Mitosis & Meiosis
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Asexual Reproduction
- DNA is a single circular chromosome attached to the membrane
-Parent cell divides in half (one cell into 2)
- Offspring are genetic replicas of parent cell because all chromosomes come from a single parent
- there are 3 kinds: Binary Fission, Mitosis and cloning
Binary Fission examples
prokaryotes, kingdom Protista, kingdom Fungi (yeast through budding)
Mitosis examples
Kingdom Plantae, Kingdom Animalia
Sexual Reproduction
- requires fertilization of an egg by a sperm (produced by meiosis, aka gametes)
- two cells are needed to create a new organisms (egg & sperm)
What are the tips of DNA called?
telomeres
What does Mitosis do?
keeps the same number of chromosomes
What does Meiosis do?
cuts the number of chromosomes in half
Diploid (2n)
- has 2 sets of chromosomes (one from each parent)
-chromosomes are in pairs
Haploid (n or 1n)
- has 1 set of chromosomes
- no pairs just one copy of each chromosome
The Cell Cycle
- Interphase: Gap 1, Synthesis (S), Gap 2
-M Phase: Mitosis and cytokinesis
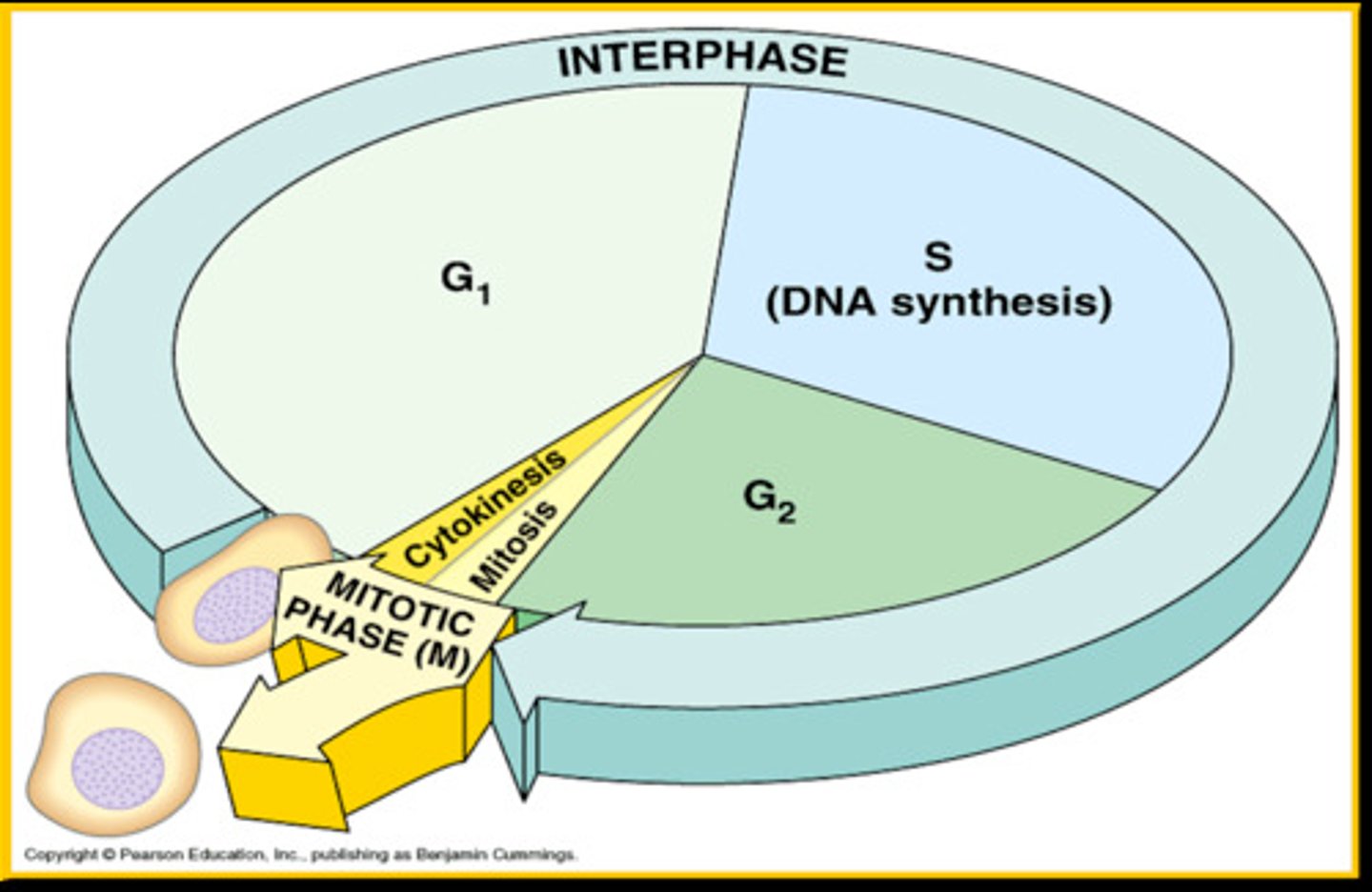
Interphase
cell growth and preparation to divide
Gap 1 (G1)
- cell growth and maintenance (neurons & heart cells spend most of their time here)
- RNA and protein synthesis
- takes about 12 hours
Synthesis (S)
- Every chromosome is copied by replication (DNA synthesis or duplication)
- Before replication: chromosomes are long & linear
- After replication: chromosomes are paired by holding them near the center via the centromere
- takes about 6 hours
Gap 2 (G2)
- growth continues, multiplication of organelles and biochemicals to prepare for division
- takes about 6 hours
M phase & Cytokinesis
- Mitosis (the division of the genetic material and formation of 2 nuclei for the 2 newly formed daughter cells separated by cytokinesis
- diploid (2n)
- takes about 30 minutes
Centromere
a section of DNA that holds chromosomes together
Centrosome
region in metaphase
Centrioles
the actual organelle that connects spindle fibers to centromere
Unwinding
- occurs in Synthesis
- unwind and separate DNA by specific enzymes
Rebuilding in DNA
- occurs in Synthesis
- DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to each template: T-A, C- G to proofread and correct mistakes
Phases of Mitosis
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
Prophase
- nuclear membrane breaks down
- sister chromatids condense
- centrioles move to the poles

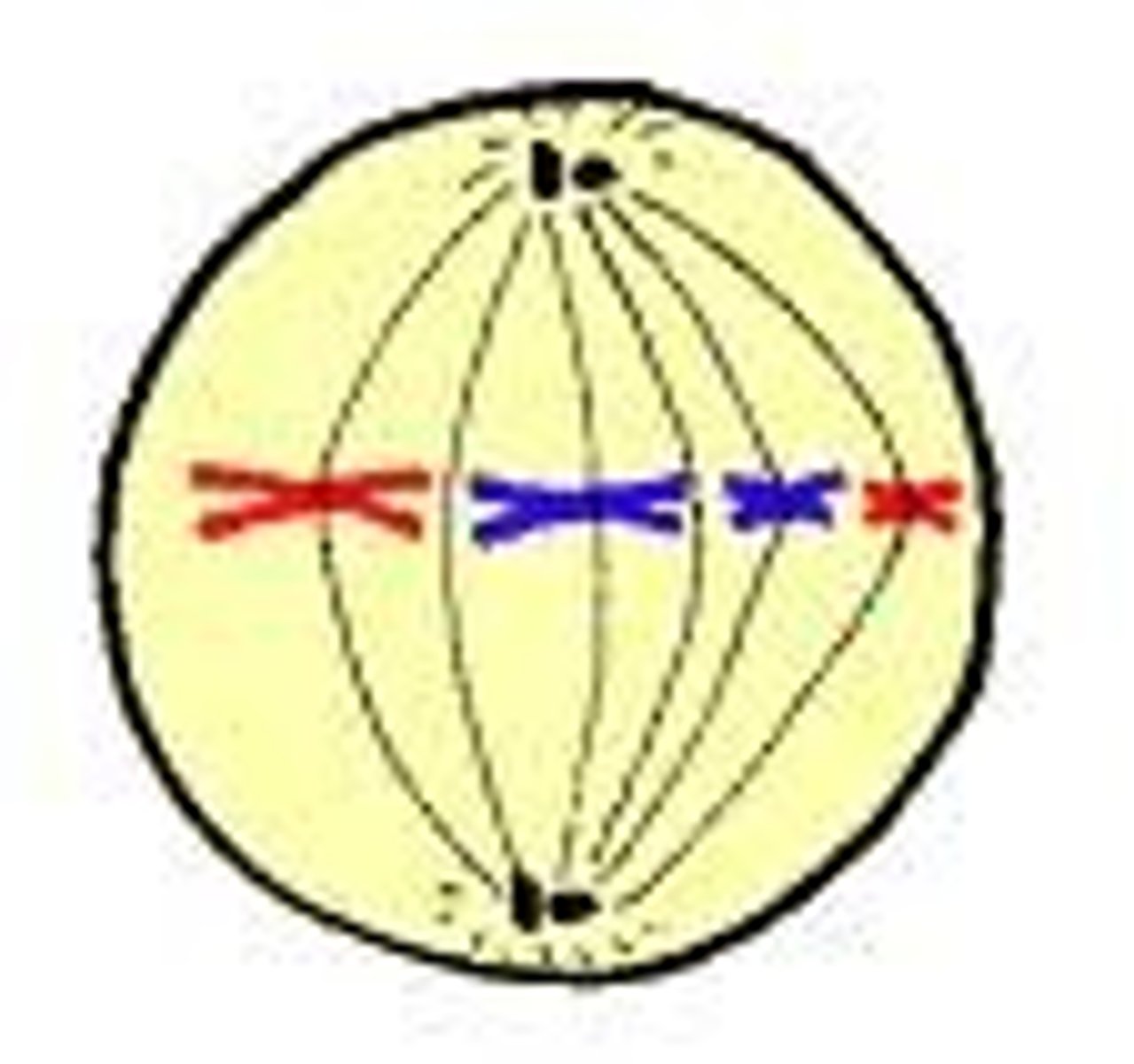
Metaphase
- chromosomes line up in the middle (metaphase plate)
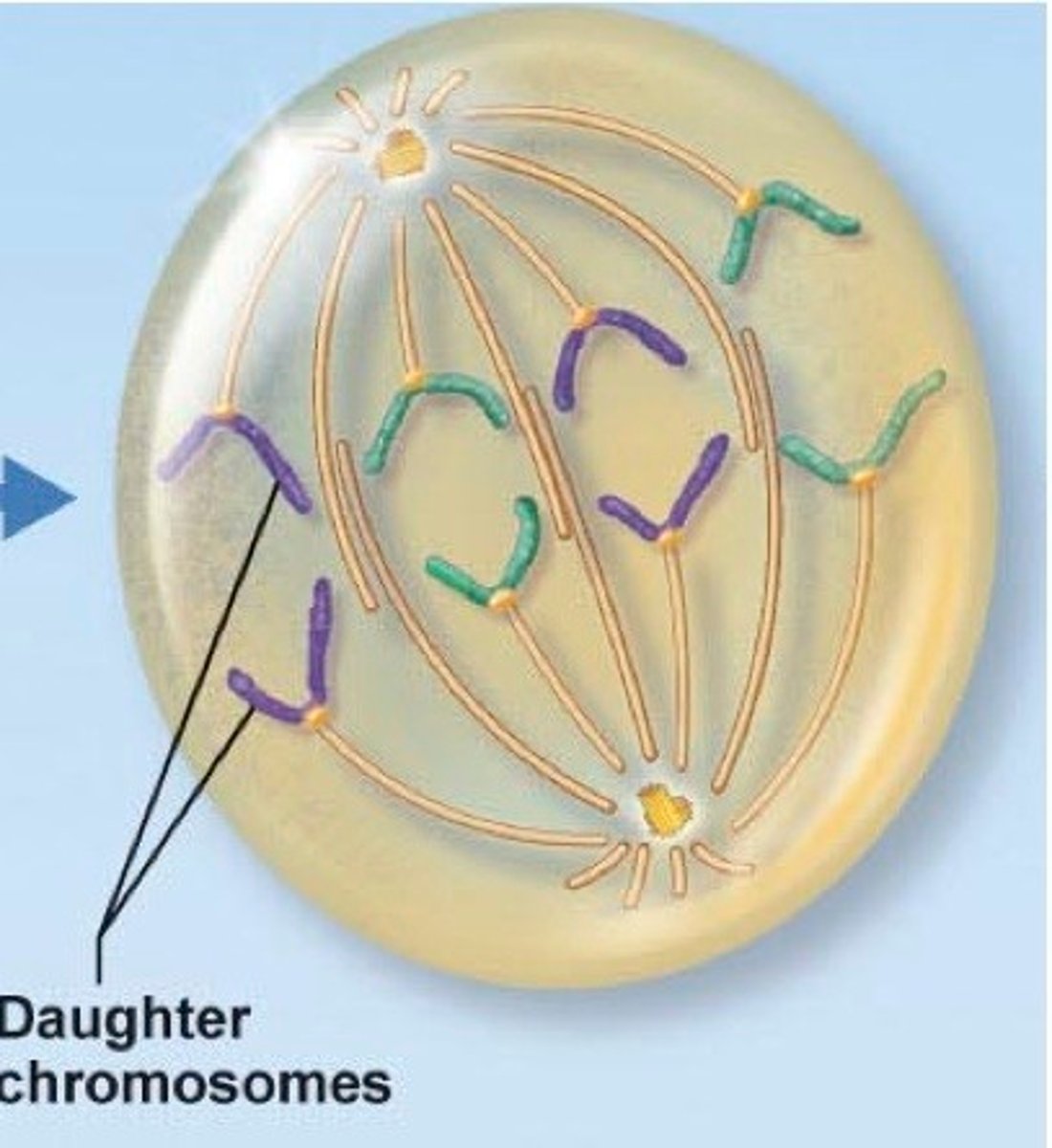
Anaphase
- sister chromatids come apart via spindle fibers that attach to their centromeres
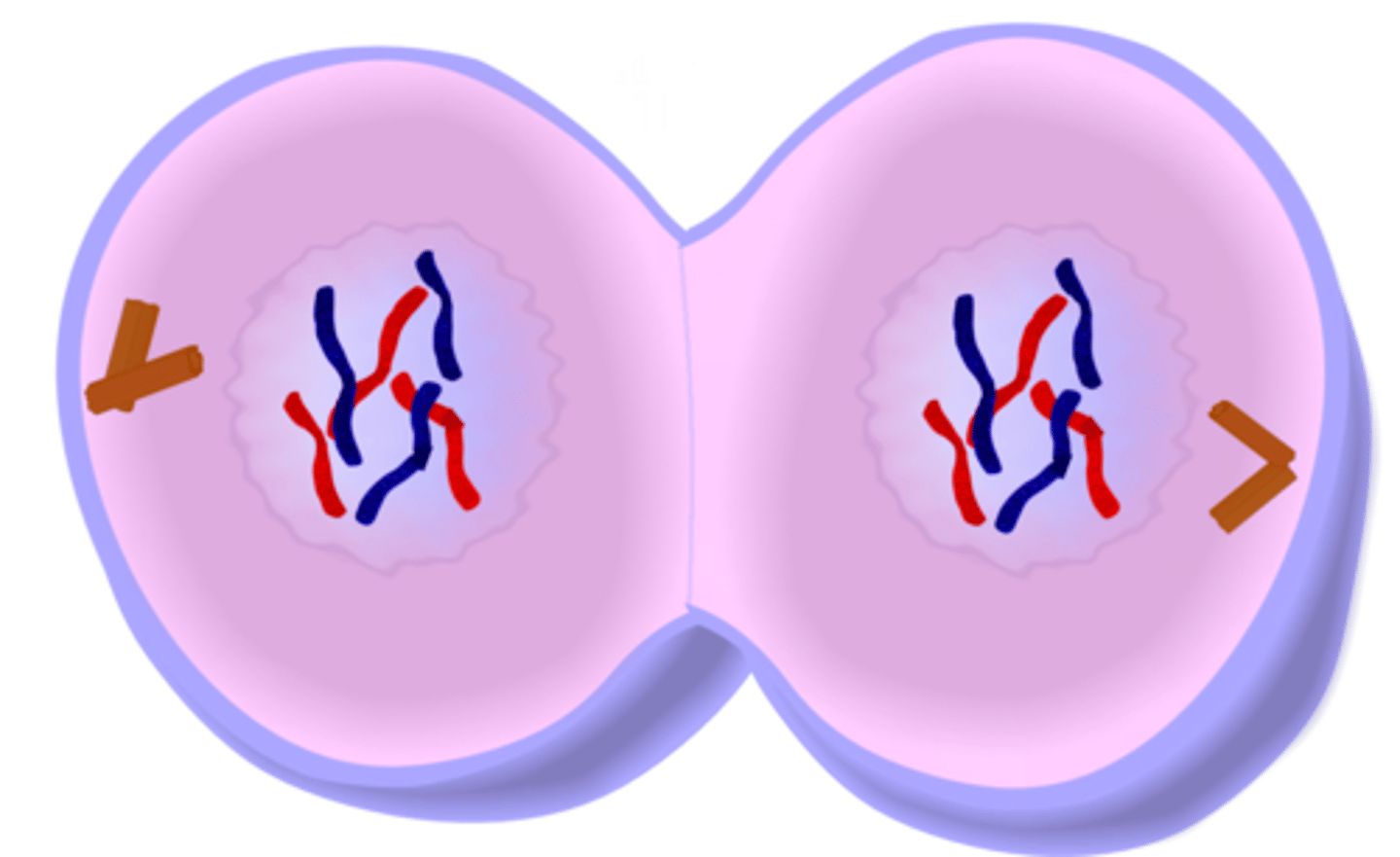
Telophase
- 2 new nuclear membrane forms
- chromosomes uncoils
Cytokinesis (in animals)
the separation of the cytoplasm and plasma membrane
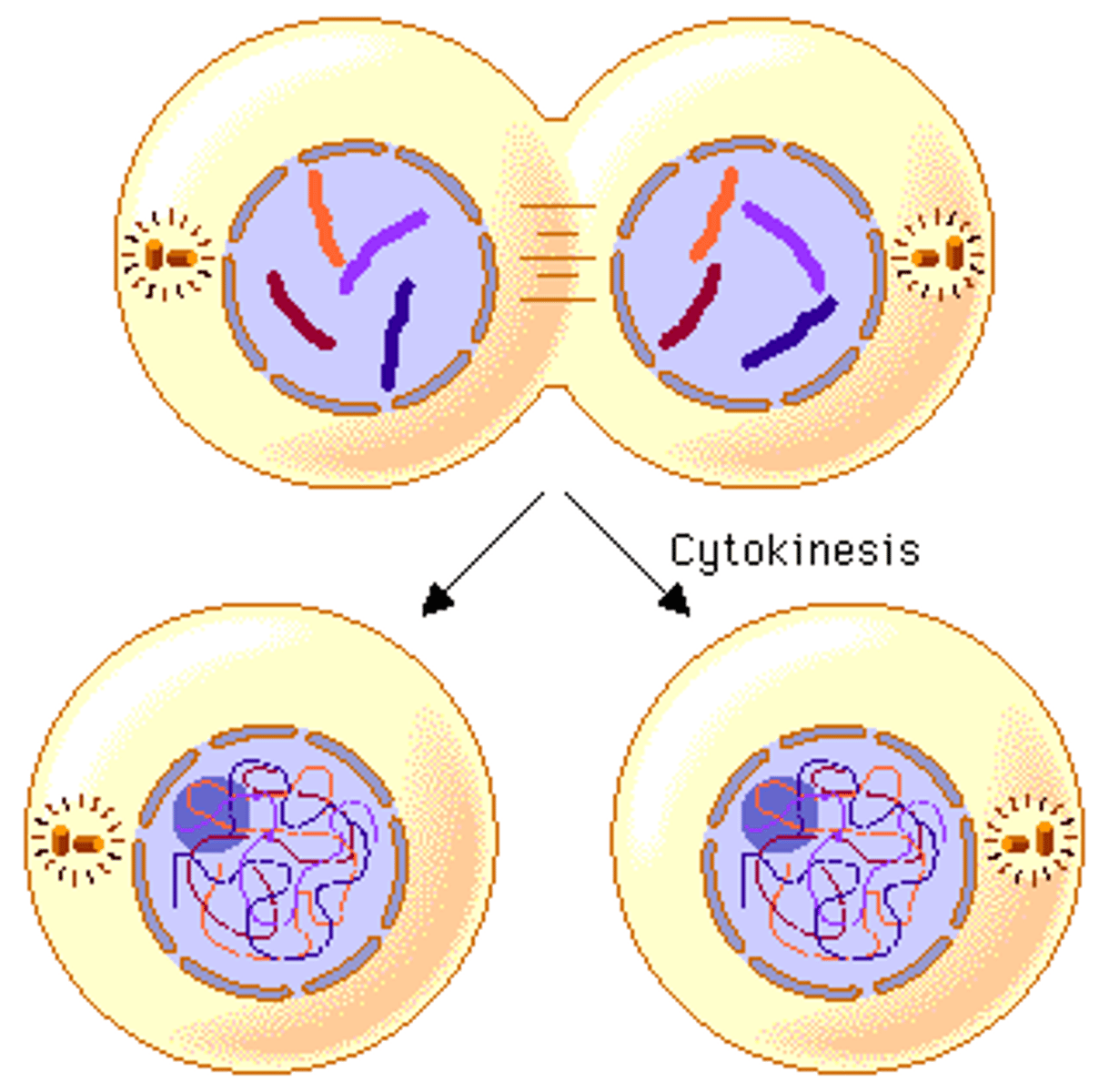
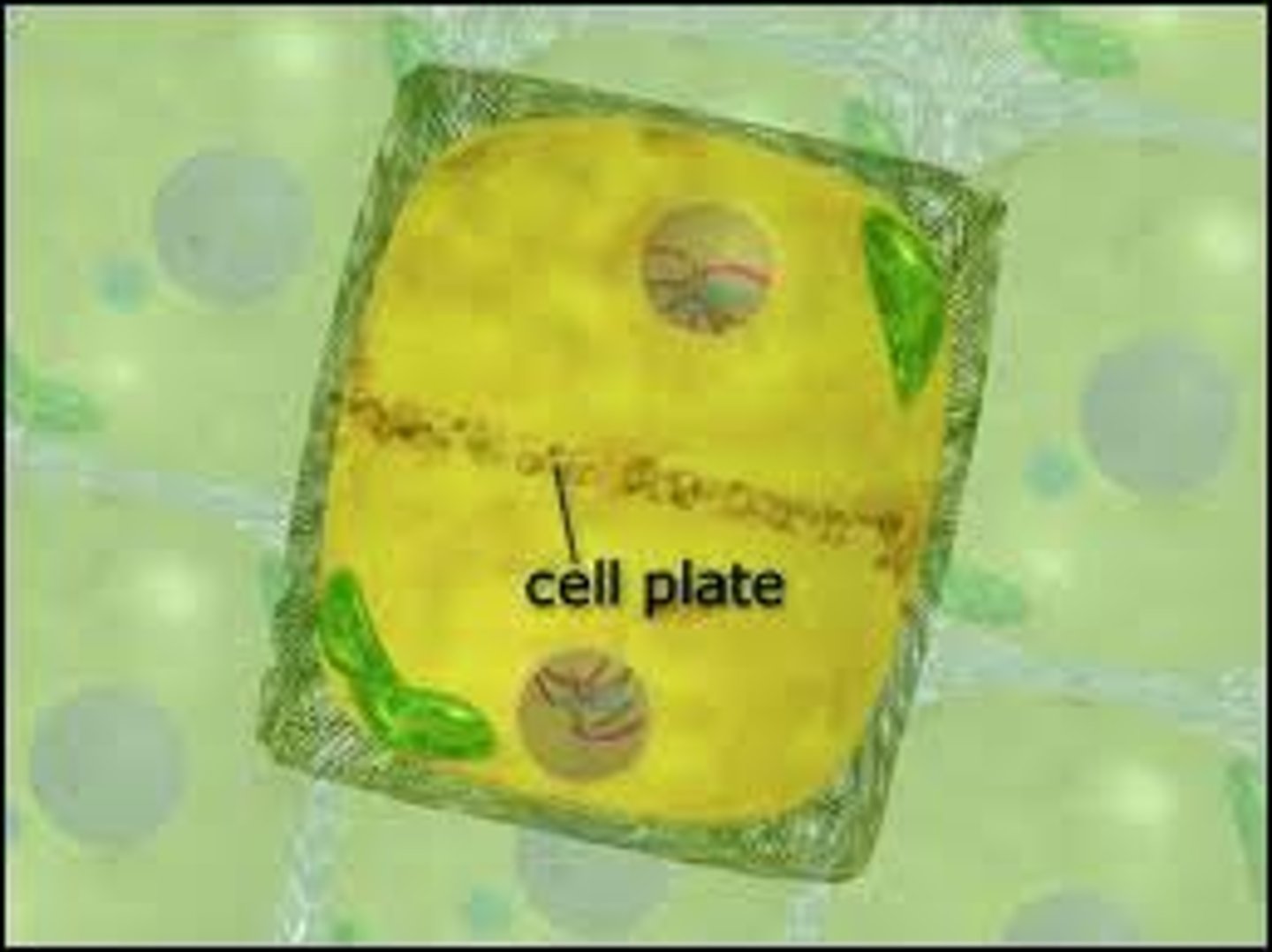
Cell plate (in plants)
- wall in between telophase to disconnect cell
Apoptosis
- programmed cell death
Cancer
- unrestrained cell growth and division caused by disruption on DNA (cell division is no longer regulated)
Characteristics of Cancerous cells
1. Lose contact inhibition and ignore high-density signal (why it keeps growing)
2. Divides indefinitely and lacks apoptosis
3. loses their normal shape (looks misshapen)
4. causes cell death by pressuring neighboring tissues and disrupting vital processes
5. Cancerous cells produce chemicals to attract capillaries (to be fed)
Types of Cancerous Tumors
1. Benign: cell mass that doesn't spread (moles, warts)
2. Malignant: cells spread through the circulatory system, becoming metastatic
Treatment for Cancer
- surgical removal or kill/slow down cell division
- chemotherapy (more generalized damages)
- radiation (more localized damages)
both affect any rapid cell division even normal cells
Side effect of cancer treatment
1. reduced red blood cells
2. shortness of breath and fatigue
3. reduce platelets and white blood cells
4. increase bruising and infection
5. reduce hair follicle cell growth (hair loss)
Human Life Cycle
1. A sexually matured adult develops from a zygote through mitosis in somatic cells
2. Haploid (1n) gametes are produced in the gonads during sexual maturity of the embryo
3. Fertilization of the egg produces a zygote (2n) that, through mitotic division in embryonic development grows into a human baby
- More mitotic divisions of somatic cells and meiotic divisions of gametes produce another sexually mature human being.
Phases of Meiosis
- Prophase 1
- Metaphase 1
- Anaphase 1
- Telophase 1 & cytokinesis
- Prophase 2
- Metaphase 2
- Anaphase 2
- Telophase 2 & cytokinesis
Prophase 1
- Nuclear membrane breaks down
- Sister chromatids condense
- Centrioles move to the poles
- Crossing over aka Recombination, occurs only here

Metaphase 1
- Homologous chromosomes line up in the middle (metaphase plate)
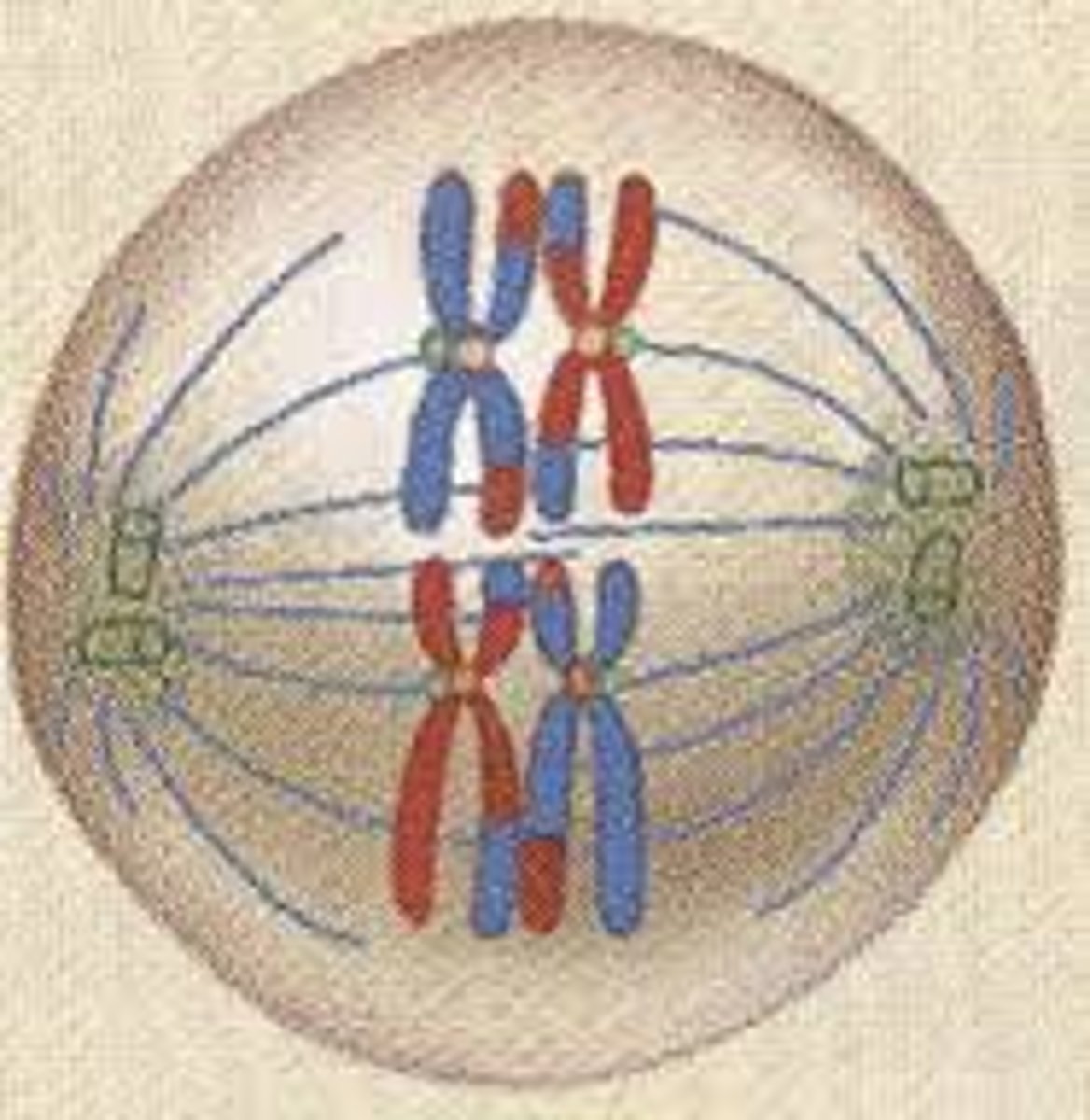
Anaphase 1
- Homologous chromosomes come apart via spindle fibers that attach to their centromeres
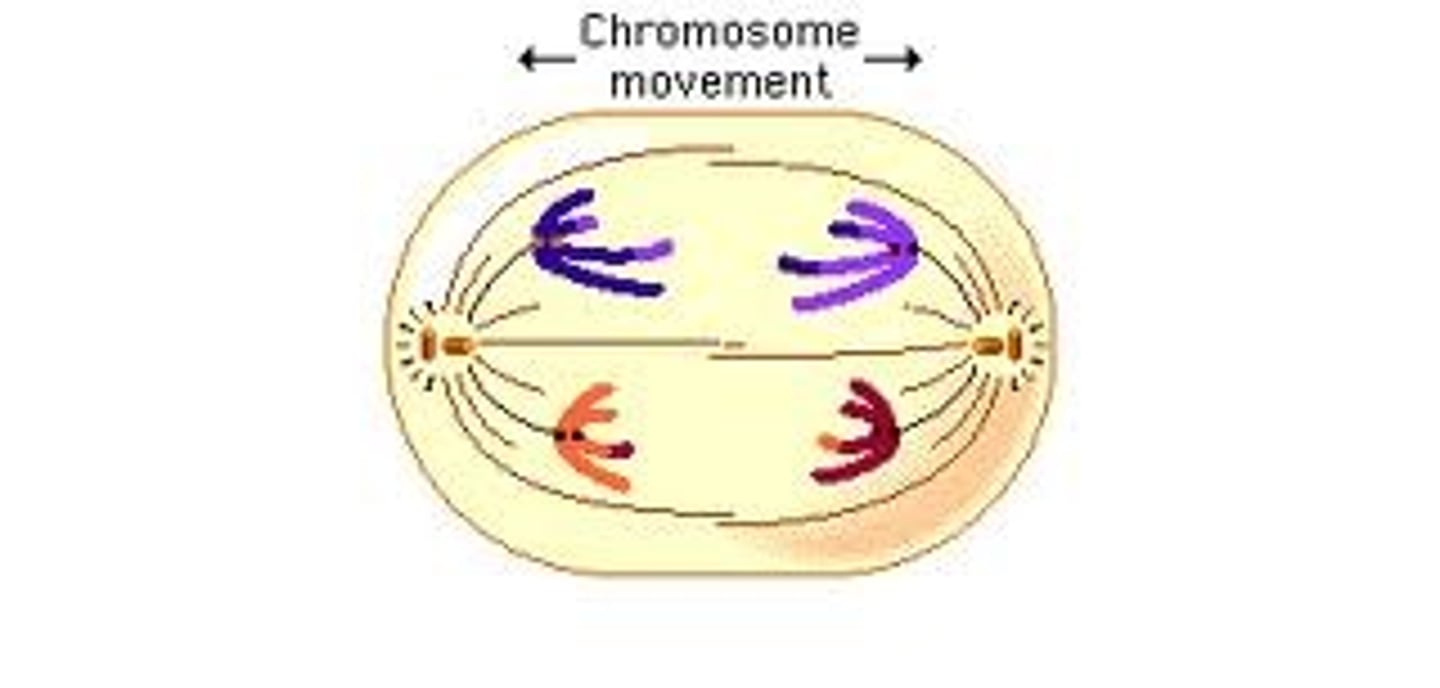
Telophase 1 & Cytokinesis
- two new nuclei form
- cytoplasm finishes dividing into 2 daughter cells
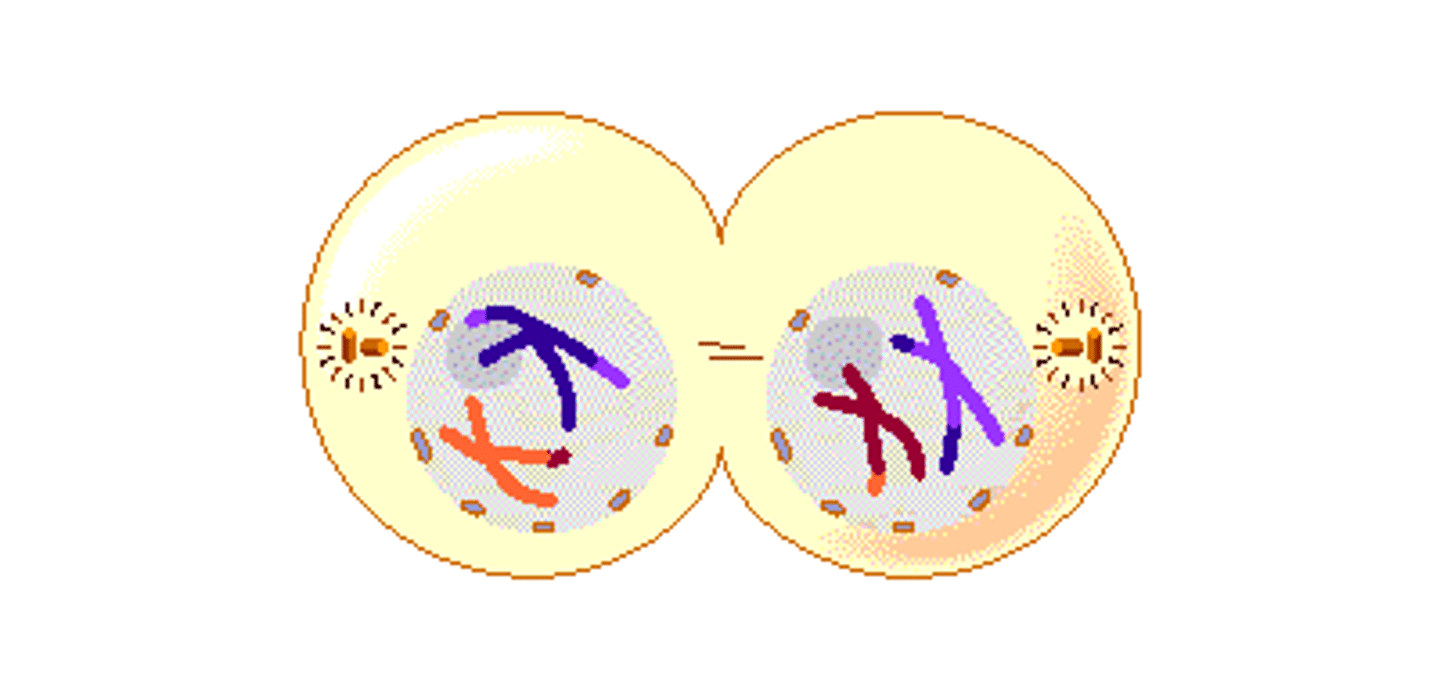
Prophase 2
-chromosomes in both daughter cells condense

Metaphase 2
- sister chromatids line up in the middle (metaphase plate)
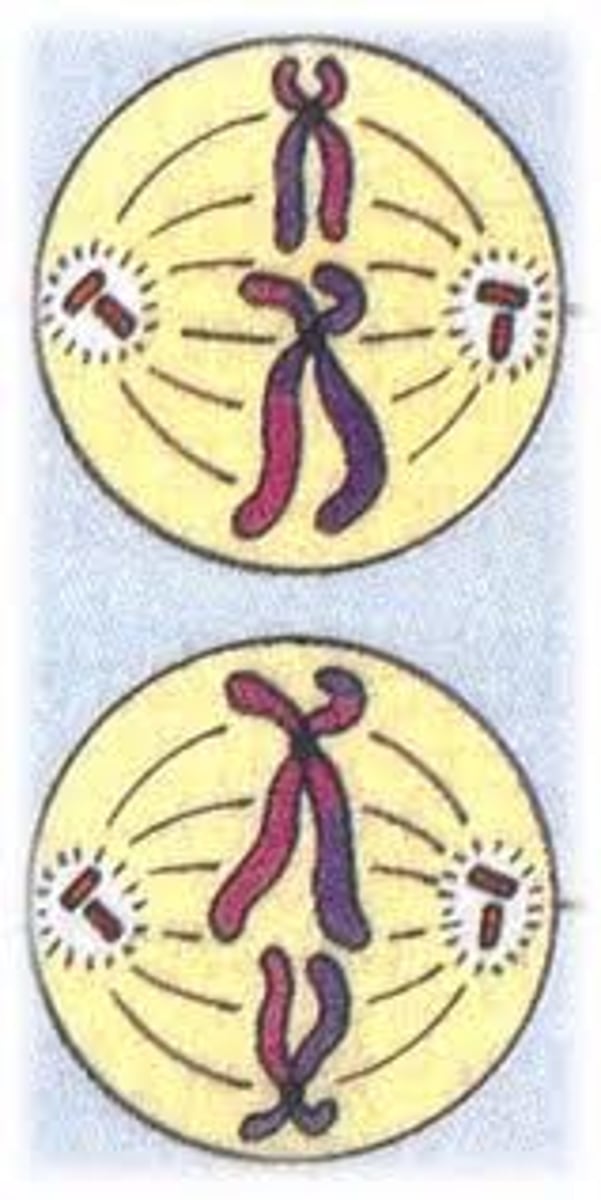
Anaphase 2
- sister chromatids come apart via spindle fibers that attach to their centromeres
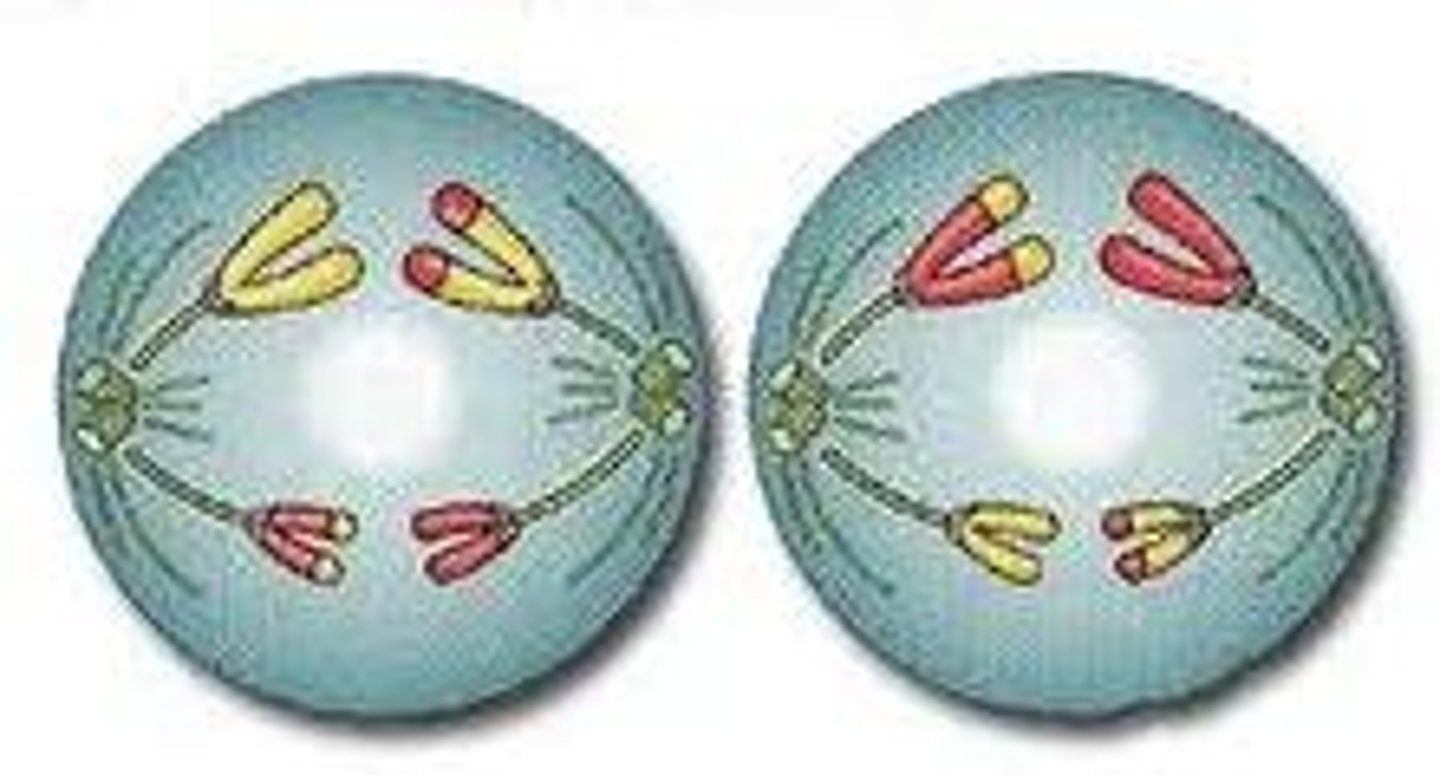

Telophase 2 & Cytokinesis
- nuclear membrane reassembles
- cytoplasm divides into two equally.
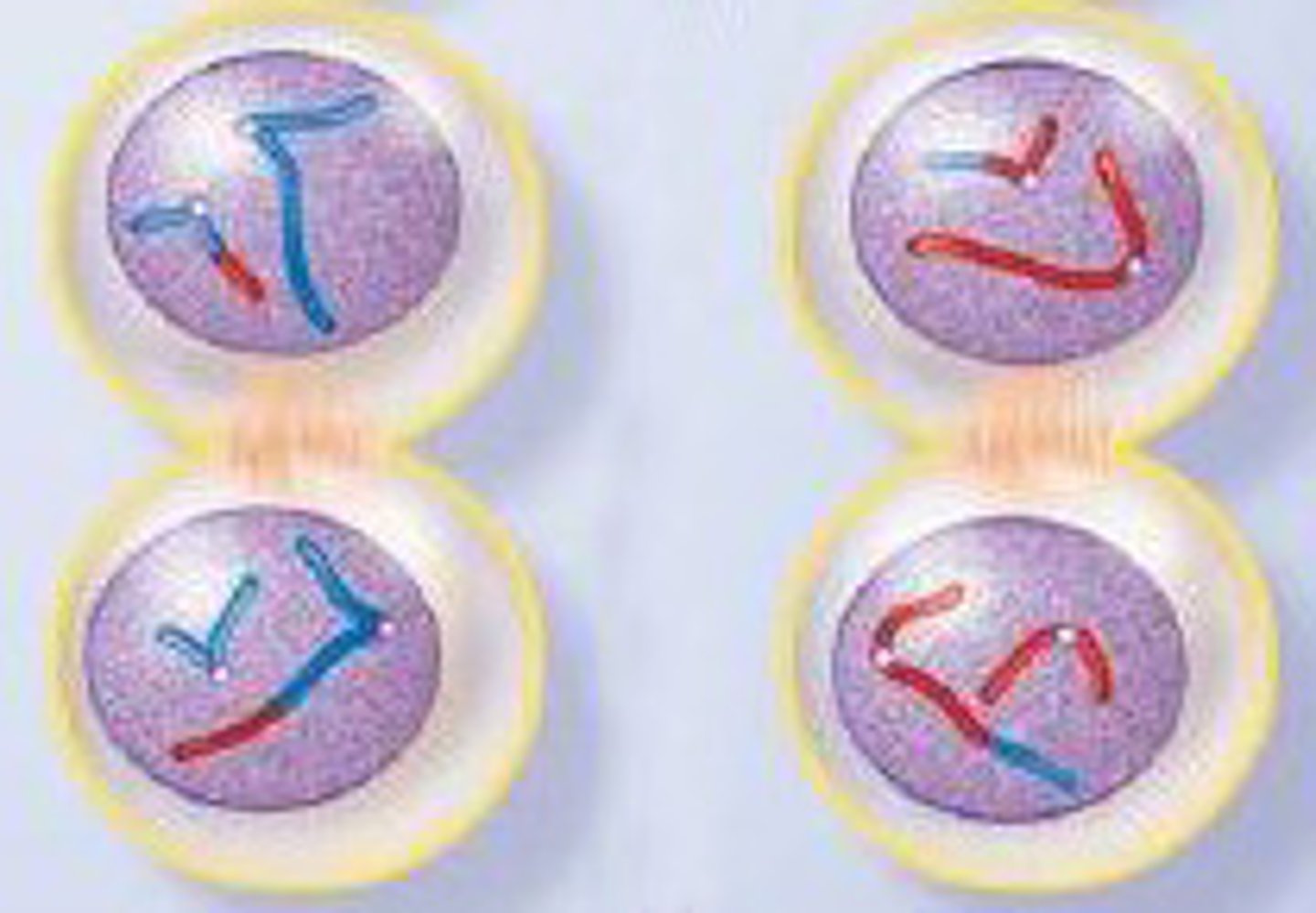
What is Spermatogenesis
- The formation of sperm cells through meiotic division
Spermatogenesis process
- formation of spermatogonia begins at puberty with primary spermatocytes entering meiosis 1, then secondary spermatocytes through meiosis 2 (this process continues throughout his life)
What is produced in Spermatogenesis
- 200-300 million sperm cells are produced daily, but only 100 million are viable (takes 74 days)
Benefits of Sexual reproduction
1. Genetic variation through Crossing over (prophase 1)
2. Random reassortment of homologues (anaphase 1)
3. Alleles come from 2 parents: enables population of organisms to cope better with changes in the environment (Asexual organisms, this is a disadvantage as offspring is an exact copy of the parent copy)
4. Random fertilization:the chance that one specific sperm fertilizes the egg
Oogenesis process
- Formation of oogonia by mitosis begins around 8 weeks of gestation
- Primary oocytes (7 million) will be formed y 20 weeks of gestation
- Birth: prophase 1 stops (1-2 million primary oocytes)
- Adolescence: the process continues, and each menstrual cycle begins with one secondary oocyte stopped at Metaphase 2 waiting for fertilization
- If no fertilization occurs, menstrual flow occurs, discarding the secondary oocyte
-Meiosis 2 concludes only at the formation of a new life, meaning it is only completed if fertilization occurs.
What is produced in Oogenesis
- Each meiotic division produces one polar body; therefore, only one egg is formed at the end of meiosis 2. In contrast, 4 mature sperm cells are produced in males.
- A female will have approximately 400,000 eggs by adolescence but only 300-400 will be ovulated
What is Oogenesis
- The formation of the egg through meiotic division
Cost of Sexual Reproduction
- dangers associated with mating rituals (vulnerability, disease) it takes time and energy to find a partner this energy may be used for reproduction by asexual organisms
Karyotype
an arrangement of chromosomes
- male: short line on Y, long line on X
- female: two long lines on X and nothing on Y
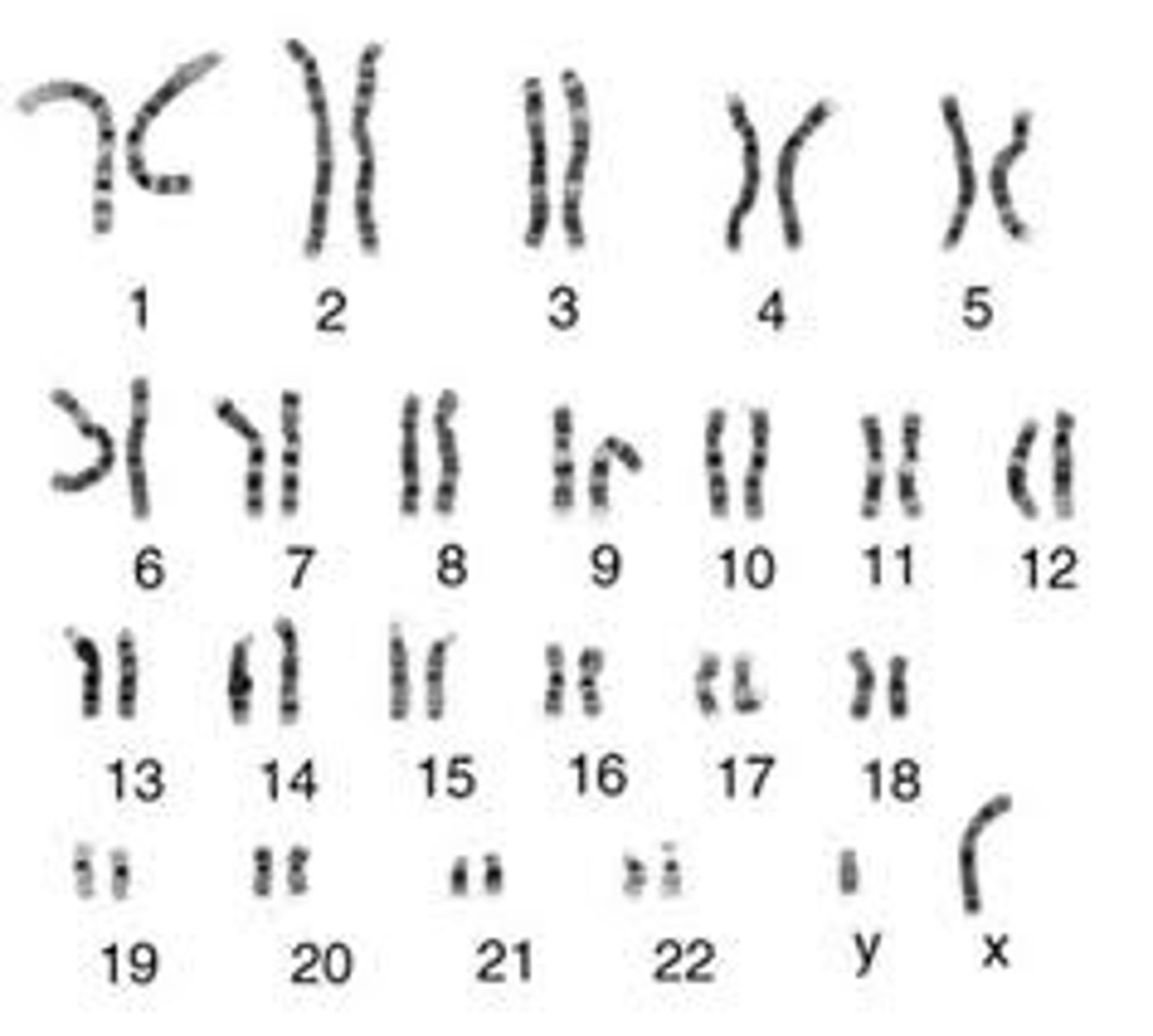
Non-Disjunction
homologous chromosomes fail to separate during meiotic 1 or meiosis 2
Down Syndrome
- caused by non-disjunction during anaphase 1 or anaphase 2 of chromosome 21, aka trisomy 21
- Risk increases as women get older to have a child with trisomy 21
Turner Syndrome
XO
- short size, ovaries don't mature, incomplete development of sex organs, and some learning difficulties
- only in females
Klinefelter Syndrome
XXY
- develops as male, feminized, smaller testes, long limbs, language impairments
- only in males
Super males
XYY
- taller than average, moderate to severe acne, slightly lower intelligence
Meta Females
XXX
- may be sterile, no obvious physical or mental problems