Ch 16 - Proteins: Structure, Function, and Enzyme Inhibition
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins - 20 naturally occurring amino acids.
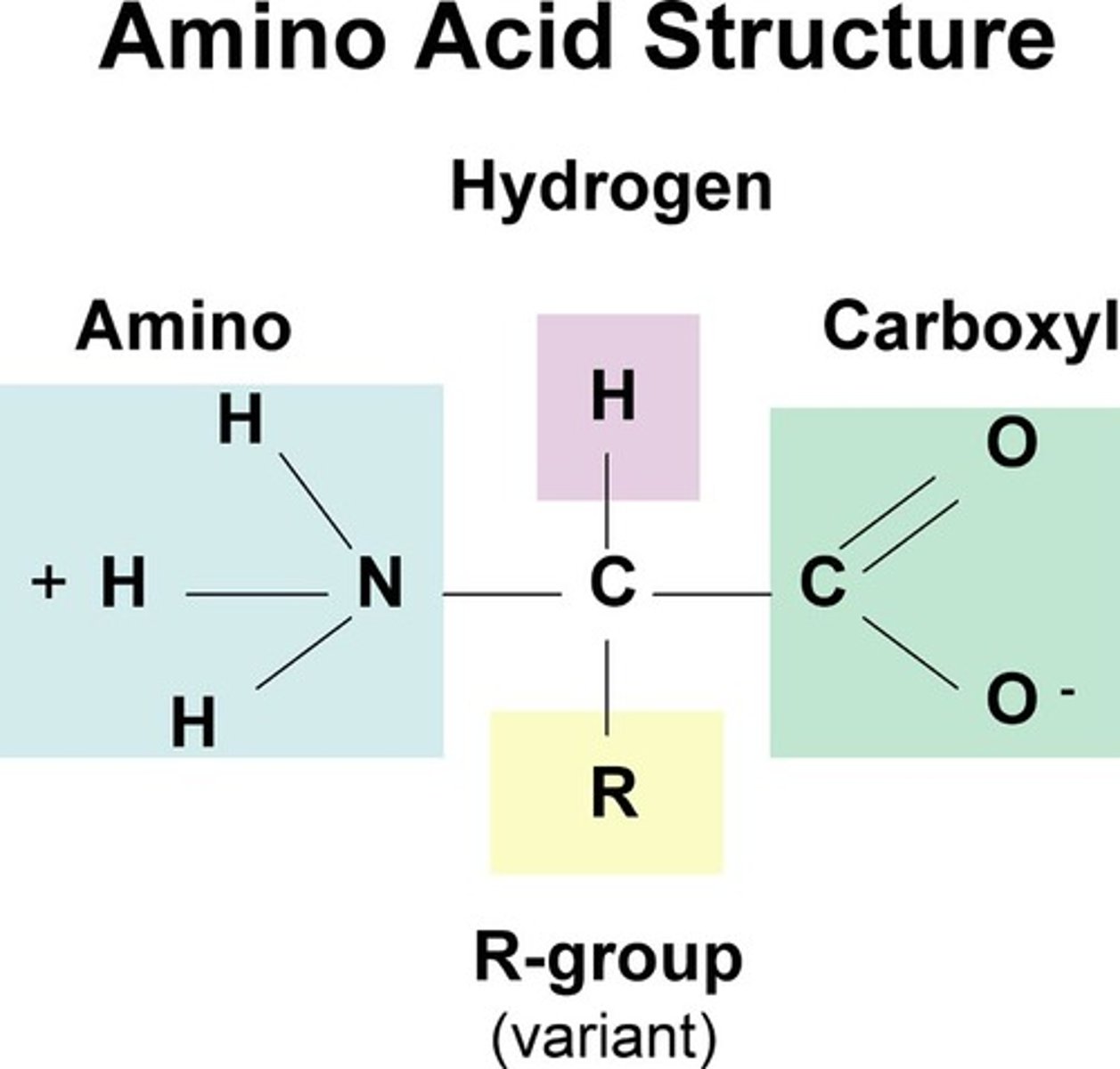
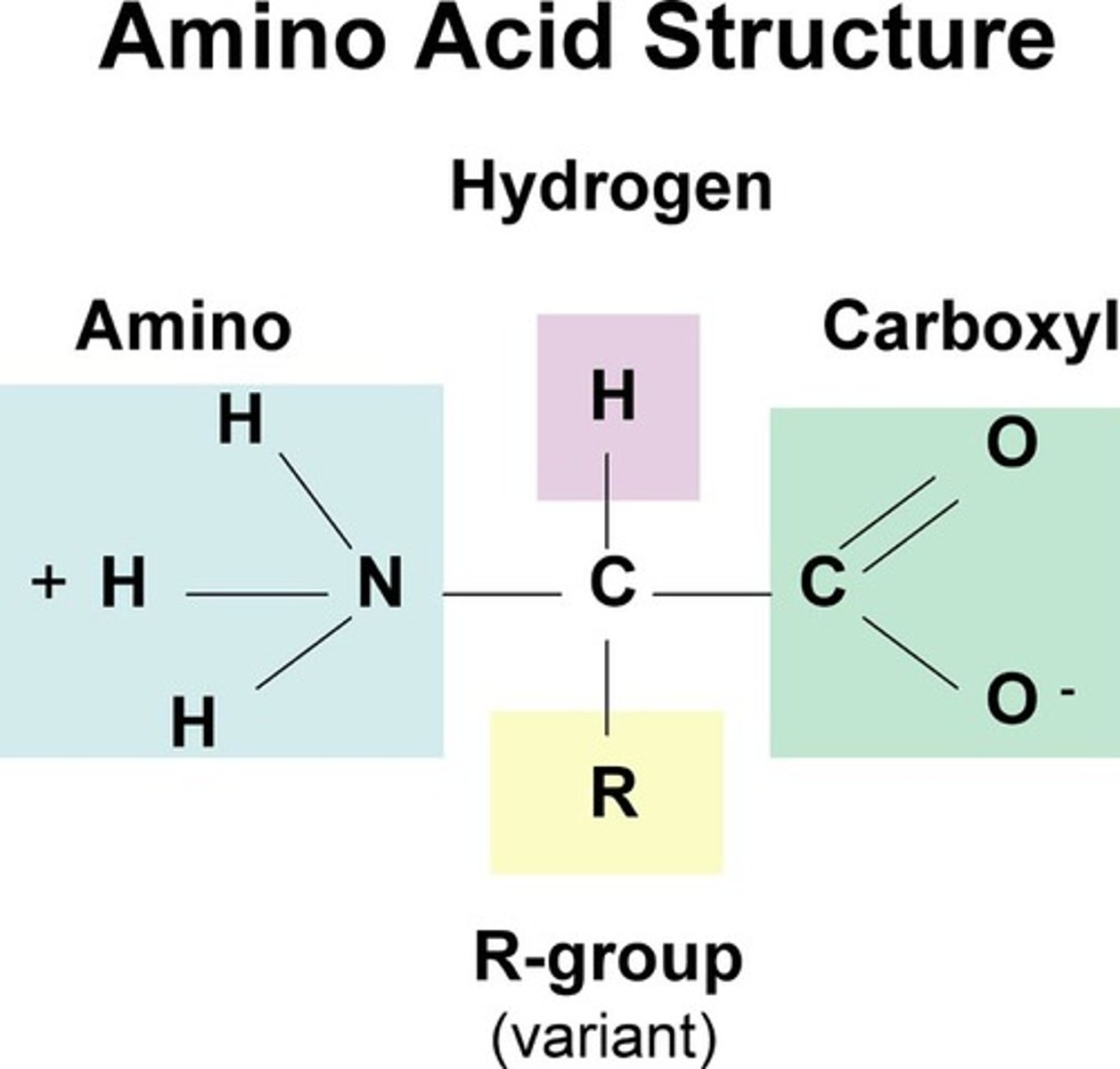
alpha carbon of amino acid
central carbon connecting amine and carboxylic acid is tetrahedral and chiral. Is bonded to the side chain that defines the amino acid
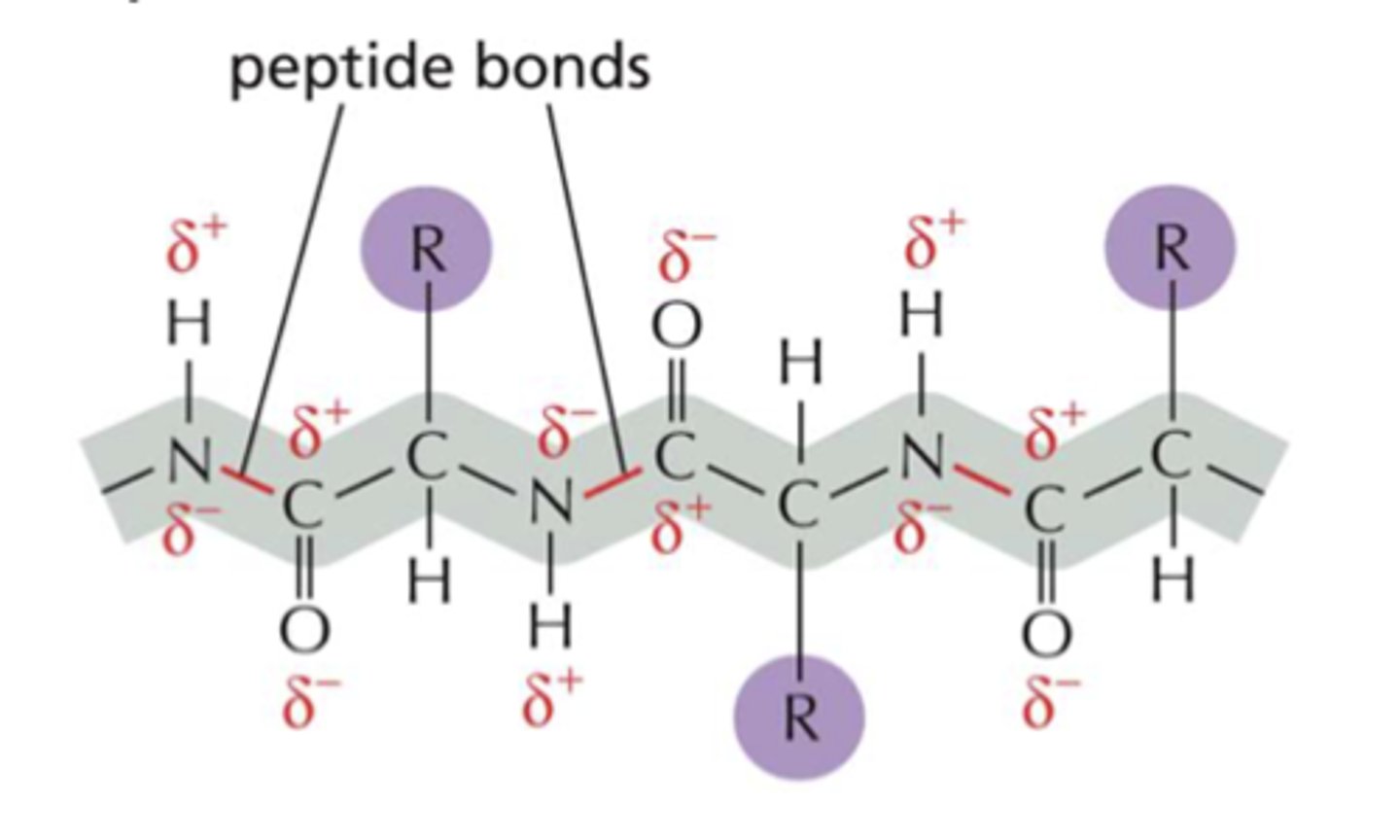
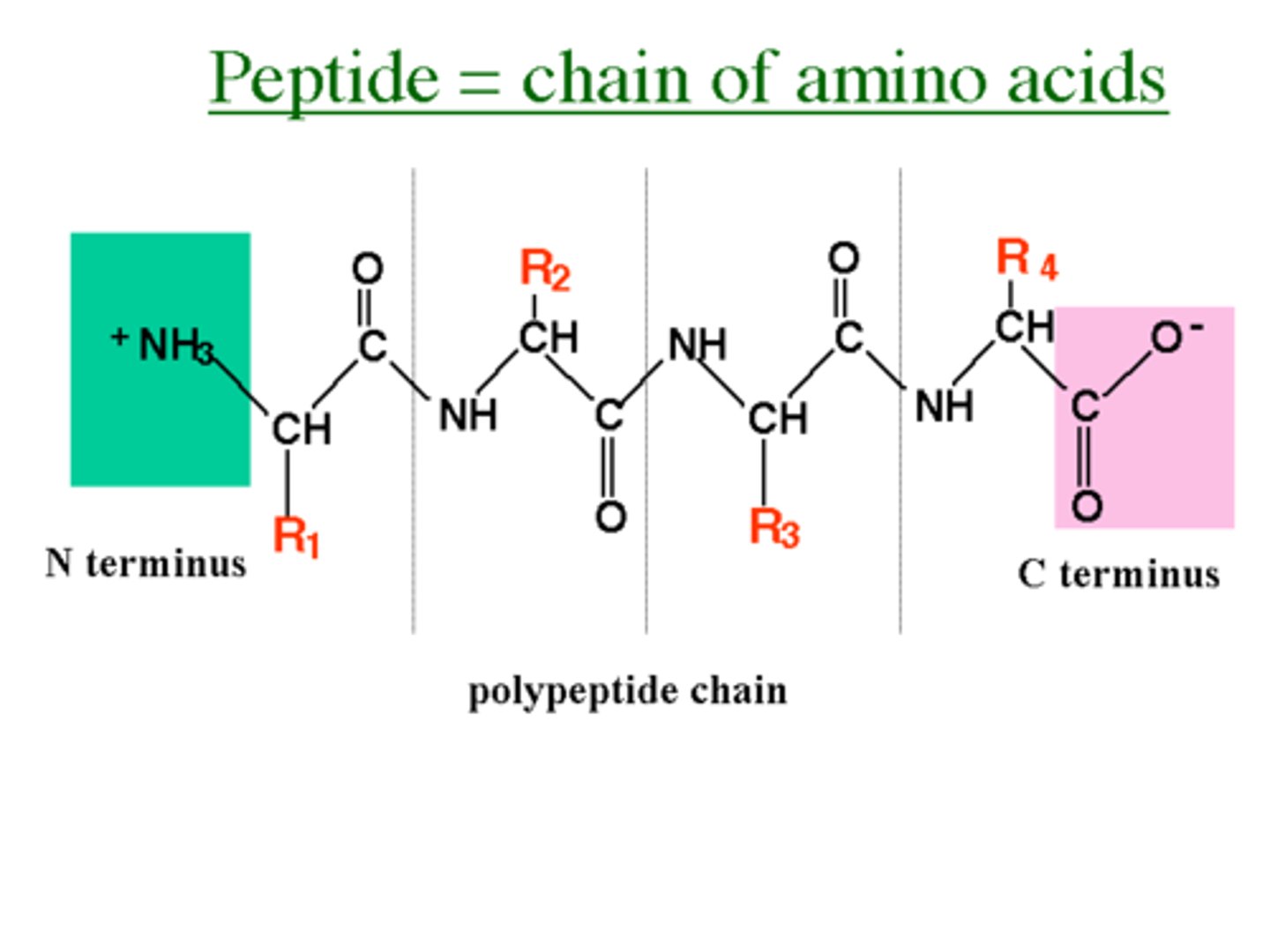
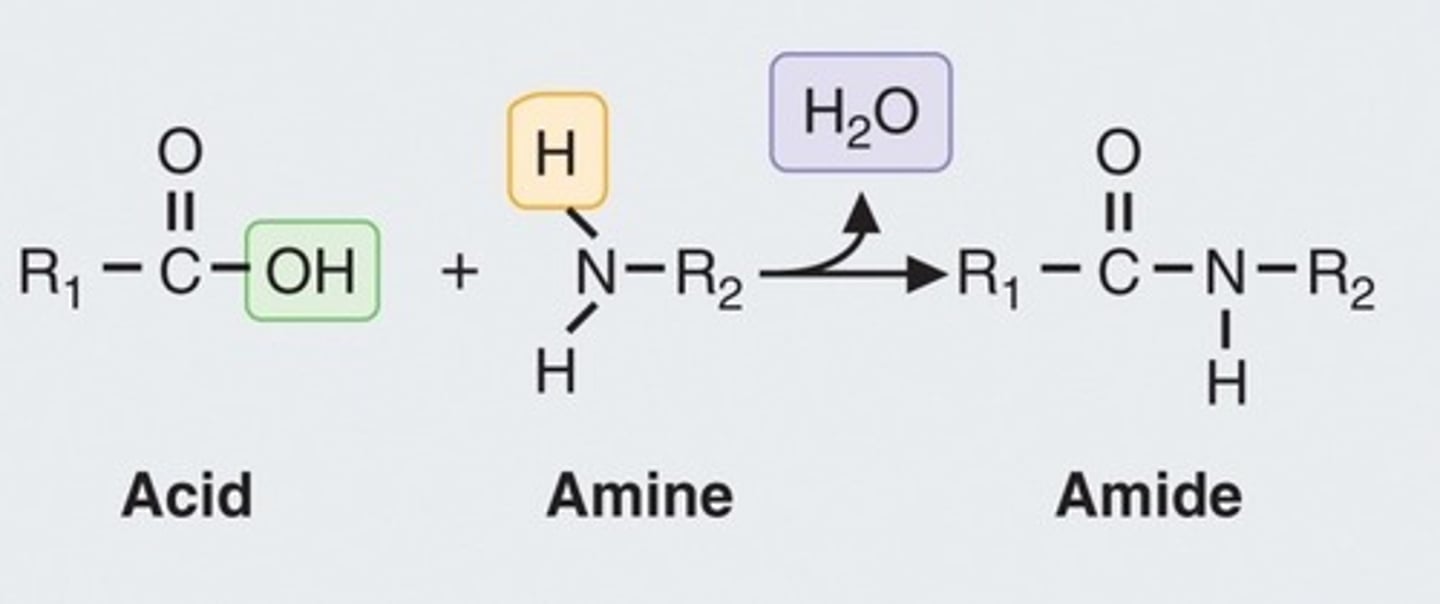
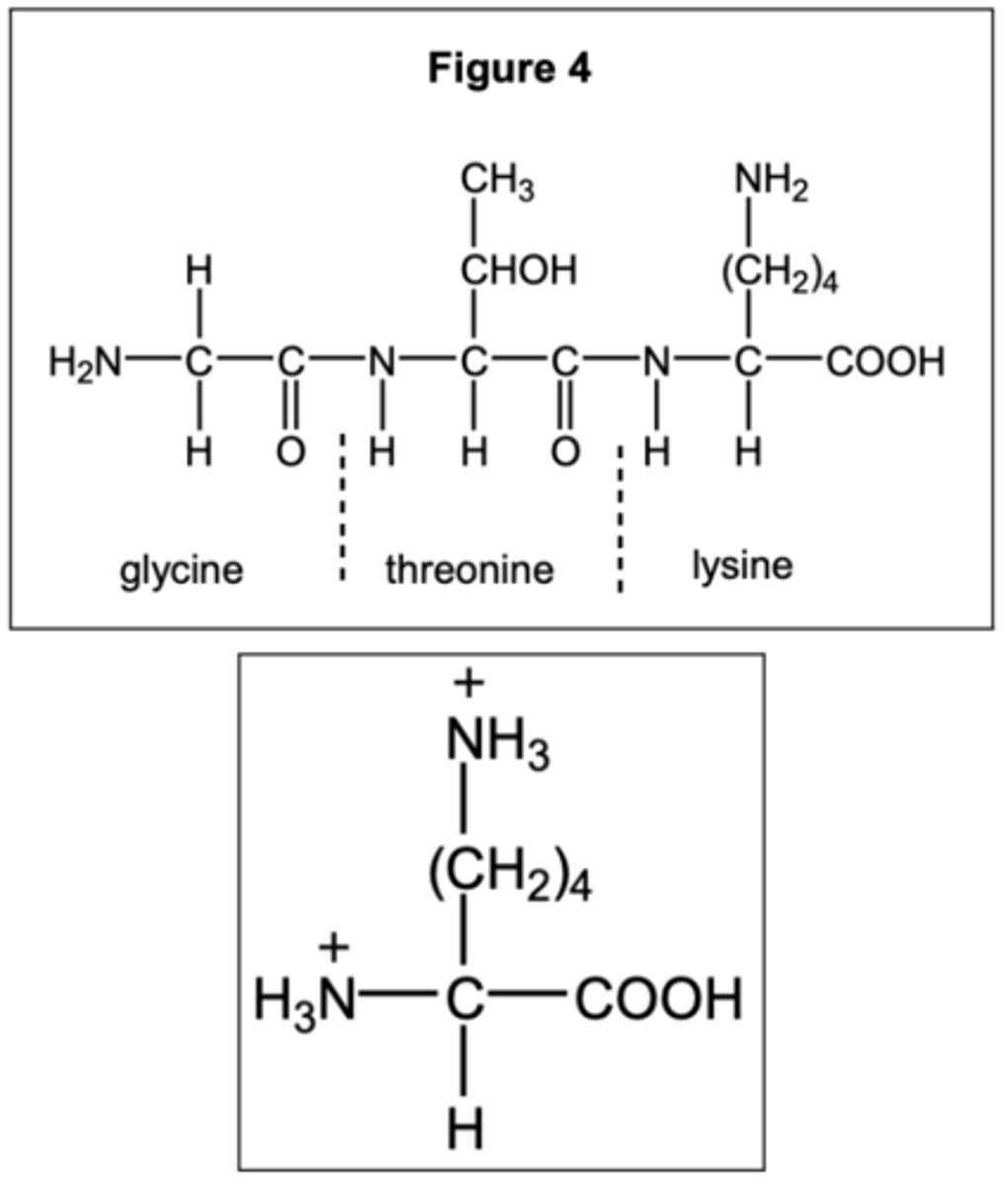
Peptide bonds
The peptide bonds between amino acids are formed through amidation reactions.
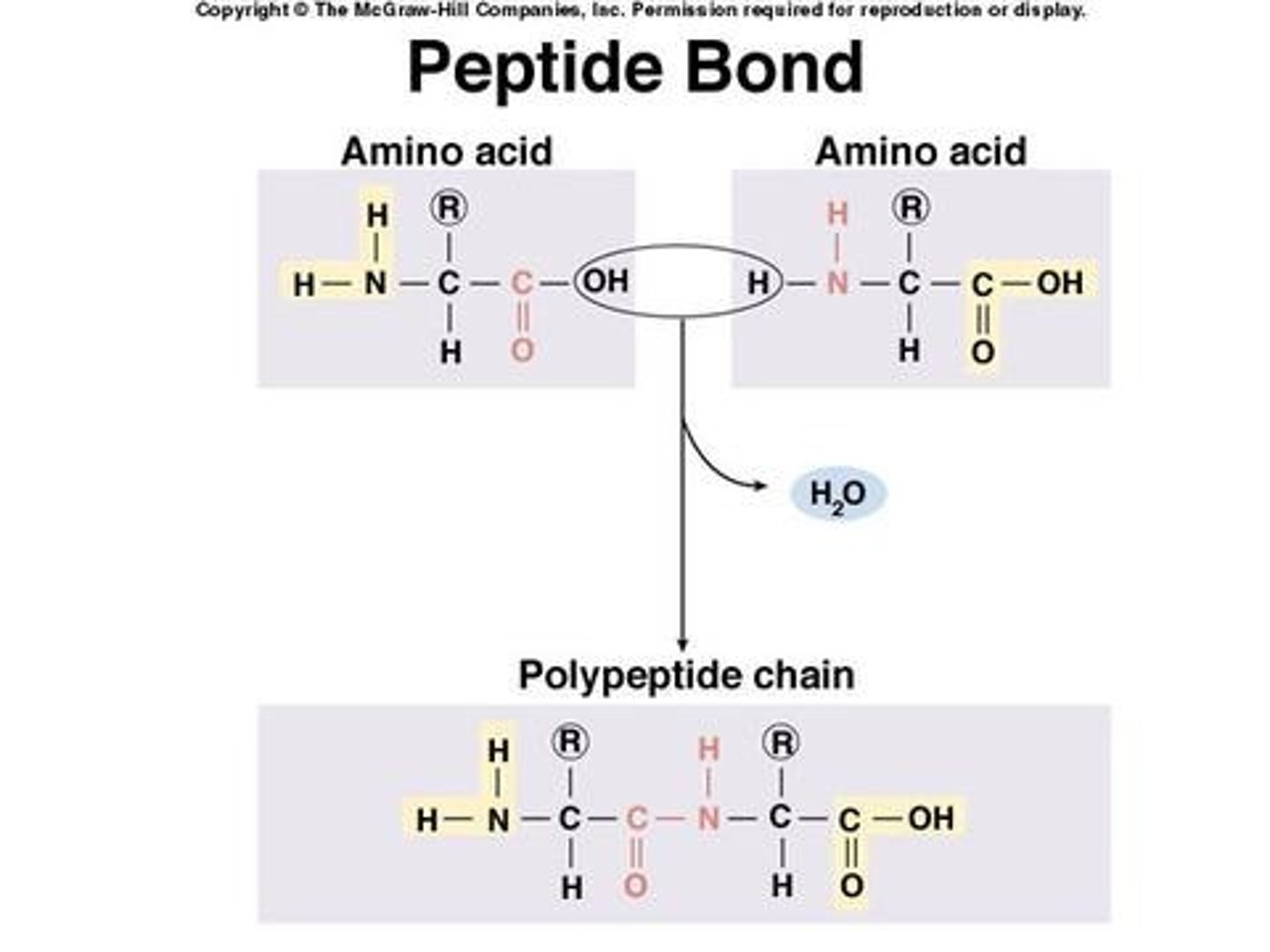
Peptide backbone
Peptides have the same amino acid backbone and the AAs are differentiated by their side chains (residues).
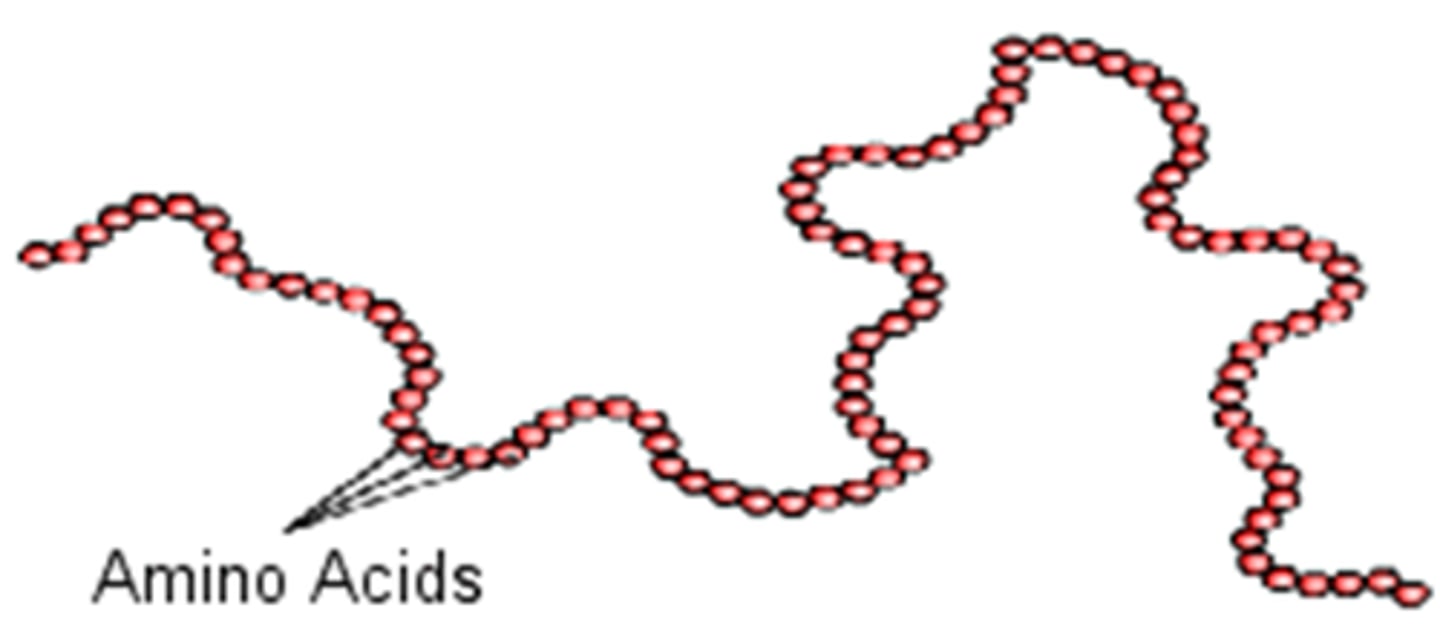
Polypeptide
Peptide with many amino acids. A polypeptide is a protein if it has >50 amino acids.
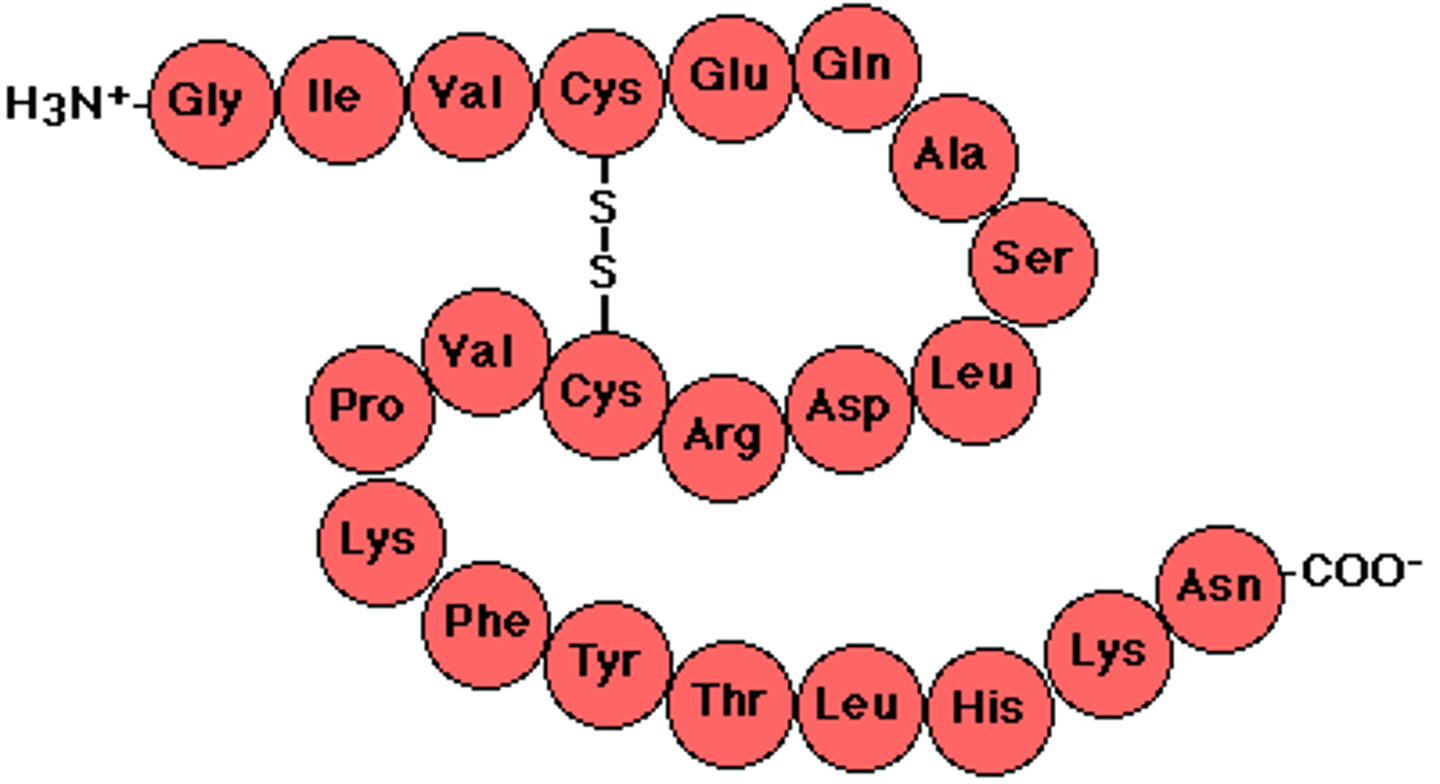
Primary structure
Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a protein.

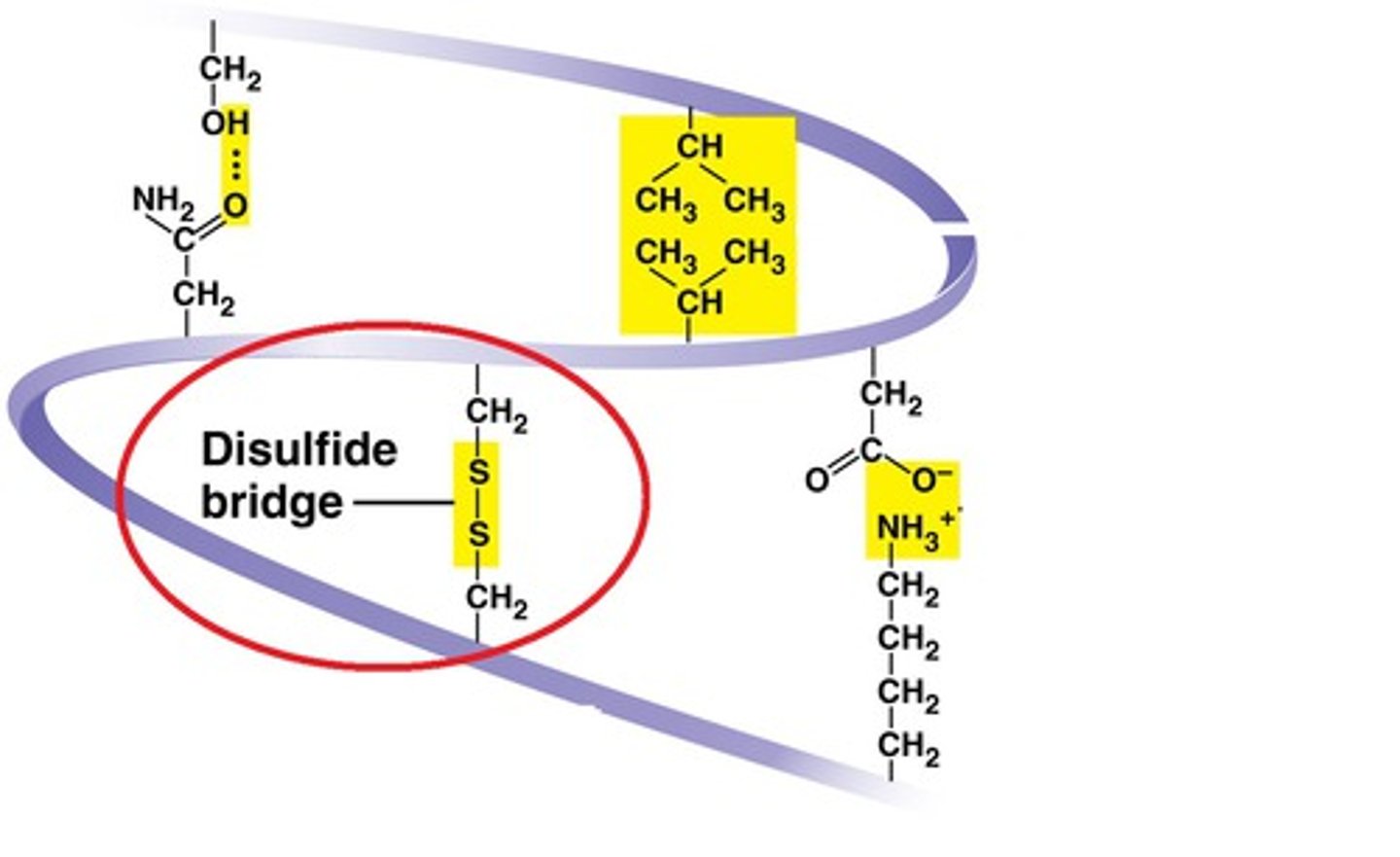
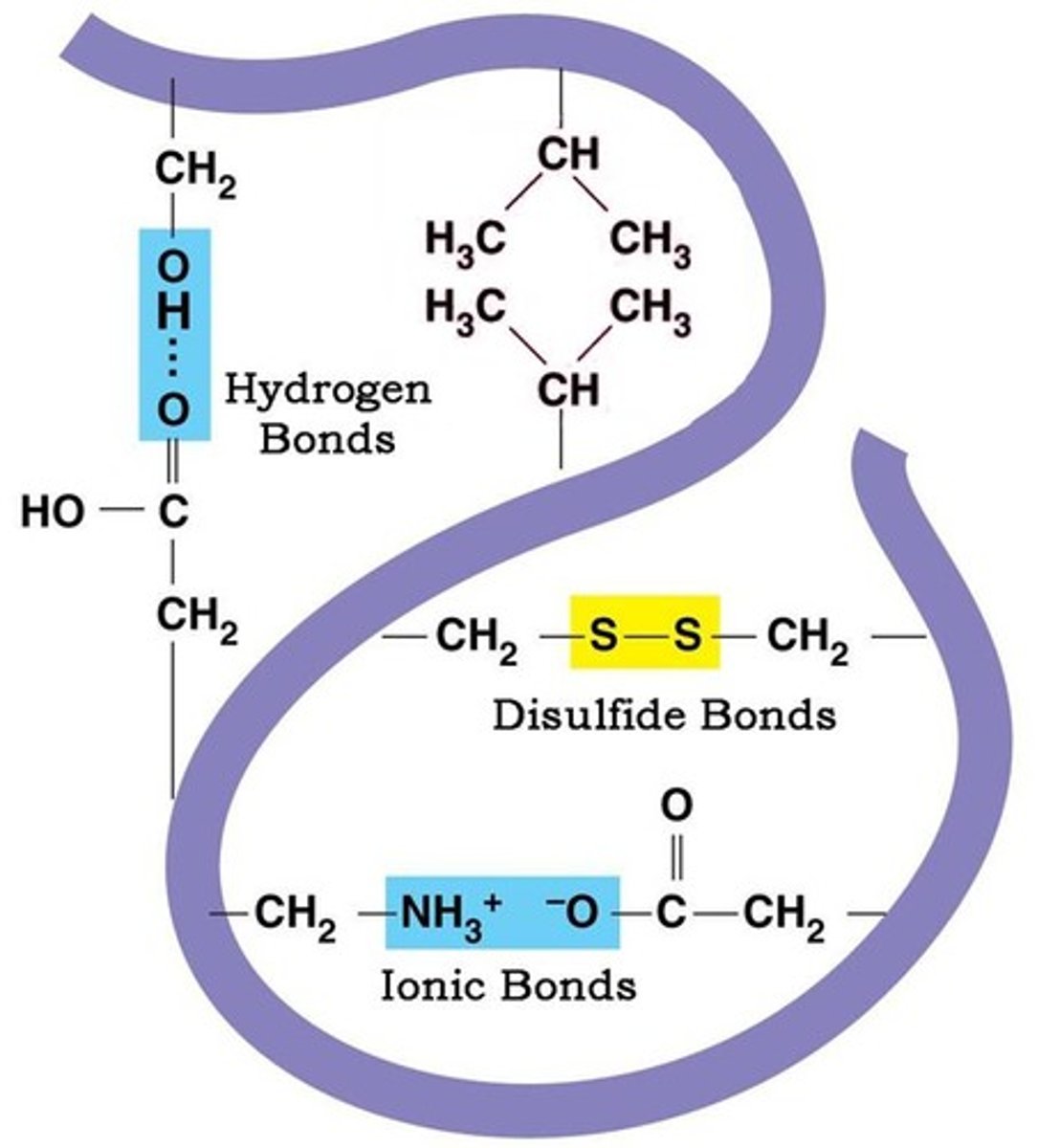
Disulfide bridge
Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds that stabilize the protein structure.
Secondary structure
Secondary structure describes the local folding of the polypeptide chain. Involves H bonding between carboxylic acid and amine in backbone
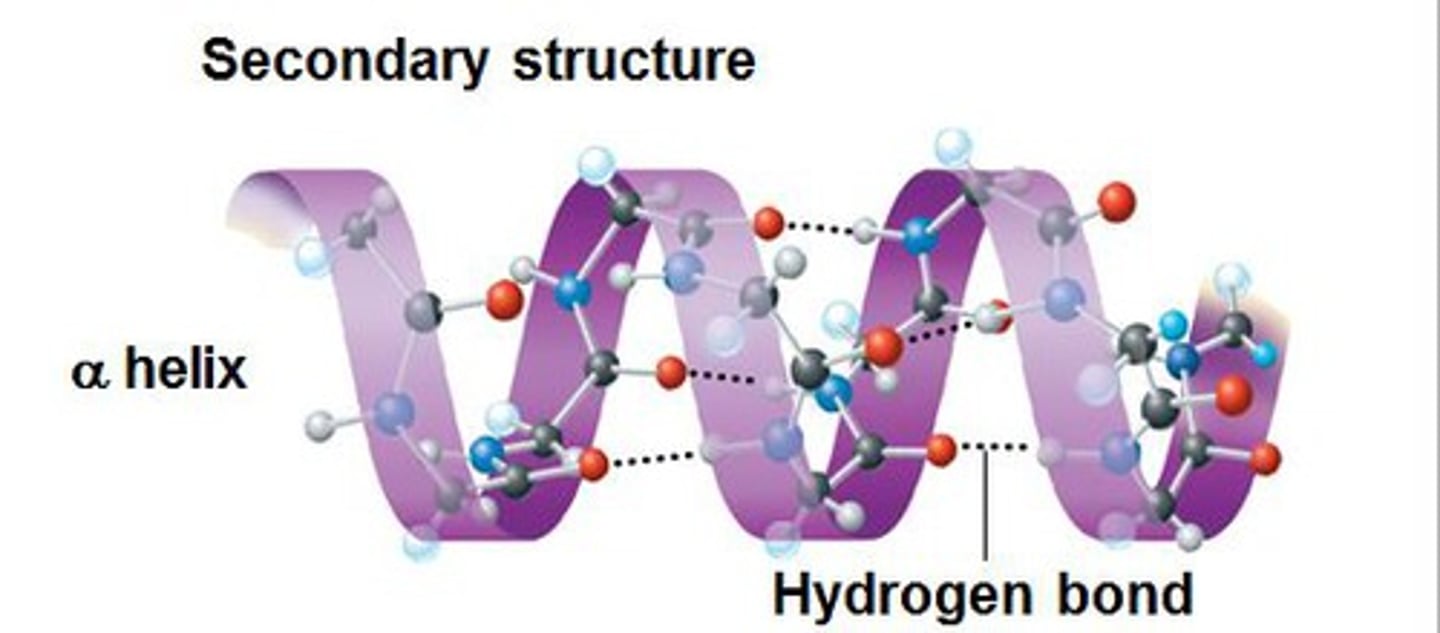
types of secondary protein structures
alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
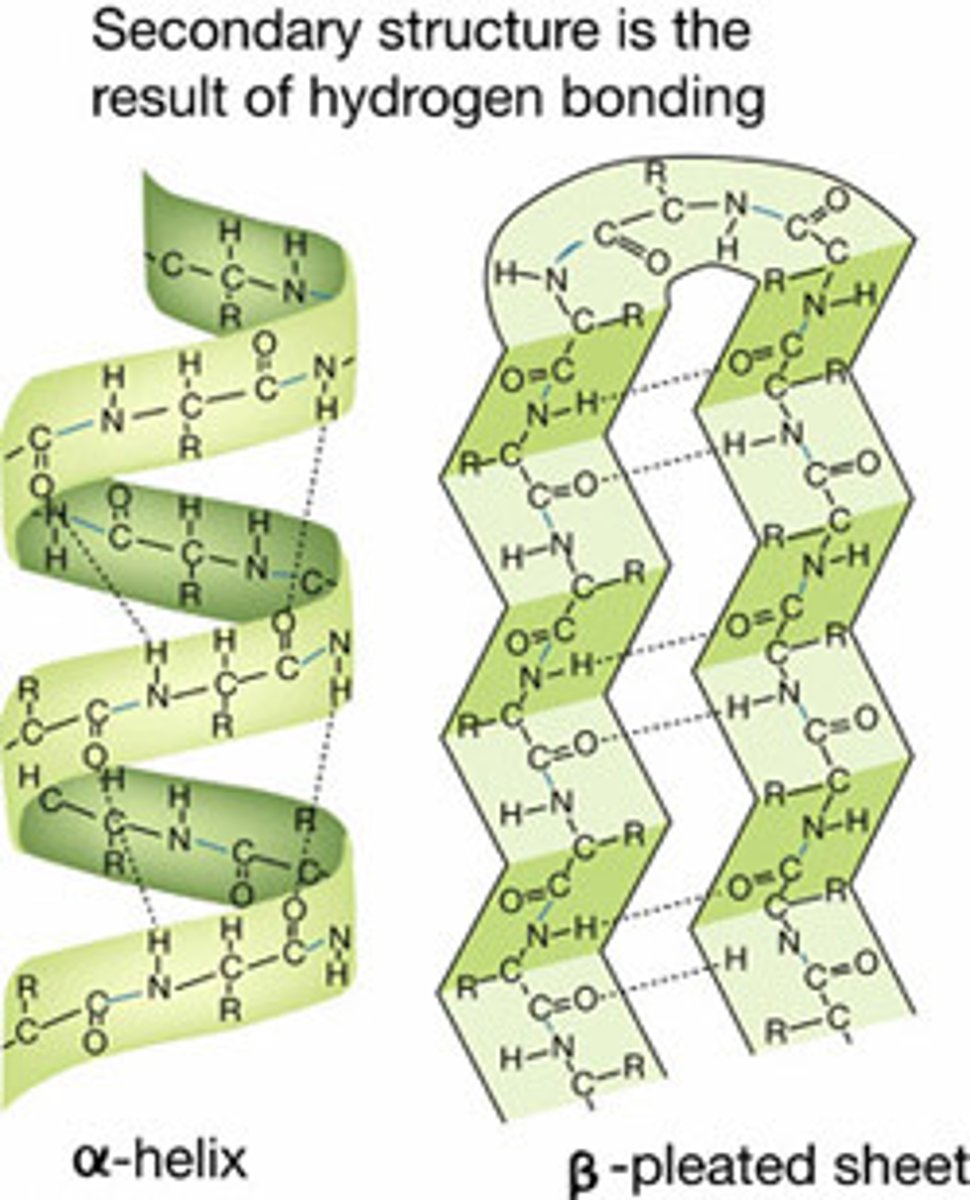
Tertiary structure
Tertiary structure describes 3D structure (folding) resulting from interactions within a single polypeptide and with the outside environment.
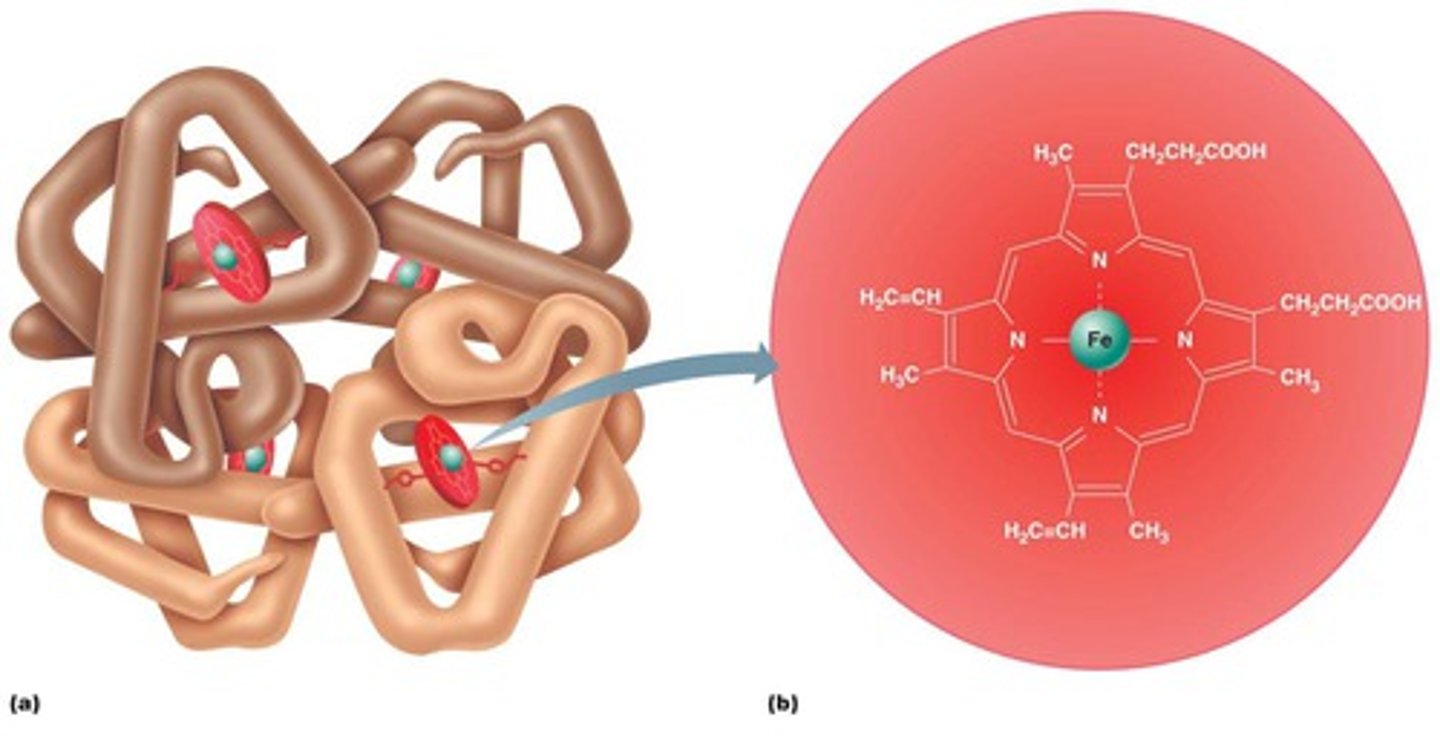
Prosthetic Group
Prosthetic groups are non-polypeptide units that are tightly and permanently attached to proteins. (example: heme)
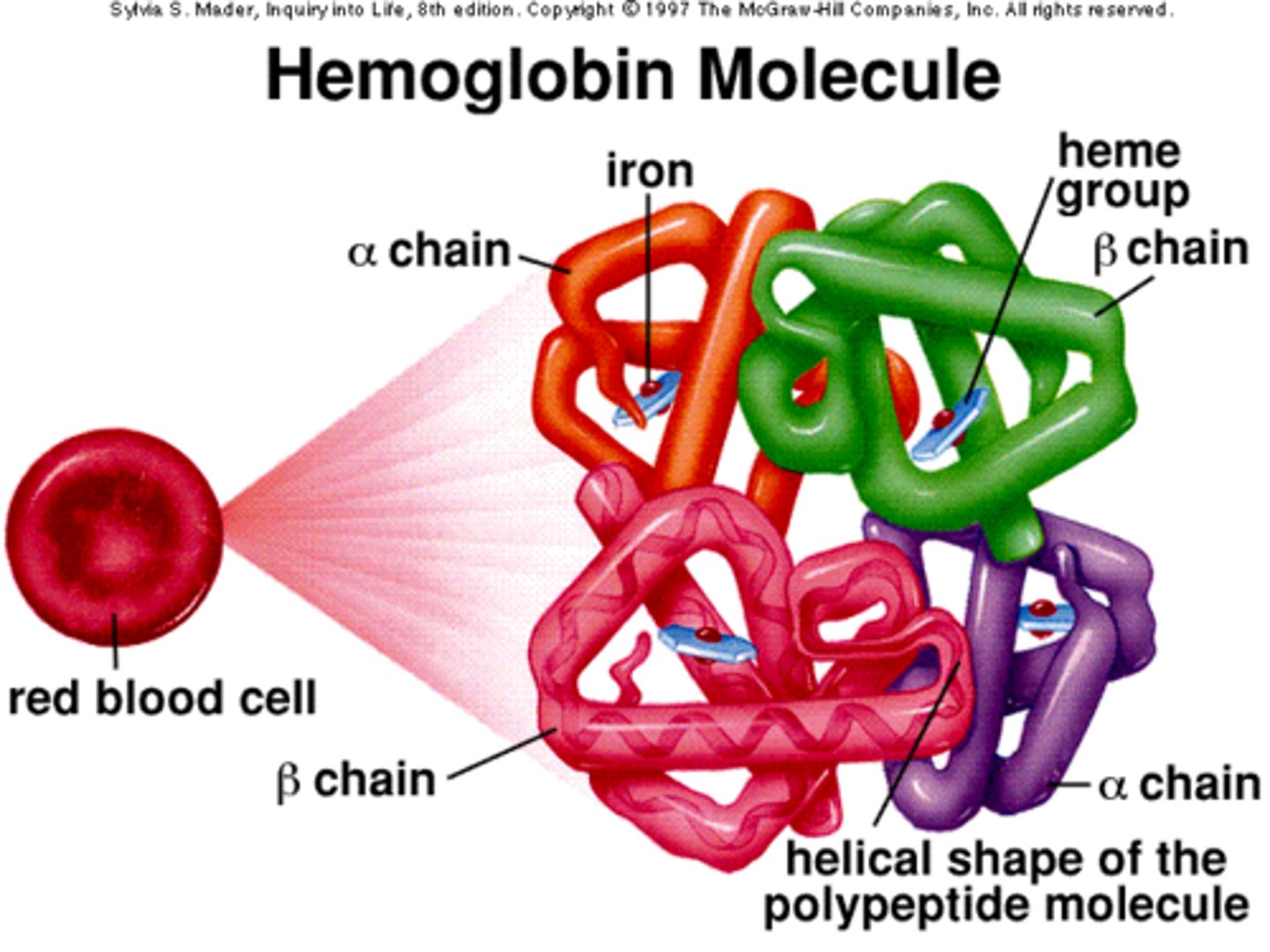
Quaternary structure
Interactions between multiple polypeptide chains. Same interactions as tertiary.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is an example of a protein with quaternary structure.
Denaturation
Denaturation is the process in which proteins lose their structure and function.
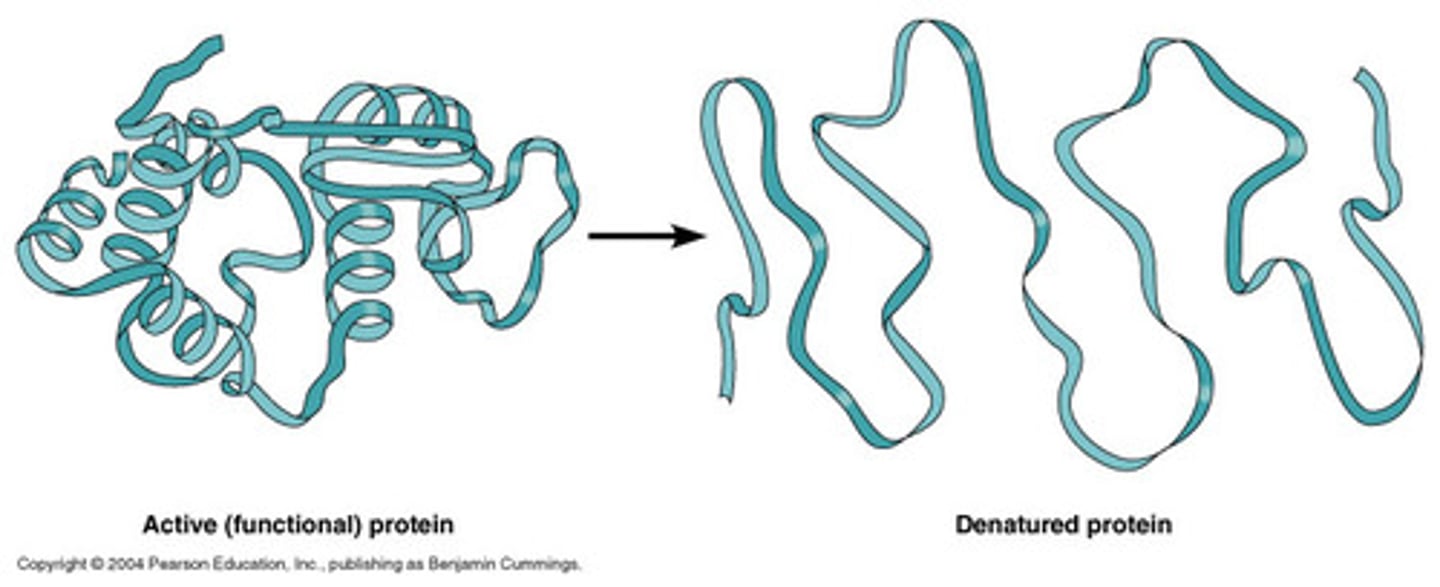
Ways to denature
Ways to denature include heat, pH changes, mechanical agitation and certain metals
Result of denaturing
The result of denaturing is the loss of biological activity.
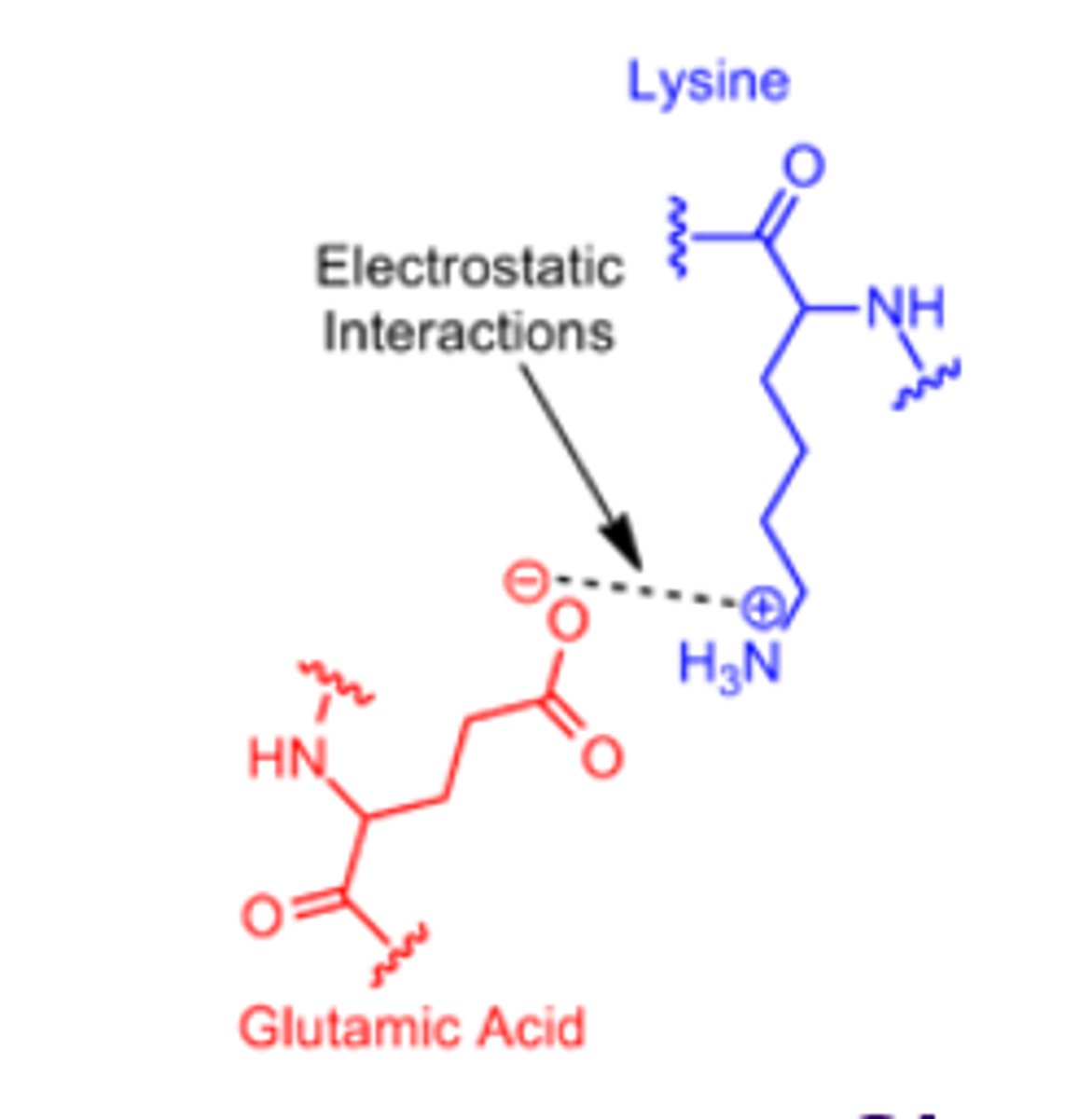
Salt bridges
Ionic interactions between charged side chains.
Peptides
Polymers made of amino acid monomers.
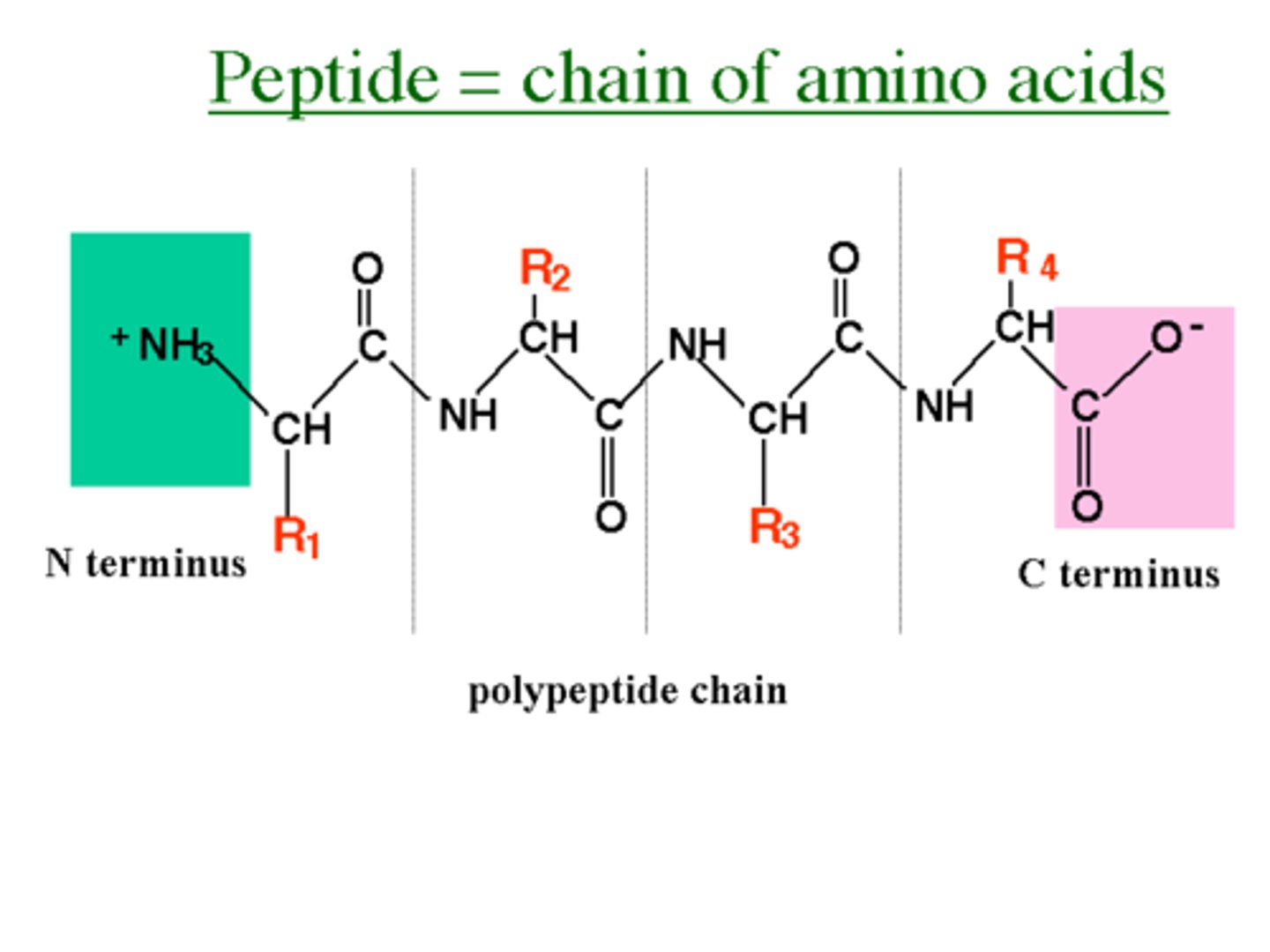
C-terminus
End of a peptide with a free carboxyl group.
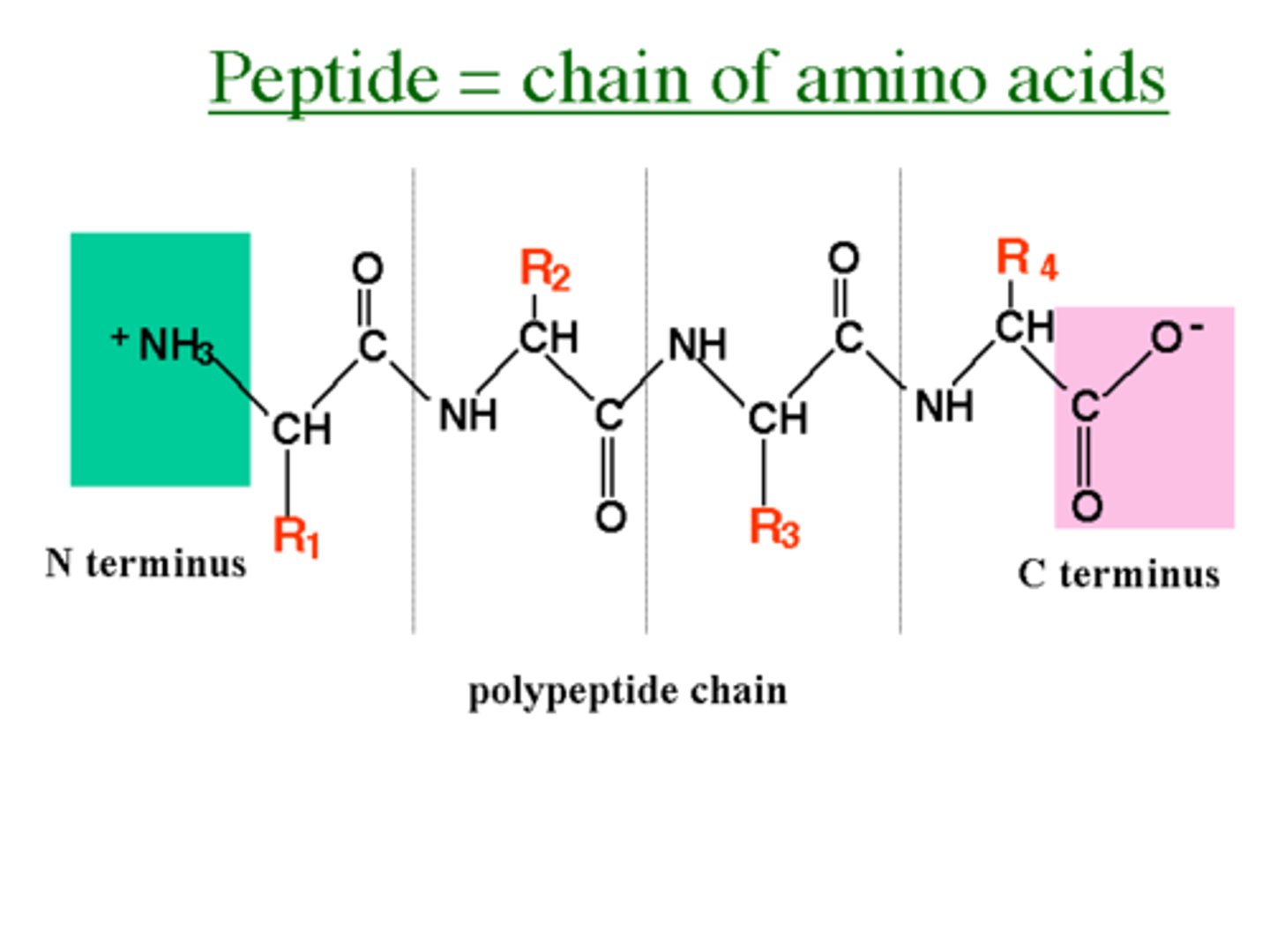
N-terminus
End of a peptide with a free amino group.
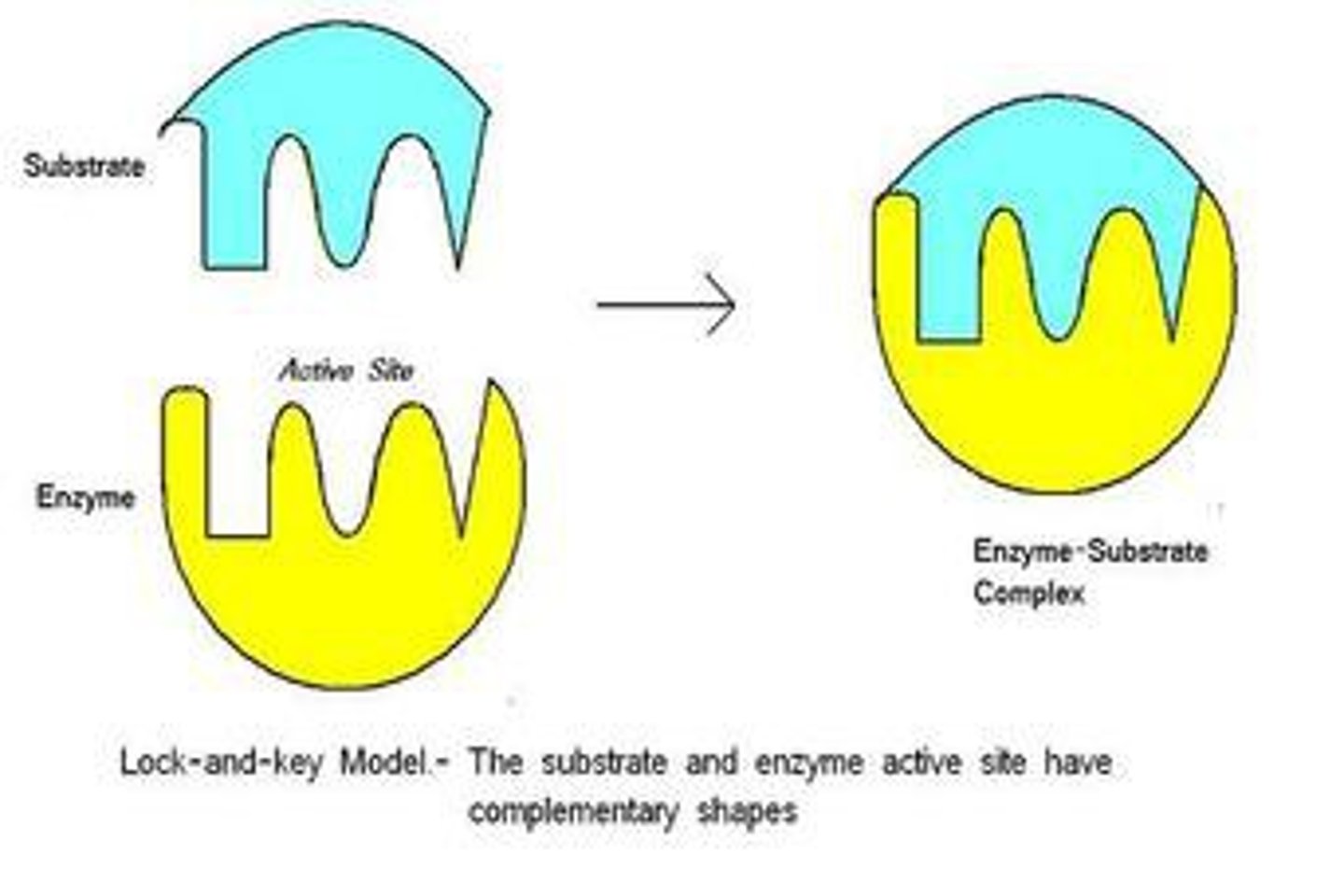
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Temporary complex formed when substrate binds enzyme.
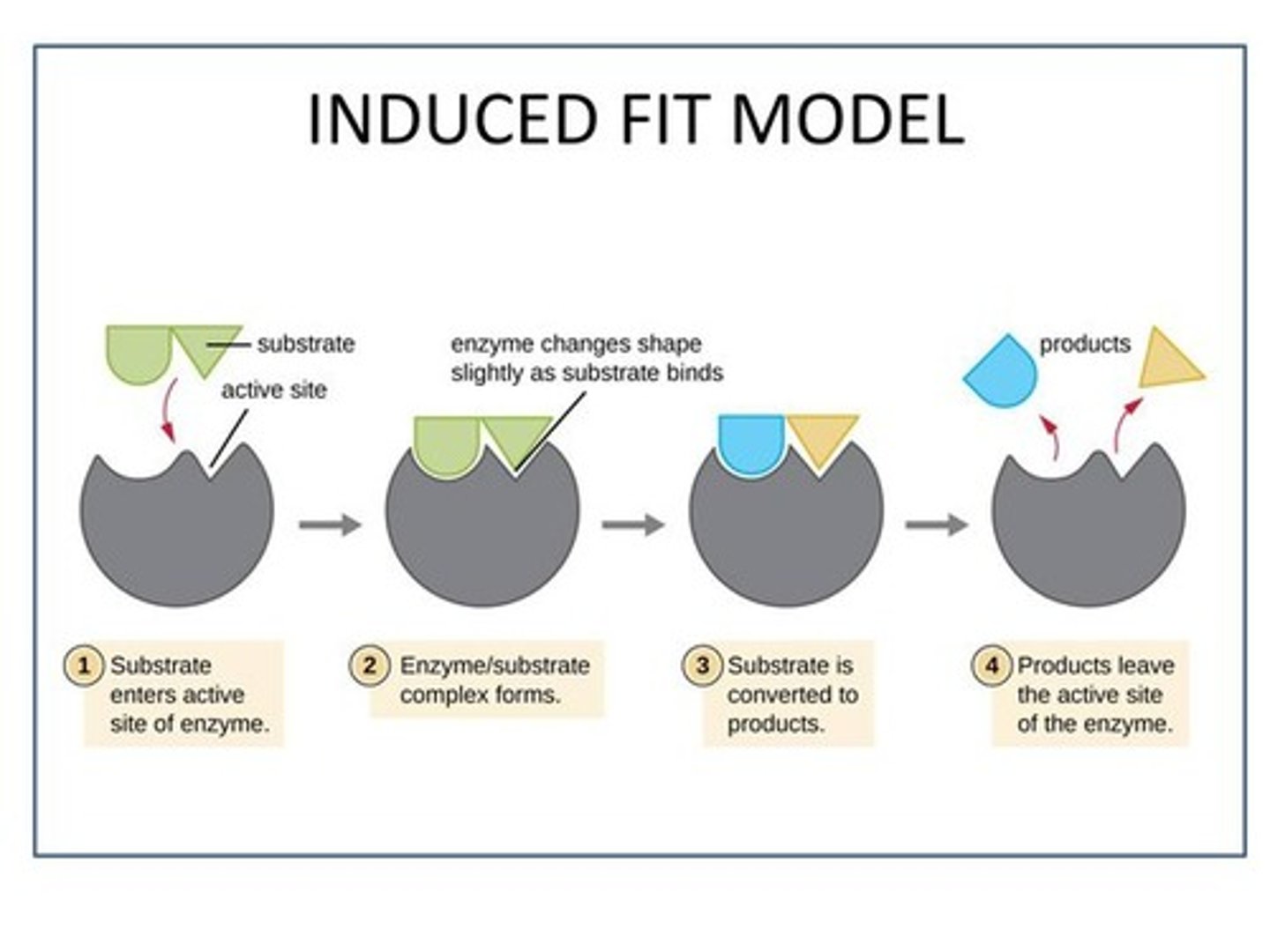
Induced fit model
Enzyme changes shape to better fit substrate after substrate initially binds via electrostatic forces
Activation energy
Energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
Enzyme inhibitors
Compounds that prevent enzyme activity.
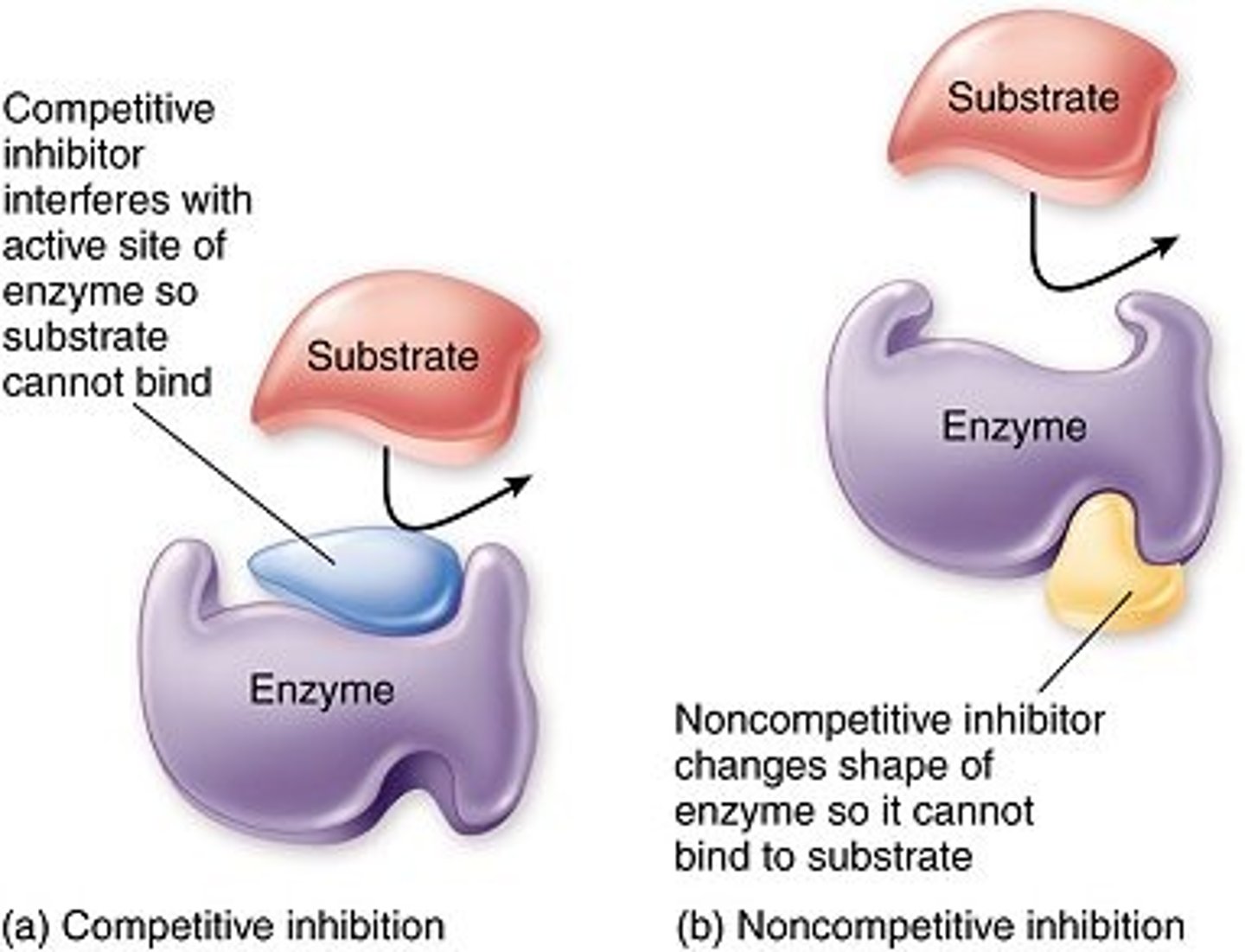
Competitive inhibitors
Compete with substrate for active site binding.

Non-competitive inhibitors
Bind elsewhere on enzyme altering enzyme activity by changing conformation of enzyme and active site without competing directly for active site
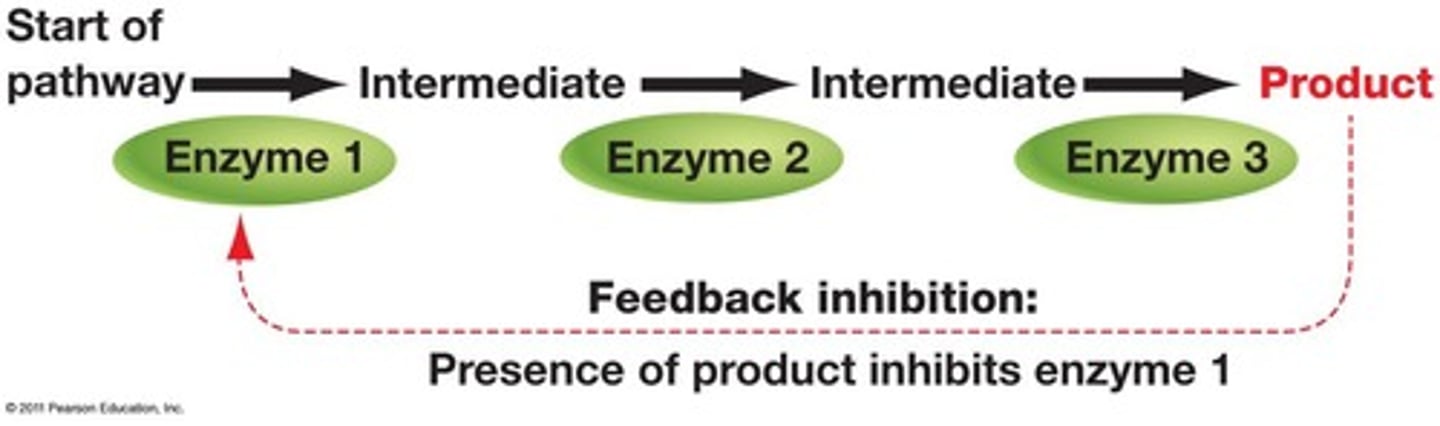
Feedback inhibition
Process where product inhibits its own production, as in cholesterol being its own non-competitive inhibitor
ACE
Enzyme converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
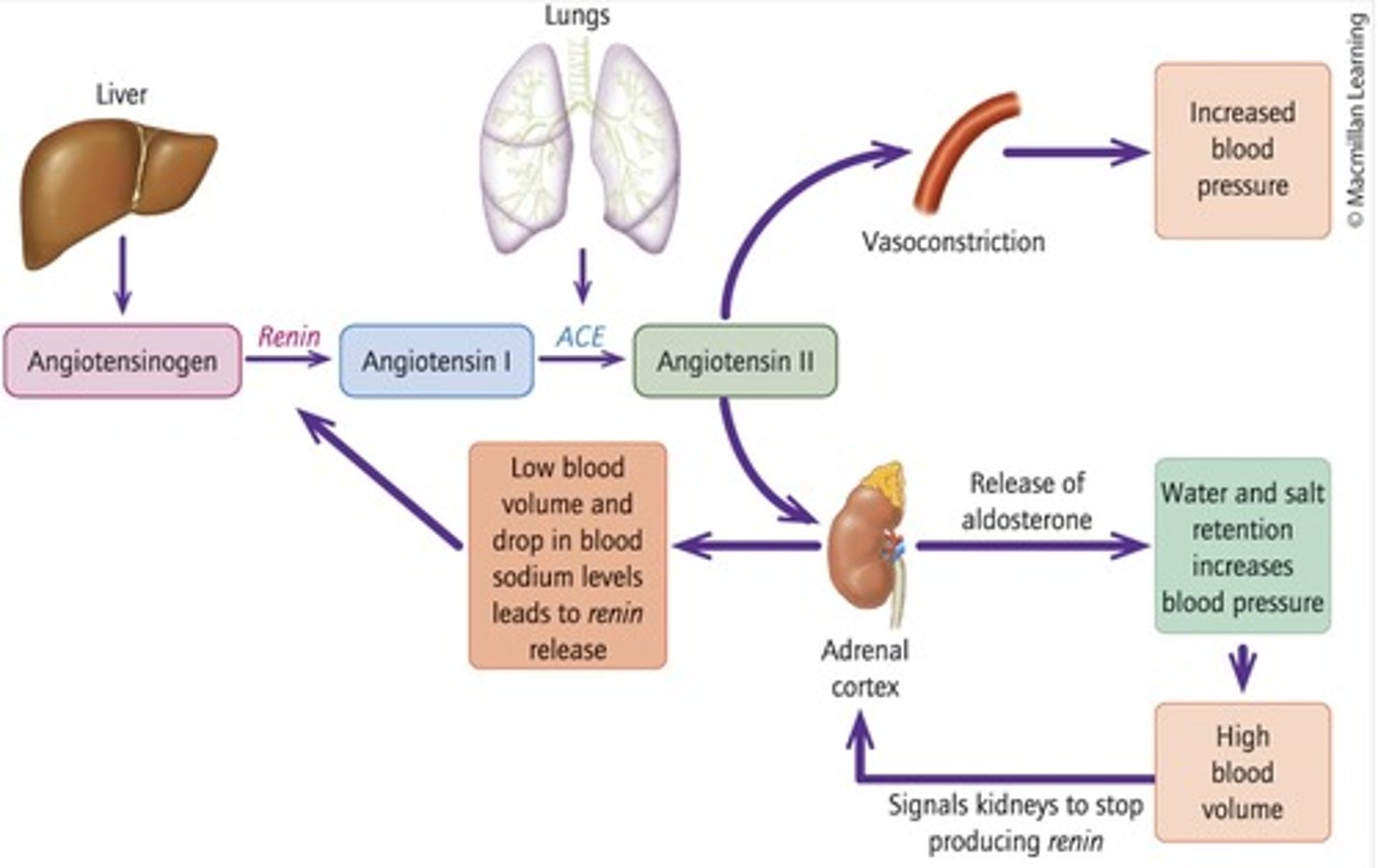
Aldosterone
Hormone that promotes salt and water retention. Produced in response to angiotensin II being produced by ACE
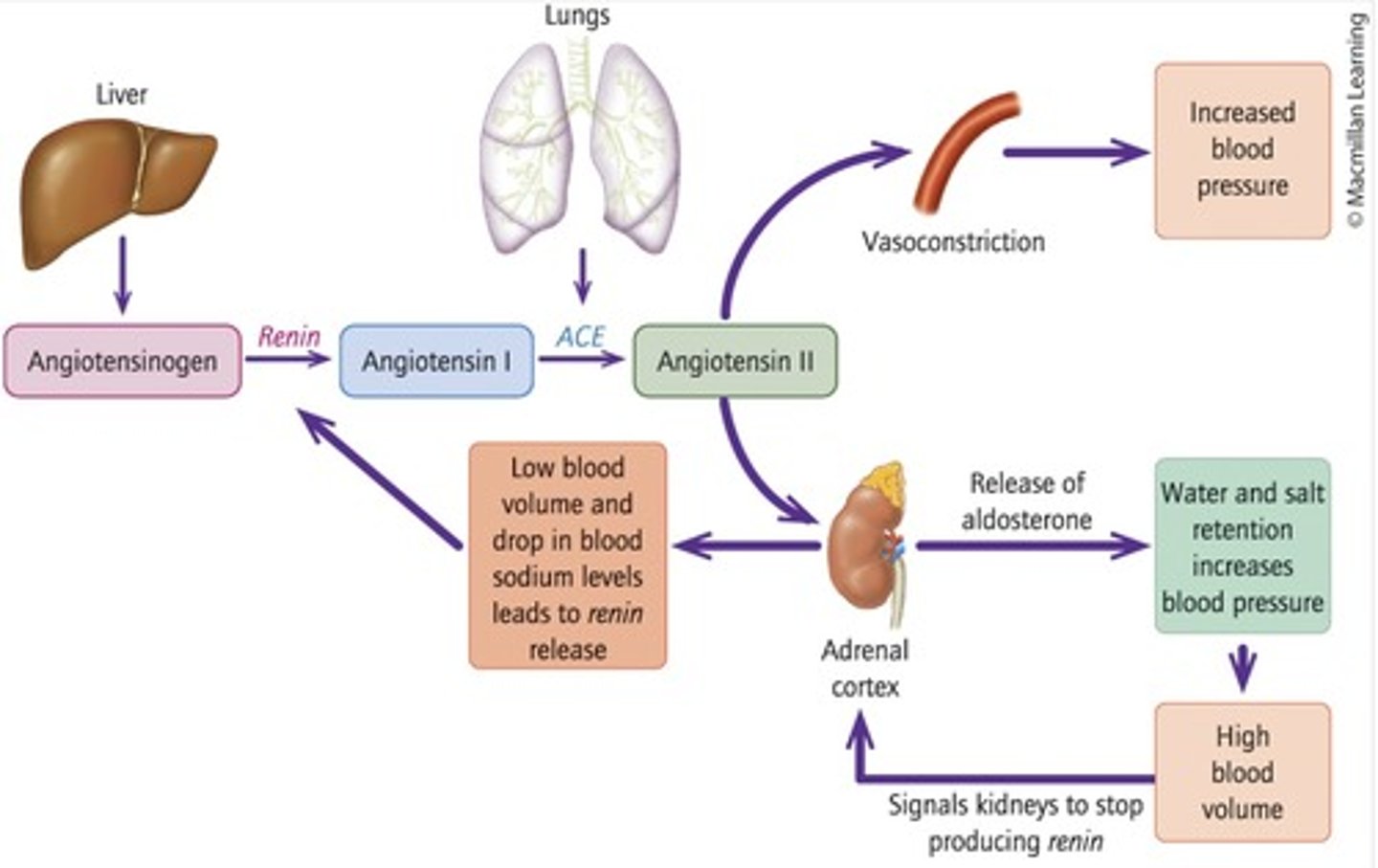
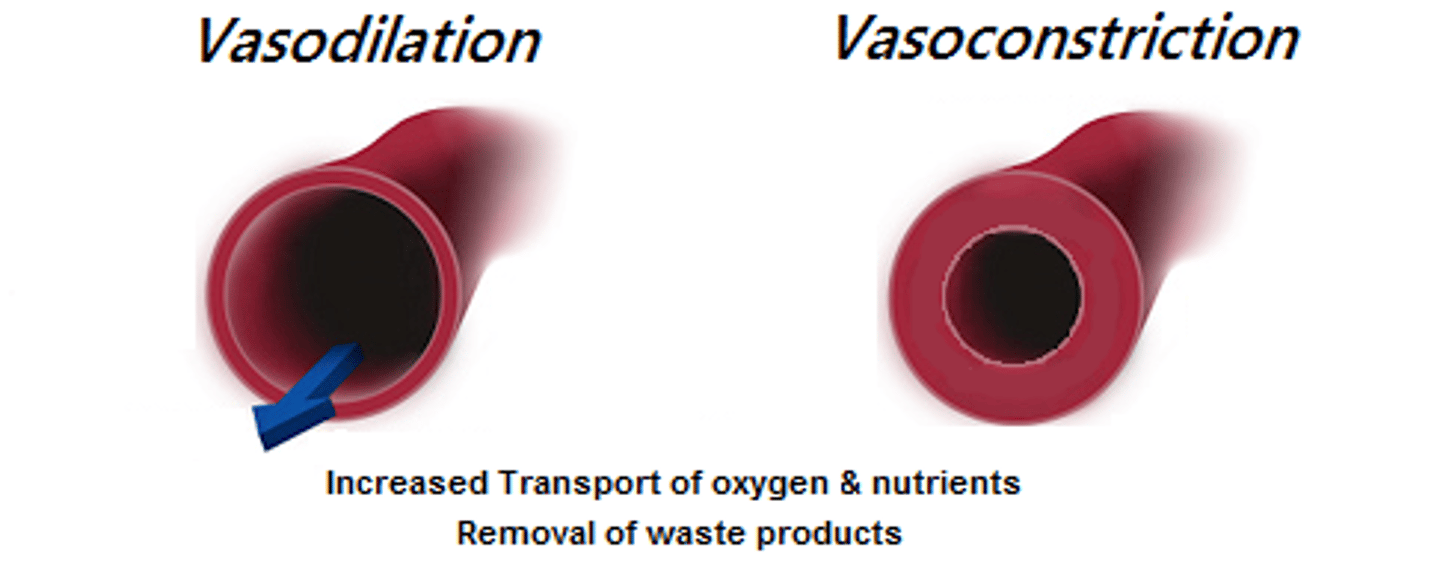
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of blood vessels to increase blood pressure, induced by aldosterone
How does the induced fit model reduce activation energy?
After substrate binding, the enzyme changes shape for better "fit" - reactants/substrate are arranged for optimal reaction efficiency.
Enzyme function
Dependent on pH and temperature conditions. A fever can reduce enzyme function
Amidation reaction
Process forming peptide bonds between amino acids.
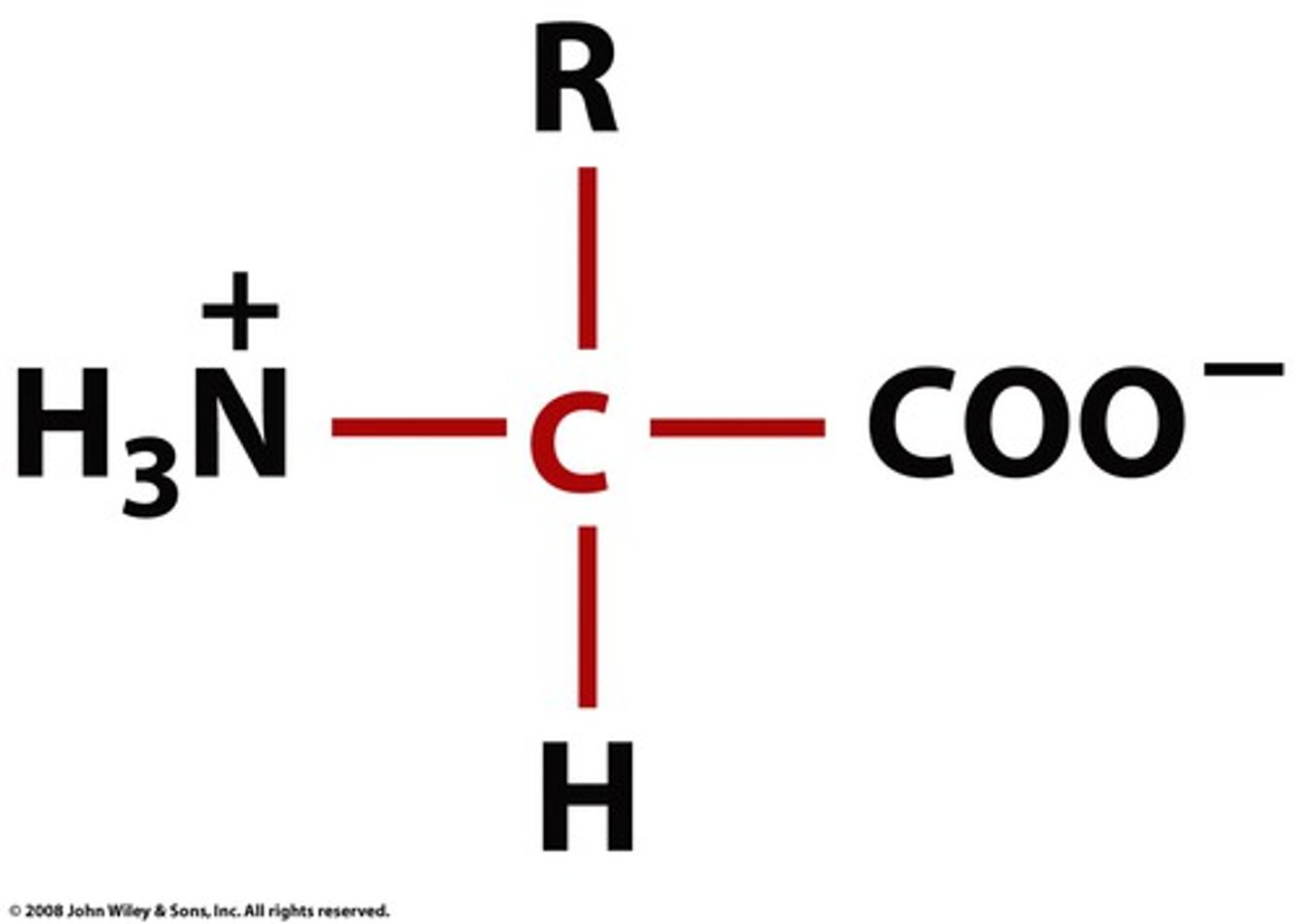
amino acid at pH 7.4 (R = neutral)
Amine is + and carboxylate is -. Charges cancel. Amino acid is neutral
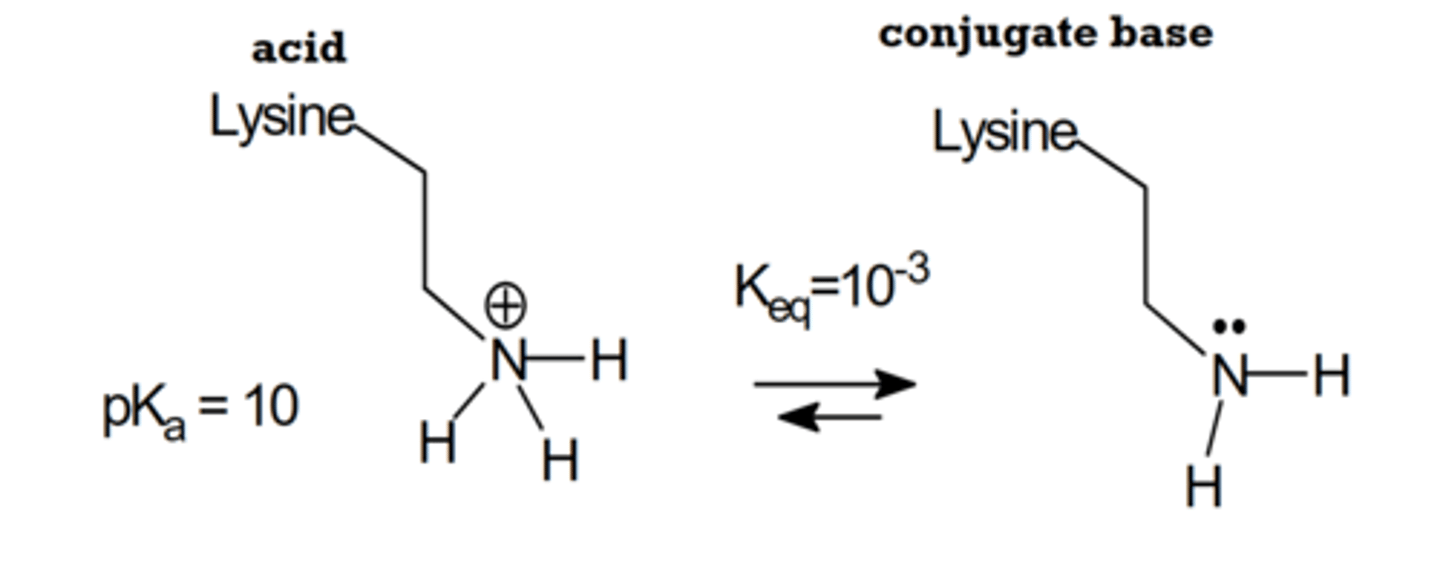
lysine at pH 10 (basic)
Amines are neutral. carboxylic acid is conjugate base with -1 charge. total charge is -1.
lysine at pH 1 (acidic)
carboxylic acid is neutral. amines are conjugate acids with +1 charge each. Total charge is +2.
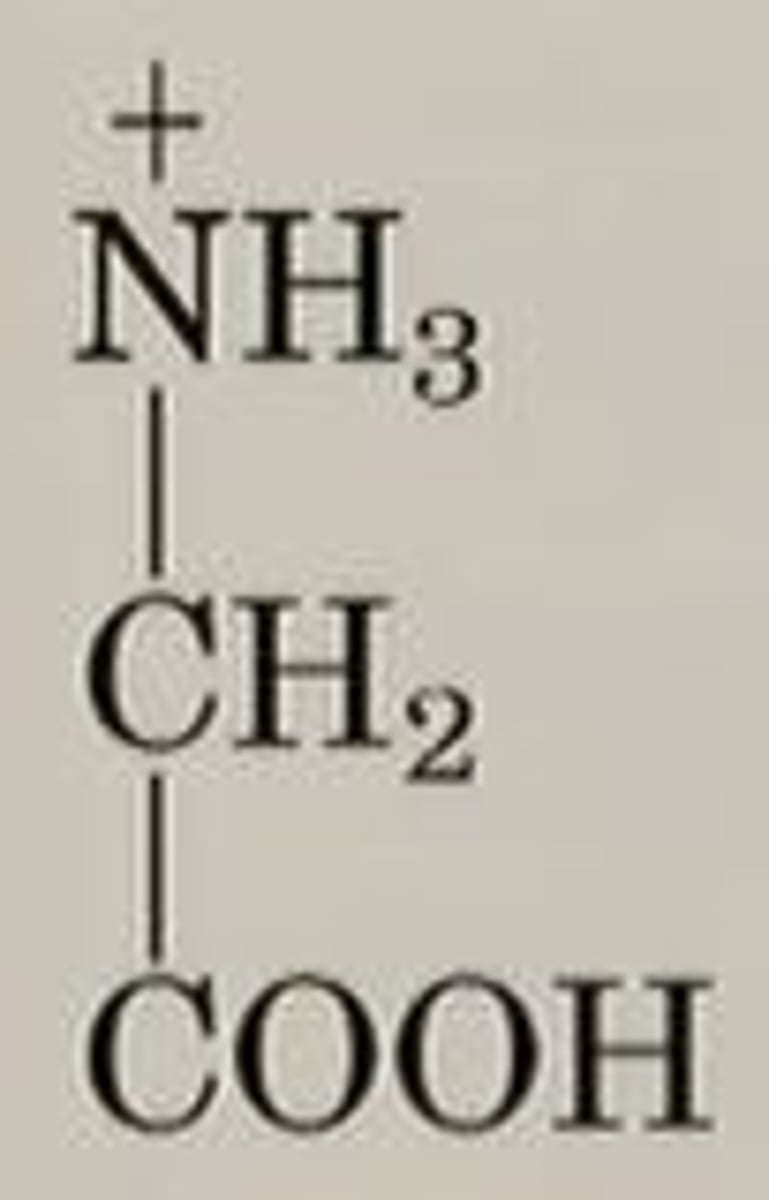
glycine at pH 1 (acidic)
carboxylic acid neutral; amine as conj. acid (+1), total charge is +1.
leucine at pH 11
base in neutral form. carboxylic acid is -. total charge is -1 (leucine is neutral)
aspartic acid acid at pH 1
acids are in neutral form. Base is in conj. acid with +1. Total charge +1

Which amino acids would be on the outside of an enzyme in aqueous solution.
the ionic and polar ones.
Which amino acids would be on the inside of an enzyme in aqueous solution?
non-polar ones.
are amino acids chiral?
Yes (19 out of 20) are chiral.
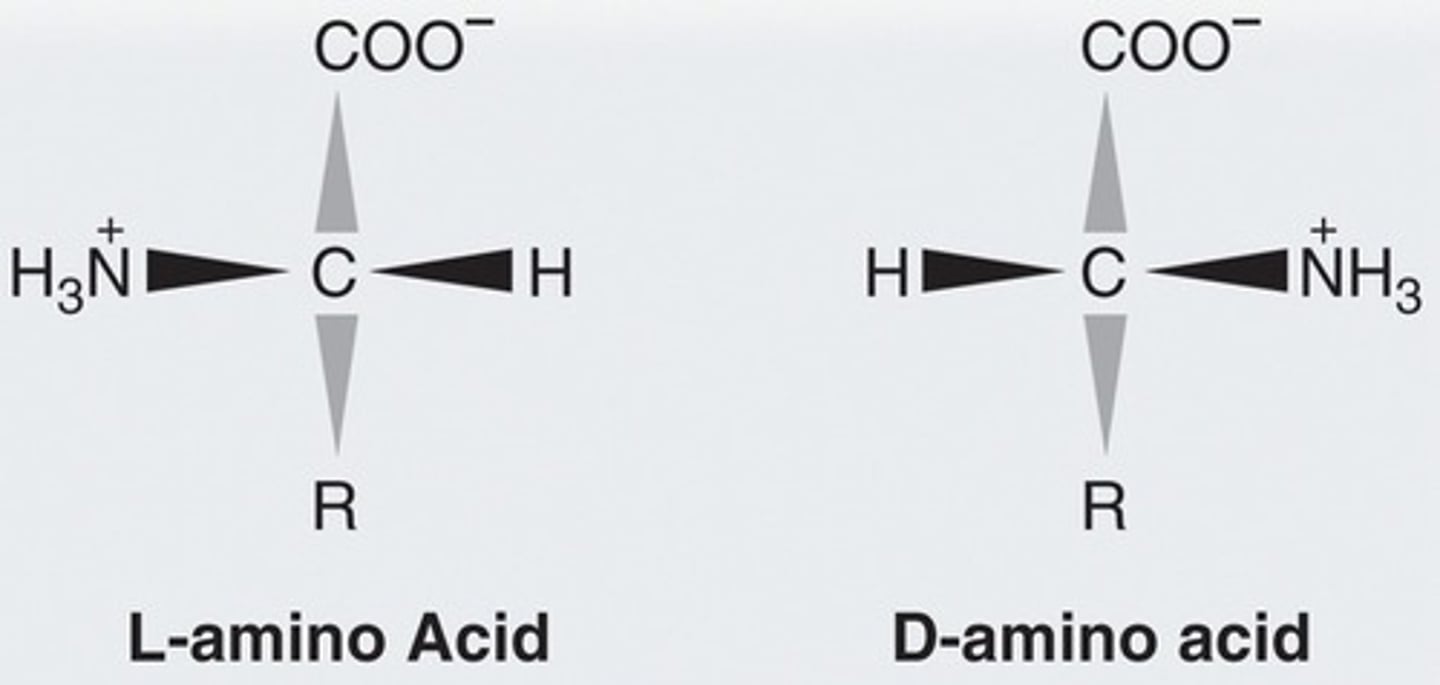
Which enantiomer of amino acids is naturally produced?
L
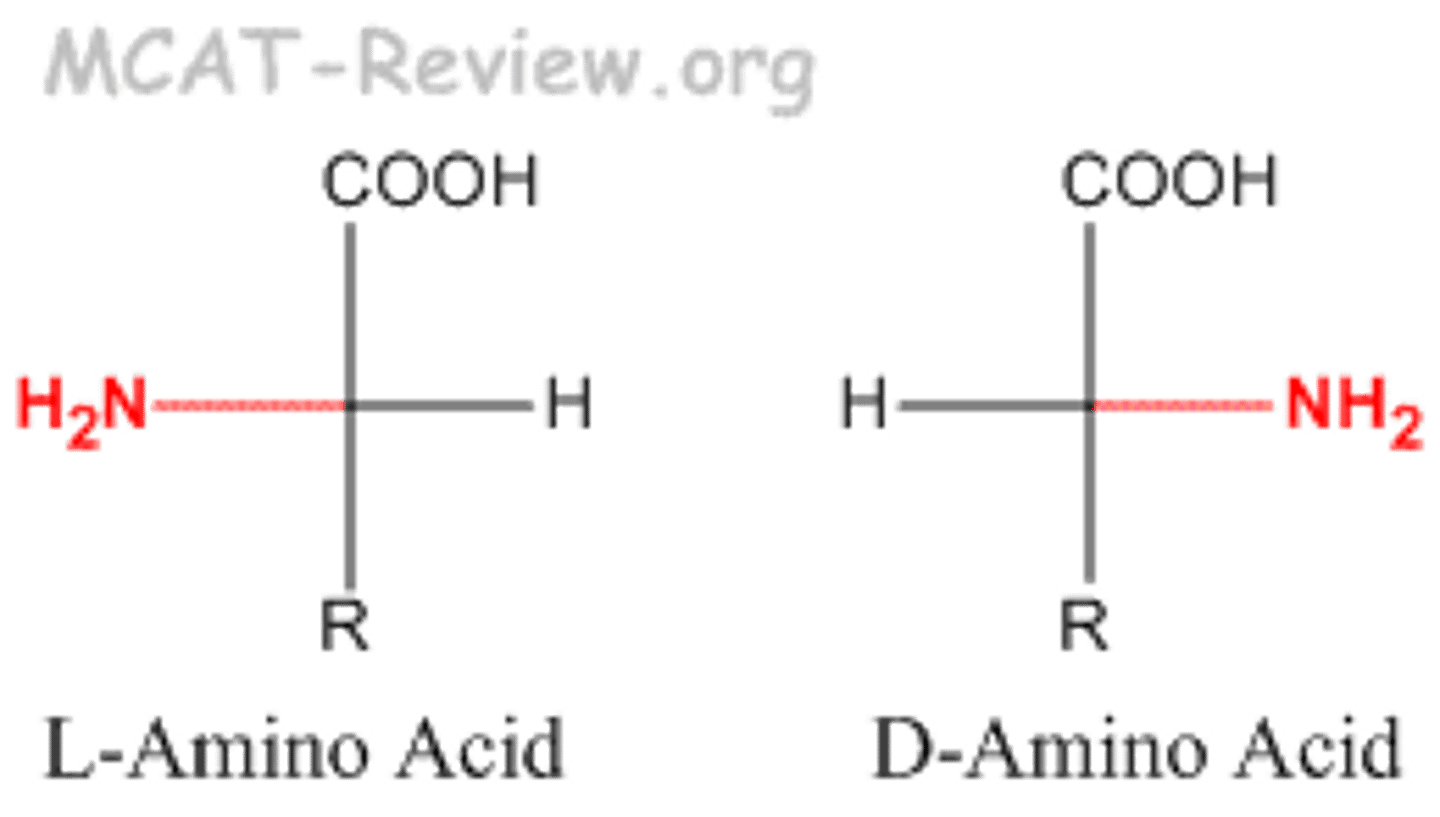
How can you tell D or L from a Fischer projection of an amino acid?
amine is on right = D; on left = L
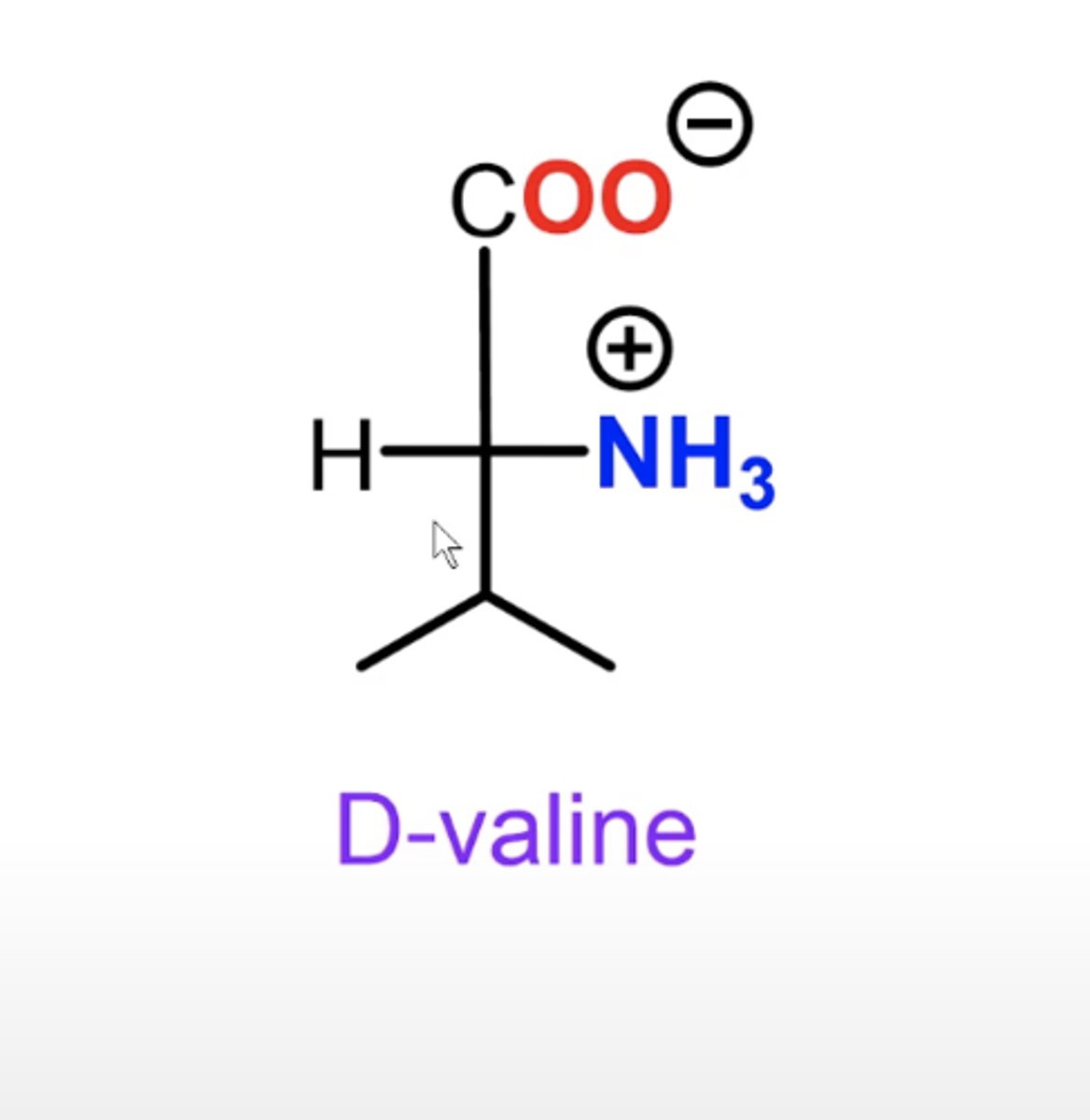
Amino acid fischer projection
C-terminus at top. N-terminus on left for L and right for D. Side chain on the bottom. H opposite amine.