B9.2 Heart
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
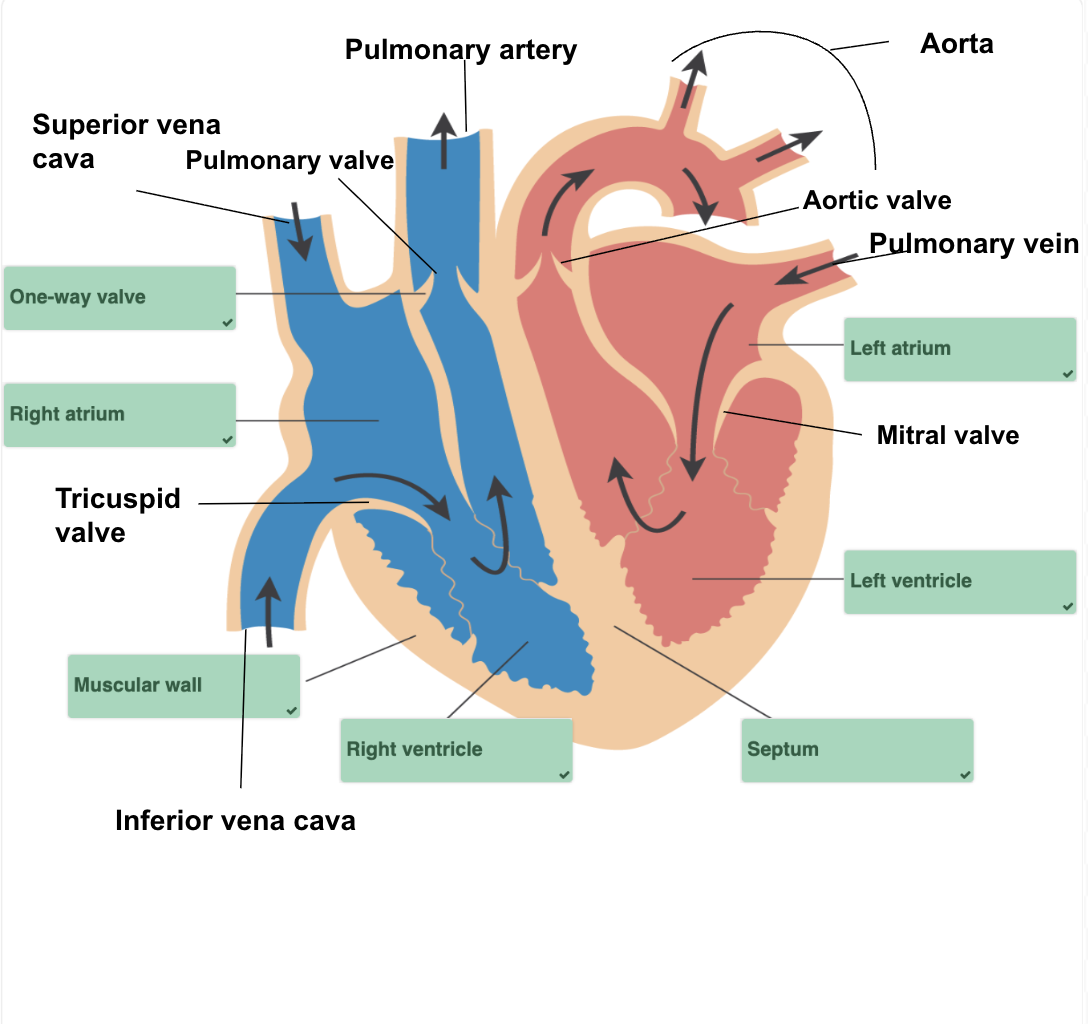
Identify the structures within a heart diagram
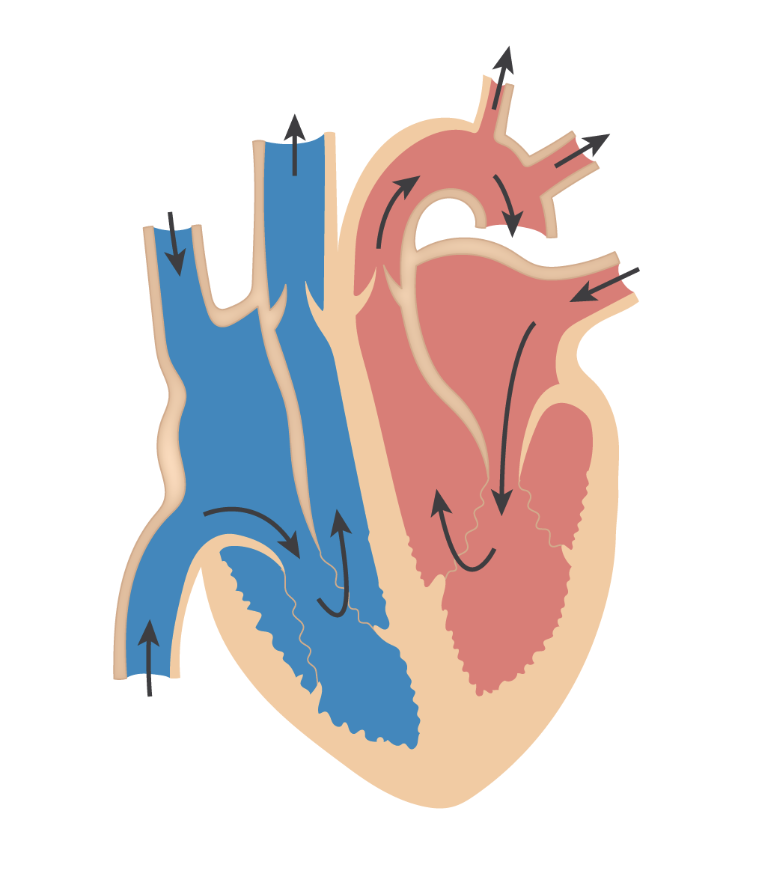
What are the differences between right and left side of the heart?
Right side:
The right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
The right side has thinner muscular walls since it doesn’t need to withstand a high pressure because it carries blood only to the lungs
Has pulmonary circulation
Left side:
The left side pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body
The left side has thicker muscular walls to withstand higher pressure since it carries blood to all of the body
Has systemic circulation
What is the function of the muscular wall?
Contracts and relaxes to create force needed to pump blood throughout the body
What is the function of the septum?
Separates the heart into right and left sides
What is the function of the vena cavas?
The largest veins in the body that collect and return deoxygenated blood from the entire body to the right atrium
What is the function of the one way valves and what are the names?
Permits the flow of blood in one direction only (from the atria to the ventricles)
Atrioventricular valves (AV): mitral valve (also known as bicuspid) and tricuspid valve
Semilunar valves: pulmonary valves and aortic valves
What is the function of the atria?
Where the blood collects once it enters the heart
What is the function of the ventricles?
Pump the blood out the heart to the lungs or the body
What is the function of each artery in the heart?
Coronary arteries: arteries that branch off the aorta to supply blood to the heart itself, as well as oxygen and nutrients
Aorta: the body’s largest artery which carries oxygenated blood from the hearts left ventricle to the rest of the body
Pulmonary artery: carries deoxygenated blood from the hearts right ventricle to the lungs
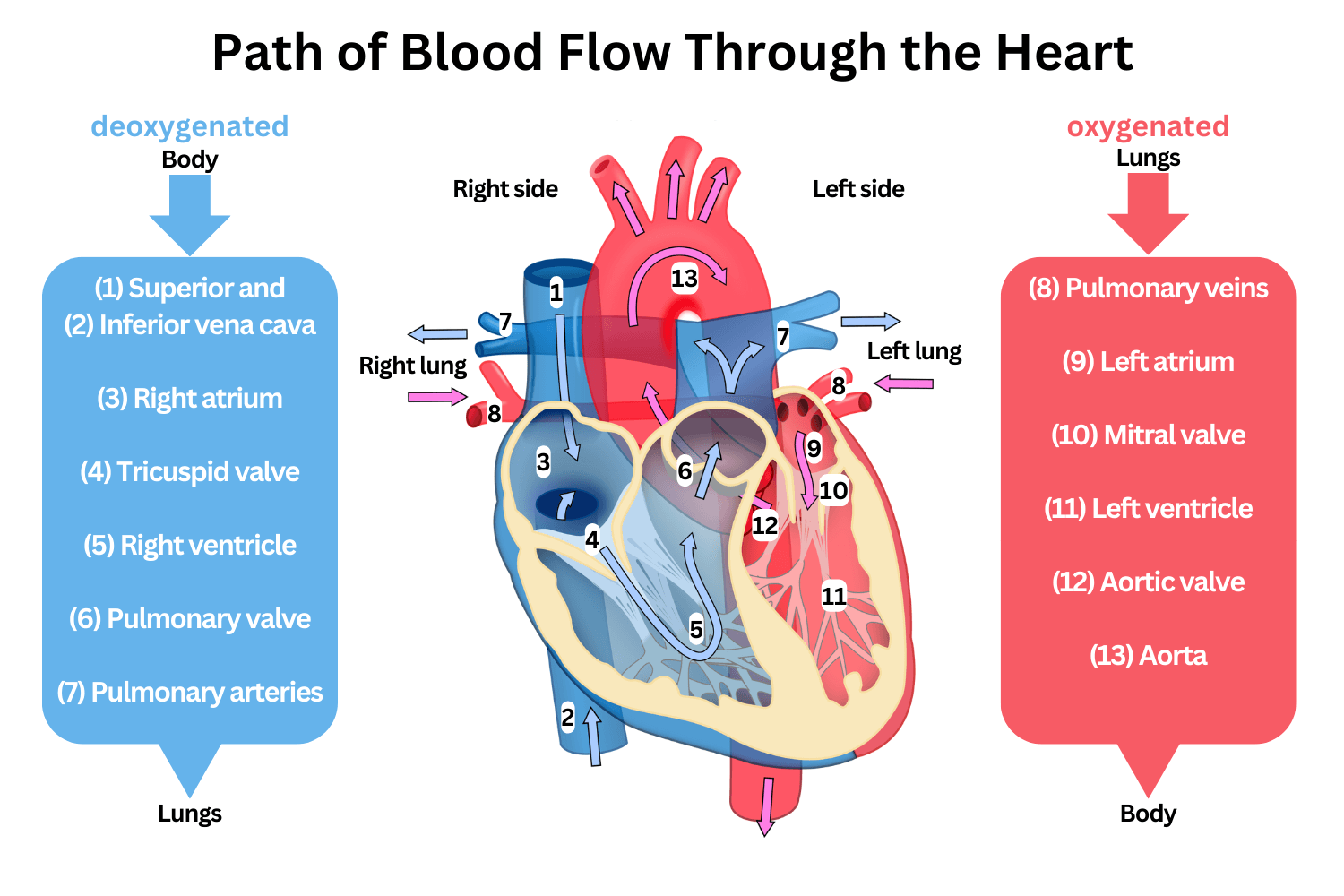
What is the pathway of the blood throughout the heart?
Body → Right atrium: deoxygenated blood enters through vena cava
Right atrium → Right ventricle: enters through tricuspid valve
Right ventricle → Lungs: blood is pumped from right ventricle to lungs via pulmonary artery where it picks up oxygen
Lungs → Left atrium: oxygenated blood returns to the atrium via the pulmonary veins
Left atrium → Left ventricle: blood is pumped from left atrium to left ventricle via mitral valve
Left ventricle → Body: blood is pumped out the heart through the aorta, delivering oxygen to the body
How can a heartbeat be monitored?
Electrocardiogram: small electrodes are fastened over the heart and other areas of the persons body to record electrical activity of the heart
Sound of valves closing: the sound of valves closing is in a pattern like ‘lub-dup’, the ‘lub’ sound being when the blood flow closes between the ventricles and atria and the ‘dup’ being when blood flow closes between atria and arteries that lead to the heart (coronary arteries)
Pulse rate: a pulse is the feeling near the skin caused by the arteries expanding and recoiling due to the pressure of blood being pumped from the heart, each time the left ventricle contracts it creates a pulse
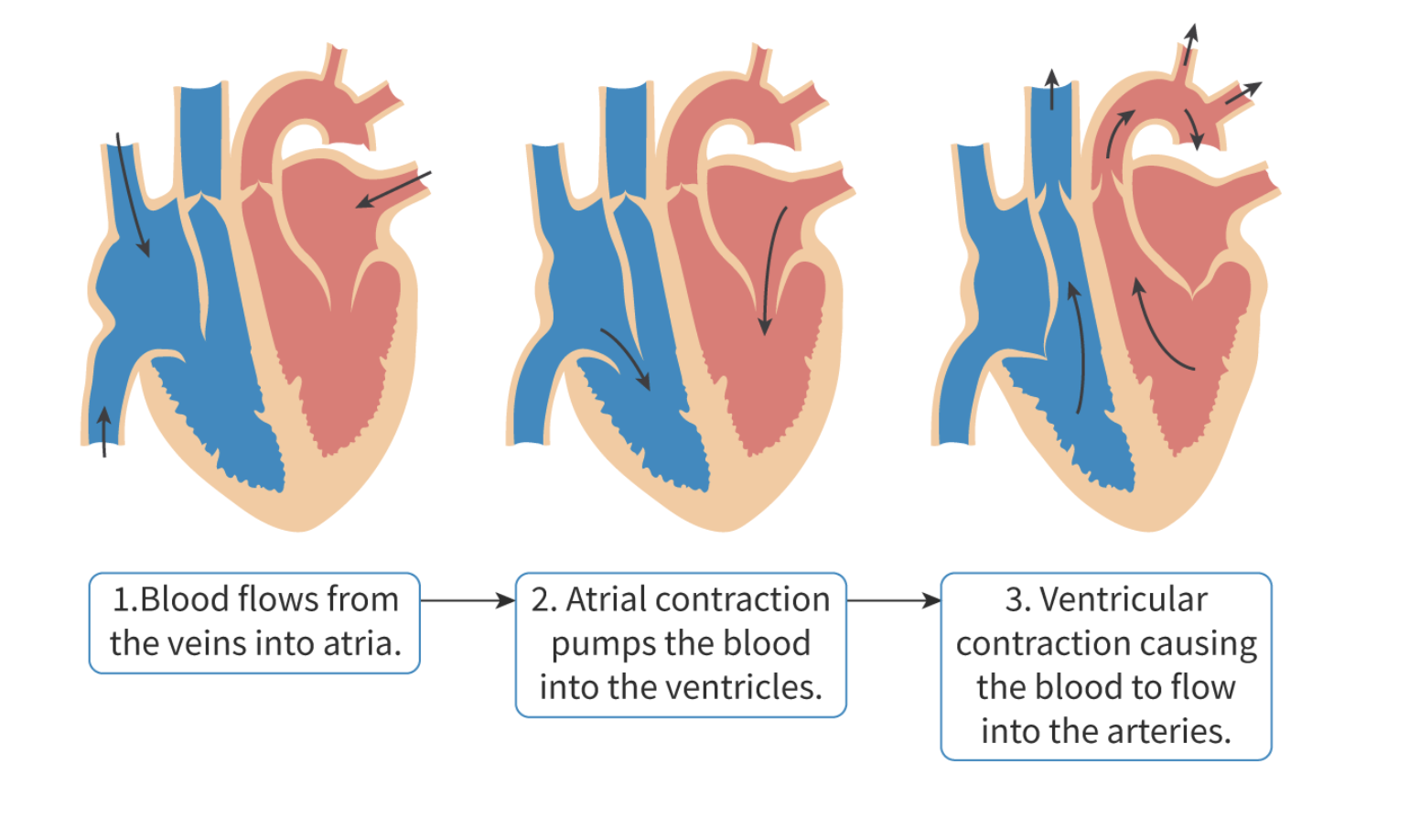
What are the stages of a heartbeat?
Blood flows from veins to atria
Atria contract
Blood is pumped into ventricles
Atrial pressure decreases
Valves between atria and ventricle close
Prevents backflow of blood from ventricles to atria
Ventricles contract
Blood is pumped into arteries
Ventricular pressure decreases
Valves between ventricles and arteries close
Prevents backflow of blood from arteries to ventricles
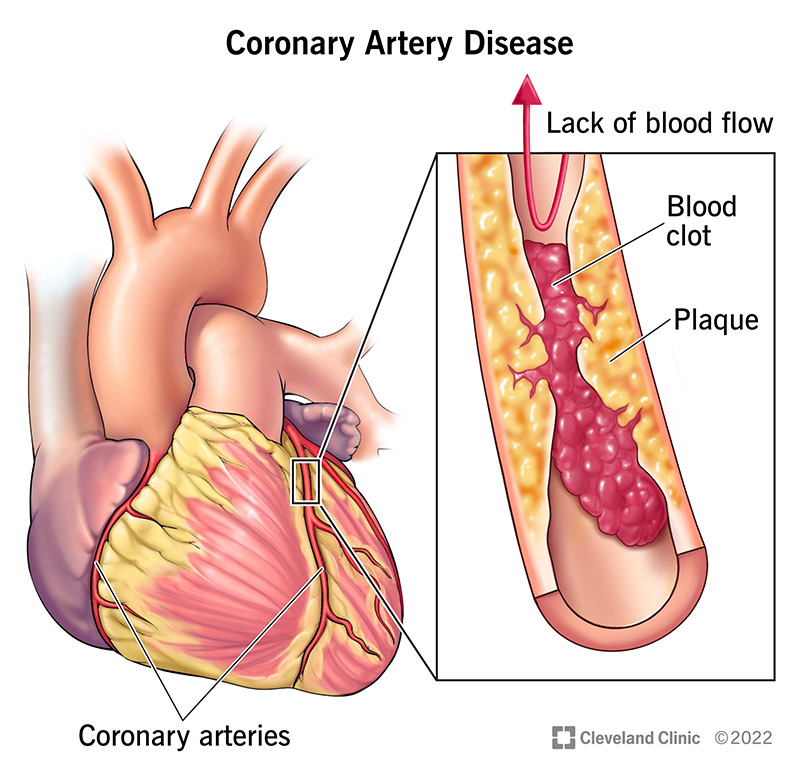
What is coronary heart disease?
Coronary arteries supply blood, oxygen and nutrients to the heart itself since the heart has very thick and active muscular walls
Blocked coronary arteries: prevents the cardiac muscle from getting enough energy for it to contract, which means the heart muscle can be damaged and may die
CHD occurs when the coronary arteries can’t supply enough oxygen rich blood to the heart because of a blockage in them
The blockages reduce the diameter of the artery, making it difficult for blood to pass through
Risk factors and preventive measures for CHD
Risk factors:
Age, genetic predisposition, diet, stress, smoking, lack of exercise, being overweight
Diet:
High risk foods: animal fat, high cholesterol food, high salt food
Preventive foods: plant-oil and fish-oil
Preventive measures:
Exercising, having a good diet