In Vivo Electrophysiology
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
in vivo electrophysiology
measuring of neuronal physiological characteristics in living organism
intracellular and extracellular recordings
many studies are invasive, some are on anaesthetized animals or post-surgery animals
Characteristics of pain in humans
hyperalgesia → increased pain response to previously painful stimulus
primary → increased sensitivity at site on injury
secondary → altered sensitivity at un-injured site
Allodynia → pain response to innocuous stimulus
decreased use of injured tissue
Pain pathway
high threshold nociceptors activated (mechanical, thermal or chemical) → primary afferent nociceptors
fed to spinal cord (process and modulation) , to thalamus and then to cortical areas for sensory and emotional pain areas (processing and perception)
spinal pathways have descending inhibitory and facilitatory influences in brain stem
Brain areas:
brainstem: changes BP, respiration and feedback to spinal cord
Thalamus: integration and modulation
Somatosensory cortex: conscious localisation and recognition of pain
Cingulate cortex and amygdala: emotional response
Hypothalamus: stress and neuroendocrine responses
Measuring pain
visual analogue scales (colours red→ green, faces happy → sad, scoring pain on a scale)
Quantitative sensory testing (QST) → assesses pain threshold by measuring how long for something to be felt → measures spinal cord excitability
in model animals
non-evoked pain behaviours
flinching, licking, reduced burrowing
reflexed → eg. moving of limb from stimulus (evoked)
facial grimace scales
eye, nose, ear and whisker changes
Problems:
experimenter bias
interpretation of behaviour
spontaneous pain (not externally caused) vs evoked pain
effects of drugs (eg. sedation)
peripheral nerve recordings
more pain = more action potentials
single-unit electrophysiology in the spinal cord
done while animals are anaesthetized as equipment is bulky
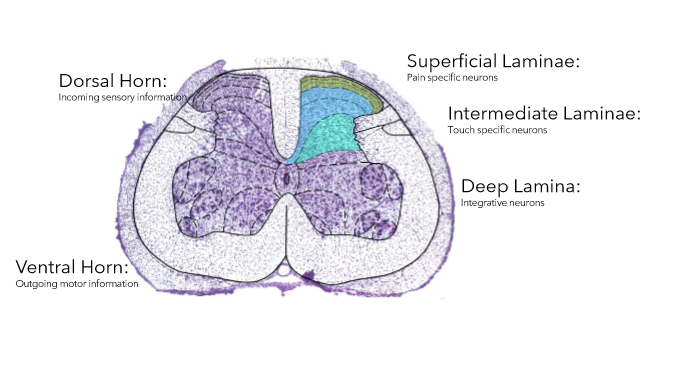
vertebrae removed to expose spinal cord and tungsten electrode into lamina 5 (layers of dorsal horn)
single units in deep dorsal horn as most stable place for electrode and the layer receives information from both painful and non-painful stimuli (wide dynamic range neurones)
analgesics reduce activity here
single-unit electrophysiology in the brain
recordings from single neurones
anaesthetized and hole drilled into skill at specific coordinates
stereotaxic coordinates determined relative to bregma
craniotomy using dental drill
electrode inserted
Electromyography (EMG)
compromise between electrophysiology and behavioural studies
measures excitability in dorsal horn using same pathways as behaviour but less subjectively
size of response = size of pain
multi-unit electrophysiology
can use electrode in dorsal horn that records from 16 locations
more data so better as not just one neurone
can locate in spinal cord and record how fast responses are
network response