IB Bio SL Y1 Unit 2
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
variation
differences within a species
sexual reproduction
leads to more variation
asexual reproduction
leads to less variation
morphological species concept
defines a species as a group that shares physical characteristics
ignores reproductive isolation
biological species concept
defines a species as having the ability to interbreed and produce fertile and viable offspring
doesn’t apply to asexual organisms
ex: mules
bacterial conjugation
allows for inter-species breeding
binomial nomenclature
genus name, species name
genome
all of the genes in an organism
single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
the replacement of one nucleotide with another
creates variation within a species
haploid
1 copy of each chromosome
diploid
two copies of each chromosome
chromosome fusion
chromosome 12 and 13 from chimpanzees fused to make chromosome 2 in humans
karyogram
number, size, and shape of chromosomes (karyotype)
aneuploidy
abnormal number of chromosomes
monosomy
only 1 copy of a specific chromosome
trisomy
having 3 copies of a specific chromosome
trisomy 21
three copies of chromosome 21
down syndrome
homologous chromosomes
matched pairs of chromosomes
autosomes
chromosomes that aren’t sex chromosomes
locus/loci
the location of a gene/chromosome
alleles
genes
dichotomous key
used to identify unknown organisms or objects by observing their characteristics
taxonomy
naming, classifying, and describing organisms based on shared characteristics
carl woese
defined the archaea domain through the taxonomy of 60S ribosomal dna
kingdom eubacteria
bacteria domain, prokaryotic, unicellular, rigid cell wall with peptidoglycan, autotroph, asexual, can move, lives everywhere
autotroph
creates its own food
kingdom archaebacteria
domain archaea, prokaryotic, unicellular, rigid cell wall without peptidoglycan, chemautotroph, asexual, some mobile with flagellum, survives in extreme habitats
chemautotroph
creates food from organic compounds
kingdom animalia
domain eukarya, eukaryotic, multicellular, no cell wall, heterotroph, sexual, can move, terrestrial and aquatic
heterotroph
creates food from other organisms
kingdom plantae
domain eukarya, eukaryotic, multicellular, cell wall made of cellulose, autotrophic, asexual and sexual, cannot move, terrestrial or aquatic
kingdom fungi
domain eukarya, eukaryotic, multicellular, cell wall made of chitin, heterotrophic, sexual and asexual, can’t move, terrestrial or aquatic
kingdom protista
domain eukarya, eukaryotic, unicellular or multicellular, some cell wall, autotrophic or heterotrophic, sexual and asexual, aquatic
cladogram
a way to represent the evolutionary relationship between species based on shared traits and/or genetic evidence
clade
a group of species with a single common ancestor and a set of common traits
node
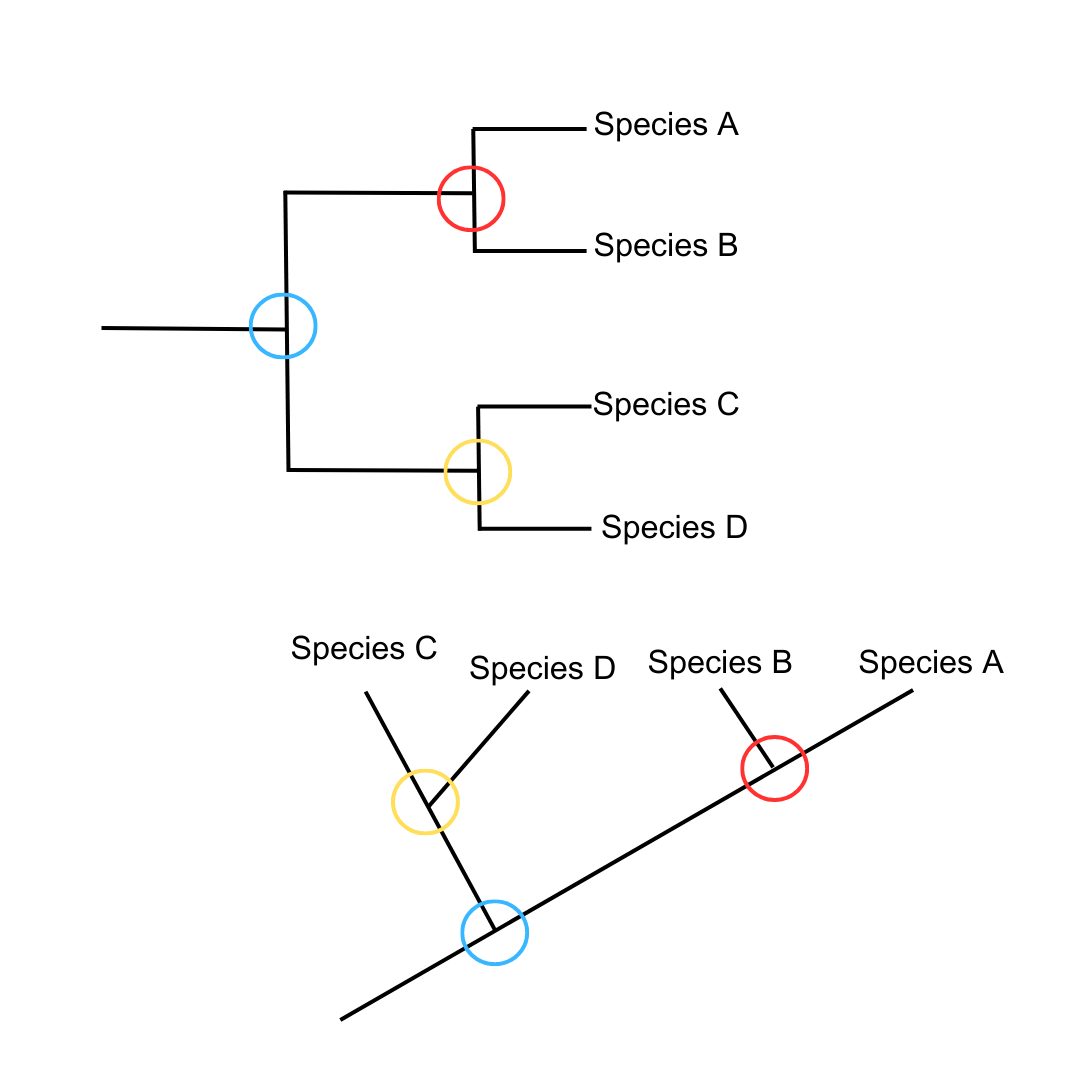
root
common ancestor shared by whole cladogram
outgroup
most distantly related species in the cladogram
figwort family
recently reclassified using cladistics
evolution
change in the heritable characteristics of a population over time
mechanisms of evolution
natural selection, gene flow, genetic drift, mutation
natural selection
organisms with successful selections will survive
sexual selection
direct competition in attracting a mate
gene flow
when organisms from one area move to another
genetic drift
change in gene frequencies due to chance
bottleneck effect
when an event drastically reduces the size of a population, leading to less genetic diversity
founder effect
when a new population is created by a small number of individuals, leading to less genetic diversity
mutation
any changes in the gene frequencies of an organism
often caused by mistakes in DNA copying
evidence of evolution
molecular data, selective breeding, comparative anatomy, embryology, biogeography, and fossil record
molecular data
analyzing dna and amino acid sequences
molecular clock
molecular clock
an estimation of the length of time since speciation occurred
comparative anatomy
homologous structures, analogous structures, and vestigial structures
homologous structures
structures inherited from a single common ancestor
analogous structures
structures that have similar functions but are not related
vestigial structures
structures that have lost their original purpose
embryology
studying organisms from the start of fertilization
biogeography
the branch of biology that deals with the geographical distribution of plants and animals.
convergent evolution
when different species independently evolve similar traits due to similar environments
divergent evolution
when organisms that share a common ancestor develop different traits due to different environments
adaptive radiation
rapid diversification of a single ancestral species due to environment
fossil record
the totality of all fossils collected and arranged in chronological order, forming a historical account of life on Earth
law of superposition
the oldest layers of sedimentary rock are at the bottom
radiometric dating
how scientists determine the age of rocks and fossils
transitional fossils
show intermediate traits between an ancestral form and its descendants
speciation
the process by which two species split creating a new species
allopatric speciation
speciation that occurs in different location
sympatric speciation
speciation that occurs in the same location
process of speciation
one species becomes reproductively isolated from the other, then the two populations become different species
prezygotic barrier
obstacle to mating/fertilization
geographic isolation
physical barrier separating populations
the congo river
chimpanzees and bonobos got separated, becoming two different species
temporal isolation
different mating seasons/times/days
behavioral isolation
different mating behaviors
mechanical isolation
different structures
postzygotic barrier
prevents offspring from developing properly
reduced hybrid fertility
hybrids aren’t fertile
reduced hybrid viability
hybrids aren’t viable
hybrid breakdown
the first generation of hybrids are fertile, but subsequence generations are sterile
gradualism
gradual speciation
punctuated equilibrium
sudden/quick speciationx
polyploidy
more than 2 copies of each chromosome
lamarck’s theory of evolution
acquired traits are passed down to your offspring
darwin’s theory of evolution
natural selection
elements of natural selection
mutation/variation, competition, fitness, and adaptation
competition
organisms fight for mates/resources
fitness
a measure of reproductive success
survival of the fittest
only those with favorable traits will survive
adaptation as a process
over time, populations change so there is a higher percentage of organisms with favorable traits
adaptation as a characteristic
any variation that helps an organism survive
structural adaptation
variations in the body of an organism
behavioral adaptation
variations in the behavior of an organism
physiological adaptation
variations in the metabolic processes of an organism
selective pressures
choose what traits are beneficial/detrimental
stipulations of natural selection
individuals don’t evolve, populations do
only works on traits where variation exists
must be studied in context
relies on differential reproductive success
birds of paradise
bright feathers to attract a mate (sexual selection)
gene pool
all of the genes within a species
neo-darwinism
evolution occurs gradually due to natural selection and genetic variation
directional selection
one extreme is favored over the other
disruptive selection
both extremes are favored
stabilizing selection
the middle is favored over both extremes