2b: Mains electricity
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
2 types of electricity
- static electricity
- current electricity
- current electricity
2
New cards
hazards of mains electricity
- damaged insulation
- overheating of cables
- damp conditions
- overheating of cables
- damp conditions
3
New cards
safety features built into domestic appliances
- double insulation
- earthing
- fuses
- circuit breakers
- earthing
- fuses
- circuit breakers
4
New cards
power
the rate of energy transfer or the amount of energy transferred per second
5
New cards
what is power dependent on
voltage and current
6
New cards
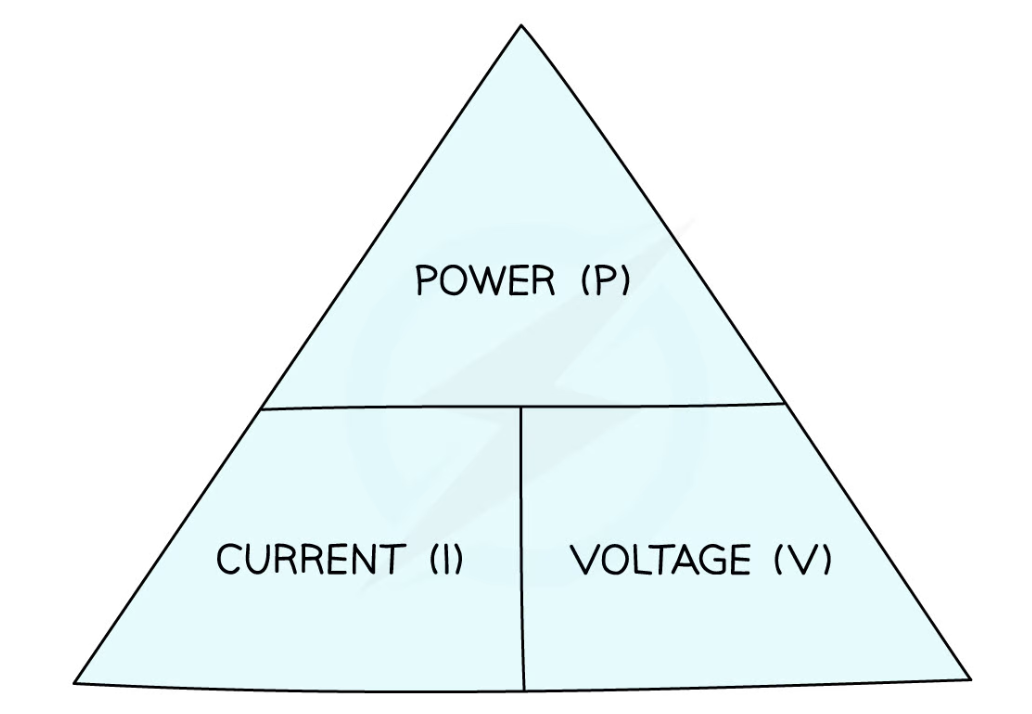
relationship between power, current and voltage
power = current x voltage
7
New cards
unit of power
watts
8
New cards
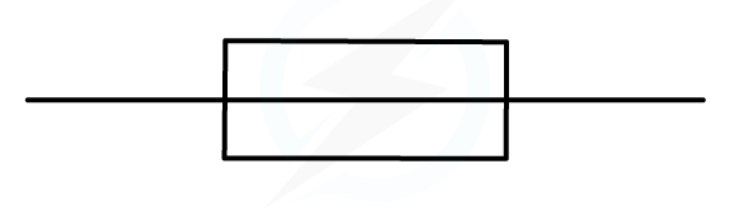
fuse
a safety device that cuts off the flow of electricity to an appliance if the current becomes too large
9
New cards
what do the ratings on a fuse tell us
how much current it can withstand
10
New cards
what does exceeding the current rating on a fuse cause
the fuse blows
11
New cards
should the fuse have a current rating higher than the current needed
yes
12
New cards
what will a low fuse current rating do
it will break the circuit even when an acceptable current is flowing through
13
New cards
what will a too high fuse current rating do
it will not be breaking the circuit in enough time before damage occurs
14
New cards
insulation
wires are covered with an insulating material as the conducting part of the wire is usually made of a metal that poses a risk of electrocution
15
New cards
double insulation
appliances with two layers of insulation
16
New cards
two layers of insulation in double insulated wires
- insulation around the wires
- a non-metallic cased
- a non-metallic cased
17
New cards
do double insulated appliances require an earth wire
no because the earth wire can't touch the metal casing
18
New cards
earthing
many electrical appliances have metal cases which poses a potential safety hazard if the live wire comes into contact with the case risking electrocution
19
New cards
how does the earth wire protects the user
the earth wire provides a low resistance path to the earth causing a surge of current causing the fuse to melt and break which cuts off electricity supply to the appliance
20
New cards
circuit breaker
an electromagnet switch that breaks the circuit if the current exceedds a certain value h
21
New cards
how does a circuit breaker work
it quickly shuts off electricity to the whole house
22
New cards
how is a circuit breaker better than a fuse
it doesn't melt and break and works much faster
23
New cards
DC
direct current
24
New cards
how does DC current travel
in one direction only
25
New cards
does a DC power supply have a fixed terminal
yes
26
New cards
AC
alternating current
27
New cards
how does AC current travel
it constantly changes direction
28
New cards
does an AC power supply have a fixed terminal
it has 2 identical terminals that switch between positive and negative
29
New cards
frequency of an alternating current
number of times the current changes direction back and forth each second
30
New cards
where is DC current produced/used
cells and batteries
31
New cards
where is AC current produced/used
electrical generators
32
New cards
when is work done
when charge flows through a circuit
33
New cards
relationship between work done and energy transferred
work done = energy transferred
34
New cards
relationship between energy transferred, current, voltage and time
energy transferred = current × voltage × time
35
New cards
why does temperature increase when electricity passes through a component
it's turned into heat
36
New cards
what is energy a transfer of
collisions between electrons flowing in the conductor and lattice of atoms within the metal conductor
37
New cards
current
flow of electrons
38
New cards
atomic configuration of metals
lattice of metals
39
New cards
what happens to electrons as they flow through metals
they collide with ions which resist the flow of electronsh
40
New cards
how does metal heat up
electrons collide and lose energy by giving it to ions which vibrate more
41
New cards
which appliances can the heating effect be utilised in
heaters, ovens, hobs, toasters, kettles