Module 5 "Team Leadership"
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
Definition of team
combination of two or more people who who try to achieve a common goal and depend on each other to achieve this goal
2
New cards
Why is a team important?
because they increase ^^productivity^^ and ^^effectiveness^^, they help reach c^^ompetitive advantage^^ in a globalised market, people are more ^^creative^^ and can ^^adapt faster^^ to changing business environments
3
New cards
Which are constitutive characteristics of a team?
1 Multipersonality
2 Interdependance
3 Goal orientation
2 Interdependance
3 Goal orientation
4
New cards
Which are descriptive characteristics of a team?
1 **interpersonal interaction**: exchange personal and proffesional info regularly
2 **membership perception**: being a part of a social unit within the organization
3 **structured relationships**: existing roles, norms and regulations control team behavior
4 **Reciprocal influence**: employees influence each others opinions and behaviors
5 **individual motivation**: being a part of a team satisfies their needs
2 **membership perception**: being a part of a social unit within the organization
3 **structured relationships**: existing roles, norms and regulations control team behavior
4 **Reciprocal influence**: employees influence each others opinions and behaviors
5 **individual motivation**: being a part of a team satisfies their needs
5
New cards
Main idea of the concept leadership in different types of teams
Leaders should respond to different behavioral patterns of teams to be successful
6
New cards
On what depend behavioral patterns of a team?
1 Relational level
2 Task- related level / factual level
2 Task- related level / factual level
7
New cards
Meaning of relational level
Gives info about ^^interpersonal interaction^^ within a team
8
New cards
Indicators of a high relational level
* Members are ^^friendly^^ to each other
* There are ^^no personal conflicts^^
* ^^Members^^ ^^enjoy^^ working on a team
* Members can ^^respond to each other^^
* Members ^^support each other^^ on personal problems
\
* There are ^^no personal conflicts^^
* ^^Members^^ ^^enjoy^^ working on a team
* Members can ^^respond to each other^^
* Members ^^support each other^^ on personal problems
\
9
New cards
Meaning of task-related /factual level
Prioritises the ^^achievement of goals^^, gives importance to task related aspects of team
10
New cards
Indicators of a high task-related / factual level
* Clear ^^standards^^ regarding performance
* ^^Problem solving techniques^^ are applied
* ^^information^^ is shared ^^regularly^^ and systematically
* team examines ^^possible alternatives^^ and its feasibility ^^before decision making^^
\
* ^^Problem solving techniques^^ are applied
* ^^information^^ is shared ^^regularly^^ and systematically
* team examines ^^possible alternatives^^ and its feasibility ^^before decision making^^
\
11
New cards
Which are the four types of teams that result from the combination of factual and relational levels?
1. Social group
2. Lone fight club
3. real team
4. expert team
\
12
New cards
Describe the Lone figther club type of team
* No ^^emotional cohesion or professional cooperation^^ within the team
* Team performs ^^poorly^^
* Evident in ^^newly formed teams^^ that are still in an early phase of development
Leaders should try to %%improve both the factual and relational levels in parallel.%%
* Team performs ^^poorly^^
* Evident in ^^newly formed teams^^ that are still in an early phase of development
Leaders should try to %%improve both the factual and relational levels in parallel.%%
13
New cards
Describe the real team type of team
* Factual (task-related) and relational levels are highly developed
* ^^Cooperation and communication flows are clearly regulated^^
* Team members ^^exchange information intensively^^ and ^^support each other^^ in personal matters
Leader should %%try to maintain the high level%%, for example by setting %%appropriate team goals%% and should keep the team %%flexible%%
* ^^Cooperation and communication flows are clearly regulated^^
* Team members ^^exchange information intensively^^ and ^^support each other^^ in personal matters
Leader should %%try to maintain the high level%%, for example by setting %%appropriate team goals%% and should keep the team %%flexible%%
14
New cards
Describe the social group type of team
* Focus is primarily on the ^^exchange of personal concerns^^ and less on fulfilling the work task
* Team spends a relatively large amount of time and energy to ^^cultivate personal relationships^^ or to deal with ^^personal conflicts^^; at the expense of the team's performance
Leaders should %%strengthen team structures%% by means of %%fact-oriented leadership instruments%%
* Team spends a relatively large amount of time and energy to ^^cultivate personal relationships^^ or to deal with ^^personal conflicts^^; at the expense of the team's performance
Leaders should %%strengthen team structures%% by means of %%fact-oriented leadership instruments%%
15
New cards
Describe the expert team type of team
* Factual level is strong and the relational level is relatively low
* ^^Performance is impaired^^ because team members ^^support^^ and ^^communicate with each othe^^r to a very ^^limited^^ extent in ^^personal matters^^
* ^^No cohesion^^ between the members
Leaders should %%improve the relational level%%
* ^^Performance is impaired^^ because team members ^^support^^ and ^^communicate with each othe^^r to a very ^^limited^^ extent in ^^personal matters^^
* ^^No cohesion^^ between the members
Leaders should %%improve the relational level%%
16
New cards
Mention another 6 set of criteria to distinguish teams
1. ^^Hierarchical position^^ ( execution teams, mngmt teams)
2. ^^Duration:^^ (project teams, permanent)
3. ^^functional heterogeneity^^ (mono or multifunctional)
4. ^^institutional heterogeneity^^ (intra organizational or interorganizational)
5. ^^intercultural heterogeneity^^ (monocultural or international)
6. ^^intensity of personal interaction^^ (F2F, virtual or bionic teams)
17
New cards
What are bionic teams?
Consists of at least ^^three members (human & robots)^^ who ^^perform joint tasks interdependently^^, ^^interact socially^^ to ^^achieve a common goal^^
18
New cards
Examples of how can robots be considered part of a team in different areas
\*In a production related team, the robot is considered an automation, a machine
\*In a office related team, the robot is compared as social companion
\*In a office related team, the robot is compared as social companion
19
New cards
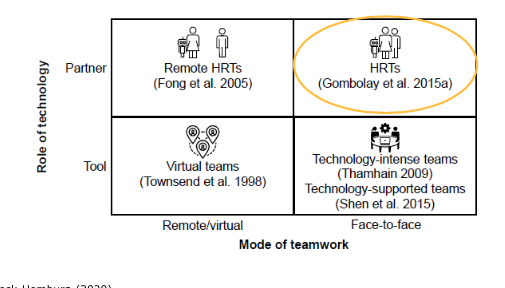
Which are the two dimensions to identify bionic teams?
y= Role of technology: partner or tool
x= Mode of teamwork: virtual/remote or F2F
x= Mode of teamwork: virtual/remote or F2F
20
New cards
Which are the four types of bionic teams?
1. Remote HRTS (human robot teams)
2. Human Robot Teams (HRTS)
3. Technology intense teams/ tech supported teams
4. Virtual teams
21
New cards
Integration of robots into teams
1. Human directed robot team
2. Robot directed team
3. Human and Robot direct mixed team (one team robot is boss, another team human is boss)
4. Autonomous mixed team (humans and robots work together to accomplish complex team tasks)
\
22
New cards
Challenges in team leadership
1. Company related
2. Employee related
23
New cards
Based on the challenges in team leadership, which are company-Related Opportunities and Risks of Teamwork
%%Opportunities%%
* %%Improved coordination%% due to interdependencies in the team
* %%Increased efficiency%% through improved coordination of specialized skills
* %%Improved decision quality%% through %%integration of different perspectives%%
* %%Better customer service%% through accumulation of competences in customer contact
==Risks==
* ==Reduction of decision quality through peer pressure==
* Increased ==coordination effort== due to interdependencies in the team
* ==Increased risk of conflicts== due to different professional or personal views of team members
* Increased ==resistance== of the team ==to change== through the ==development of a “subculture”==
* %%Improved coordination%% due to interdependencies in the team
* %%Increased efficiency%% through improved coordination of specialized skills
* %%Improved decision quality%% through %%integration of different perspectives%%
* %%Better customer service%% through accumulation of competences in customer contact
==Risks==
* ==Reduction of decision quality through peer pressure==
* Increased ==coordination effort== due to interdependencies in the team
* ==Increased risk of conflicts== due to different professional or personal views of team members
* Increased ==resistance== of the team ==to change== through the ==development of a “subculture”==
24
New cards
Based on the challenges in team leadership, which are employee-Related Opportunities and Risks of Teamwork
%%Opportunities%%
* %%Faster familiarization%% through %%information exchange%% with other team members
* %%Self-reflection of own behavioral patterns%% through %%feedback%% from other team members
* Beneficial %%learning of new skills and knowledge%%
* Increase of %%identification with the company%% due to the team membership
* %%Increased motivation%% by satisfying central needs for social contacts and recognition
* %%Faster familiarization%% through %%information exchange%% with other team members
* %%Self-reflection of own behavioral patterns%% through %%feedback%% from other team members
* Beneficial %%learning of new skills and knowledge%%
* Increase of %%identification with the company%% due to the team membership
* %%Increased motivation%% by satisfying central needs for social contacts and recognition
25
New cards
Which are sources of conflicts in teams?
\*Healthy : ^^Focus on task issues^^, ^^differences of opinion^^ about the task, ^^differences in values and perspectives^^, ^^different expectations^^ about th^^e impact of dec^^isions
\*Unhealthy: ==competition over power,== ==rewards and resources,== hold ==grudges of the past==, conflicts between individual & group goals, ==poor team meetings, bad communication==
\*Unhealthy: ==competition over power,== ==rewards and resources,== hold ==grudges of the past==, conflicts between individual & group goals, ==poor team meetings, bad communication==
26
New cards
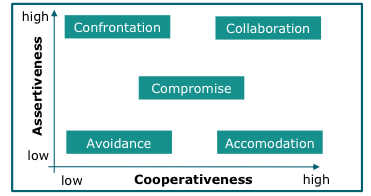
Which are the two dimensions for conflict resolution approaches?
Based on two dimensions,
^^y= Leader assertiveness :^^ extent to which a leader can influence others to reach his goals
^^x=cooperativeness of a team^^
^^y= Leader assertiveness :^^ extent to which a leader can influence others to reach his goals
^^x=cooperativeness of a team^^
27
New cards
Which are the conflict resolution approaches?
There are 5 approaches
1. ^^Confrontation^^: high level of leader assertiveness but no cooperativeness of team
2. ^^Collaboration:^^ high level of cooperativeness of team and high level of leader assertiveness
3. ^^Compromise:^^ middle level of leader assertiveness and middle level of cooperativeness of team
4. ^^Avoidance:^^ team avoids conflicts at all costs
5. ^^Accommodation:^^ members try to keep actual status and avoid changes
1. ^^Confrontation^^: high level of leader assertiveness but no cooperativeness of team
2. ^^Collaboration:^^ high level of cooperativeness of team and high level of leader assertiveness
3. ^^Compromise:^^ middle level of leader assertiveness and middle level of cooperativeness of team
4. ^^Avoidance:^^ team avoids conflicts at all costs
5. ^^Accommodation:^^ members try to keep actual status and avoid changes
28
New cards
What is social loafing?
the extent to which ^^**members reduce their own performance**^^ ^^**by relying on the performance of others**^^. Also known as free riders or sucker effect
29
New cards
Why is social loafing important to address?
Because as some members give different engagement to their tasks and other members notice it, this can interfere with the team performance
30
New cards
How to avoid or reduce social loafing?
**1.- Make performance transparent**
**2.- Increase motivation for each member**
\*^^divide tasks^^ into ^^individual responsibilities^^
\*implement metrics to ^^measure individual contributions^^
\*give ^^individual bonuses^^ or rewards
\*implement ^^individual objective performance measures^^
**2.- Increase motivation for each member**
\*^^divide tasks^^ into ^^individual responsibilities^^
\*implement metrics to ^^measure individual contributions^^
\*give ^^individual bonuses^^ or rewards
\*implement ^^individual objective performance measures^^
31
New cards
**Lifecycle Concept of Teams**
It focuses on the relation between the ^^**team formation**^^ and ^^**team performance**^^
^^Newly formed teams^^ take ^^time^^ to ^^reach^^ its ^^**full performance potential**^^
^^Newly formed teams^^ take ^^time^^ to ^^reach^^ its ^^**full performance potential**^^
32
New cards
**Lifecycle of Teams**
1. Forming
2. Storming
3. Norming
4. Performing
33
New cards
What is the importance of the factual level and relational level in the lifecycle of teams?
1. Forming: Relational level %%HIGH%%, factual level @@LOW@@
2. Storming: Relational level %%HIGH%%, factual level @@LOW@@
3. Norming: Relational level @@LOW,@@ factual level %%HIGH%%
4. Performing: Relational level %%HIGH,%% factual level %%HIGH%%
34
New cards
What is the intensity of team leadership?
Extent to which a leader ^^influences the activities^^ of a team
35
New cards
Which are the effects of team leadership intensity on team success?
1. Intensity of team leadership AND degree of communication/ collaboration (processes)
2. Intensity of team leadership AND degree of personal/ task conflict
36
New cards
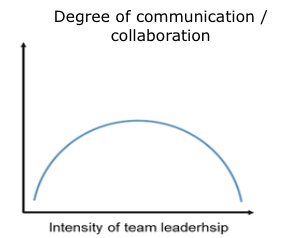
Explain the graph of intensity of team leadership AND degree of communication/ collaboration (processes)
When degree of team leadership is low, degree of collaboration starts to increase, as the degree of team leadership keeps increasing level of communication increases too until it reaches a point that it starts to decrease again when the degree of team leadership is high.
\
\-→ Lack or extreme team leadership leads to negative effects of team success due to lack of identification of members with goals, limited creativity due to no group dynamics
\-→ Medium degree of team leadership is most suitable for team communication
\
\-→ Lack or extreme team leadership leads to negative effects of team success due to lack of identification of members with goals, limited creativity due to no group dynamics
\-→ Medium degree of team leadership is most suitable for team communication
37
New cards
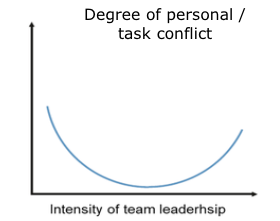
Explain the graph of intensity of team leadership AND degree of personal conflicts
Medium level of team leadership is related with lowest level of conflict because members have a joint agreement of team goals and they use creativity techniques
\
Lack or extreme degree of team leadership leads to high level of conflicts.
\
Lack or extreme degree of team leadership leads to high level of conflicts.
38
New cards
What is the assumption on team constellations as a function team leadership
the more involved a leader on operational activities is, the bigger the influence on the team
39
New cards
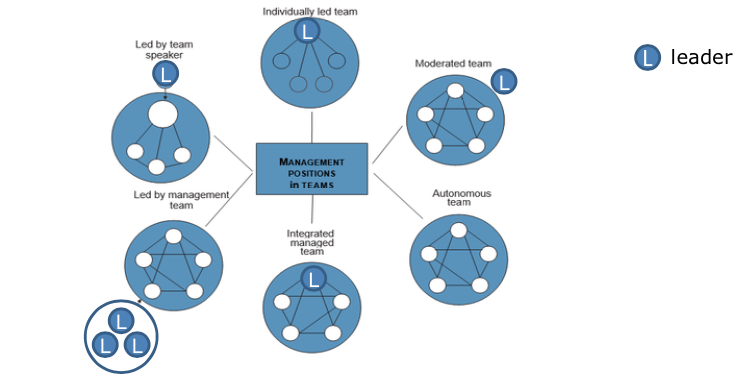
Which are the team constellations? (management positions in teams)
1. **Moderated team**: leader acts as a moderator, coordinating and supporting the team
2. **Autonomous team**: leader doesn’t exist, team is responsible for their own task achievement
3. **Integrated managed team** : leader has fixed role, he is responsible for decision making, task implementation and fulfilment
4. **Led by management team**: several team members who also act as leaders, decide tasks and responsibilities
5. **Led by team speaker:** team speaker acts as a mediating role AND team member
6. **Individually led team:** members have a bilateral interaction with leader but there is almost no connection between team members