PDA Lecture 27: Toxicology: Toxidromes lecture 2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
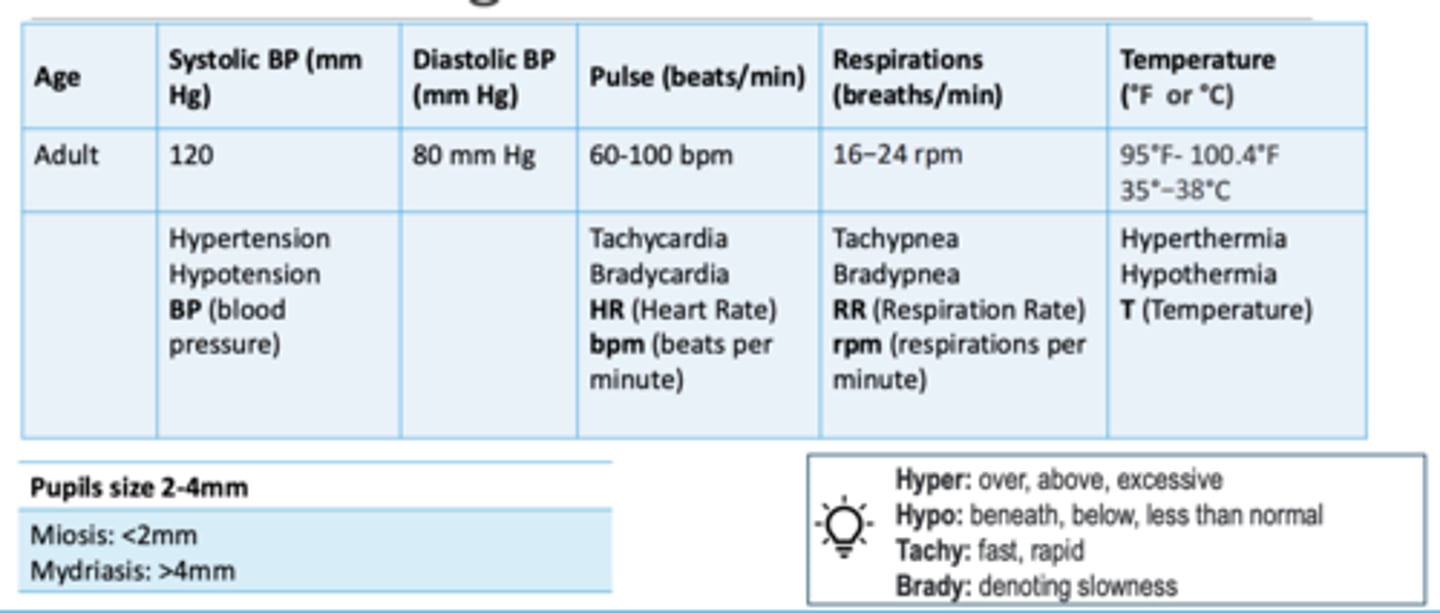
Normal vital signs chart (review)
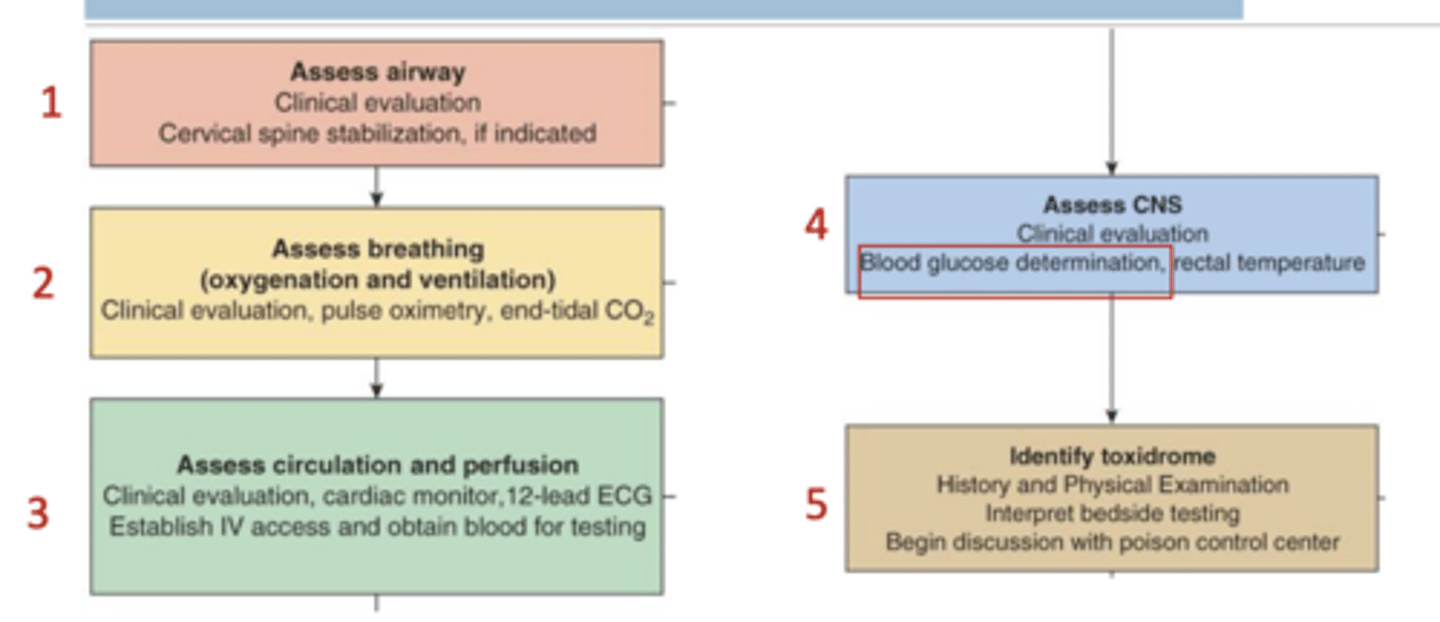
Basic Guide of the Poisoned Patient (review)
Common Mental Status in Overdose Patients: Agitation
A state of heightened psychomotor activity, restlessness, and emotional tension
Common causes: Sympathomimetics, anticholinergics, withdrawal syndromes
Common Mental Status in Overdose Patients: Delirium
An acute, fluctuating disturbance in attention, awareness, and cognition. Often includes confusion and hallucinations
Common causes: Anticholinergics, sedative-hypnotic withdrawal, organophosphates, severe infections
Common Mental Status in Overdose Patients: Psychosis
A loss of contact with reality, often involving hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized thinking
Common causes: Hallucinogens (LSD, PCP), amphetamines, synthetic cannabinoids, anticholinergics
Common Mental Status in Overdose Patients: Euphoria
Intense feelings of pleasure, well-being, or excitement
Common causes: Opioids, stimulants, some hallucinogens
Common Mental Status in Overdose Patients: Somnolence
Drowsiness or sleepiness; patient is easily arousable but may fall asleep without stimulation
Common causes: Opioids, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, sedatives
Common Mental Status in Overdose Patients: Stupor
A state of unresponsiveness from which the patient can only be aroused with vigorous or painful stimulation
Common causes: High-dose sedatives, opioids, ethanol, barbiturates
Common Mental Status in Overdose Patients: Coma
A deep state of unconsciousness in which the patient cannot be aroused by any external stimulus
Common causes: Severe opioid overdose, large sedative/hypnotic ingestion, hypoglycemia, or hypoxia
Common Mental Status in Overdose Patients: Confusion
A lack of clarity in thinking, disorientation, or inability to concentrate
Common causes: Anticholinergics, sedatives, hypoglycemia, serotonin syndrome
Toxidromes describe the groups of signs and symptoms that consistently result from a group of toxins or drugs
describe the groups of signs and symptoms that consistently result from a group of toxins or drugs
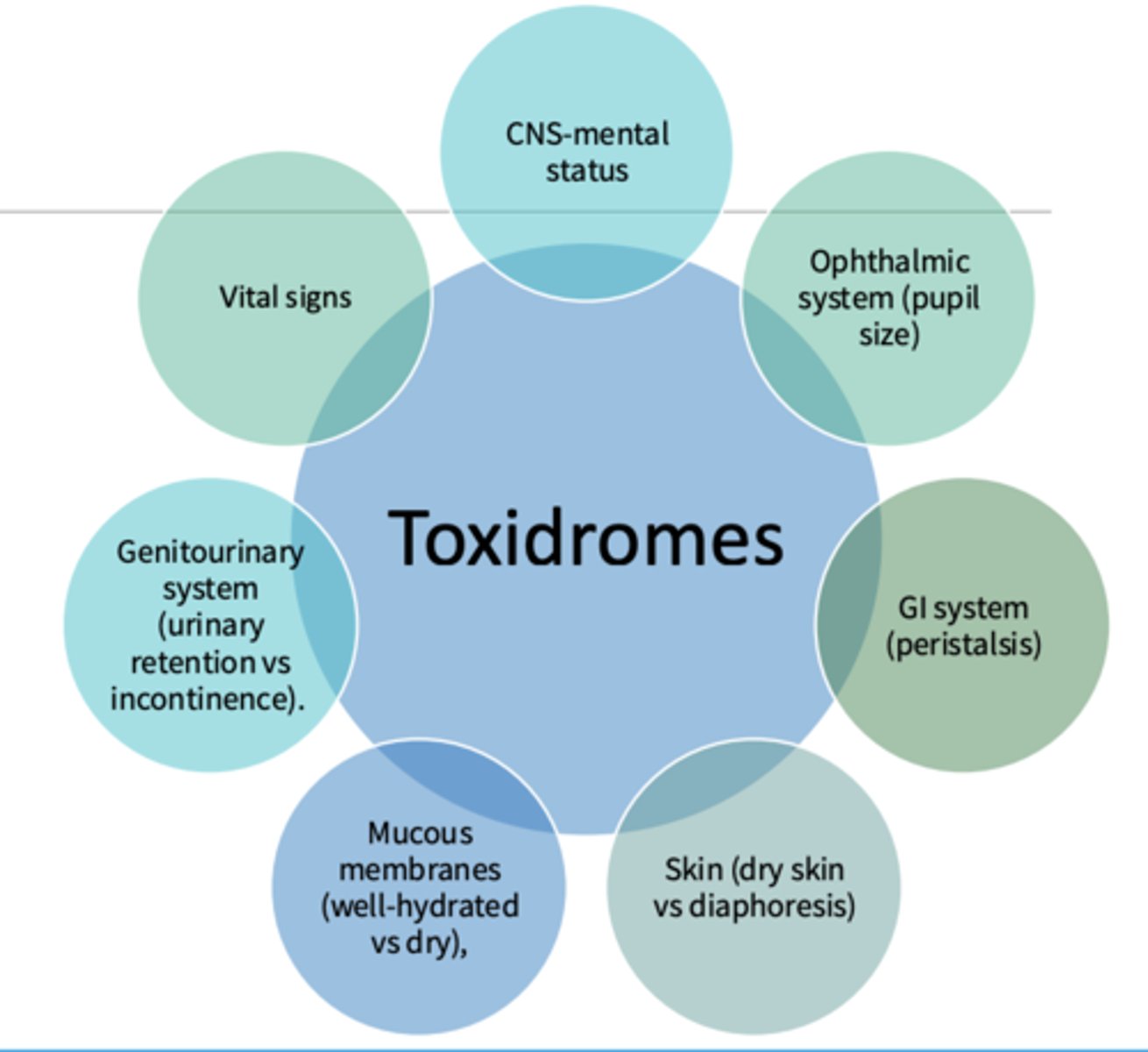
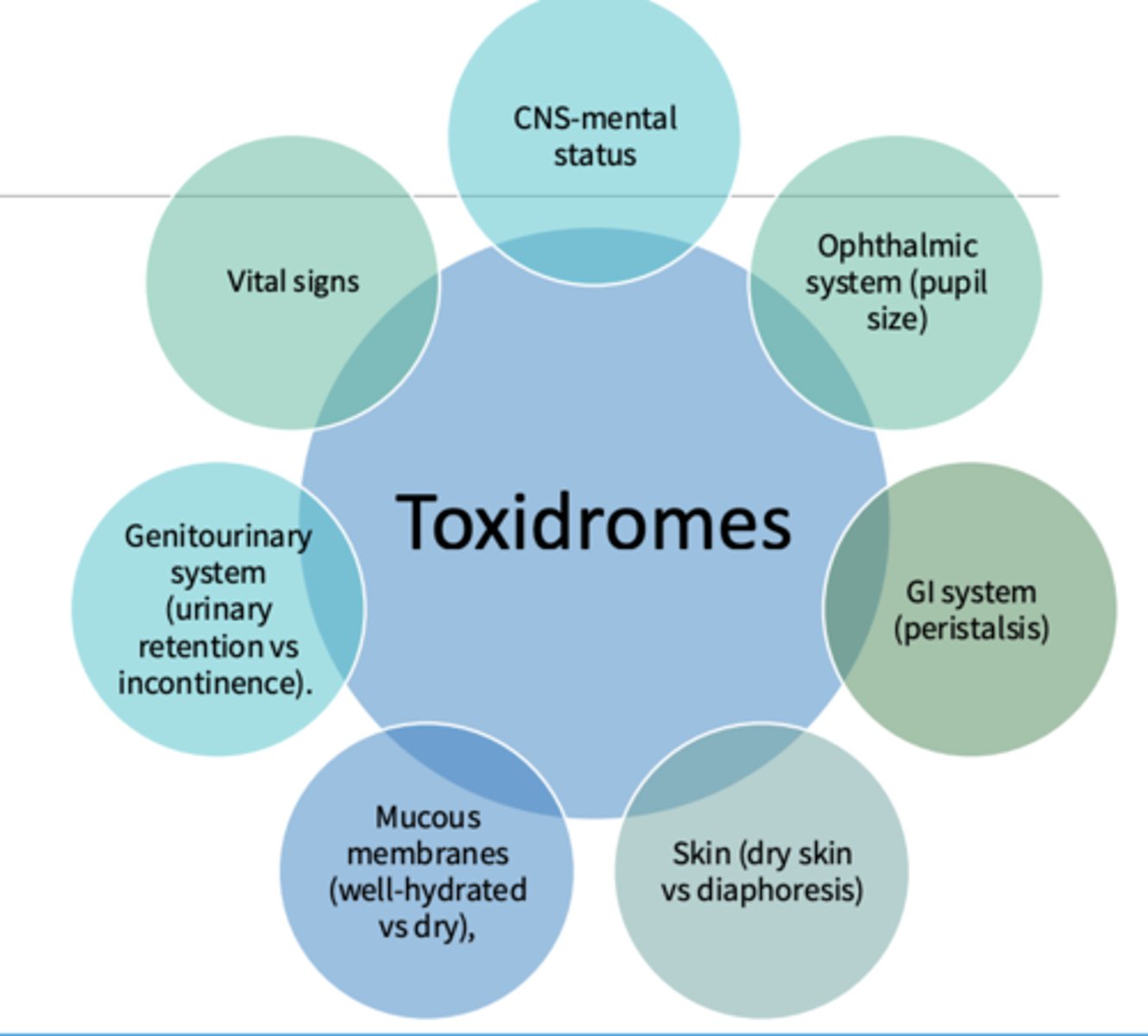
Toxidrome examples (7_
- CNS-mental status
- Ophthalmic system (pupil size)
- GI system (peristalsis)
- Skin (dry skin vs diaphoresis)
- Mucous membranes (well-hydrated vs dry)
- Genitourinary system (urinary retention vs incontinence)
- Vital signs
Peristalsis
The involuntary constriction and relaxation of the muscles of the intestine
Diaphoresis
excessive sweating due to a secondary condition
Toxidromes are a constellation of f signs and symptoms associated with exposure to a specific class or group of toxins or drugs including... (5)
- Anticholinergic
- Cholinergic
- Opioids
- Serotonin toxicity
- Sympathomimetics

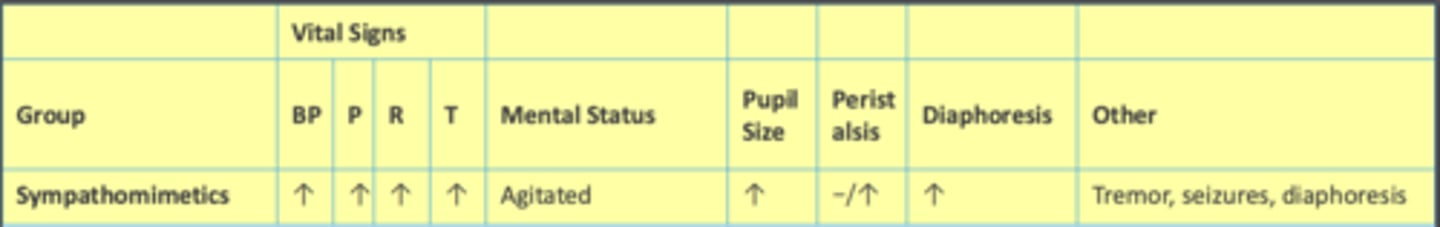
How sympathomimetics affect vital signs, mental status, etc.:
BP:
Pulse:
Respirations:
Temperature:
Mental Status:
Pupil size:
Peristalsis:
Diaphoresis
Other:
BP: increased
Pulse: increased
Respirations: increased
Temperature: increased
Mental Status: agitated
Pupil size: increased
Peristalsis: may not change or may increase
Diaphoresis: Increased
Other: tremor, seizures, diaphoresis
Chief complaint of sympathomimetics
altered mental status and euphoria
Sympathomimetic case:
History of Present Illness: Joy, a 25-year-old female, is brought to the emergency department. In the last 4 hours, her behavior has become increasingly hyperactive, and she is now expressing extreme joy and euphoria.
Vital Signs: Temperature: 37.8°C (100.0°F), Heart Rate: 160 bpm, Blood Pressure: 140/85 mmHg
Physical Examination:
• General:
• Neurologic:
• Cardiovascular:
• Respiratory:
• GI:
• General: Euphoric, talkative, hyperactive
• Neurologic: Dilated pupils, increased deep tendon reflexes
• Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, slightly increased blood pressure
• Respiratory: Slightly increased respiratory rate, no signs of distress
• Gastrointestinal: No obvious abnormalities

Hyperreflexia
the presence of hyperactive stretch reflexes of the muscles
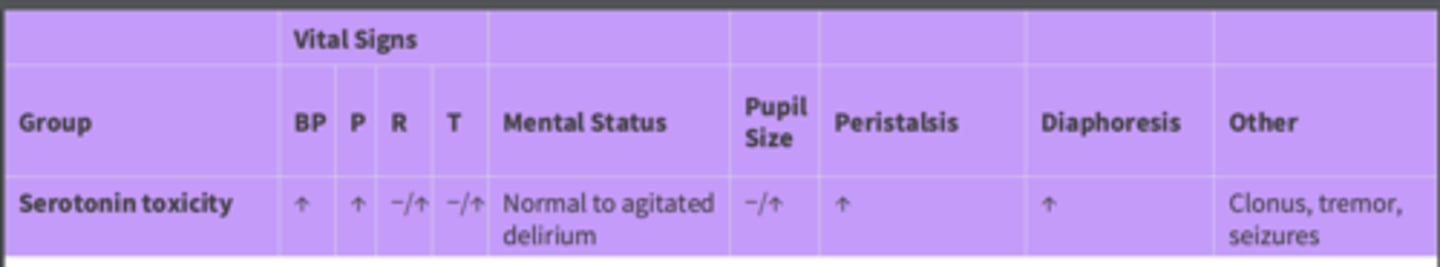
How serotonin toxicity affects vital signs, mental status, etc.:
BP:
Pulse:
Respirations:
Temperature:
Mental Status:
Pupil size:
Peristalsis:
Diaphoresis
Other:
BP: increased
Pulse: increased
Respirations: may not change or increase
Temperature: may not change or increase
Mental Status: normal to agitated delirium
Pupil size: may not change or increase
Peristalsis: increased
Diaphoresis: increased
Other: Clonus, tremor***, seizures
Chief complaint of serotonin toxicity
Agitation and Tremors
Serotonin toxicity case:
History of Present Illness: Fear, a 22-year-old male, is brought to the ED by his friends after he began exhibiting bizarre behavior and intense anxiety at a music festival.
Vital Signs: Temperature: 38.9°C (102.0°F), Heart Rate: 130 bpm, Blood Pressure: 150/85 mmHg, Respiratory Rate: 24/min
Physical Examination:
General:
• Neurologic:
• Cardiovascular:
• Respiratory:
• General: Agitated, trembling***, and anxious
• Neurologic: Dilated pupils, hyperreflexia, myoclonus
• Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, slightly increased blood pressure
• Respiratory: Increased respiratory rate, no signs of respiratory distress

Myoclonus
sudden brief involuntary twitching or jerking of a muscle or group muscles
How anticholinergics affect vital signs, mental status, etc.:
BP:
Pulse:
Respirations:
Temperature:
Mental Status:
Pupil size:
Peristalsis:
Diaphoresis
Other:
BP: may not change or increase
Pulse: increased
Respirations: variable
Temperature: increased
Mental Status: delirium
Pupil size: increased
Peristalsis: decreased
Diaphoresis: decreased
Other: Dry mucous membranes****, flush, urinary retention

Chief complaint of anticholinergics
agitation and confusion
Anticholinergic case:
History of Present Illness: Anger, a 30-year-old male, is brought to the ED due to sudden onset of agitation and confusion. He was behaving aggressively at home, exhibiting bizarre and hostile actions.
Vital Signs: Temperature: 38.3°C (100.9°F), Heart Rate: 110 bpm, Blood Pressure: 140/90 mmHg, Respiratory Rate: 18/min
Physical Examination:
• General:
• Neurologic:
• Cardiovascular:
• Respiratory:
• General: Agitated, combative, and confused
• Neurologic: Dilated pupils, dry oral mucosa, decreased bowel sounds
• Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, slightly increased blood pressure
• Respiratory: Normal respiratory rate, no signs of respiratory distress

Anticholinergic toxidrome acronyms

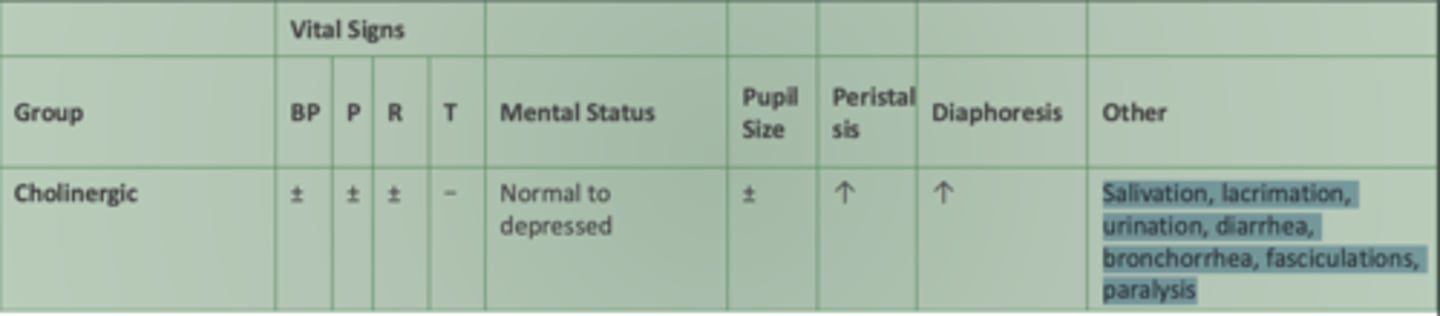
How cholinergics affect vital signs, mental status, etc.:
BP:
Pulse:
Respirations:
Temperature:
Mental Status:
Pupil size:
Peristalsis:
Diaphoresis
Other:
BP: variable
Pulse: variable
Respirations: variable
Temperature: change unlikely
Mental Status: normal to depressed- more hypoactive
Pupil size: variable
Peristalsis: increased****
Diaphoresis: increased****
Other: Salivation***, lacrimation***, urination***, diarrhea, bronchorrhea, fasciculations, paralysis
- vital signs not greatly changed, increse in water
Chief complaint of cholinergics
Nausea and vomiting
Bronchorrhea-
Fasciculations-
Bronchorrhea- production of voluminous water sputum
Fasciculations- involuntary rapid muscle twitches (weak)
Cholinergic case:
History of Present Illness: Disgust a 21-year-old female, is brought to the ED by his coworkers after she suddenly developed severe nausea, vomiting, and abdominal cramps at a work event.
Vital Signs: Temperature: 37.2°C (99.0°F), Heart Rate: 90 bpm, Blood Pressure: 120/80 mmHg, Respiratory Rate: 18/min
Physical Examination:
• General:
• Neurologic:
• Cardiovascular:
• GI:
• General: Pale, diaphoretic, and visibly distressed.
• Neurologic: Confused, salivating excessively.
• Cardiovascular: Normal heart rate, normal blood pressure.
• Gastrointestinal: Active vomiting, abdominal cramps, increased bowel sounds

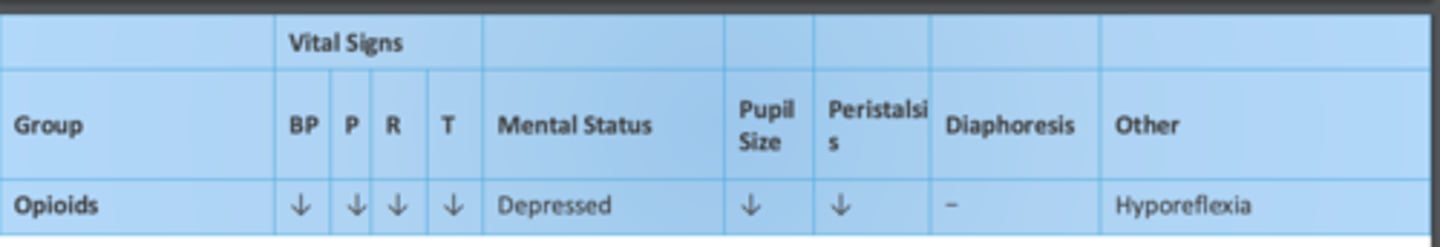
How opioids affect vital signs, mental status, etc.:
BP:
Pulse:
Respirations:
Temperature:
Mental Status:
Pupil size:
Peristalsis:
Diaphoresis
Other:
BP: decreased
Pulse: decreased
Respirations: decreased
Temperature: decreased
Mental Status: depressed
Pupil size: decreased
Peristalsis: decreased**
Diaphoresis: change unlikely
Other: Hyporeflexia
Chief complaint of opioids
altered mental status and depressed breathing

Opioid case:
History of Present Illness: Sadness, a 28-year-old female, is brought to the ED by her roommate who found her unresponsive and breathing slowly in their apartment.
Vital Signs: Temperature: 37.0°C (98.6°F), Heart Rate: 60 bpm, Blood Pressure: 110/70 mmHg, Respiratory Rate: 8/min, Oxygen Saturation: 91% on room air
Physical Examination:
• General:
• Neurologic:
• Cardiovascular:
• Respiratory:
• General: Unresponsive, lethargic, and breathing at a slow rate
• Neurologic: Pinpoint pupils, decreased level of consciousness
• Cardiovascular: Bradycardia, hypotension
• Respiratory: Shallow respirations, occasional sighing

Diaphoresis can be present in the following toxidromes...
A. Anticholinergic
B. Sympathomimetic
C. Serotonin toxicity
D. All of the above
E. B and C
E. B and C
What signs and symptoms would you expect to find in a patient with an anticholinergic toxidrome?
A. Miosis
B. Tachycardia
C. Dry skin
D. Salivation
E. Delirium
B. Tachycardia
C. Dry skin
E. Delirium
A 43-year-old man was brought to the ED, after being found on the ground next to a vegetable patch. He has white powder on his face and clothing. During the physical exam he began vomiting
- Vital signs: T: 35.7°C, HR: 53 bpm, R: 25 rpm, BP: 110/55 mm Hg, SPO2: 85%
- He exhibits gurgling respirations with pooled secretions in oropharynx
- Pupils 2mm
- Skin cool and diaphoretic
Which toxidrome is this patient experiencing?
A. Anticholinergic
B. Cholinergic
C. Sympathomimetic
D. Opioid
B. Cholinergic
A 21-year-old-woman was found unresponsive in her dorm by her roommate. Empty pill bottles standing next to her bed.
- Vital signs: T: 36.7 °C, HR: 72 bpm, RR: 4 rpm, BP: 110/60 mm Hg, SPO2: 81%
- Pupils 1mm
- Skin cyanotic but dry
Which toxidrome is this patient experiencing?
A. Anticholinergic
B. Cholinergic
C. Sympathomimetic
D. Opioid
D. Opioid
A 35-year-old man with depression was found altered at home by his spouse. Over-the-counter-pill bottles were found in the trash. Patient is alert but agitated and combative
- Vital signs: T: 38.6 °C, HR: 127 bpm, RR: 23, BP: 156/98, SPO2: 99%
- Pupils: 8mm
- Skin flushed and dry
- Dry mucous membranes
Which toxidrome is this patient experiencing?
A. Anticholinergic
B. Cholinergic
C. Sympathomimetic
D. Serotonin Toxicity
A. Anticholinergic
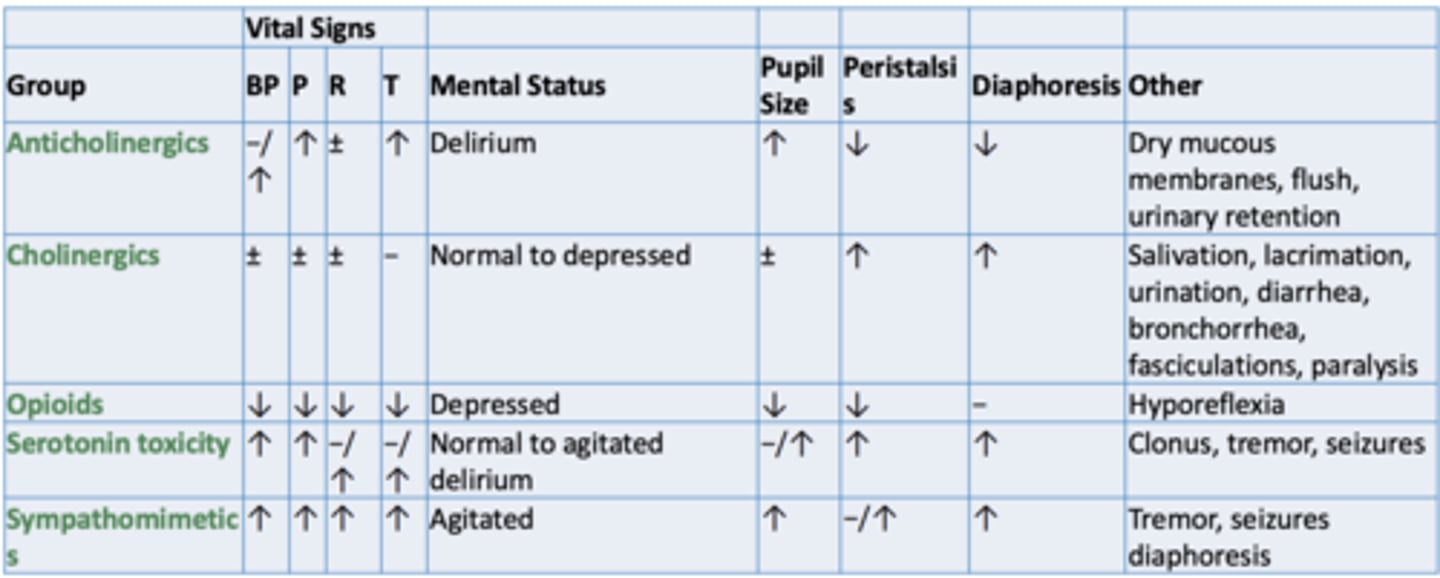
Summary chart of the toxidromes and their effects
Sympathomimetics physiology
• SNS stimulation by increasing circulating levels of catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine)
• Adrenergic receptors, specifically activation of beta-adrenergic receptors

Sympathomimetic drugs (4)
• Amphetamines
• Bath Salts
• Cocaine
• Ketamine
Clinical features of sympathomimetics (7)
• Hyperthermia
• Tachycardia
• Hypertension
• Agitation / Psychosis
• Seizures
• Dilated Pupils (but will react to light)
• Diaphoresis, secondary to hyperthermia
Antidote for sympathomimetics
Manage signs and symptoms
Physiology of serotonin drugs/toxicity
• Associated with increased serotonergic activity in both the peripheral (PNS) and central nervous systems (CNS)
• 5-HT receptor activation

Serotonin drugs (6)
• Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
• Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
• Tramadol
• MDMA
• Amphetamines
• Lamotrigine
Serotonin drugs are usually precipitated by the simultaneous initiation of _______________________, can also occur after the initiation of a _____________ serotonergic drug in a susceptible individual
- 2 or mor serotonergic drugs
- single
Clinical features of serotonin drugs (5)
• Tremor, Myoclonus, Hyperreflexia, Trismus, Rigidity
• Diaphoretic
• Hypertension, hyperthermia, tachycardia, tachypnea
• Mydriasis
• Confusion, agitation, coma
Antidote of serotonin drugs
Cyproheptadine
Physiology of anticholinergic drugs/toxicity
Inhibition of muscarinic cholinergic neurotransmission (blocking acetylcholine from binding receptors) gives these drugs their effect

Anticholinergic drugs
• Antihistamines
• Sleep aids
• tricyclic antidepressants
• cold preparations
• atroping
Plants: deadly nightshade (belladona, killed R & J), jimson weed
Clinical features of anticholinergic toxicity (6)
• "Red as beet' - vasodilation
• "Dry as a bone" - inhibition of sweat glands
• "Hot as a hare" - lack of sweating and increased stimulation cause hyperthermia
• "Blind as a bat" - blurry vision due to inability to constrict pupil and accommodate.
• "Mad as hatter" - central muscarinic blockade causing delirium, hallucinations, psychosis, seizures. Picking at skin common.
• "Full as a flask" - urinary retention due to detrusor muscle and urethral sphincter inability to relax
Antidote to anticholinergic toxicity
physostigmine
What is used as an antidote for a tricyclic antidepressant overdose?
sodium bicarbonate
Physiology of cholinergic drugs/toxicity
• Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) causes increased levels of acetylcholine.
• Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors

Cholinergic drugs (2)
• Pesticides resulting in field workers exposed (dermal, inhalation) to sprayed chemicals.
• Organophosphates
Clinical features of cholinergic toxicity: SLUDGE & the Killer B's (main cause of deaths in cholinergic) (muscarinic effect)
• Salivation
• Lacrimation (crying-key feature)
• Urination
• Defecation (diarrhea)
• GI cramping (distress)
• Emesis
• Bronchorrhea
• Bronchospasm
• Bradycardia
• Pinpoint pupils (nicotinic)
• Muscle weakness / fasciculations. (nicotinic)
• Paralysis (nicotinic)
• CNS depression / Coma / Seizure (nicotinic)
Antidote to cholinergic toxicity
atropine
T/F: Cholinergic toxicity is the LEAST common toxidrome
TRUE
Physiology of opioids/opioid overdose
Stimulation of three receptors provides CNS depression and analgesia: mu (MOP), kappa (KOP) and sigma (DOP)

Opioid drugs
Natural opiate derivatives:
Synthetic:
• Natural opiate derivatives: codeine, heroin, hydrocodone, morphine, oxycodone
• Synthetic: buprenorphine, dextromethorphan, fentanyl, methadone, meperidine
Clinical features of opioid overdose (6)
• Bradypnea (key finding)
• Bradycardia
• Hypotension
• CNS depression, coma
• Pinpoint pupils
• Bowel obstruction
Antidote to opioid overdose
Naloxone
Which of the following toxidromes is caused by an overdose of APAP?
A. Opioid
B. Serotonin toxicity & sympathomimetic
C. Cholinergic
D. None of the above
D. None of the above
- anticholinergic
