06.3C U6P1 (PART C) Stimulation of Skeletal Muscle ONLY
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Dendrites
Branch-like extensions of the neuron that detect signals from other neurons and conduct impulses toward the cell body
Cell body
The part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and produces the energy needed for the activity of the cell.
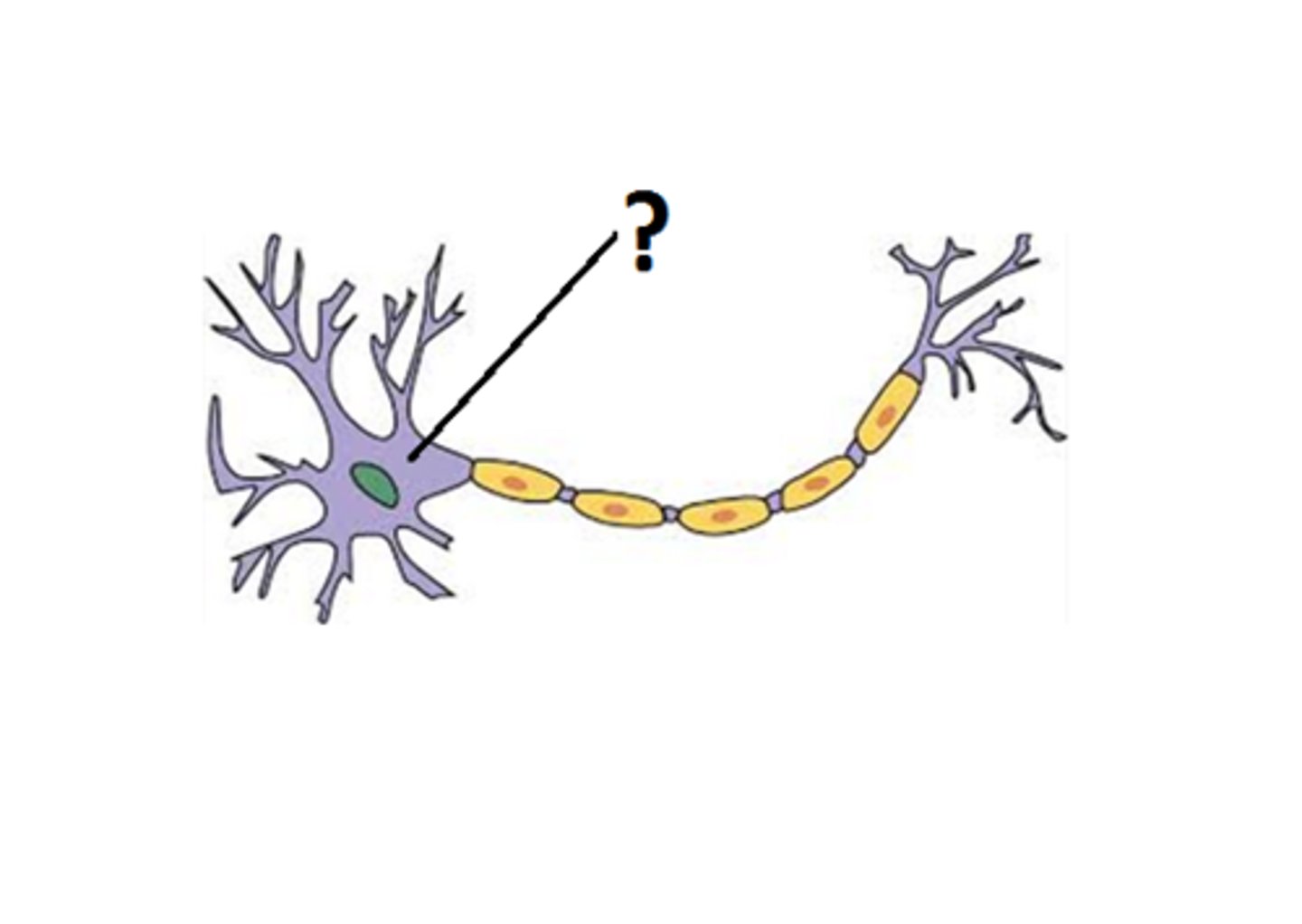
Axon
Long extension of a neuron that conducts impulses away from the cell body to the axon terminals
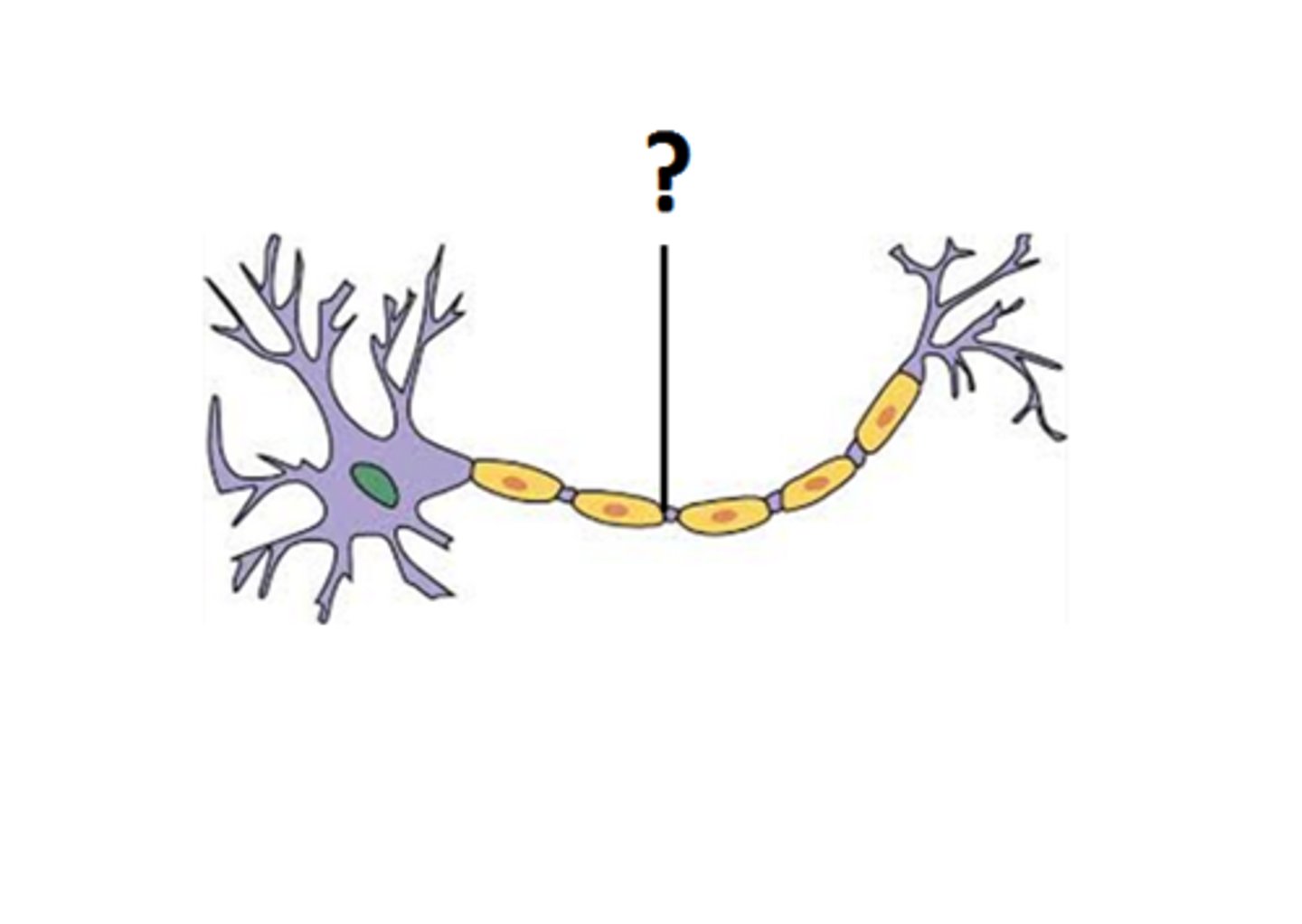
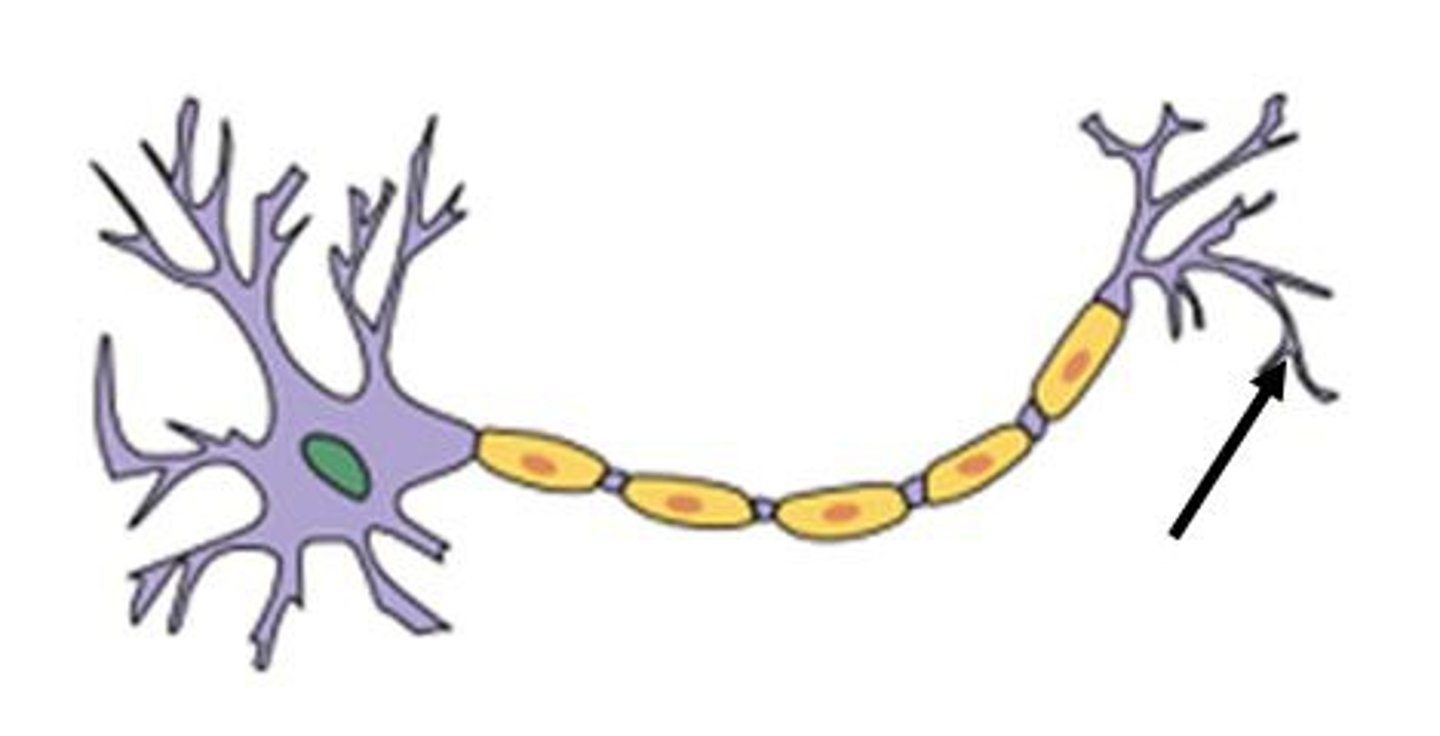
Axon terminals
Structures at the end of axons that secrete neurotransmitters when stimulated by the action potential
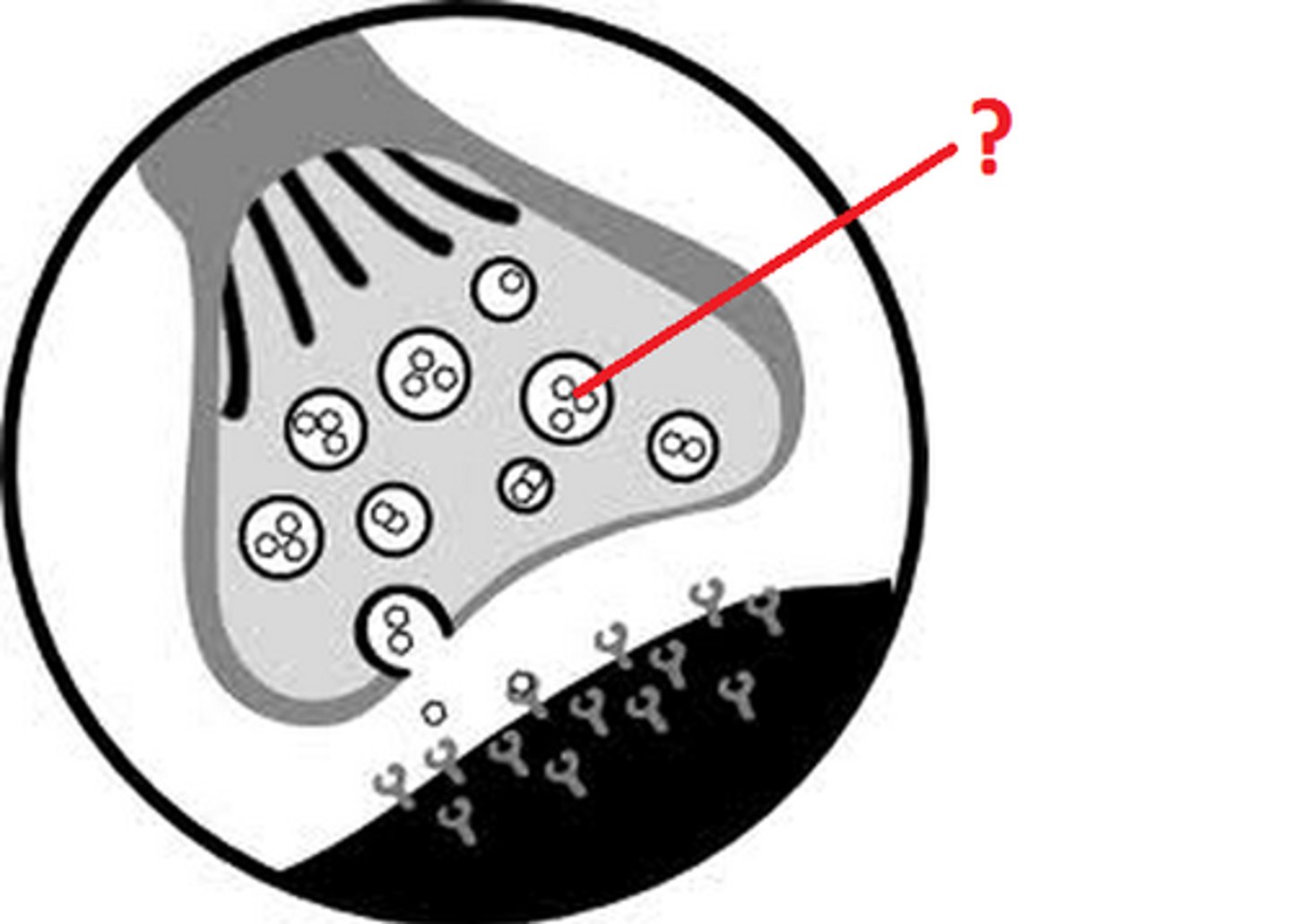
Neurotransmitter
Chemicals released by neurons that stimulate other neurons, muscles, or glands.
Stimulated Membrane (Neuron)
A state in neurons that results when a neurotransmitter like acetylcholine binds to a receptor on a sodium channel causing it to open and sodium to flood into the cell; some potassium also diffuses out
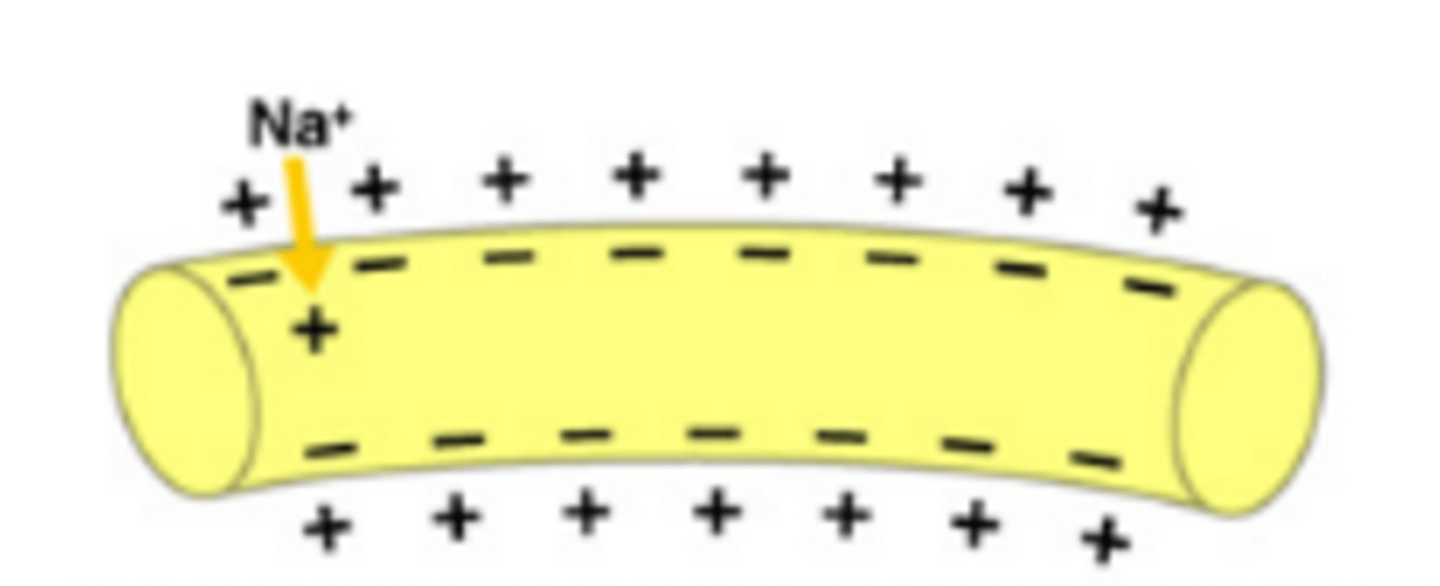
Depolarized Membrane (Neuron)
A state in neurons that results when sodium channels open allowing sodium to rush INTO the cell via facilitated diffusion that causes the membrane to become more positive on the inside than on the outside
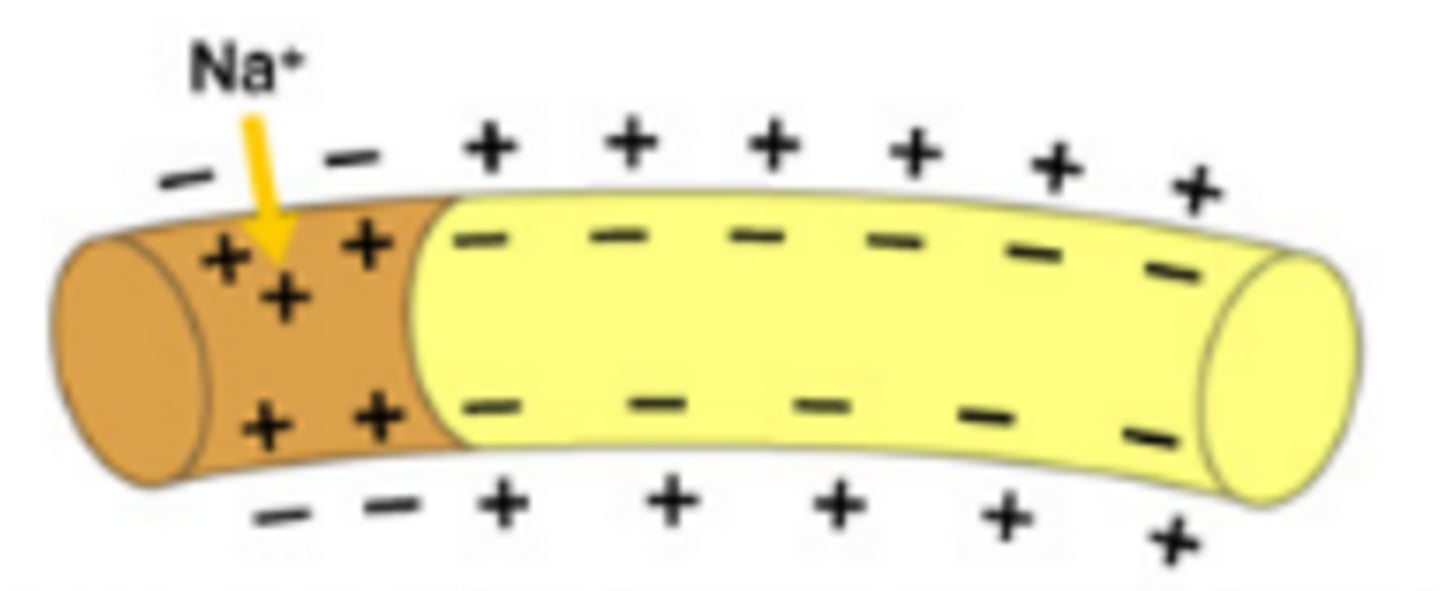
Propagation of an Action Potential (Neuron)
Occurs when sodium ions flood into a neuron triggering the opening of additional sodium channels along the membrane resulting in a more positive charge inside the cell than outside the cell
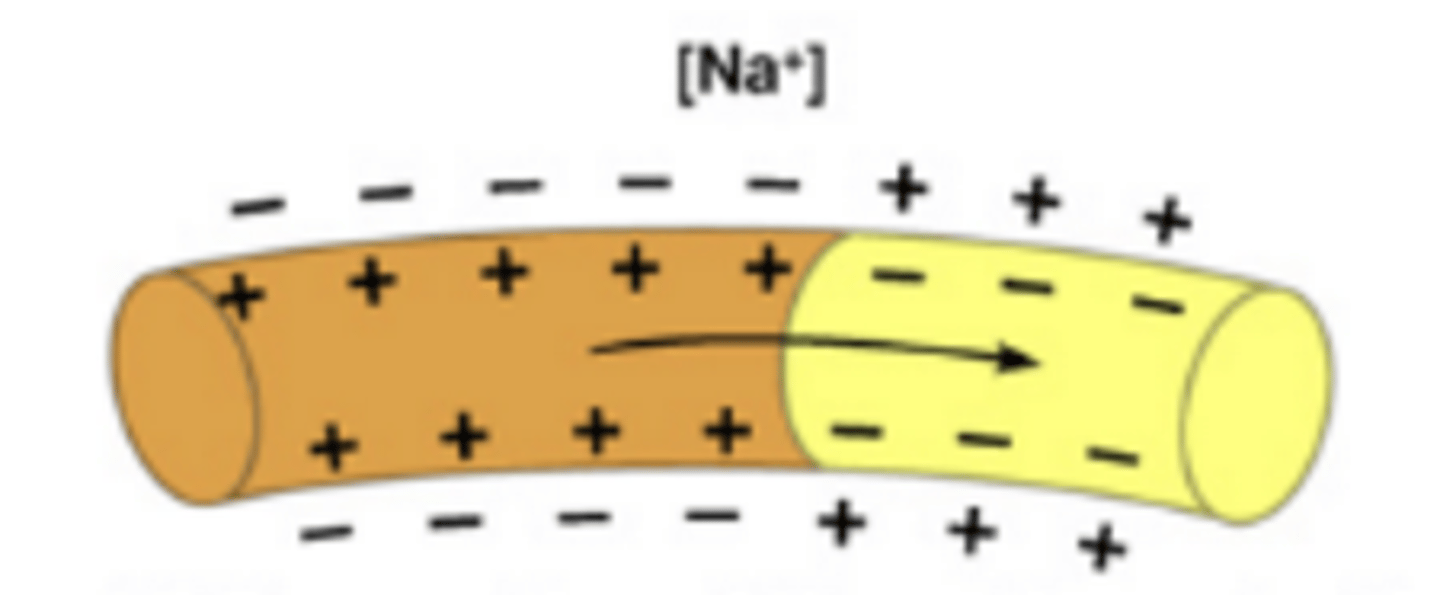
Repolarized Membrane (Neuron)
A state in neurons that results when sodium channels close and potassium channels open allowing potassium to rush OUT of the cell via facilitated diffusion that causes the membrane to once again become more positive on the outside than the inside
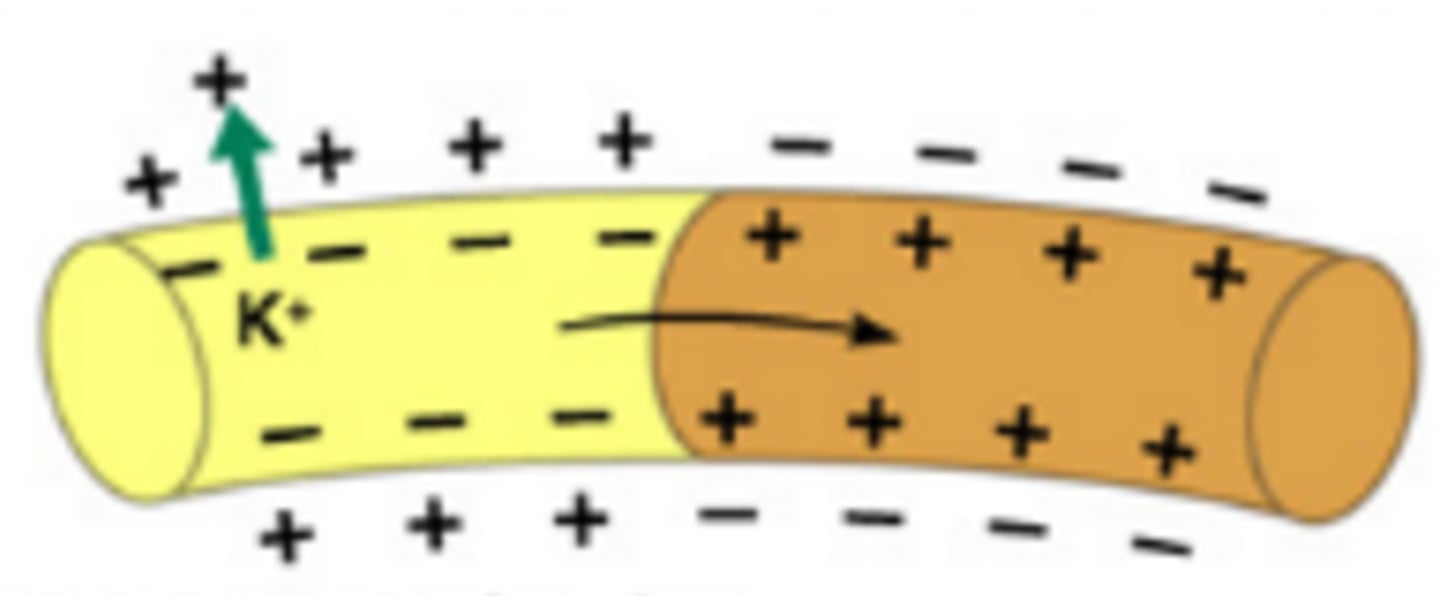
Neuromuscular Junction
The synapse between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
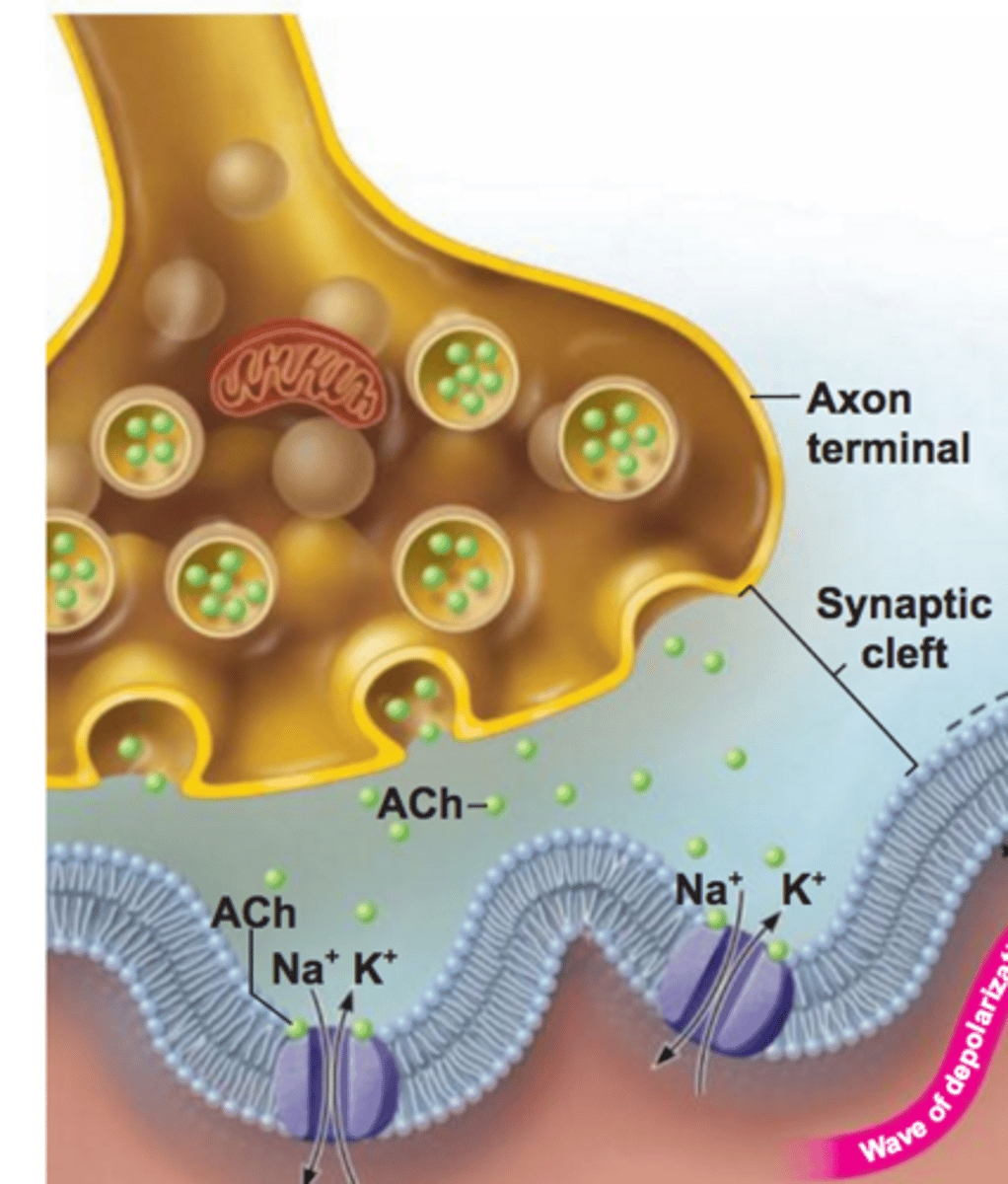
Synapse
The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
Acetylcholine
Neurotransmitter that diffuses across the neuromuscular junction and binds to receptors on the sarcolemma to produce an impulse along the muscle cell
Calcium ions
A type of ion that is responsible for initiating the release of neurotransmitters from synaptic vesicles and also helps to initiate muscle contractions
Acetylcholinesterase
An enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine which terminates the stimulation of the muscle
Sodium-Potassium pump
Ion channel found in the membrane of muscles and neurons that at rest when the membrane is polarized uses ATP to actively pumps 3 sodium ions out of the cell and 2 potassium ions into the cell
Sodium Channel
A voltage-gated channel found in the membrane of muscles and neurons that during depolarization allows for the movement of sodium ions into the cell from high to low concentration through facilitated diffusion
Potassium Channel
A voltage-gated channel found in the membrane of muscles and neurons that during repolarization allows for the movement of potassium ions out of the cell from an area of high concentration to low concentration through facilitated diffusion.
Polarized Membrane (Charge)
Membrane at rest that is more positive on the outside than on the inside
Depolarized Membrane (Charge)
Membrane that has been stimulated and allows sodium ions to rush in so the membrane is more positive on the inside than outside