specs revision
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:44 AM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
field signal: enemy ahead
thumbs down sign, arm extended to your left
2
New cards
field signal: friendly / ally ahead
thumbs up sign, arm extended to your left
3
New cards
field signal: halt
raise your left arm by your shoulder, palm facing forward
4
New cards
field signal: take cover
arm bent with open palm facing inwards below right shoulder, move down to left twice
5
New cards
field signal: double up
arm bent with clenched fist slightly below right shoulder, moving arm quickly to the side multiple times
6
New cards
take note for field signals
use left arm; right arm holds rifle
flush fingers
big actions
flush fingers
big actions
7
New cards
field signals to use w/ enemy ahead
enemy ahead, take cover, halt
8
New cards
field signals to use w/ passing enemy
double up
9
New cards
field signals to use w/ ally ahead
friendly ahead
10
New cards
movement by day: do not know where enemy is
normal alert; hold rifle 45° downwards, fingers off the trigger, left hand supporting barrel
11
New cards
movement by day: know enemy is near
high alert; point rifle straight ahead, butt of the rifle at your shoulder hollow
12
New cards
movement by day: some cover up to waist level
high crawl: crawl on all fours, move opposite arm and leg together
hold rifle in front of you w/ ejection port facing up, muzzle should not touch ground
hold rifle in front of you w/ ejection port facing up, muzzle should not touch ground
13
New cards
movement by day: low cover (minimal cover & concealment)
low crawl: lie as flat as possible w/ stomach on ground, move opposite arm and leg together
hold rifle normally, dust cover up, muzzle should not touch ground
hold rifle normally, dust cover up, muzzle should not touch ground

14
New cards
judging distances
* stretch out left hand w/ thumb pointing up, place in front of object
* for a 1.7m object:
* 50m = 2 thumbnails
* 100m = 1 thumbnail
* 200m = 1/2 thumbnail
* for a 1.7m object:
* 50m = 2 thumbnails
* 100m = 1 thumbnail
* 200m = 1/2 thumbnail
15
New cards
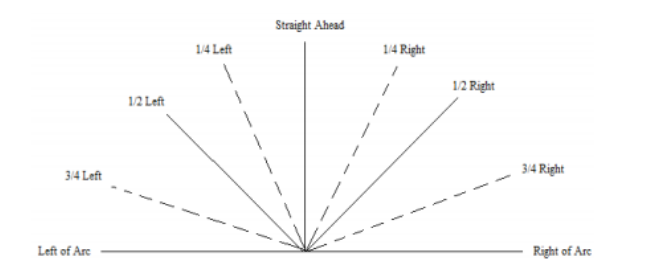
FCO: target indication
* arc of fire
* clock ray (12 is straight ahead, 9 is left arc, 3 is right arc)
* clock ray (12 is straight ahead, 9 is left arc, 3 is right arc)
16
New cards
FCO: GIRLRO
* Group (group, platoon, squad)
* Indication (arc of fire or clock ray)
* Range (distance)
* Location (landmark + where enemy is)
* Rate (regular or rapid)
* Order (“fire!“)
* Indication (arc of fire or clock ray)
* Range (distance)
* Location (landmark + where enemy is)
* Rate (regular or rapid)
* Order (“fire!“)
17
New cards
GK: vision of NCC
extraordinary youth leaders
18
New cards
GK: core values of NCC
LULDCCAS
* loyalty to country
* uprightness
* leadership
* discipline
* commitment & responsibility
* care for fellow cadets
* adventurous spirit
* safety
* loyalty to country
* uprightness
* leadership
* discipline
* commitment & responsibility
* care for fellow cadets
* adventurous spirit
* safety
19
New cards
GK: mission of NCC
to nurture inspiring leaders and committed citizens through fun, adventurous and military-related activities
20
New cards
GK: what does the sword held by the lion on the NCC flag symbolise?
defence of our country
21
New cards
GK: what does the white colour on the NCC flag \n symbolise?
everlasting purity and virtue
22
New cards
GK: what does the red colour on the NCC flag \n symbolise?
universal brotherhood and equality of man
23
New cards
GK: what does the lion on the NCC flag represent?
bravery, courage and strength of the youth of Singapore
24
New cards
GK: what makes an NCC cadet “cadet strong”?
being one with a resilient mind, fit body and committed heart
25
New cards
GK: key thrusts of NCC
leadership, fitness, commitment to Singapore
26
New cards
GK: describe how NCC played a part in the defence of Singapore during WW2
during the outbreak of WW2, many NCC cadets joined the Singapore Volunteer Corps and fought against the Japanese troops in the defence of Singapore
27
New cards
GK: NCC pledge
we, the members of the National Cadet Corps and youth of the Republic of Singapore, do hereby pledge to be loyal to the Republic and the Corps, and to maintain a high standard of discipline and performance so that we may better serve our country
28
New cards
GK: mission of SAF
to enhance Singapore’s peace and security through deterrence and diplomacy, and should these fail, to ensure a swift and decisive victory against the aggressor
29
New cards
GK: 4 services of SAF
army, navy, air force, digital & intelligence service
30
New cards
GK: armour, combat engineers & artillery are divisions in which SAF service?
army
31
New cards
GK: littoral mission vessels (LMVs) and missile corvettes are equipment operated by which SAF service?
navy
32
New cards
GK: F-15SG and chinooks are systems operated by which SAF service?
air force
33
New cards
GK: how many years must able-bodied Singaporean men serve as NSFs?
2 years
34
New cards
GK: which pillar of total defence is associated with the SAF?
military defence
35
New cards
GK: colour of rubber wrist band that is worn by soldiers with medical conditions?
yellow
36
New cards
GK: signs of heat injury
* extreme fatigue (unable to continue with physical activity)
* hot and flushing (redness of skin)
* severe muscle cramps
* nausea and/or vomiting
* headache
* giddiness and/or fainting spells due to sudden change in position
* change in mental state (confused, disoriented, agitated)
* hot and flushing (redness of skin)
* severe muscle cramps
* nausea and/or vomiting
* headache
* giddiness and/or fainting spells due to sudden change in position
* change in mental state (confused, disoriented, agitated)
37
New cards
GK: how many hours of uninterrupted rest must cadets get the night before any strenuous activity?
7 hours
38
New cards
GK: safety tool used before start of training
cadet risk assessment checklist (RAC)
39
New cards
GK: what should be reported to your teacher officer?
hazards, near misses, safety breaches
40
New cards
GK: before training, i must ensure that:
my buddy is with me and they have also completed their risk assessment checklist (RAC)
41
New cards
GK: five main groups of SAR-21
upper receiver group, lower receiver group, barrel assembly group, bolt carrier group, magazine group

42
New cards

GK: what group is shown?
barrel assembly group
43
New cards
GK: maximum effective range of SAR-21 rifle
460m
44
New cards
GK: how many 5.56mm rounds can the SAR-21 box magazine hold?
30 rounds
45
New cards
GK: magnification capability of SAR-21 optical scope
1\.5 times
46
New cards
GK: during firing of SAR-21, when firer encounters a weapon stoppage, what immediate action (IA) should be taken?
safe, tilt, check
47
New cards
GK: what parts can be used in case the SAR-21 optical scope fails?
iron sights
48
New cards
GK: five characteristics of SAR-21 rifle
* semi-automatic
* air-cooled
* gas operated
* magazine feed
* closed bolt system
* air-cooled
* gas operated
* magazine feed
* closed bolt system
49
New cards
GK: procedures taken to remediate double feeding in IA drills
* safe, tilt, check
* remove magazine
* tilt weapon to right
* cock weapon multiple times until stuck rounds are out of the chamber
* check bolt and chamber clear
* insert magazine
* cock fully
* resume firing
* remove magazine
* tilt weapon to right
* cock weapon multiple times until stuck rounds are out of the chamber
* check bolt and chamber clear
* insert magazine
* cock fully
* resume firing
50
New cards
GK: procedures taken to remediate no feeding in IA drills
* safe, tilt, check
* slap base of magazine upwards
* pull charging handle fully to rear and hold it there
* observe that magazine is seated properly and a round is ready to be chambered
* release charging handle
* engage enemy, resume firing
* slap base of magazine upwards
* pull charging handle fully to rear and hold it there
* observe that magazine is seated properly and a round is ready to be chambered
* release charging handle
* engage enemy, resume firing
51
New cards
GK: during stripping of the weapon, what is the first standard accessory that is removed?
magazine
52
New cards
GL: three checks conducted upon assembling weapon
* safety mechanism check
* trigger mechanism check
* sear check
* trigger mechanism check
* sear check
53
New cards
GK: what should you do when instructor gives command “firers for inspection, port arms”?
* engage last round catch
* place rifle butt on right shoulder with chamber facing upwards
* place rifle butt on right shoulder with chamber facing upwards
54
New cards
GK: how to read a grid reference?
take coordinates of bottom left corner
across the corridor & up the stairs - x-coordinate then y-coordinate
format: x, y (e.g. 265, 425)
across the corridor & up the stairs - x-coordinate then y-coordinate
format: x, y (e.g. 265, 425)
55
New cards
GK: bearing format
\[direction\] \[degree°\] \[direction\]
e.g. N 45° W
e.g. N 45° W
56
New cards
GK: azimuth navigation format
draw a line pointing north from ref. point, then draw another line to destination
take the angle measured in a clockwise direction (N = 0°, E = 90°, S = 180°, W = 270°)
take the angle measured in a clockwise direction (N = 0°, E = 90°, S = 180°, W = 270°)
57
New cards
GK: during orienteering, how do you head to a known location?
turn whole body until orienteering arrow aligns with magnetic arrow to face direction of travel
58
New cards
GK: why would you apply intersection in navigation?
determine an unknown point which can be seen in the far distance with reference to two or more known points
59
New cards
GK: why would you apply resection in navigation?
find your exact current location by identifying at least two distinct points on the map
60
New cards
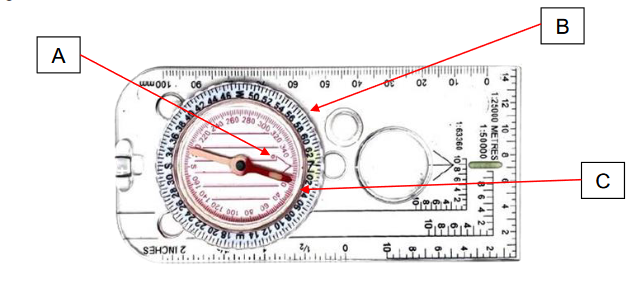
GK: identify the parts of the compass shown
A: orienteering arrow
B: rotating bezel
C: magnetic needle
B: rotating bezel
C: magnetic needle
61
New cards
GK: what action will increase your average pace (taking more steps than usual)?
walking up a steep slope
carrying heavy bag / equipment
carrying heavy bag / equipment
62
New cards
GK: which IFC skillset is used to help hide personnel and equipment from enemy forces by applying colour & materials to blend in with the environment?
camouflage & concealment
63
New cards
GK: why are field signals essential for soldiers?
to keep voice conversations to a minimum, to observe noise discipline, to keep silence when approaching the enemy
64
New cards
GK: in a hostile situation, how many seconds does a cadet have to move from one cover to another cover swiftly?
4 seconds
65
New cards
GK: field signals to use when enemy is spotted
take cover, enemy ahead
66
New cards
GK: limitations of using field signals
can be greatly disrupted during periods of poor visibility, can be unreliable when range is too far from one soldier to another
67
New cards
GK: how do we apply clock-ray method to project direction of determined target?
identify a landmark at the front & determine clock direction of target from the landmark
68
New cards
GK: 7 factors that affect judging of distances
CVESTS + W
* colour
* visibility
* elevation
* sun position
* terrain
* size
* water
* colour
* visibility
* elevation
* sun position
* terrain
* size
* water
69
New cards
GK: what is equivalent to the size of a person 100m away?
length of thumbnail
70
New cards
GK: what is equivalent to the size of a person 200m away?
1/2 length of thumbnail
71
New cards
GK: what is equivalent to the size of a person 300m away?
1/4 length of thumbnail
72
New cards
GK: how do you apply halving method in judging distances?
* to judge further distances (>300m), pick a halfway point between target and yourself
* estimate distance to halfway point using unit of measurement method (use unit you’re familiar with)
* double distance to obtain estimated distance from target to yourself
* estimate distance to halfway point using unit of measurement method (use unit you’re familiar with)
* double distance to obtain estimated distance from target to yourself
73
New cards
GK: what does “indication” refer to in FCO sequence?
direction of target