SURVEY - SOCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Inclusion is a two-way street
Included and excluded have responsibilities
Typical ways of protecting excluded
Hardware interventions - infrastructure, equipment
Software interventions - education, training, institutions
Social Protection as a third pillar
Never at the center of development discussions
Broadly understood as public measures to provide income security to the population
static state (chronic, persistent)
Povery is not a
Poverty
Social security and other safety nets are difficult to establish during deep crises or when experiencing chronic or persistent poverty
Various risks and complexities are now more translational and global or universally-affecting
Development programs are challenged to sustain
What needs to be done now
What needs to be sustained in the future
Developing countries post more grave challenges
Cost and cost-effective concerns can’t be guaranteed for all
Poorer countries are disproportionately affected by all forms of risks, compounding on one another
accelerate and sustain development
Risk management is necessary to
the vulnerability of the poor
Addressing risks of the poor means addressing
vulnerable
To be poor is to be
Vulnerability
One’s predisposition to risk
Probability of falling into poverty as a consequence of exposure to risks
Everyone experiences or has some form of vulnerability
Why are the poor especially vulnerable?
Lower future outcomes than current outcomes because risks are higher
May increase depth of poverty
Lower future income than current income
Decline in food consumptions compared to current consumption
Factors of Vulnerability
Exposure
Sensitivity
Adaptive Capacity
Exposure
Nature and degree to which a group is exposed to significant hazards
Sensitivity
Degree to which a group is affected, either adversely or beneficially
Adaptive Capacity
Ability of a group to adjust, to moderate the potential damage, to take advantage of its opportunities, or to cope with its consequences
Poor as risk averse
When current outcomes decline, the poor is more affected than the non-poor due to higher vulnerability
Willingness to engage in high-risk, high-return activities for the poor is lower
Not just income poor but also vulnerable (elderly, women, child laborers, PWDs, orphans, IPs, etc.)
Government and other groups cut back on programs for the poor during crisis
Reasons for Vulnerability
Lack of productive assets, lack of human capital, lack of savings, lack of accses to social assistance, voicelessness, informal livelihood, insecure property rights
MEANS
Income deprivation
Entitlements failure
Capabilities failure
Social exclusion
Sources of Risks
Natural disasters
Health shocks
Social diasters and risks
Economic shocks
Political or governance shocks
Environmental shocks
Life cycle shocks
Characteristics of Risks
Source: Natural or man-made
Pattern: Idiosyncratic, covariant, repeated, bunched
Impact: Catastophic, catastrophic
Pattern of Risks ICRB
Idiosyncratic - Individuals or particular households
Covariant - Affecting many people
Repeated - occurs over times
Bunched - together with other risks
Impact of Risks
Catastrophic - Low frequency but severe welfare effects
Non-catastrophic - High frequency but low welfare effects
Risk of Irreversibility
Chronic poverty - long-term poverty
Persistent or situational poverty - insistent movement from poor to non-poor; poverty caused by sudden or temporary shocks
Common Risk Management Practices of the Poor
Reducing consumption of goods/services
Dissaving (spending beyond one’s income)
Increasing productivity by making women and children work
Selling productive assets
Many coping mechanisms provide temporary relief
Reduce available assets
Negative long-term consequences
Often Counterproductive
Risk Management Mechanisms
Ex ante - Implement before event (prevention, mitigation)
Ex post - Implement after the event (coping)
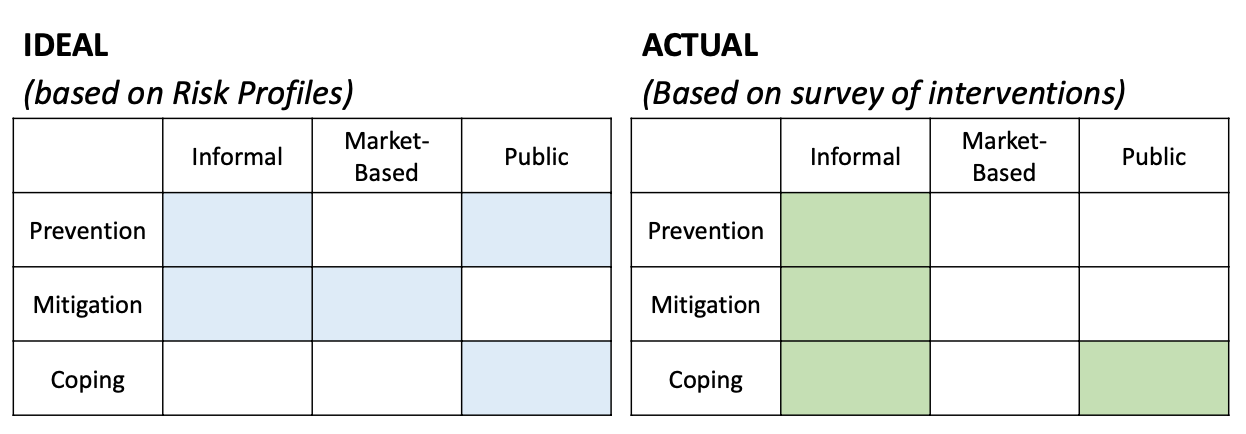
Strategies and interventions to address risks vary depending on the risk profile
Risk Reduction (Prevention)
Reducing the probability and severity of shocks
Ex: Pursuing education, vaccination, climate-adaptive plant varieties
Risk Management (Mitigation)
Reducing the impact of shocks
Ex: Self, mutual, formal
Risk Coping
Relieving the impact of experiencing shocks
Ex: Borrowing, selling assets, migration, child labor, consumption or expenditure postponement
Risk Management Arrangements
Informal - Social networks
Market-Based - Market forces, money, banks, insurance companies
Public - Limited coverage in developing countries
Mechanisms x Arrangements
Challenges for Risk Management (esp the poor)
Think long-term
Acknowledge vulnerabilities
Anticipate risks
Pay for risk management