bonding alevel chemistry
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
ionic bonding
electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions formed by electron transfer.
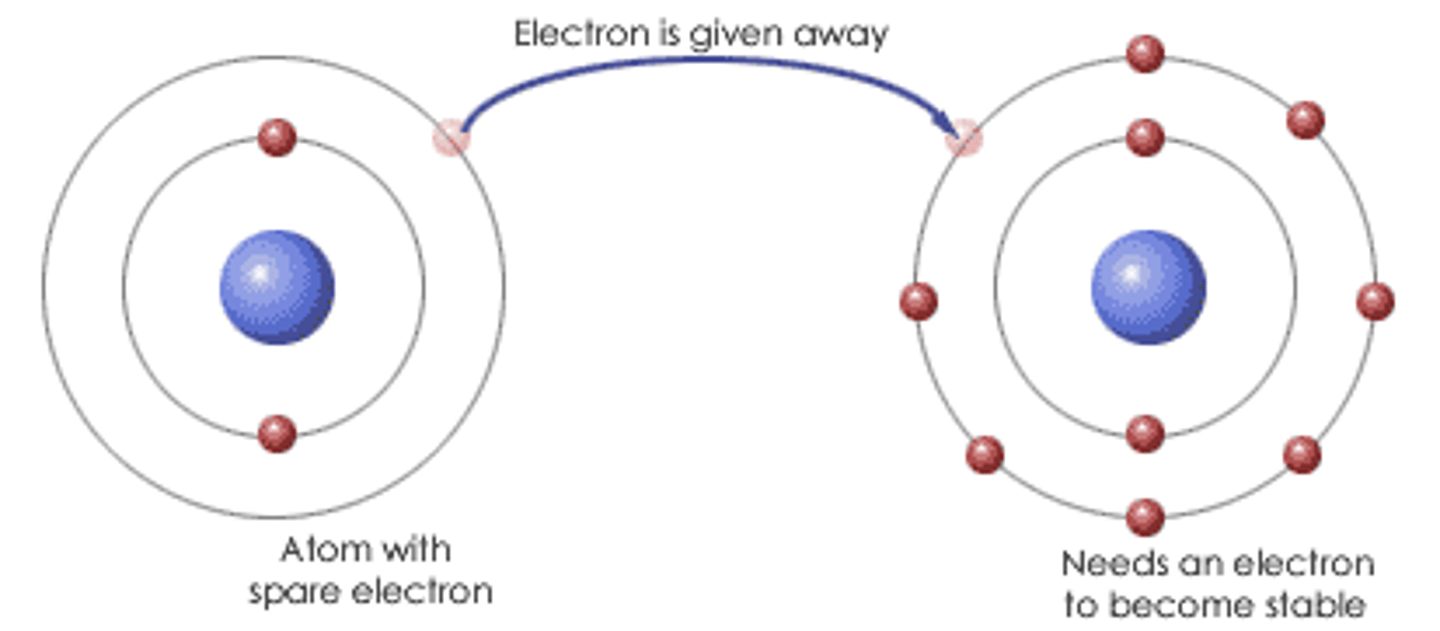
how can ionic bonds be stronger
stronger and the melting points higher when the ions are smaller and/ or have higher charges
giant ionic lattice and ionic bonds reaction in water
-regular structure -cubic shape -giant repeating pattern -most ionic compounds dissolve in water as water is polar -attracts the + and - charges break up structure
ionic bonds conduct electricity and have high melting points because?
-molten or dissolved as ions are free to move around -there are many electrostatic forces between ions -lots of energy to overcome these forces
Covalent bonding
sharing of outer electrons to form a full outer shell -electrostatic attraction between nucleus and shared electrons
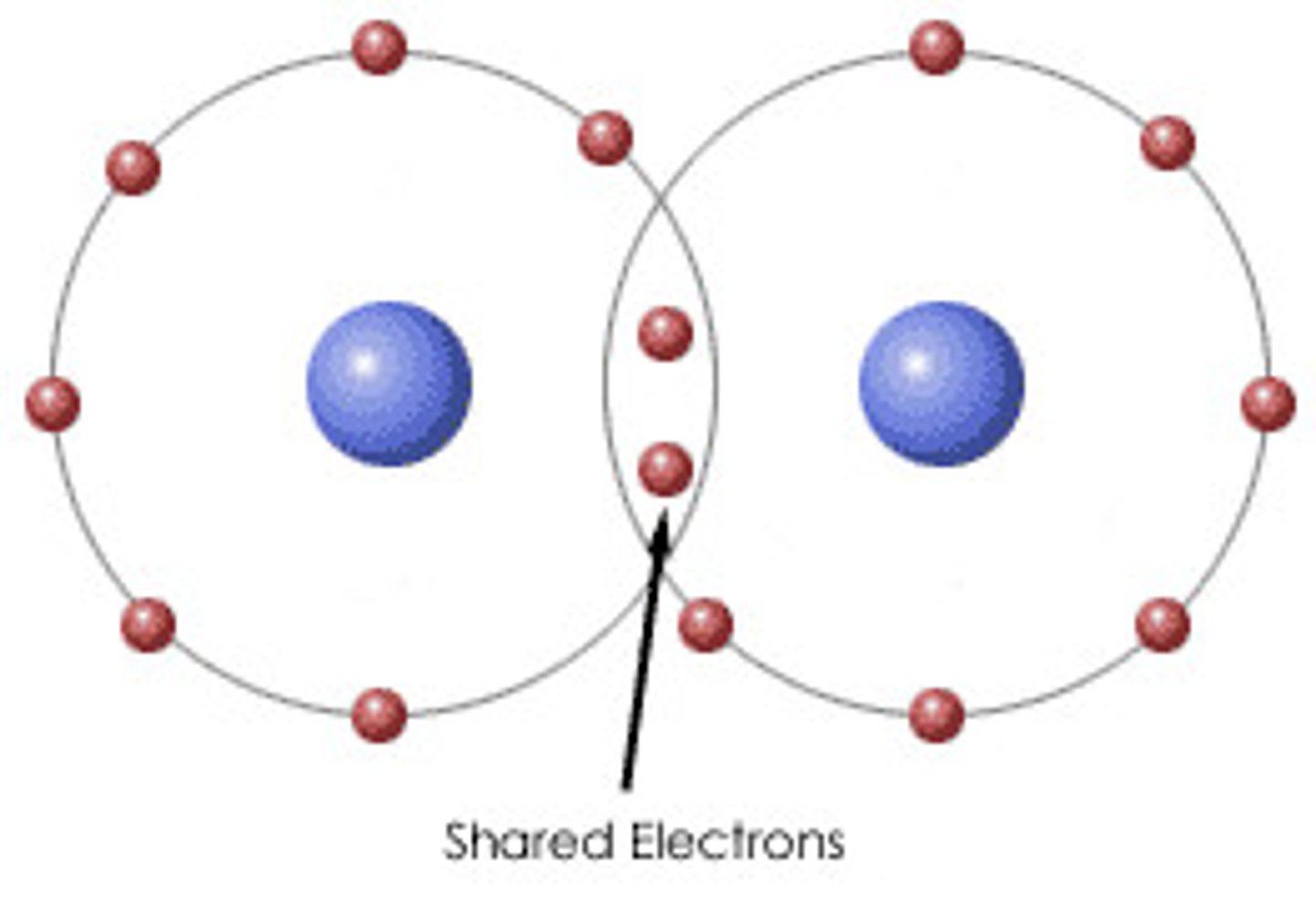
electrons in covalent bonds
pair to form multiple covalent bonds
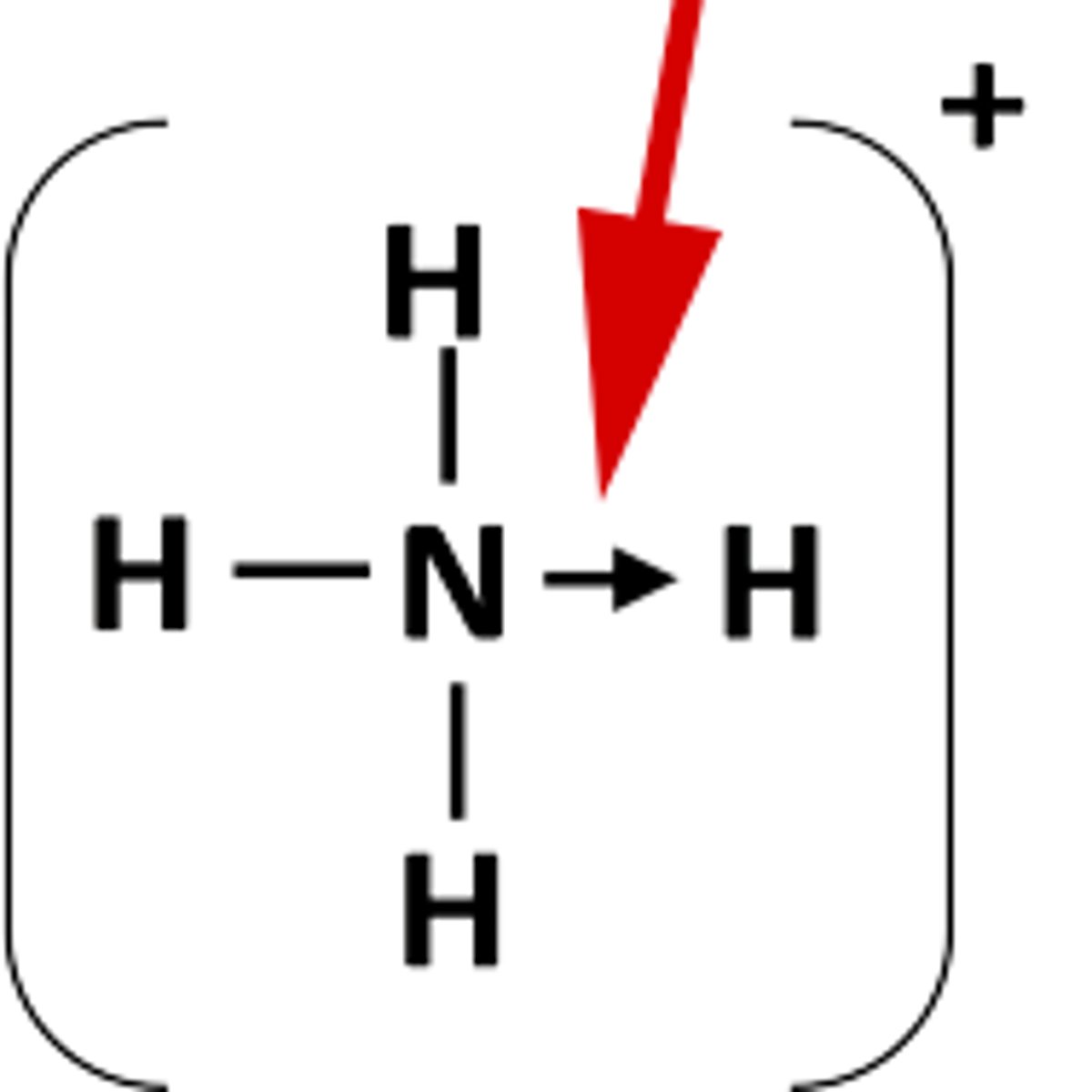
dative covalent bonds
the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond come from only one of the bonding atoms. A dative covalent bond is also called co-ordinate bonding.
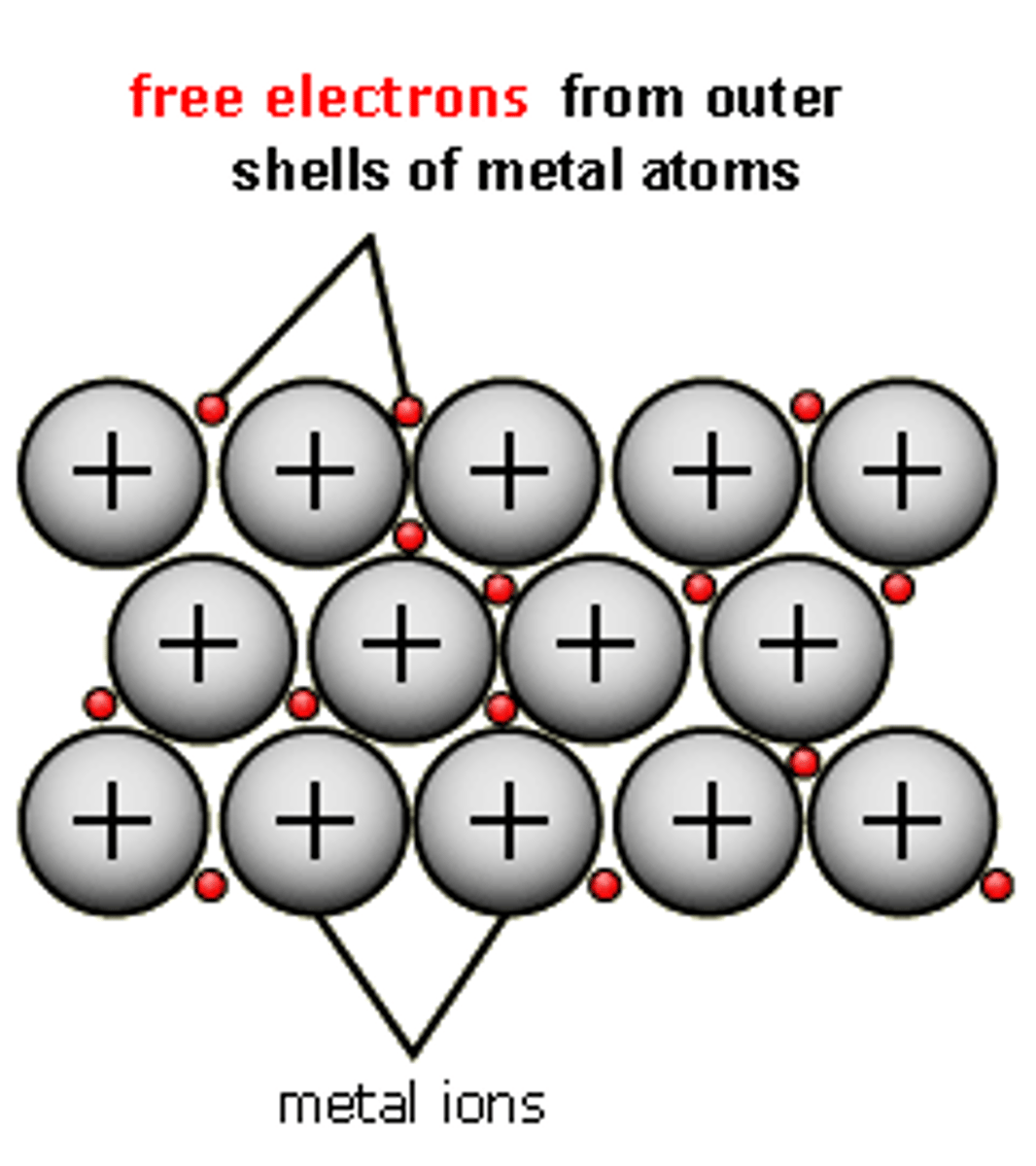
metallic bonding
electrostatic force of attraction between the positive metal ions and the delocalised electrons
the factors affecting metallic bonding
-Number of protons/ Strength of nuclear attraction. -Number of delocalised electrons per atom -Size of ion
there are 4 types of crystal structure
ionic, metallic, simple molecular, macromolecular
molecular properties
low bp because of weak intermolecular forces between molecules -poor solubility -poor conductivity no ions -mostly liquids and gases -electrons localised
macromolecular properties
-high melting points -many strong covalent bonds in macromolecular structure -lot of energy to break many strong bonds -insoluble -conductivity poor (not graphite) -poor when molten -solids
metallic bonding properties
-high mp/bp strong electrostatic forces between + ions and negative sea electrons -good conductivity -delocalised electrons and molten
description of metallic bonding
shiny metal -Malleable as the positive ions in lattice are all identical -planes of ions can slide easily over one another -attractive forces in the lattice are same whichever ions are adjacent
Shapes of molecules
-bond pairs and lone pairs -specific shape specific angles -bond pairs repel each other equally -electrons repel -lone pair repel bonding pairs more as they are attracted to same nucleus -2.5 degrees -and repel bonding bonding pairs
rules shapes of molecules
maximum repulsion -minimum separation
Lone pair repulsion
-lone pairs around central atom provides additional repulsive forces, because the lone pair closer to nucleus of atom, while bp is attracted to other nucleus
-for every lone pair there is a reduction of 2.5 degrees
Molecule shape
-linear -trigonal planar -tetrahedral -trigonal pyramidal -bent -trigonal bipyramidal -octahedral
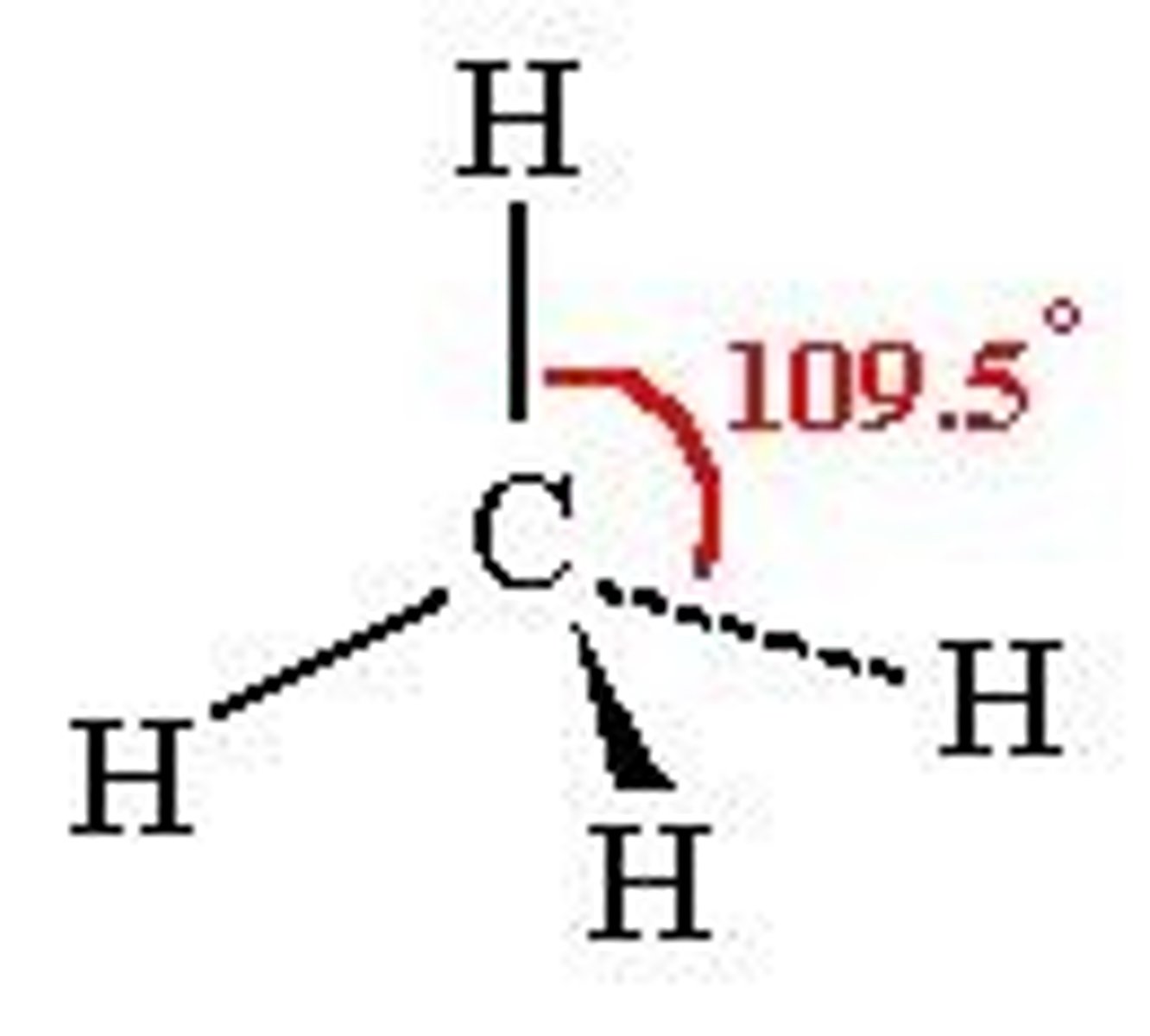
Tetrahedral
109.5 bp: 4
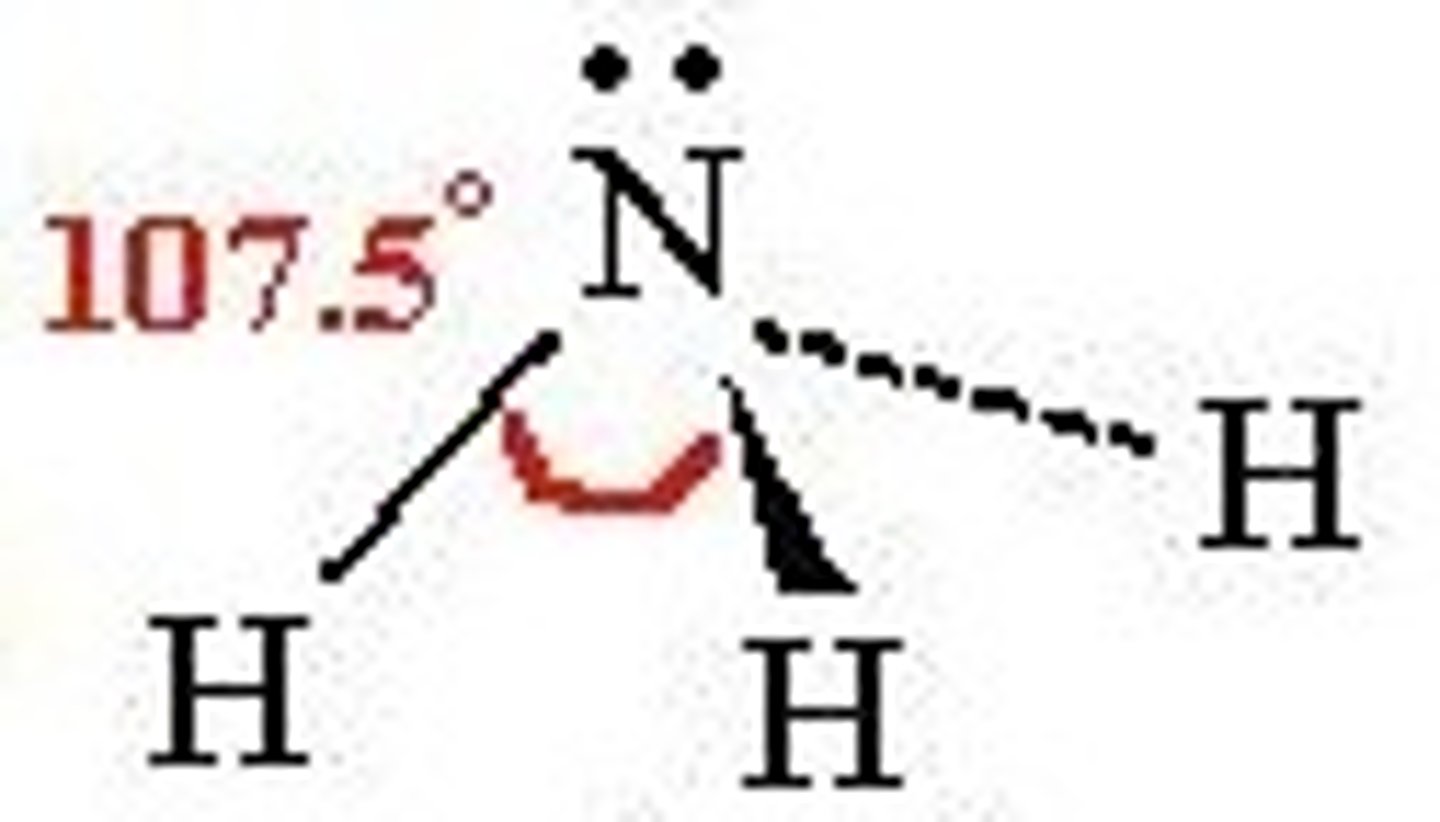
trigonal pyramidal
3 bonds, 1 lone pair, 107 bond angle
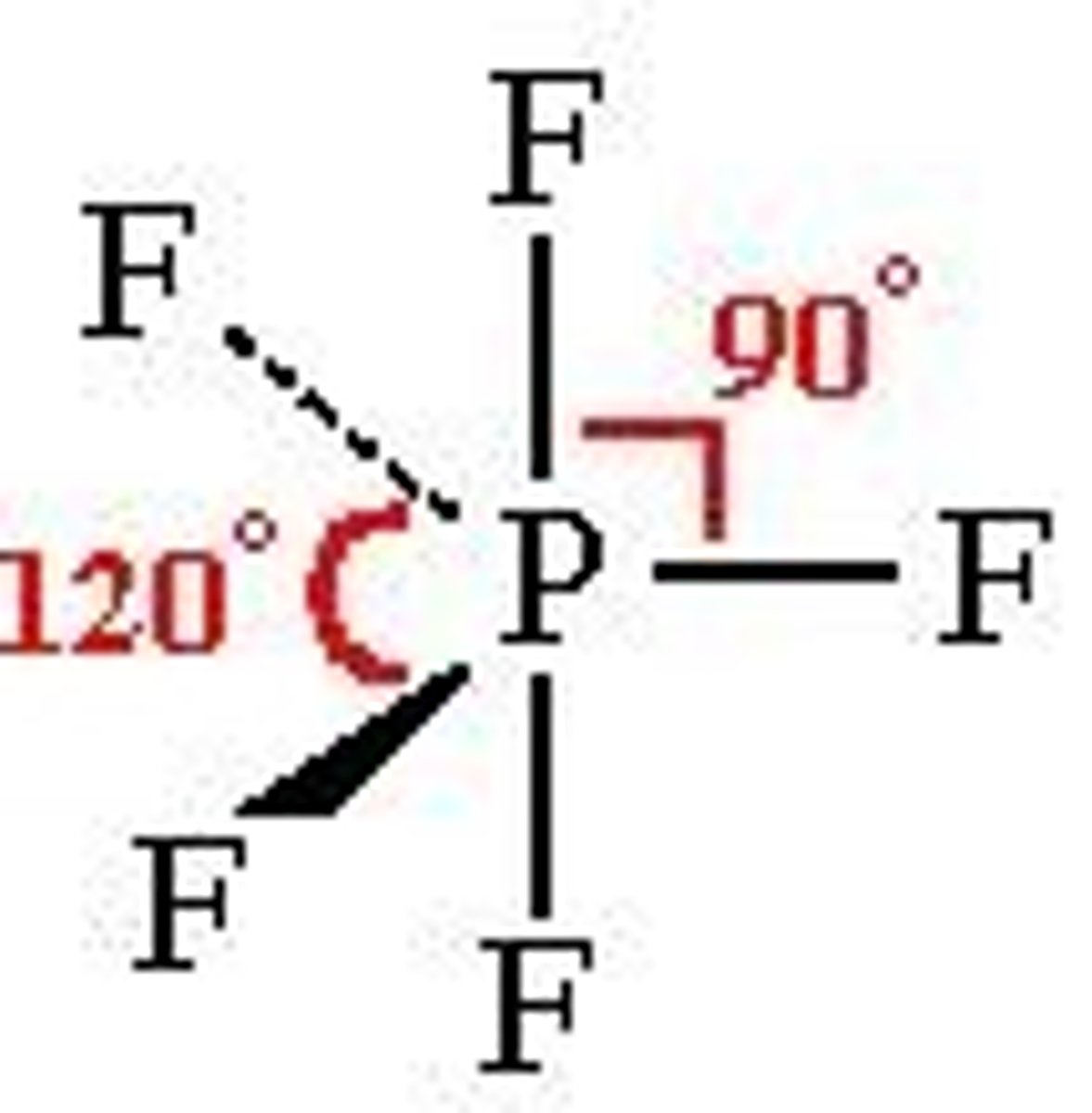
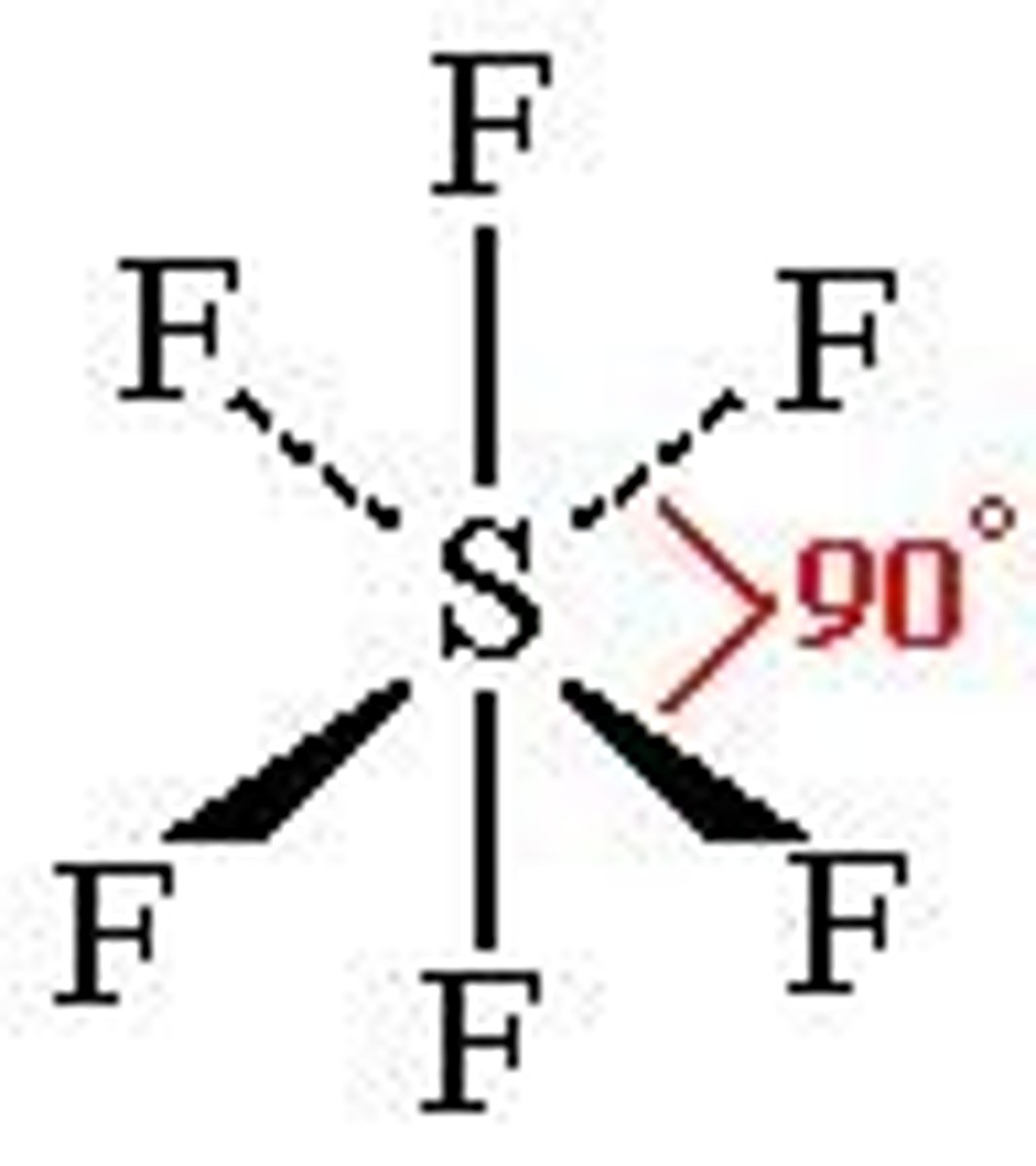
trigonal bipyramidal
90-120 bp: 5
octahedral
bp: 6 90 degrees
Linear
BP: 2 LP: 0 ANGLE: 180
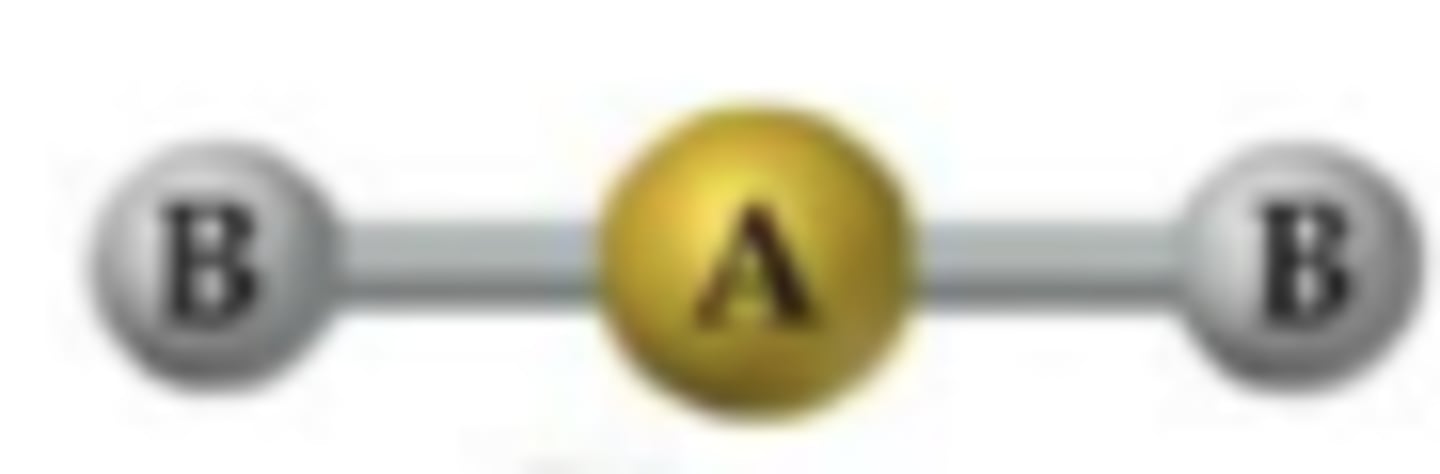
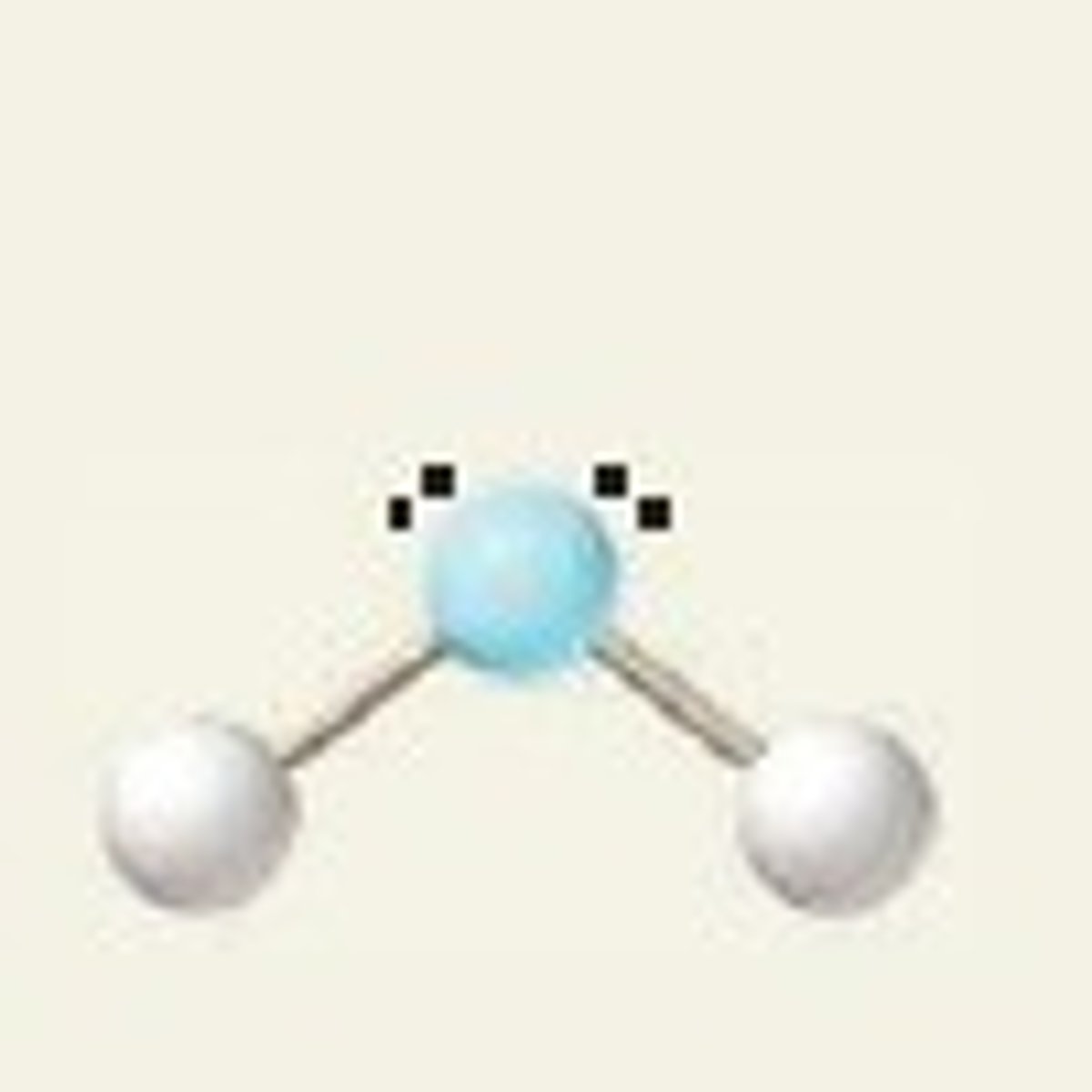
V-shaped (bent)
BP:2 LP:2 ANGLE:104.5
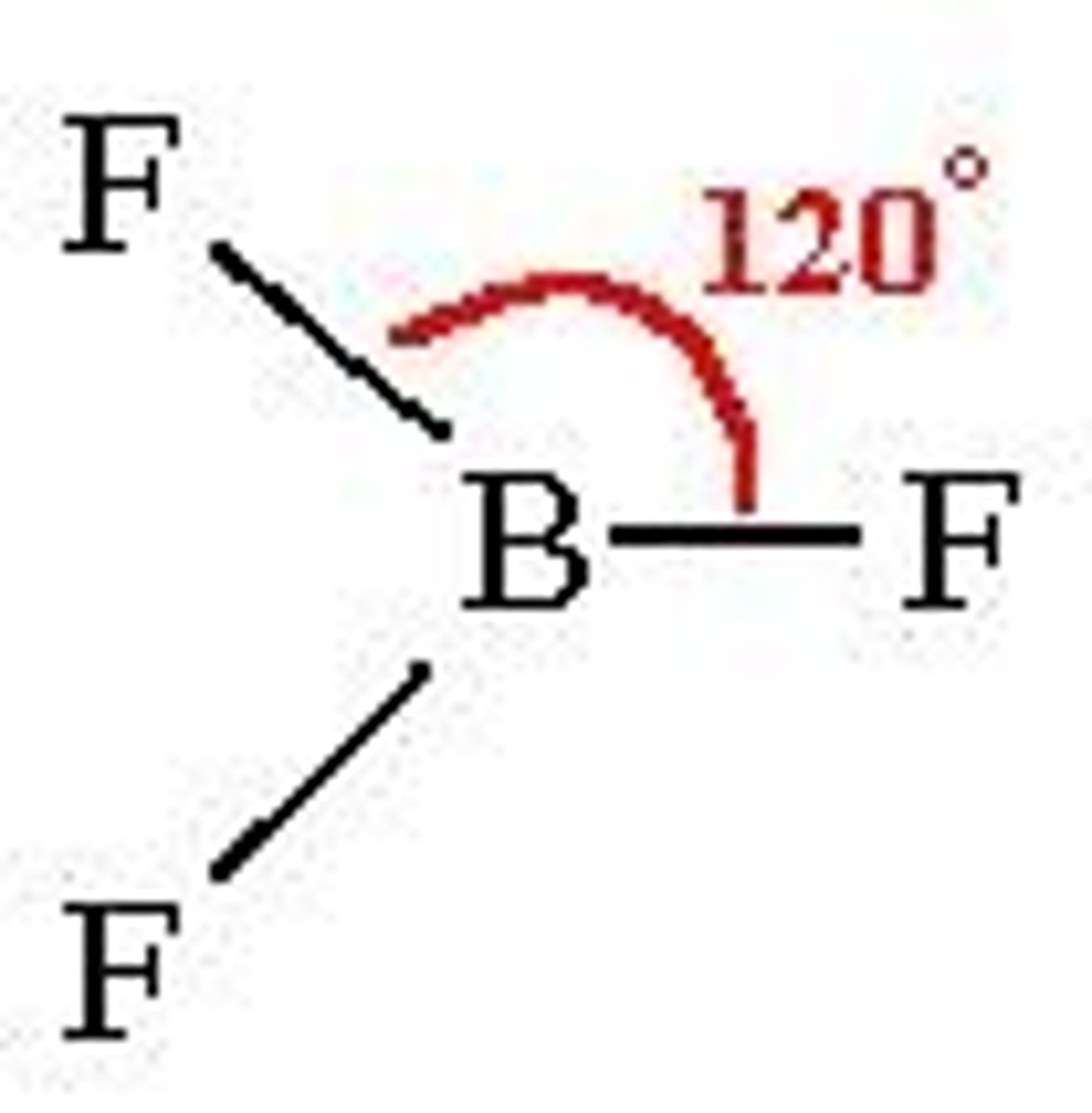
Trigonal planar
BP:3 LP: 0 120
Electronegativity
tendency of an atom in a covalent bond in a molecule to attract electrons in a covalent bond to itself.
how is it measured
Electronegativity is measured on the Paulings scale(ranges from 0 to 4) F, O, N, CL are the most electronegative -most en is fluorine
how is electronegativity affected?
-increases across a period as the number of protons increases and the atomic radius decreases because the electrons in the same shells
-distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons increases and the shielding of inner shell electrons increases
intermediate bonding
Ionic and covalent bonding are the extremes of a continuum of bonding type. Differences in electronegativity between elements can determine where a compound lies on this scale
elements of similar electronegativity and hence a small electronegativity difference will be
will be purely covalent
elements in a compound with a large electronegativity difference
>1.7 ionic
polar covalent bond
-different electronegativities -unequal distribution of electrons -produces charge separation -dipole -unsymmetric
symmetric molecules
non-polar as dipoles cancel out -not net dipole moment
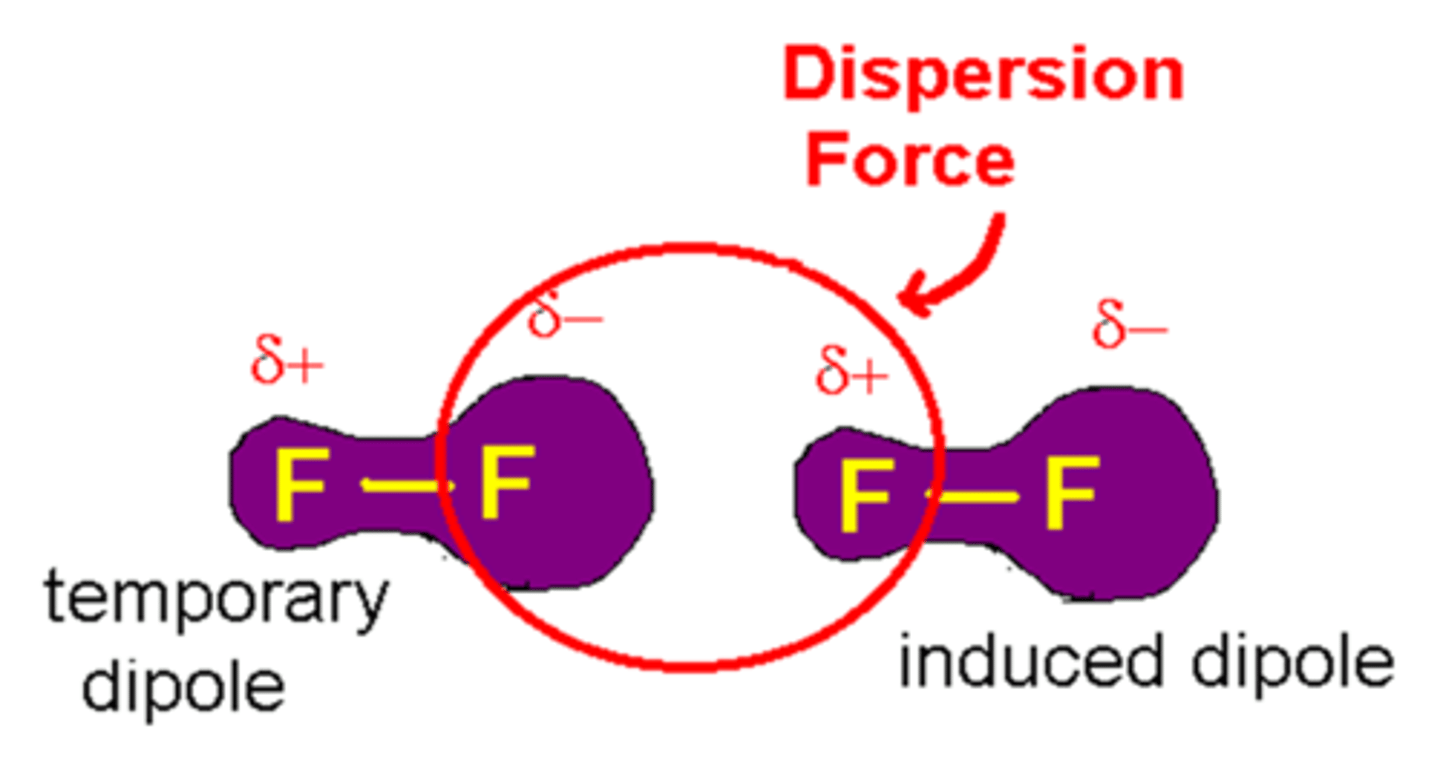
vaan der waals occur in
-all molecular substances and noble gases-do not occur in ionic substances -transient, induced dipole-dipole interactions -occur between all simple covalent molecules and the separate atoms in noble gases
van der Waals forces
a slight attraction that develops between the oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules
Why do van der Waals interactions occur?
electrons are moving constantly, randomly -electron density can fluctuate -parts of the molecule become more or less negative i.e. small temporary or transient dipoles form.
factors affecting van der waals?
-more electrons there are in the molecule the higher the chance that temporary dipoles will form. -Van der Waals stronger between the molecules and so boiling points will be greater
Van der waal in branched vs straight chained alkanes
-Long chain alkanes -larger surface area of contact between molecules -Van der Waals to form than compared to spherical shaped branched alkanes and so have stronger Van der Waals
Permanent dipole-dipole force
between polar molecules -stronger than Van der Waals and so the compounds have higher boiling points -Polar molecules have a permanent dipole
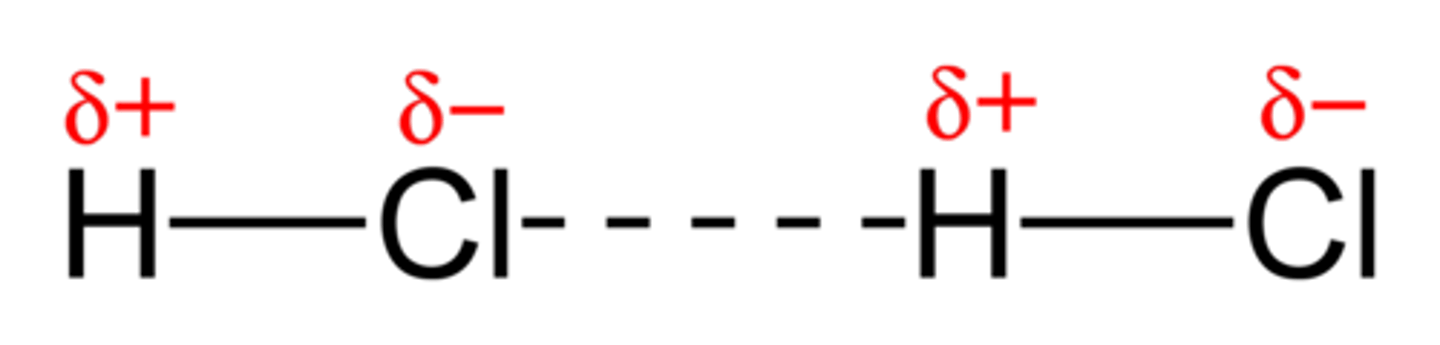
polar molecules are
asymmetrical and have a bond where there is a significant difference in electronegativity between the atoms -permanent dipoles have electrostatic forces between them
hydrogen bonding
hydrogen atom attached to one of the three most electronegative atoms of nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine -an available lone pair of electrons -large electronegativity difference between the H and the O,N,F
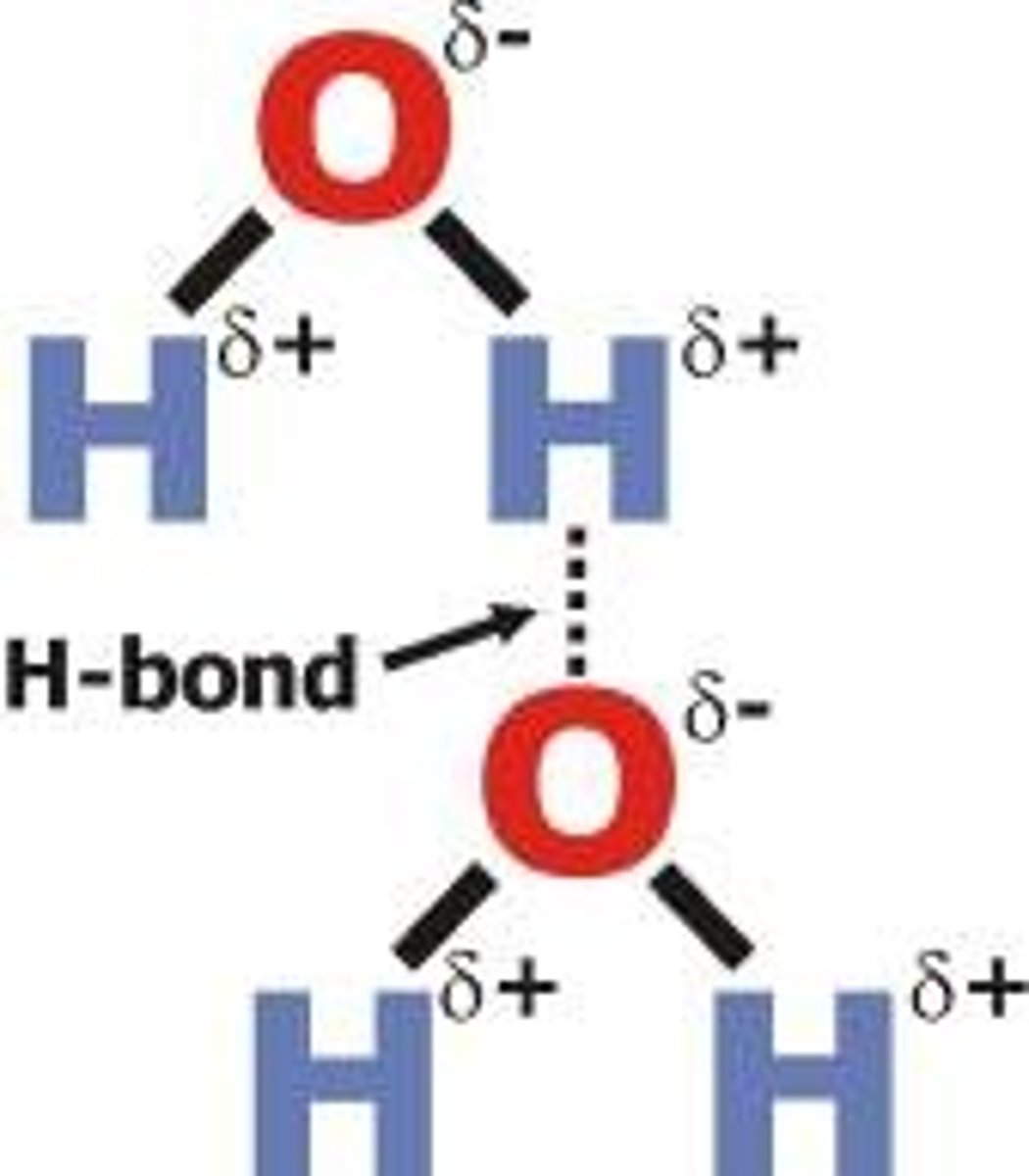
all intermolecular forces must
have van der waals as well
ice
-forms a regular structure -held by hydrogen bonding -molecules further apart -less dense then water
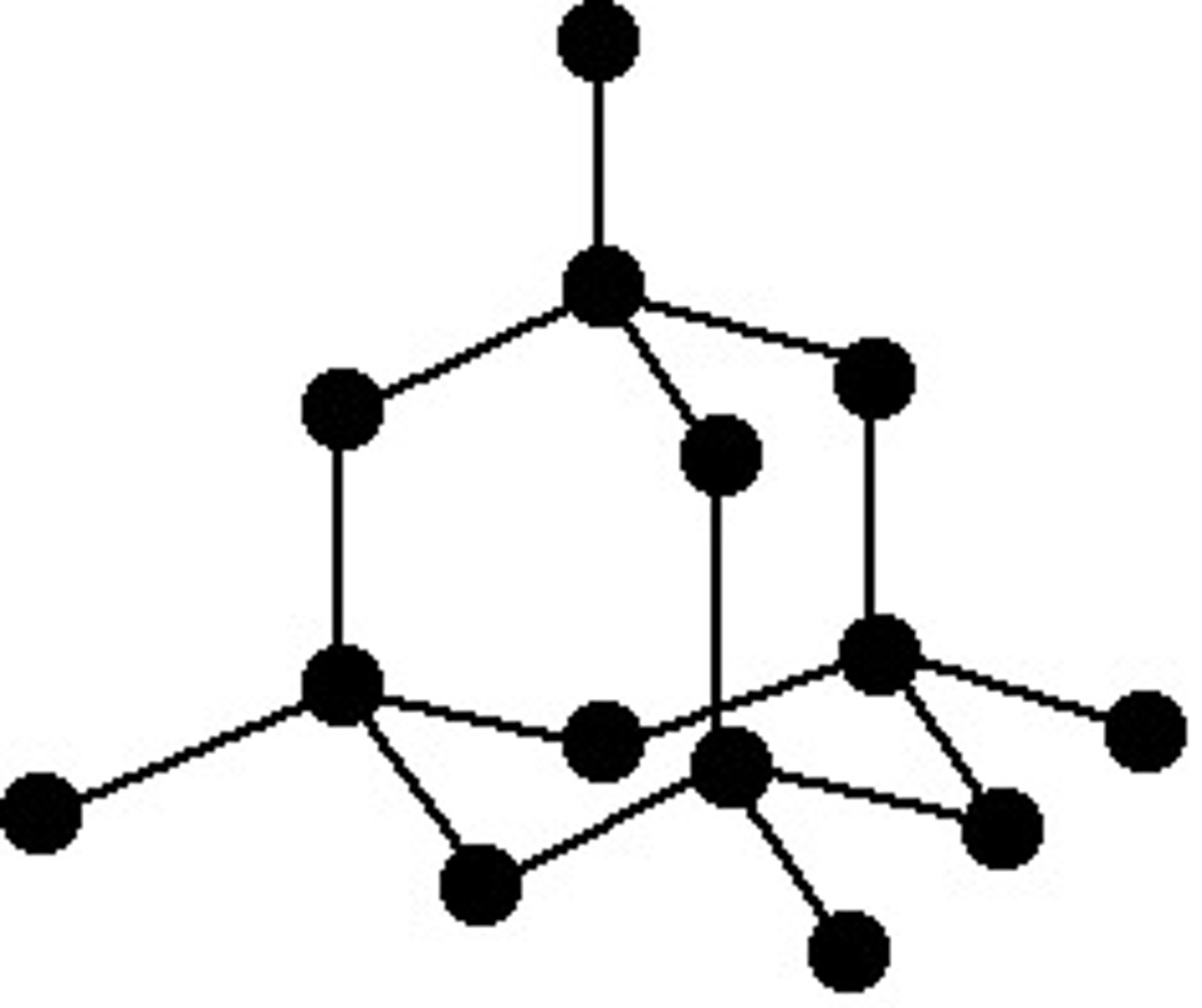
graphite (macromolecule giant covalent)
-pencil lead -layers slide easily (weak forces) -delocalised electrons -conduct electricity -low density -layers are far apart -insoluble high mp -covalent bonds
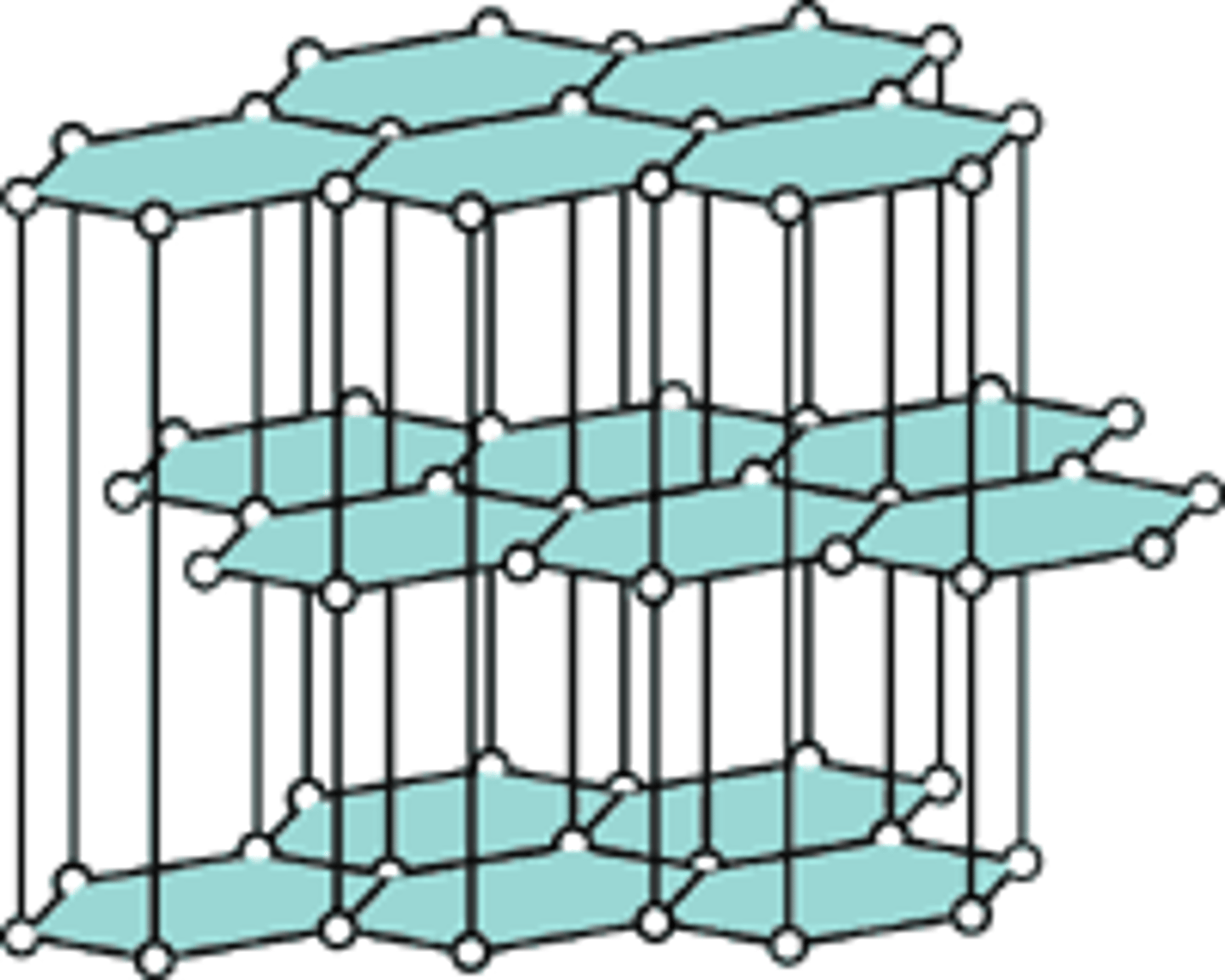
diamond
-tightly packed rigid arrangement -allows heat to conduct well -doesn't conduct electricity -insoluble and high mp because of covalent bonds -gemstones -no delocalized electrons