MICR5832 L4: Skin, Soft Tissue & Wounds Infection 8/4/25
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
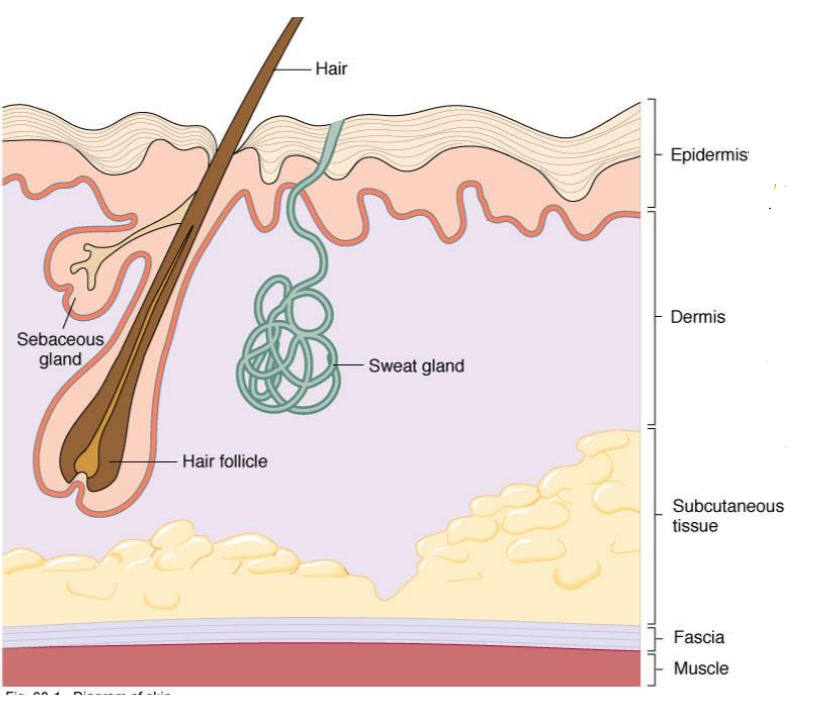
What layer of the skin is this?
-Layers of squamous epithelial cells
-Keratinized outer layer called stratum corneum
Epidermis
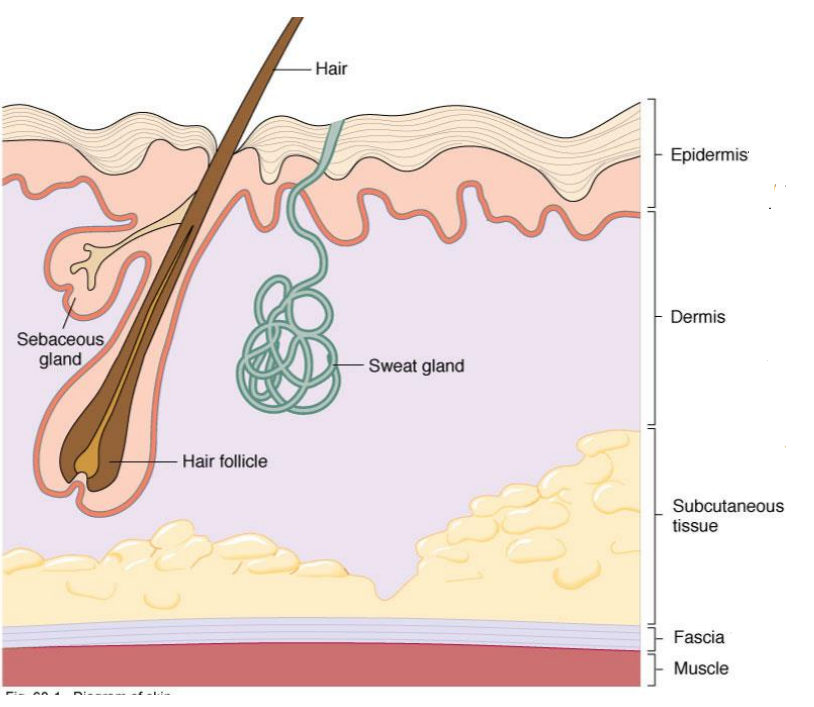
What is this?
-Tough, dry barrier to invading pathogens
-Keratinized outer layer of epidermis
Stratum corneum
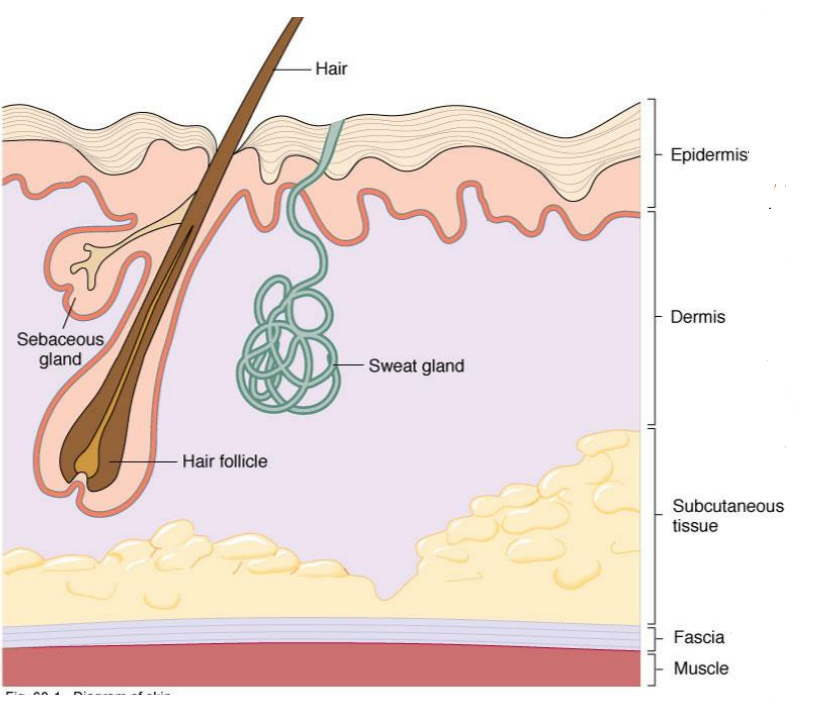
What layer of the skin is this?
-Connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves
-Contains sweat gland ducts, hair follicles and oil gland ducts producing sebum
Dermis
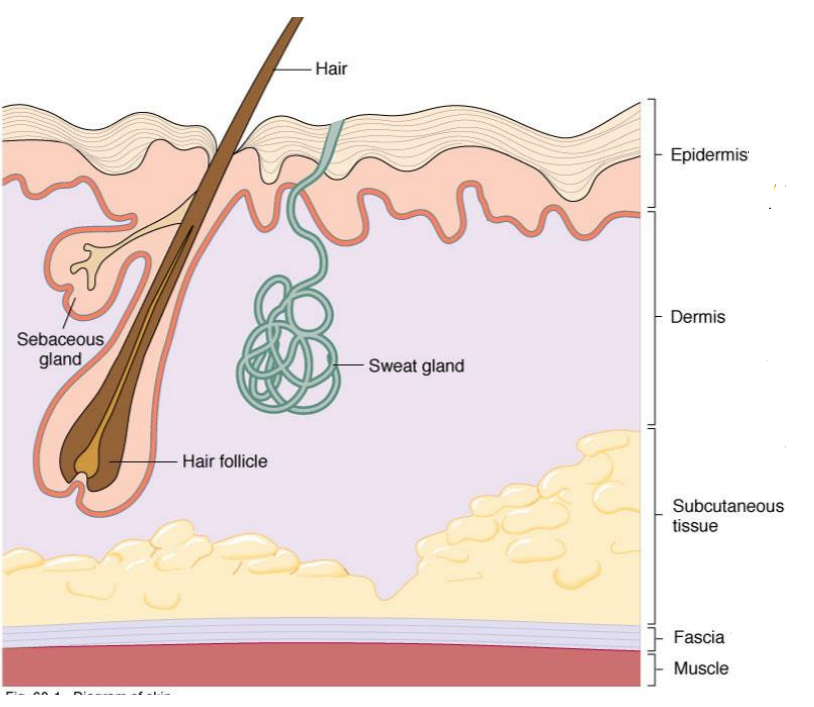
What layer of skin lies between the Dermis and Fascia (Muscle)?
Subcutaneous Tissue
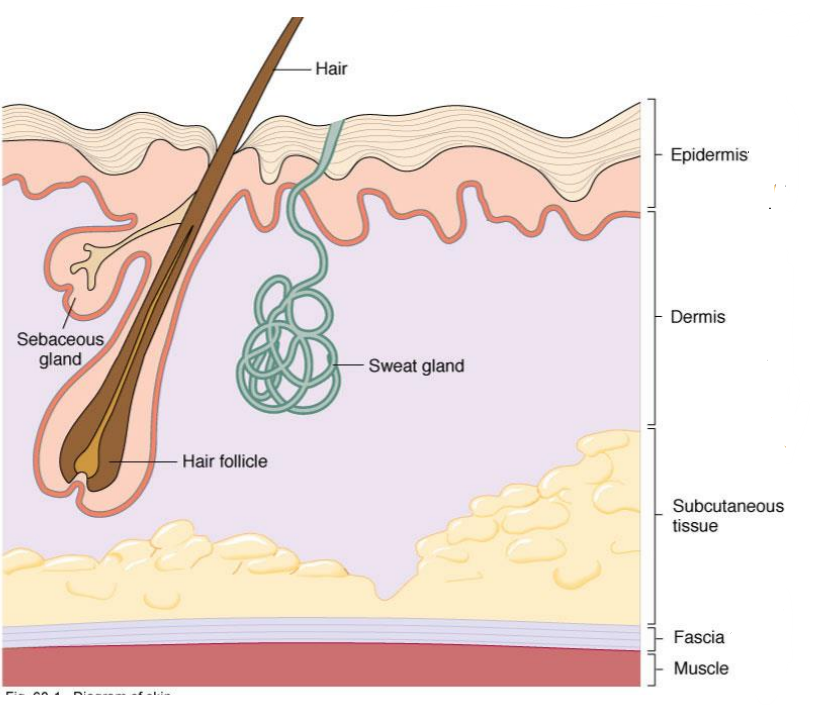
What layer of the skin is this?
-Fibrous sheets of connective tissue
-Barrier to infection
Fascia of muscle
What are some normal flora that competitively inhibit pathogenic bacteria?
-Corynebacterium, diphtheroids
-Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus
-Propionibacterium
What is this?
-Metabolises sebum to toxic fatty acids
-Inhibits growth of non-skin bacteria
-Associated with acnes, opportunistic pathogen
Propionibacterium acnes
True or False: Corynebacterium diphtheriae is a normal flora
False
What do these skin secretions found in sebum/sweat help to do?
1) Fatty Acids
2) NaCl
3) Lysozyme
4) Defensins
1) Low pH
2) Inhibitory
3) Disrupt cell wall
4) Disrupt cell membrane
What is this?
-Group of inflammatory skin disorders caused by bacteria that produce pus
-Examples: Impetigo, Cellulitis, Folliculitis, Erysipelas, Furuncle, Carbuncle
-ICFEFC
Pyoderma
What is this?
-Emerging coagulase-negative pathogen causing pyodermas
-Severe invasive disease, septicaemia, wound infections, and abscesses
Staphylococcus lugdunensis
What Hair Follicle Infection is this?
-Minor infection of hair follicle
-Blockage of hair follicle with sebum
-Minor trauma, friction from rubbing
Agents:
-Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is caused by what bacteria?
-Staphylococcus aureus
-Enterobacteriaceae
-Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Where is Pseudomonas aeruginosa commonly found?
-Swimming pools, hot tubs
-Rarely causes Folliculitis
What Epidermis/Dermis Infection is this?
-Dermis/Subcutaneous Tissue infection (superficial parts)
-Red, swollen, painful, indurated patches with raised margin
-Local lymphadenitis, often fever
Agents:
-GAS, BCG Strep, Staph Aureus
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is caused by what bacteria?
-Group A Streptococcus (GAS)
-B, C, G Streptococci
-Staph Aureus
True or False: Fever associated with Erysipelas is rare and indicates life-threatening bacteremia
True
What groups of people tend to get Erysipelas?
Infants/Elderly
What Epidermis/Dermis Infection is this?
-"School sores" that are highly infectious, especially to children
-Red, bullous or non-bullous lesions
-Painless, do not scar
-May have local lymphadenitis
Agents:
-Staph aureus, Strep pyogenes, GAS
Impetigo
Impetigo is caused by what bacteria?
-Staph aureus (Bullous)
-Strep pyogenes (Non-bullous)
True or False: Impetigo is most common in cold, dry climates and spreads via body fluids and aerosols
False, it is common in hot humid climates and spreads via direct contact with skin or clothing
What Epidermis/Dermis Infection is this?
-Strep pyogenes antibodies cross-react with glomerular basement membrane after skin infection
-Autoimmune inflammatory disease of kidneys
-Leads to kidney failure, dialysis and renal transplant
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is caused by what bacteria?
Streptococcus pyogenes
What is another example of Type III immune reaction where streptococcal M proteins cause antibodies to crossreact with the heart tissue?
Rheumatic fever
What Epidermis/Dermis Infection is this?
-Skin peels off in sheets due to secretion of exfoliative toxin
-Skin, wound or more generalised infection
-Usually affects infants & neonates and immunosuppressed patients
Agents:
-Staph aureus
Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSS)
Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSS) is caused by what bacteria?
Staphylococcus aureus
True or False: Epiderminal/dermal SSS can progress to subcutaneous infection
True
What Epidermis/Dermis Infection is this?
-Localized collection of pus
-Can penetrate lower in hair follicles
Agent:
-Staphylococcus aureus
Abscesses
What Epidermis/Dermis Infection is this?
-Boil or abscess that starts in hair follicle
-Becomes painful and full of pus
Agent:
-Staphylococcus aureus
Furuncle
What Epidermis/Dermis Infection is this?
-Tissue infection surrounding a boil progresses into dermis/subcutaneous tissue
-Often a cluster of boils
-Fever, malaise
Agent:
-Staphylococcus aureus
Carbuncle
Abscesses, Carbuncles and Furuncles are caused by what bacteria?
Staphylococcus aureus
What Epidermis/Dermis Infection is this?
-Common spreading infection of connective tissue/deeper layers of skin
-Red, flat, painful, local lymphadenitis
-Poorly defined margins, warmth of area
-Pus drainage, fever, malaise may occur
Agents:
-Strep pyogenes, Staph aureus, Aeromonas hydrophila, Vibrio, Hemophilus influenzae
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is caused by what bacteria?
-Streptococcus pyogenes
-Staphylococcus aureus
-Aeromonas hydrophila
-Vibrio
-Hemophilus influenzae
Your patient has cellulitis. What bacteria caused the infection?
1) They got it from marine/freshwater
2) Patient is an unvaccinated child with facial cellulitis
1) Vibrio
2) Hemophilus influenzae
Are these abscess bacteria most likely aerobic or anaerobic?
-Perineal, inguinal & buttock abscesses
Anaerobic
Are these abscess bacteria most likely aerobic or anaerobic?
-Non-perineal
Facultative and obligately aerobic
What Subcutaneous Infection is this?
-Often in extremities of patients with poor circulation
-Diabetes mellitus, poor blood supply w/ venous insufficiency
-Acute cellulitis and lymphangitis associated with it
Agent:
-Staphylococcus aureus, but usually mixed (3-5 including anaerobes)
Ulcers
Ulcers are caused by what bacteria?
-Staphylococcus aureus
-Typically mixed with 3-4 other microbes including anaerobes
Why is an ulcer more likely to be polymicrobial if it infects the subcutaneous tissue?
-Not salty or dry
-More microbes grow there
What Subcutaneous Infection is this?
-Ulcer that progresses to infect underlying bone
Osteomyelitis
What diseases are ulcers associated with?
-Acute cellulitis
-Lymphangitis
What diseases cause a risk factor for ulcers?
-Diabetes mellitus due to poor circulation/venous insufficiency
-Poor blood supply, can't get immune cells to key sites
What Subcutaneous Infection is this?
-Decubitous ulcers found in sacral area of bedridden patients
-Poor circulation -> Ulcer -> Infection w/ bowel flora
Agents:
-Bacteroides fragilis, Enterobacteriaceae, Staph aureus, Ps. aeruginosa
Pressure sores
Pressure sores are caused by what bacteria?
1) Anaerobes (Hint: Gram Negative pleiomorphic rods)
2) Facultative Anaerobes
3) Nosocomial pathogens
-Bacteroides fragilis
-Enterobacteriaceae
-Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What happens if the following epidermal/dermal infections progress to subcutaneous infections?
1) Erysipelas
2) Folliculitis
3) Cellulitis
1) Erysipelas → Subcutaneous cellulitis -> Streptococcal necrotising fasciitis
2) Folliculitis -> Cellulitis or Furuncle
3) Cellulitis often extends to Subcutaneous Tissue -> Anaerobic Cellulitis associated with subcutaneous gas production
What Subcutaneous Infection is this?
-Often localized in extremities, can be post-operative infection
-Common in patients w/ diabetes and poor blood circulation
-Bacteremia not usually present
Agents (Usually mixed anaerobes + aerobes):
-Staph. aureus, Strep. pyogenes, non-haemolytic Streptococci, Enterobacteriaceae
-Peptostreptococcus, Bacteroides fragilis, Clostridium (anaerobes)
Anaerobic Cellulitis
Anaerobic Cellulitis is caused by what bacteria?
Hint: Typically mixed aerobes and anaerobes
-Staph. aureus, Strep. pyogenes, non-haemolytic Streptococci, Enterobacteriaceae
-Peptostreptococcus, Bacteroides fragilis, Clostridium (anaerobes)
What Fascia/Muscle Infection is this?
-Infection of fascia overlying muscle, aka hospital gangrene
-Rapid spread, very serious
Agents:
-Strep pyogenes, Staph aureus, Bacteroides, Clostridium
Necrotizing Fasciitis
Necrotizing Fasciitis is caused by what bacteria?
1) Flesh Eating Bacteria
2) Anaerobes
-Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus
-Bacteroides, Clostridium
What Fascia/Muscle Infection is this?
-An infrequent postoperative complication after abdominal or thoracic surgery
-Needs broader range of antibiotics due to mixed infection
-Take both aerobe and aerobe culture samples
Agents (Mixed):
-Staph aureus, microaerophilic Streptococci like S. anguinosis
Progressive bacterial synergistic gangrene
Progressive bacterial synergistic gangrene is caused by what bacteria?
-Staph aureus
-Streptococcus anguinosis (microaerophile)
What Fascia/Muscle Infection is this?
-Muscle inflammation, possibly gas gangrene
Agents:
-S. aureus, Clostridium perfringens
Myositis
Myositis is caused by what agents?
1) Acute bacterial myositis, can have skin involvement
2) Gas gangrene
-Staphylococcus aureus
-Clostridium perfringens
What are some common aerobic pathogens introduced into wound infections via surgery/trauma?
-Staph. aureus
-Strep. pyogenes
-Enterobacteriaceae
-Ps. aeruginosa
-Enterococcus
What are some common anaerobic pathogens introduced into wound infections via surgery/trauma?
-Bacteroides
-Clostridium
-Peptostreptococcus (Gram P cocci)
What Wound Infection is this?
-Subcutaneous infections with draining sinuses, cellulitis
Traumatic wound infection with Nocardia
Traumatic wounds are caused by what bacteria?
Hint:
-Brittle texture
-Aerobic and Acid Fast Gram Positive branching rods
-Slow growth on SAB or routine culture media
Nocardia
How would you identify the species of Nocardia in a traumatic wound?
-PCR amplification/sequencing of 16S rDNA
-MicroSeq 500 system
Sporothrix schenckii is suspected. What medium would you use for this fungi?
Sabouraud Agar
True or False: Nocardia will not show up in a Kinyoun's stain, but it will stain Gram Positive
False, it is both Gram Positive and Acid-Fast
Actinomycetes or Nocardia?
-Gram Positive, long branching filaments similar to fungi
-Aerobe and Acid-Fast
-Pulmonary infections in immunocompromised, like TB
-Cutaneous infections after trauma in immunocompetent
-Can spread to CNS
Nocardia
Actinomycetes or Nocardia?
-Gram Positive, long branching filaments similar to fungi
-Anaerobe, does not show up in Kinyoun's stain
-Normal oral, reproductive, and GI flora
-Causes oral/facial abscesses that drain through sinus tracts
-Often associated with dental caries/extraction
-Yellow "sulfur granules"
-Cause PID with IUDs
Actinomyces
What do you use to treat Nocardia?
Sulfonamides (TMP-SMX)
What do you use to treat Actinomyces?
Penicillin
What Wound Infection is this?
-Gram Positive, Acid-Fast rods
-Identified via Biochemical tests, PCR/Hybridization assay via 16S rDNA like Hain Lifescience
Traumatic wounds w/ Non-TB Mycobacteria
Traumatic wounds are caused by what bacteria?
Hint:
-Gram Positive, acid fast rods
-Grow up to a week on routine culture media
M. abscessus, chelonei, fortuitum
What are some aerobes that cause bite infections from cats/dogs?
-Pasteurella
-Strep mitis
-Staph aureus
What are some anaerobes that cause bite infections from cats/dogs?
-Fusobacterium nucleatum
-Porphyromonas
-Bacteroides testus
What is this?
-Slow-growing Gram Negative capnophilic bacteria
-Rare cause of serious infections from dog saliva
-"Bite of death"
Capnocytophaga canimorsus
Why do bacteria associated with cat/dog bites cause rapidly-spreading cellulitis, abscess formation, and infection of underlying bones/joints?
-Capnophiles (high CO2 lovers)
-Makes it easier to spread
What skin lesion is this?
1) Bullae ulcerate and form black eschar on skin
2) Arising from seafood or seawater exposure
3) Bull's eye lesion
4) Initial rash, papule, ulceration
5) Symptoms depend on species
1) Ecythma gangrenosum
2) Bullae, ulcers, necrosis
3) Erythema migrans
4) Syphilitic chancre
5) Lepros, gummas
What bacteria causes this?
1) Ecythma gangrenosum
2) Bullae, ulcers, necrosis
3) Erythema migrans
4) Syphilitic chancre
5) Lepros, gummas
1) Pseudomonas aeruginosa
2) Vibrio vulnificus
3) Borrelia burgdorferi
4) Treponema pallidum
5) Mycobacteria
Name some zoonoses where the type of rash is determined by the species
1) Rickettsiosis
2) Leptospirosis
3) Bartonellosis
4) Tularemia
How would you collect this specimen?
-Fluid/pus-filled lesions (Boils, Bullae, Carbuncles)
-Erysipelas
-Cellulitis
-Needle aspirate
-Swabs of ruptured lesions (less useful due to skin flora, need to go deep to where anaerobes are)
How would you collect this specimen?
-Subcutaneous infections
Biopsy of tissue at base of nodules/ulcers
How would you collect this specimen?
-Necrotizing Fasciitis
Tissue biopsy, pus aspirate, swab of infected tissue
How would you collect this specimen?
-Wounds
-Needle aspirate from deepest part (best)
-Swabs of open wounds (discouraged)
What transport media would you use for swabs, considering anaerobes lose viability after 48 hours?
-Amie's Medium if aerobic
-Stuarts Medium if anaerobic (up to 24hrs viable)
What anaerobic transport media would you use for liquids, aspirates and biopsies?
-Vacutainer
-Oxygen-elimination system
-Activated by depressing the plunger
-Includes a color change indicator
What transport media would you use for anaerobic liquid specimens?
-Port-A-Cul
-Vial contains anaerobic atmosphere
-Specimen injected through rubber stopper
-Resazurin redox indicator turns pink-lavender when oxidized
What transport media would you use for anaerobic tissue biopsies?
-GasPack Pouch
-Pouch generates anaerobic atmosphere
How would you process a specimen?
1) Gram stain on direct smear
2) Kinyoun stain for acid-fast bacilli (Nocardia/Mycobacterium)
3) Selective media to isolate polymicrobial infections
What are some good media for superficial lesions with aerobes/facultative anaerobes?
-Blood agar (BA)
-Colistin-Nalidixic Acid Agar (CNA)
-MacConkey Agar (MAC)
-Chocolate Agar (less common)
-Incubate at 37C with 5% CO2 for 48h
What routine culture medium would you use to culture anaerobes from wounds and deeper lesions?
-CDC Anaerobe Blood Agar (ABA)
-KV Agar (Kanamycin + Vancomycin + ABA)
What anaerobic routine culture medium is this?
-Nonselective medium supports growth of most anaerobes
-TSA (Tryptic soy agar) base with Vitamin K1, Hemin and Sheep blood
-Prepared and packaged under O2-free conditions
-Incubate 37°C, anaerobic atmosphere, 48h
CDC Anaerobe Blood Agar (ABA)
What anaerobic routine culture medium is this?
-Selects against facultative Gram Negative anaerobes (Kms) and Gram Positive bacteria (Vans)
-Useful in primary isolation of Gram Neg obligate anaerobes
-Incubate 37°C, anaerobic atmosphere, 48h
KV Agar (Kanamycin + Vancomycin + ABA)
What would you do if you found out your routine culture was Mycobacteria or Nocardia due to finding Gram positive acid fast bacteria?
Nocardia:
-Incubate up to 7 days
-SAB Dextrose Agar culture
Mycobacterium:
-Incubate up to 7 days
Non culture-based tests:
-Serum antibody tests, PCR assays, DNA probes for M. tuberculosis
Scalded skin syndrome is caused by:
A. Ps aerogenosa
B. Group A streptococcі
C. Aeromonas hydrophilia
D. Staphylococcus aureus
D. Staphylococcus aureus
Nocardia is:
A. An obligate anaerobe
B. Weakly positive for the the Kinyoun stain for acid-fast bacilli
C. Common skin commensal
D. Usually found in water
B. Weakly positive for the the kinyoun stain for acid fast bacilli
Describe how would process a swab sample for identification of fastidious anaerobic bacteria
-Specimen should be collected using a sterile swab.
-Place into an anaerobic transport medium (Amie's, or Stuart's will last up to 24hr).
-Store and transport at room temperature, as low temperatures can increase oxygen diffusion.
-Aim to get the sample to the lab within 2 hours.