves”)
rhizomes (not roots)
asexual AND sexual reproduction
some heterospores
Identify the organism and the structures of this depicted
Club moss
a) spore
b) sporophyll
c) sporangium
What genus is the only one found among horsetails?
Equisetum
What type of rhizomes do horsetails have?
horizontal
What is special about the stems of horsetails?
They’re photosynthetic
What are elators?
Surface extensions on the spores of horsetails that move in response to humidity
What do the epidermal cells of horsetails contain?
silica (good scrubbers)
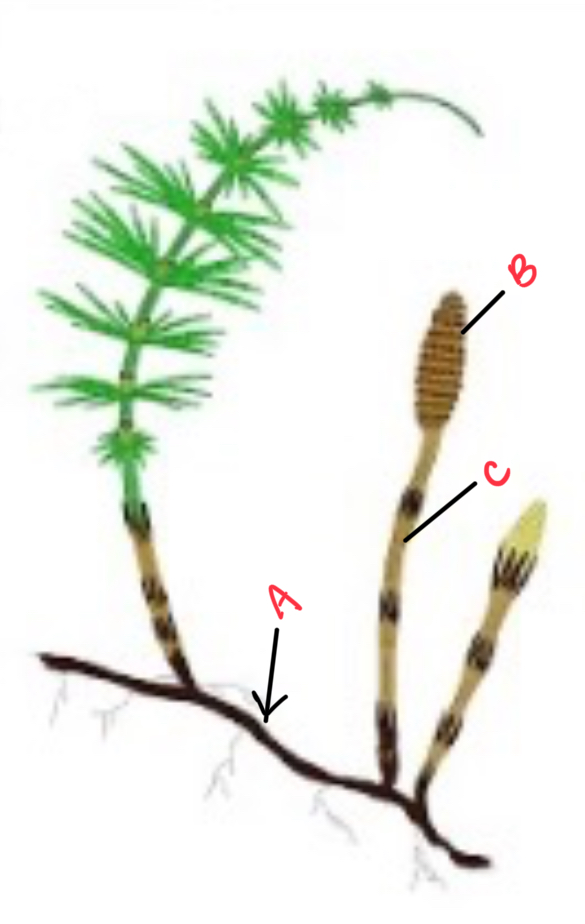

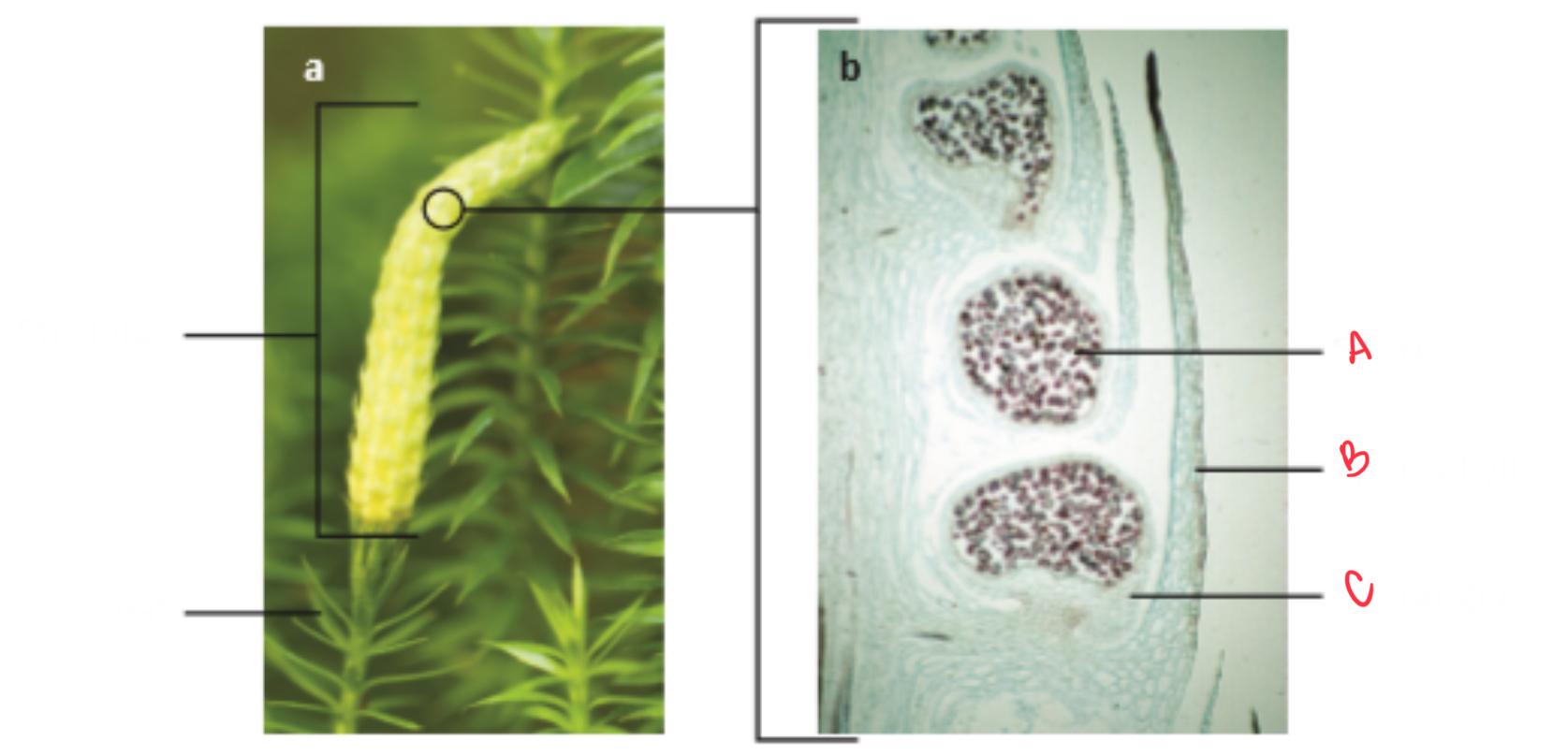
Identify the organism and the structures depicted
Horsetail
a) rhizome
b) strobilus
c) stem
Where are the sporangia located on horsetails?
sporangiosphores located in strobilus
Dominant generation in ferns
sporophyte
Adaptations in the ferns:
vascular tissues (xylem/phloem)
stomata on leaves
lignin in cell walls
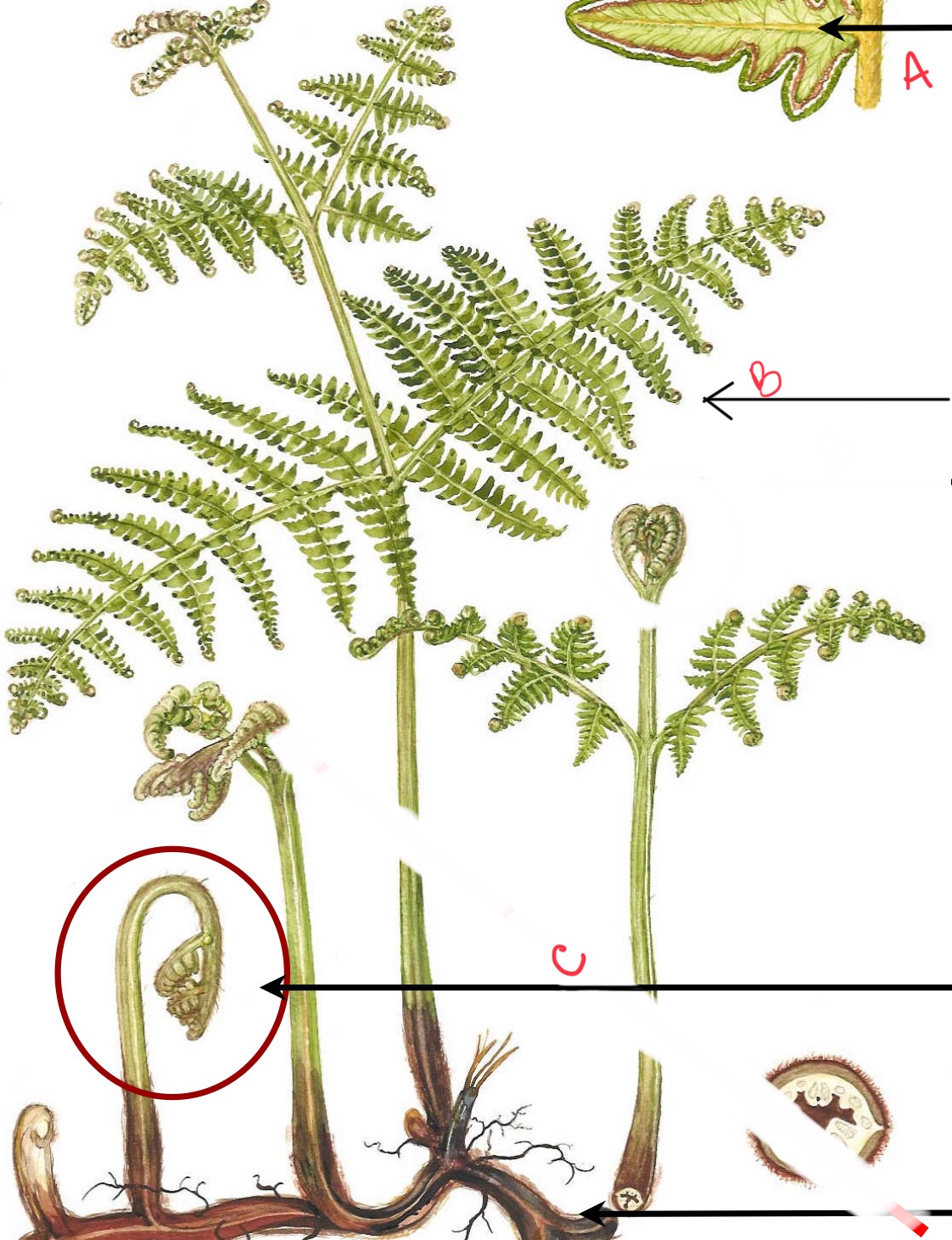
Identify the organism and the structures indicated
Fern
a) leaflet/pinnule
b) frond
c) fiddlehead
What are the frond spores called and where are they located?
sori; underside of fronds
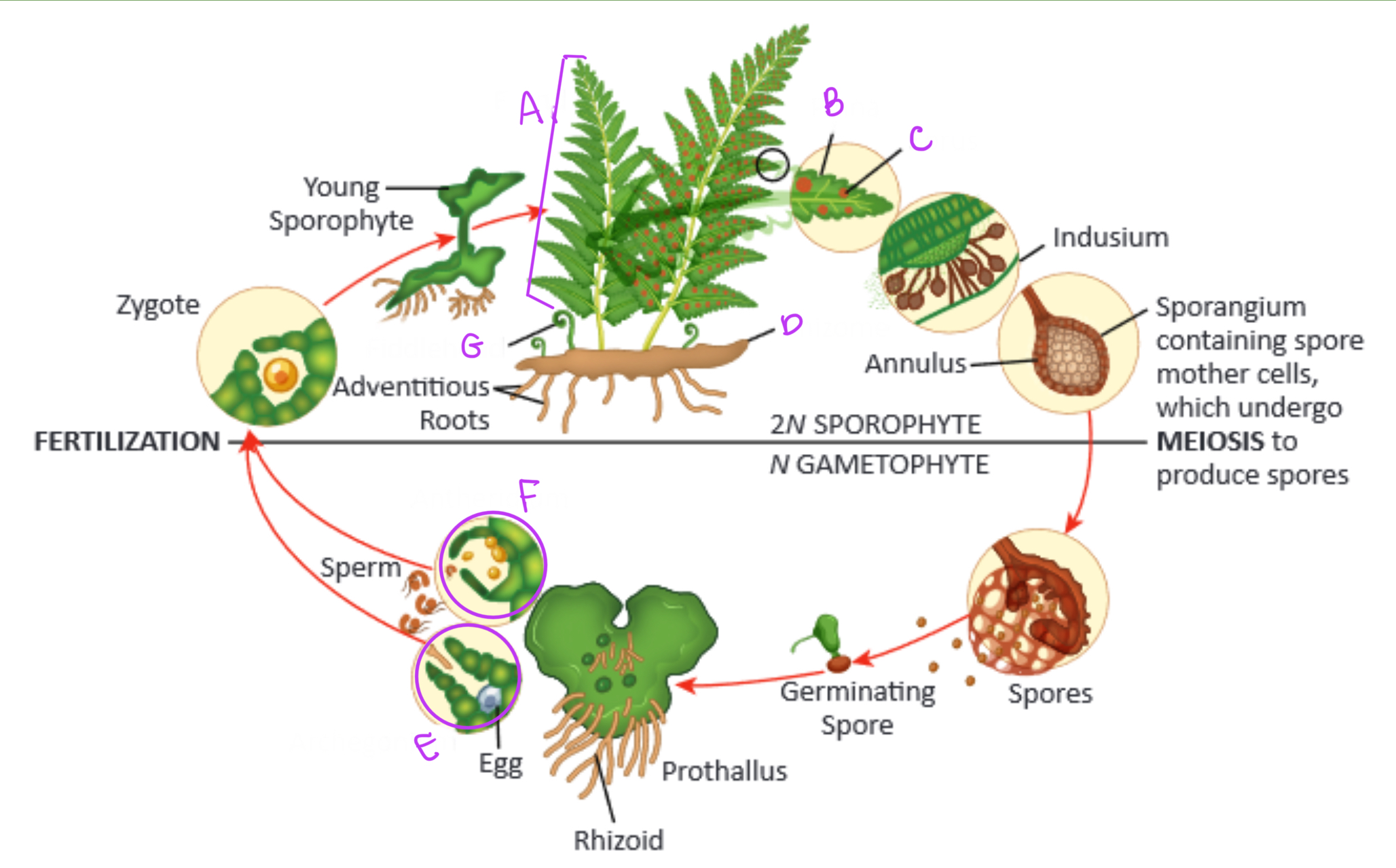
Identify the parts of the fern within its life cycle
a) frond
b) leaflet/pinnae
c) sori
d) rhizome
e) archegonia
f) antheridia
g) fiddlehead