Session 3: Energy production from carbohydrates 3
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What enzyme facilitates the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)
What is the name of the reaction facilitated by PDH which converts pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
Oxidative decarboxylation by PDH
Which vitamin provides most of the various cofactors requires for oxidative decarboxylation?
B-vitamins - so this reaction is sensitive to vitamin B deficiencies
What is oxidative decarboxylation inhibited by?
High energy signals - acetyl CoA, NADH+ + H+ and ATP
What is oxidative decarboxylation stimulated by?
Low energy signals - pyruvate, CoA, NAD+, ADP, Insulin
What is the inheritance pattern of the rare genetic defect in PDH (PDH deficiency)?
X-linked genetic defect
PDH deficiency is the most common cause of...
Congenital lactic acidosis
(no acetyl CoA formation from pyruvate so pyruvate will be reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism instead)
What is the clinical presentation of PDH deficiency?
Neurological and muscular abnormalities - may be fatal during neonatal period
What is standard management of PDH deficiency? Is there any treatment available for this condition?
There is no treatment available for PDH deficiency - only management.
Management includes: dietary restriction of carbohydrates & proteins, ketogenic diet, vitamin B supplementation
What is stage 3 of carbohydrate catabolism?
The TCA cycle/citric acid cycle/Krebs cycle
Where does TCA cycle take place in the cell
Mitochondrial matrix
How many cycles of TCA take place PER glucose molecule?
2 cycles per glucose
Which steps in the TCA cycle are irreversible?
Reactions 1, 4 and 5
What enzyme catalyses the conversion of Acetyl CoA + Oxaloacetate to Citrate?
Citrate synthase
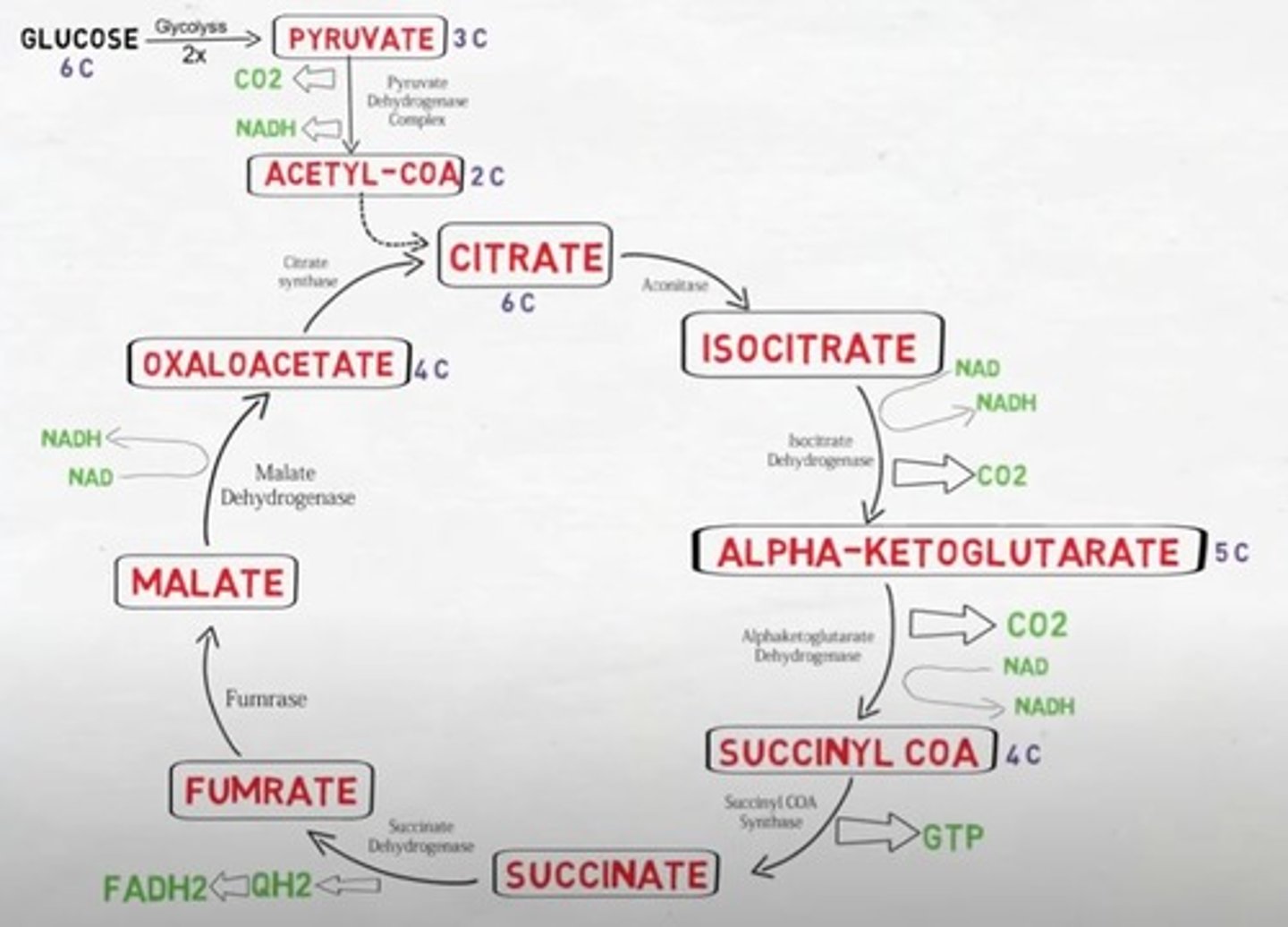
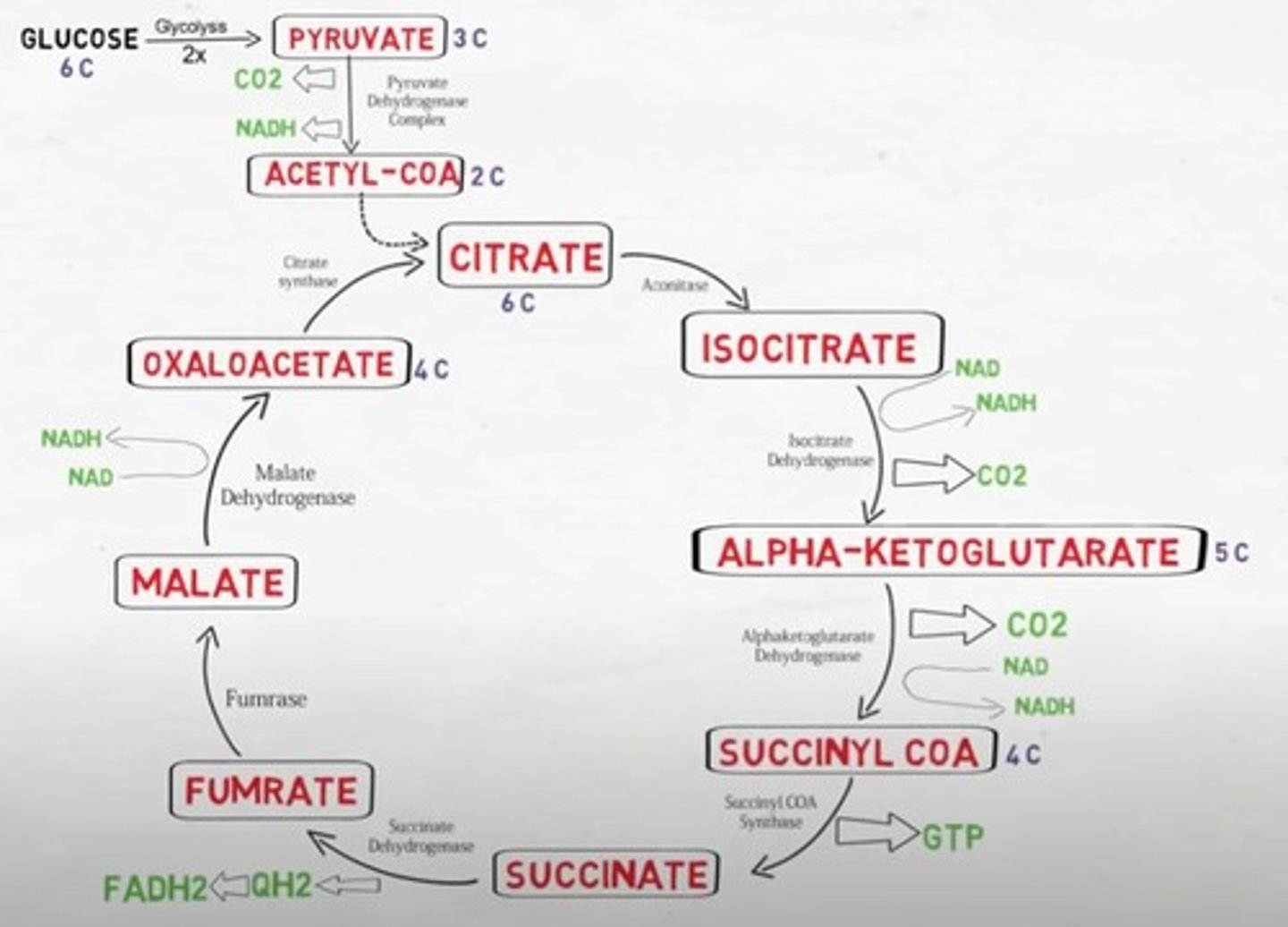
Is the TCA cycle oxidative/reductive & exergonic/endergonic?
The TCA cycle is a oxidative and exergonic pathway
What is the output of one cycle of the TCA pathway?
2CO2 + CoA + 3NADH+ + H + FADH2 + GTP
What is the output of two cycles of one TCA pathway?
6NADH + H + 2 FADH2 + 2GTP + 2CoA
Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur in the cell?
inner mitochondrial membrane
What are the names of the electron carriers involved in oxidative phosphorylation
It occurs via protein complexes (PC I-IV) in the inner mitochondrial membrane
PC1 and PC2 pass their electrons from [NADH + H+] and [FADH2] to PC3 and PC4
PC4 passes electrons to molecular oxygen which forms H2O with 2H+
Which protein complexes are also proton translocating complexes (PTC)?
PC1, 3 and 4 are proton translocating complexes (PTC) - these also pump H+ atoms from the mitochondrial matrix to the inter membrane space using the free energy released during electron transport
How much free energy from electron transport chain is used to move H+ across the mitochondrial membrane?
30% of energy released during electron transport is used to move H+ across mitochondrial membrane
Oxidative phosphorylation is a very efficient way of generating large amounts of ATP
What is the name of the H+ proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane?
Proton motive force (pmf) / proton concentration gradient / electrochemical gradient
What is the name of the protein which synthesises ATP from ADP and Pi using the energy from the dissipation of the proton gradient?
The energy from the dissipation of the proton gradient across the inner membrane is used by ATP synthase to synthesise ATP from ADP + Pi
Is more energy released during transport of electrons from [NADH + H+] or from FADH2?
More energy is released during transport of electrons from [NADH + H+] = (-220kJ/mol)
Oxidation of 1 mole of [NADH + H+] = produce 2.5 molecules of ATP
Oxidation of 1 mole of FADH2 = produce 1.5 molecules of ATP (-152kJ/mol)
____ releases large amounts of energy which is used to generate ATP
O2 releases large amounts of energy which is used to generate ATP
What is the final acceptor of electrons in oxidative phosphorylation?
Oxygen
How many moles of ATP is produced per mole of glucose in total from glycolysis to TCA cycle?
32 moles of ATP produced per mole of glucose
What does the efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation depend on?
Efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation depends on the tightness of coupling of electron transport to ATP synthesis.
This can vary depending on tissues...
- Brown adipose tissue (BAT): allows extra heat generation
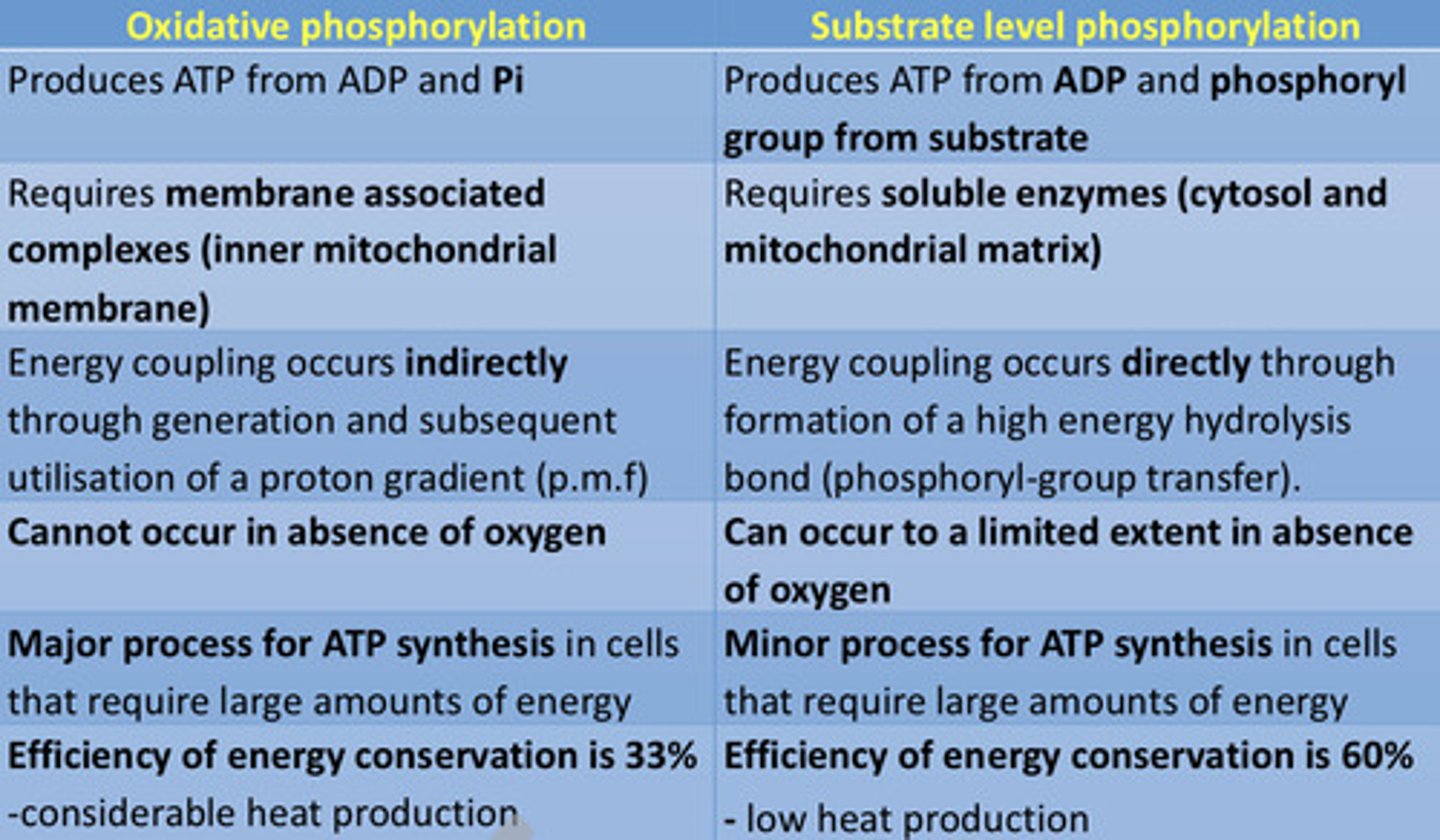
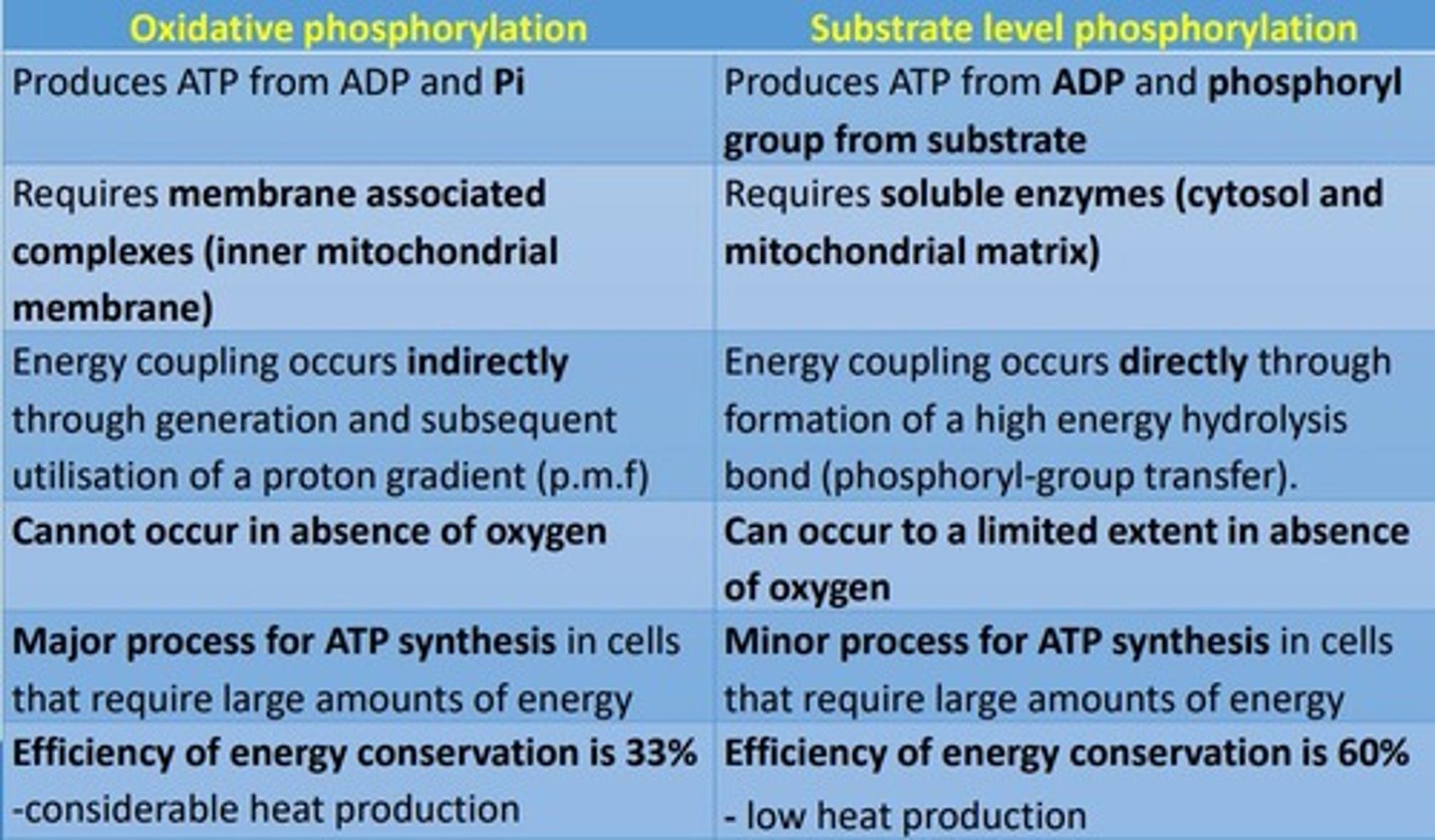
What are the differences between oxidative phosphorylation and substrate-level phosphorylation?
When ATP is low... there is an increase/decrease of oxidative phosphorylation
When ATP is low - there is an increase of oxidative phosphorylation
When ATP is high... there is an increase/decrease of oxidative phosphorylation
When ATP is high - there is a decrease of oxidative phosphorylation
there is no substrate for ATP synthase and it stops, therefore inward flow of H+ atoms stops. The concentration of H+ atoms in the inner-mitochondrial space increases - preventing further H+ pumping (stops electron transport)
What conditions/substances inhibit oxidative phosphorylation?
Anaerobic conditions inhibit oxidative phosphorylation (oxygen is final acceptor in oxidative phosphorylation) and substances such as carbon monoxide, antimycin, azide, rotenone and cyanide inhibit oxidative phosphorylation
Why does cyanide (CN-) inhibit oxidative phosphorylation?
Cyanide (CN-) prevents the acceptance of electrons by oxygen
Give examples of synthetic uncouplers in oxidative phosphorylation (which increase the permeability of the mitochondrial inner membrane to protons)
Synthetic uncouplers such as dinitrophenol (DNP) and dinitrocresol (DNC) increase the permeability of the mitochondrial inner membrane to protons, dissipate the proton gradient and therefore reduce the proton motive force (pmf)
What is UCP1 known as?
Thermogenin - it is an uncoupling protein
Pantothenic acid is another name for
Vitamin B5
Name the process by which triacylglycerols are broken down into fatty acids for fuel
Lipolysis
What is the name of the process which oxidises fatty acids into acetyl CoA
Beta-oxidation
In response to cold, noradrenaline (norepinephrine) stimulates....
Non-Shivering Thermogenesis
1) Lipolysis of triacylglycerols which releases fatty acids - fatty acids are oxidised (beta-oxidation) providing reducing power for oxidative phosphorylation
2) Fatty acids activate UCP1 (thermogenin) in Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT)
3) UCP1 transports H+ from intermembrane space into the matrix but there is NO ATP synthesis - HEAT GENERATION!
Energy from the dissipation of proton gradient is used to generate _____ (non-shivering thermogenesis).
Energy from the dissipation of the proton gradient is used to generate heat (non-shivering thermogenesis).
Give an example of two oxidative phosphorylation diseases
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is caused by a mutation in gene coding for protein complex I (PC I)
Leigh's syndrome is caused by a mutation in gene coding for ATPase

What is the efficiency of energy conservation in oxidative AND substrate-level phosphorylation?
- Oxidative phosphorylation: 33% with CONSIDERABLE (higher) heat production
- Substrate-level phosphorylation: 60% with LOW heat production
What are some stimulations of oxidative phosphorylation
When [ATP] is LOW
What are some inhibiters of oxidative phosphorylation
- When [ATP] is HIGH - there is no substrate for ATP synthase and it stops - therefore inward flow of H+ ions stops. The [H+] increases in the inner mitochondrial space - preventing further [H+] pumping (stops electron transfer)
- Anaerobic conditions
- Various substances e.g., carbon monoxide, antimycin, azide, rotenone, cyanide - all inhibit oxidative phosporylation as they dissipate the electrochemical gradient = no ATP synthesis
- Uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation by certain synthetic uncouplers such as e.g., dinitrophenol (DNP) and dinitrocresol (DNC) = dissipate the proton gradient, reduce pmf - no ATP synthesis
In which tissue does the process of non-shivering thermogenesis via UCP1 (thermogenin) mainly take place?
Brown adipose tissue (BAT)
Name some defects in oxidative phosphorylation which arise from mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mt-DNA)
1) Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON)
- Mutation in gene coding for PROTEIN COMPLEX 1 (PC1)
- Presents with: loss of vision
2) Leigh's syndrome
- Mutation in gene coding for ATPase transporter protein
- Presents with: loss of mental & physical abilities in infancy
Name the family of diseases arising from defective oxidative phosphorylation
Mitochondrial, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS)
Name the key protein naturally occurring in the inner membrane of mammalian cells which uncouples the proton gradient so protons enter mitochondria to produce heat (non-shivering thermogenesis)
Uncoupling protein 1
Name one inhibitor of electron transport in mitochondria.
Cyanide
The majority of energy released during electron transport during oxidative phosphorylation is used to move H+ atoms cross inner mitochondrial membrane and the remaining energy is lost as heat.
True or false?
False
NADH+ H+ yields less ATP than FADH2.
True or false?
False
What creates H+ gradient across inner mitochondrial membrane?
Electron transport
Name the enzyme catalysing formation of ATP from ADP and Pi using H+ gradient across inner mitochondrial membrane.
ATP synthase
The largest amount of ATP is synthesised during oxidative phosphorylation.
True or false?
True
Which enzyme catalyses conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Which intermediate of the TCA cycle is combined with Acetyl CoA to initiate the cycle and is regenerated by it?
Oxaloacetate
The TCA cycle is the only pathway that may occur under anaerobic conditions.
True or false?
False
Where does the TCA cycle take place in cells?
Mitochondrium
Name the molecule that enters the TCA cycle.
Acetyl CoA
Electron transport chain
- PC I and PC II pass electrons from NADH + H and FADH2 to PC III and PC IV
- PC IV passes electrons to oxygen to form water
- PC I, PC III and PC IV are the proton translocating complexes (PTC)
PC___, PC___ and PC___ are the proton translocating complexes (PTC) - they pump H+ atoms from the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space using free energy generated in the electron transport chain (ETC)
PC I, PC III and PC IV
There is ___ energy released during transport of electrons from NADH⁺ + H⁺ than from FADH2 as NADH⁺ + H⁺ ‘uses’ four protein complexes
More
Oxidation of 1 mole of NADH + H in the ETC produces -___kJ/mol energy which is equivalent to ___ moles of ATP
-220kJ/mol, 2.5 moles of ATP
Oxidation of 1 mole of FADH2 in the ETC produces -___kJ/mol energy which is equivalent to ___ moles of ATP
-152kJ/mol, 1.5 moles of ATP
The efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation depends on...
The tightness of coupling of electron transport chain (ETC) to ATP synthesis
Energy from the dissipation of the proton motive force (pmf) is coupled to the synthesis of ___
ATP
Compare oxidative phosphorylation to substrate-level phosphorylation
Name two synthetic uncouplers of ETC to oxidative phosphorylation
Dinitrophenol (DNP)
Dinitrocresol (DNC)
How does dinitrophenol (DNC) work?
- Increases permeability of mitochondrial inner membrane to protons
- Dissipates proton gradient
- Reduces pmf
- No drive for ATP synthesis
- Heat is generated
- Can be fatal
Uncoupling protein (UCP-1) found in brown adipose tissue (BAT) is also known as...
Thermogenin
What is the process by which energy from dissipation of proton gradient is used to generate heat in brown adipose tissue (BAT)?
Non-shivering thermogenesis
Name two oxidative phosphorylation diseases
1) Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) = mutation in gene coding for PC1 in ETC
2) Leigh's syndrome = mutation in gene coding for ATPase
Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)
- Mutation in gene coding for protein complex I (PC I) in the ETC
- Causes progressive loss of central vision & blindness
- Inherited through mitochondrial DNA
Leigh's Syndrome
- Mutation in gene coding for ATPase protein in oxidative phosphorylation
- Causes loss of mental & physical abilities in infancy
- Inherited through mitochondrial DNA
The [H+] proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane is also known as the...
Proton motive force (pmf)
TCA cycle
Name the family of diseases arising from defective oxidative phosphorylation
Mitochondrial, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS)
How many moles of ATP are directly produced as a result of processing one mole of glucose in glycolysis and the TCA cycle?
4