Module E - Ambulatory Monitoring
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
-Describe the uses and function of ambulatory monitoring. -Describe the education and patient preparation required for ambulatory monitoring. -Describe the application and removal of ambulatory monitors.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
describe a “typical” ambulatory monitor
-also known as a Holter monitor
-small box strapped to the patient waist or shoulder to record ECG over set period of time while patient goes about daily activities
-inside box is recording device (less than 2 lbs) that looks like a cell phone
-most monitors are digital recorders
define ambulating
walking
determine the number of leads used with ambulatory monitors
3-5 attached to chest, depending on type of monitor used
explain the responsibilities of the healthcare provider when initiating an ambulatory monitor on a patient
-ask patient to keep diary of unusual and usual activities, symptoms or abnormal sensations (chest pain, indigestion, dizziness)
-if symptoms occur, patient to monitor and record what they were doing prior and during
-application and removal of monitor
-providing patient education
-ensuring results are placed in the patient chart
-transferring content from digital storage device (depending on place of employement) for analyzing
identify the purpose of ambulatory monitoring
documentation of electrical activity in the heart and identification of abnormal heart behaviours (dysrhythmias) as correlated by the symptoms experienced by the patient
list the reasons for ambulatory monitoring on patients that have already had a 12-lead ECG
-infrequent symptoms or no symptoms (during stress test
-evaluation of cardiac meds (such as antidysrhythmic drugs)
-evaluation of artificial pacemaker function (after implantation or if problems arise)
-evaluation of heart function after myocardial infaction (MI)
define antidysrhythmic (antiarrhythmic) meds
type of medication given to prevent cardiac rhythm abnormalities
list the most common types of ambulatory monitors
-Holter monitors
-cardiac event recorders
-telemetry monitors
describe holter monitor
-instrument that continuously records the electrical activity of the heart during patient normal daily activities and at exact time of patient symptoms
-24-48 period, patient records all daily activities, abnormal experiences, and symptoms in diary
-named after Norman _____
describe the type of patient that could use a Holter monitor
can understand the process (dementia patient would not suffice)
describe cardiac event recorders
-ambulatory ECG intermittent recording during symptoms
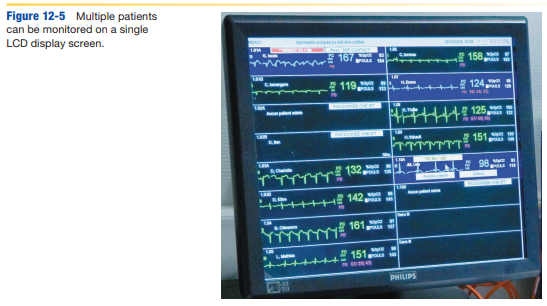
describe telemetry monitors
-real-time continuous ambulatory monitoring of outpatients as it occurs (common in healthcare facilities)
-done with small transmitting device attached to the chest with 3 or 5 electrodes, sometimes with defibrillator, single or multiple patients monitored at once
-for patients recovering from heart attack or stroke or have had recent heart procedure
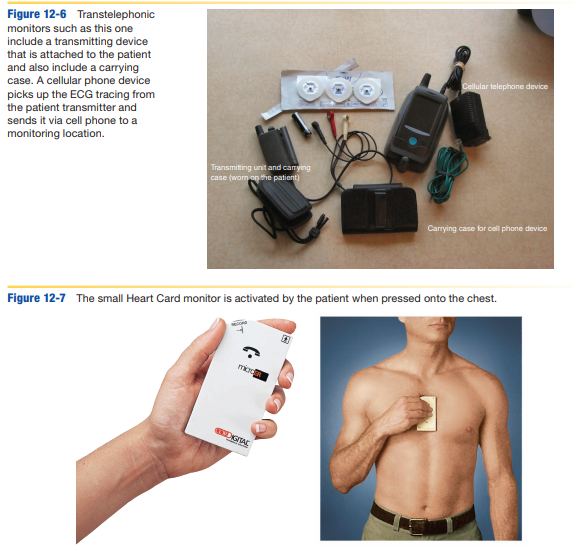
describe cardiac event recorders (transtelephonic)
-small and portable ambulatory monitoring of patients with pacemakers or anyone requiring long-term monitoring with certain dysrhythmias
-info stored in monitor and transmitted over phone line, cell tower, wifi in real-time or at the end of monitoring period
-symptom event monitor and loop-memory types
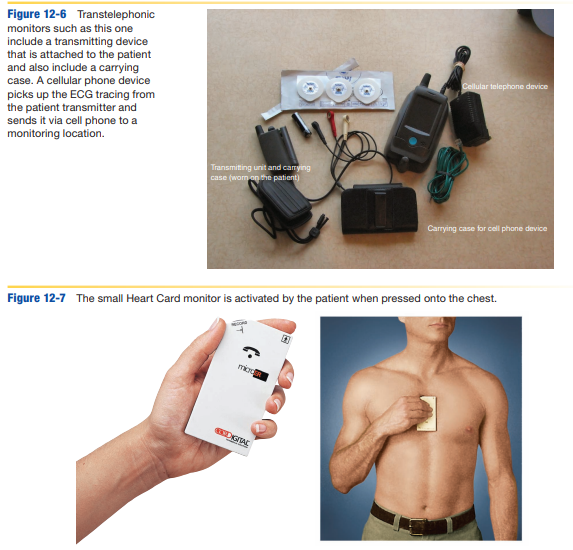
describe symptom event monitor
-type of cardiac event recorder (ambulatory monitor) activated when patient experiences symptoms (intermittent)
-worn like wristwatch (records 2D or bipolar lead I tracing) or handheld (electrode feet record lead II tracing) that has electrode feet that record HR
-records heart activity immediately after symptoms for dysrhythmias that last more than a few seconds (A-fib, A-flutter, supraventricular tachycardias)
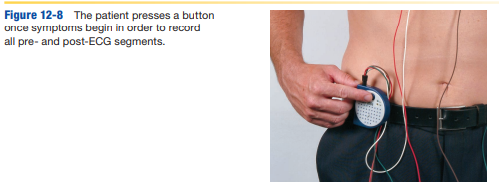
describe loop-memory monitor
-type of cardiac event (ambulatory) monitor attached to the chest with 2 lead wires to record intermittent heart activity
-remains in place continuously (30 days or more) holding up to 5 mins of ECG based on patient symptoms and complaints (before, during, after episode), sent to be evaluated to determine cause
list the components vital to educating the patient about ambulatory monitoring
-patient understanding
-instructions for use
-patient diary
-documentation (patient checklist and instructions)
describe how to confirm patient understanding of the ambulatory monitoring procedure
-thorough instruction of proper use and documentation of education on chart
-have patient repeat instructions back to you, or by placing sample entry into diary
-provide complete set of instructions with name and facility number in event patient has questions or problems (if they dont understand will have to repeat procedure)
-remind patient of any new or discontinued med changes prescribed
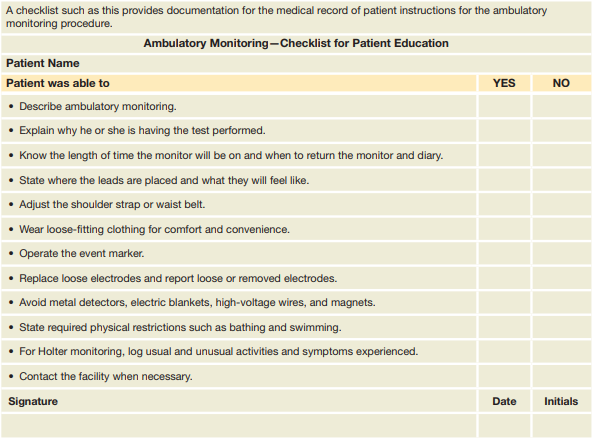
describe the instructions for proper use of ambulatory monitor
-wear loose-fitting clothing (front-buttoning preferred) for comfort and convenience and reduce artifact
-no diet change
-not tamper or disconnect lead wires or electrodes, only sponge bath (cannot get equipment wet)
-sleep in any position that does not apply tension to the lead wires or electrodes
-avoiding magnets, metal detectors, high-voltage areas, electric blankets that interfere with tracing
-know how equipment works and intermitently check it works during
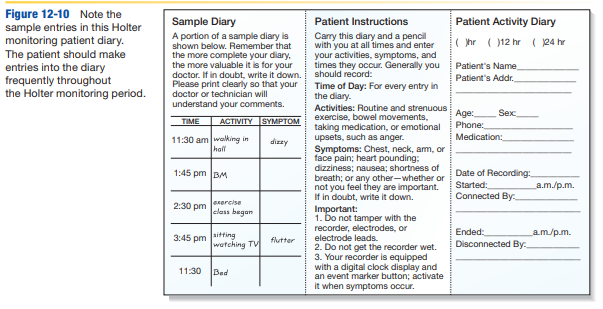
describe details of patient diary for ambulatory monitoring
-accurate record of events and symptoms that occur while monitor in place
-provide time blocks to mark when all activities (usual or unusual) and symptoms (physical and emotional stress) occur for easy patient entry
-emphasize need for accurate and complete diary
what are the steps required to mentally prepare patient for ambulatory monitor placement
-describe methods to reduce anxiety
-describe electrode site prep
describe how to emotionally prepare the patient for ambulatory monitoring placement
-might be apprehensive or fearful, tell them it is normal to have some fear and allow expression of feelings and questions, and answer to the best of your ability
-help understand procedure, taking time with each step as it is performed, in terms they can understand
describe how to physically prepare the patient for ambulatory monitoring placement
-patient should understand physical requirements of the monitoring procedure
-remove chest hair (shave) if present for electrode placement
-might be discomfort with electrode placement
-remind patient to maintain all regular physical activity
list general steps for the application of the ambulatory monitor
-equipment required for the application of ambulatory monitor
-prepare the monitor for use
-skin prep procedure and special precautions for elderly
-electrode placement and attachment to ambulatory monitor
identify equipment required for the application of an ambulatory monitor
-monitor with holder and shoulder strap or belt
-new batteries and digital disk
-electrodes (3-5 depending on type of monitor)
-lead wires
-alcohol and gauze
-patient diary
-skin prep items (prep pads, benzoin, abrasive cleaner, or skin rasp)
-shaving equipment
-tape
-checklist for patient education
-manufacturers directions for specific monitor used
-pen

Describe the steps required to prepare the ambulatory monitor for use
-before entering the room to begin procedure, prepare monitor and review manufacturers instructions for type of monitor used
-check to see that the monitor is adequately charged, and replace batteries to ensure it doesnt lose charge during procedure
-insert new blank digital disk if required
describe the skin prep procedure for the electrode sites of ambulatory monitor
-have patient remove their clothing from waist up for electrode positioning and provide drape
-have patient lie or sit down in comfortable position on bed or exam table, with patient relaxed
-prepare sites for electrodes by rubbing the site with alcohol swab and let dry, if hairy shave dry (or clip for telemetry to prevent itch and artifact), remove excess hair with tape
-abrade skin using 4×4 dry gauze, skin rasp or other abrasive cleaner by rubbing firmly and briskly at each of the sites where the electrodes will be placed
describe the special precautions required for an elderly patient or patient with fragile skin during ambulatory monitor skin prep
-manipulate electrodes as little as possible when applying and removing them, with care for prevention of skin damage and pain
-apply less pressure when abrading skin and avoid abrasive cleaners when prepping
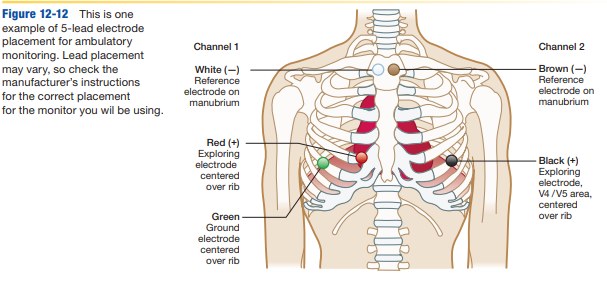
Explain where the electrodes will be placed and how they are attached to an ambulatory monitor
-electrode placement depends on number of lead wires, type of monitor used, lead tracing to be produced, check manufacturer instructions for proper placement for specific monitor
-if lead wires are snap-on type, attach electrodes to the lead wires prior to placing them on the patient (reduces discomfort)
-remove backing from adhesive, apply each to proper position by pressing firmly at center, run a finger around edge to ensure firm attachment
-attach lead wires to electrodes, check wire color and cable ID to ensure proper attachment
-arrange lead wires and cable comfortable on the patient, tape each electrodes in place to reduce tugging and pulling on the electrodes during movement
-attach cable to ECG and run baseline, have patient put on shirt with lead wire btw buttons or out bottom of shirt, attach cable to monitor in carrying case, attached to waist or shoulder, double check for wire tension
-start monitor and have patient place first entry into diary (beginning time and review instructions and time for removal)
describe health care practitioner responsibilities when patient returns to have ambulatory monitor removed
-review completed diary briefly
-document (checklist and instruction) return and removal procedure on patient chart
-prepare report for evaluation and placed in medical record, put in proper format, some with LED display viewed by cardiologist. OR digital disk sent to outside lab for analysis, then returned to physician to be provided by the patient
identify 3 factors that may affect the results of an ambulatory monitor
-improper lead attachment
-incomplete patient diary
-failure of the patient to maintain normal routine
what do abnormal ambulatory monitoring results indicate
-electrical-conduction defects in the heart rate and rhythm-controlling system
-rhythm abnormalities
-premature A or V contractions
what are some examples of additional tests that may be needed to confirm the diagnostic process after discussing the results with the physician
-echocardiogram
-coronary angiogram
-CT, MRI, PET scan