Body Systems Vocabulary
Due: Nov 21, 2025, 5:00 AM
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Starred items will be on the quiz tomorrow 10/9.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

36 Terms
Cell
The smallest units of life.
Tissue
A group of cells that work together to perform a specific function
Organ
A structure made up of different types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. Examples:
Brain
Heart
Stomach
Organ System
A group of organs that work together to perform a specific function or set of functions in the body. Examples of organ systems:
Digestive system
Skeletal system
Reproductive system
Organism
A living individual that can carry out all the processes of life.
It can be unicellular, such as a bacterium, or multicellular, such as a human.
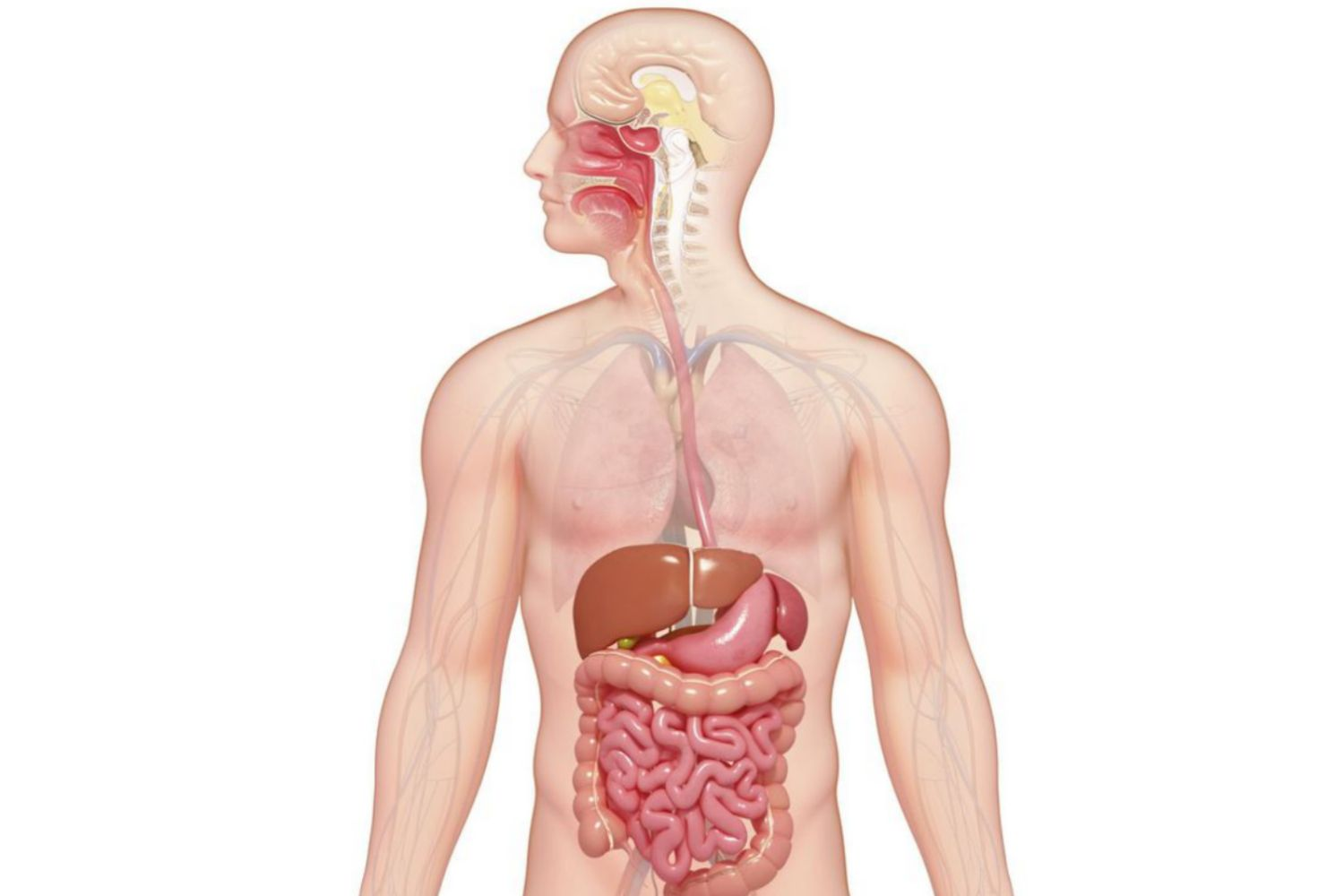
Digestive System
A system that is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body.
It includes organs such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and intestines, as well as the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
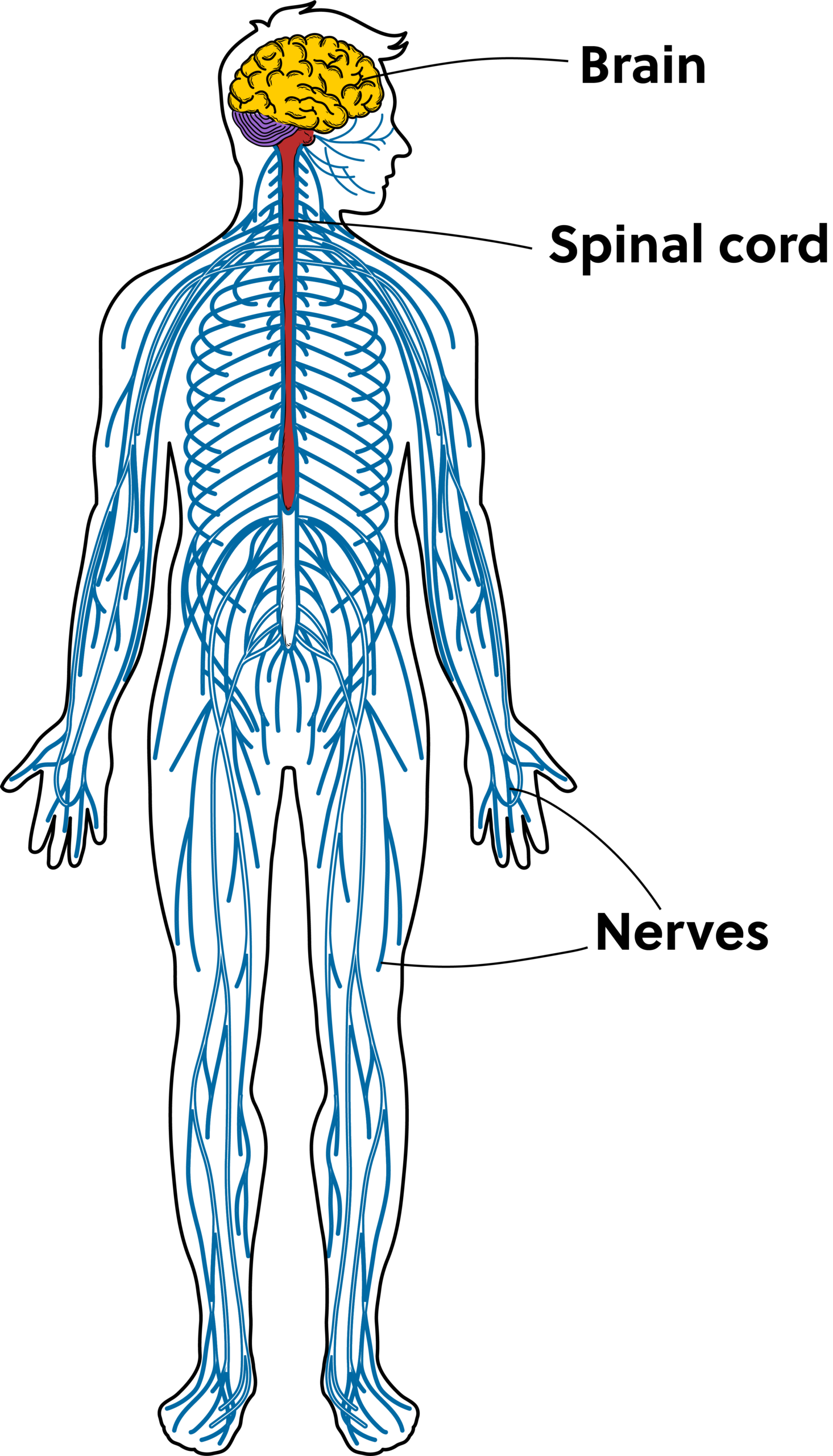
Nervous System
A system that is responsible for coordinating and controlling the body's activities.
Includes the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
It receives and processes information from the senses, sends signals to muscles and glands, and helps regulate bodily functions.
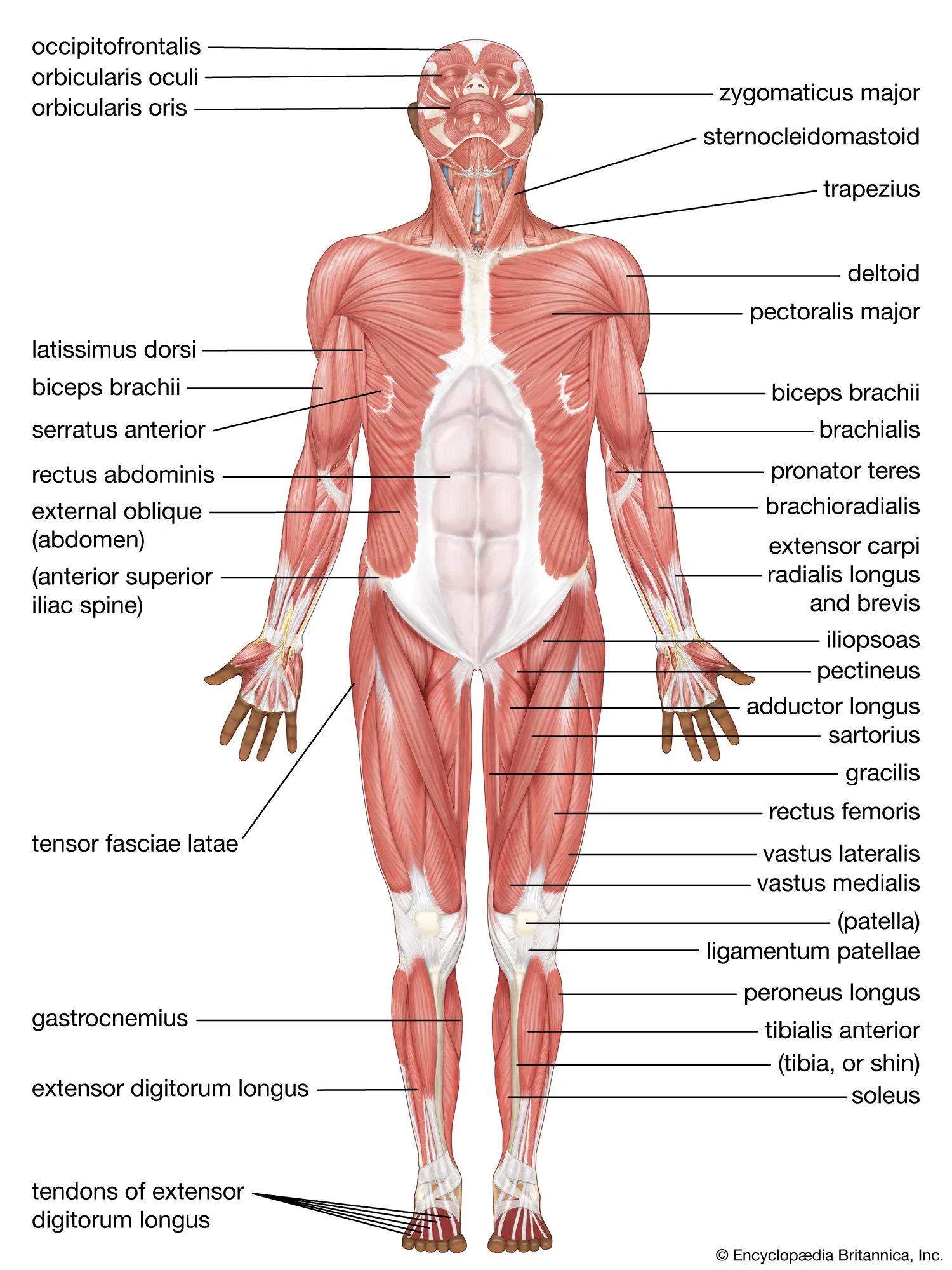
Muscular System
A system that is responsible for movement and locomotion.
Includes three types of muscles with different functions: skeletal muscles,; smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles.
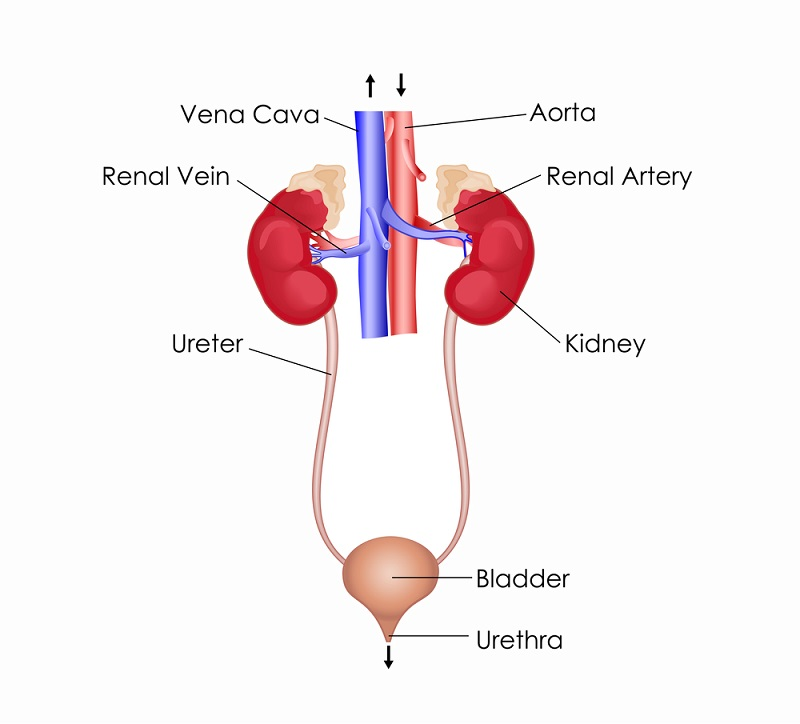
Excretory System
A system that is responsible for movement and locomotion.
Includes three types of muscles with different functions: skeletal muscles,; smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles.
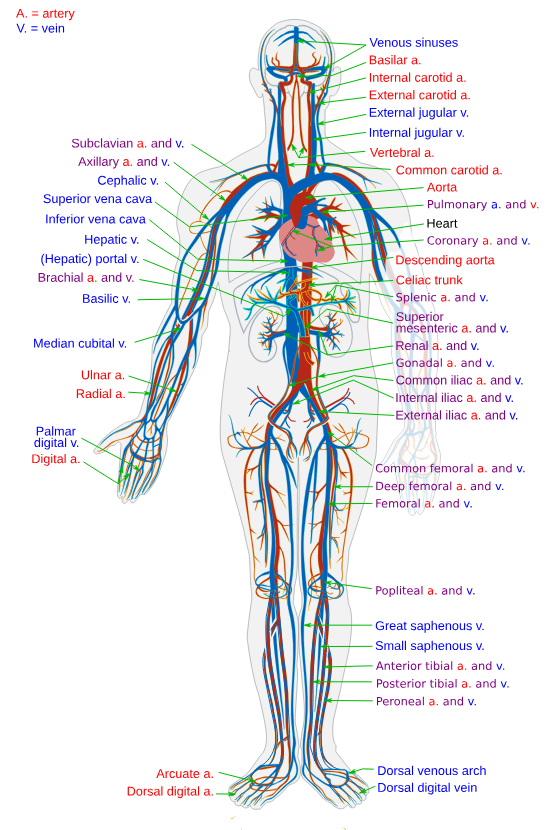
Circulatory System
A system that is also known as the cardiovascular system, is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
It includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
It helps maintain homeostasis and supports the functioning of other organ systems.
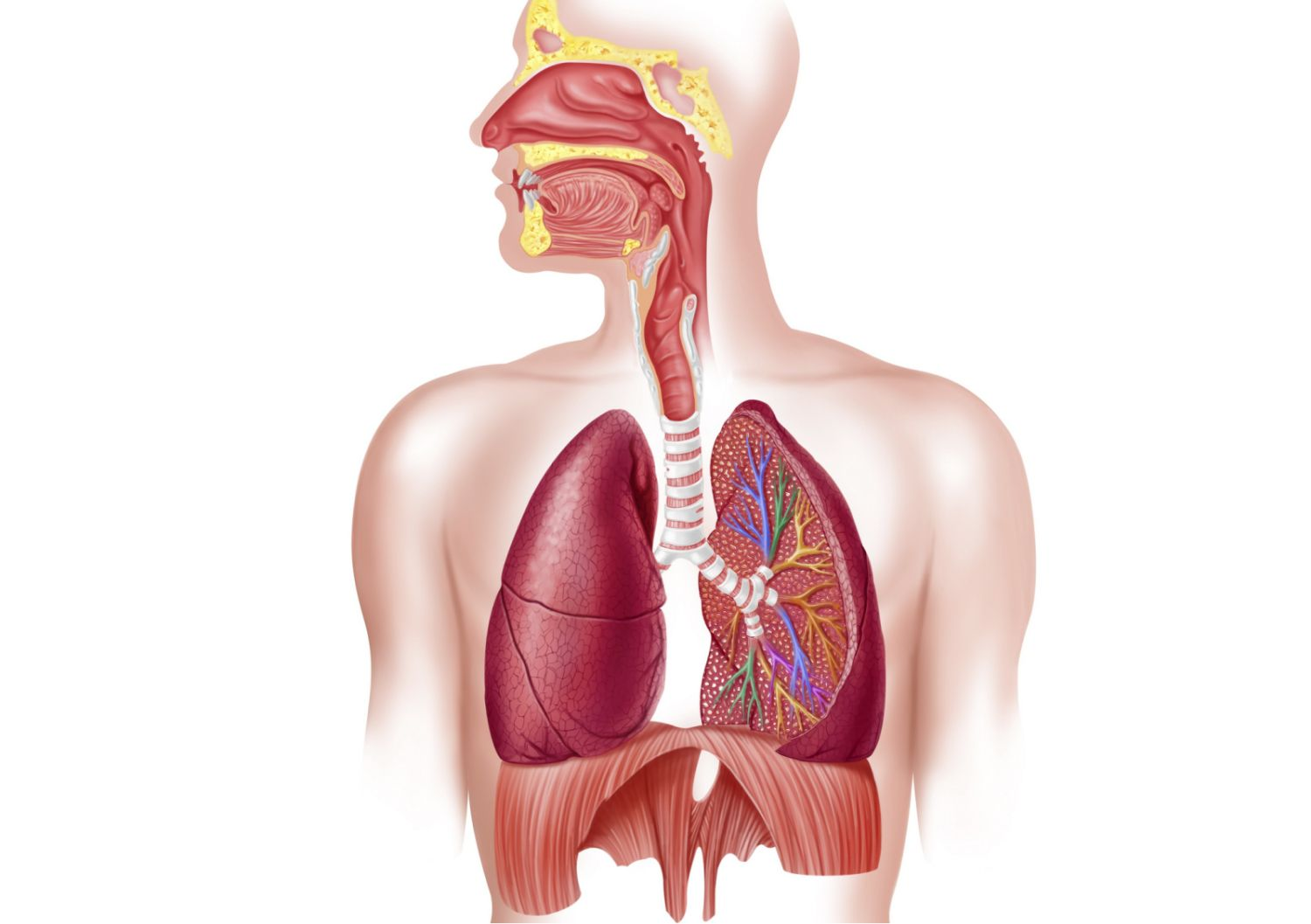
Respiratory System
A system that is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and the environment.
It includes organs such as the nose, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
It allows for the intake of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide, supporting cellular respiration.
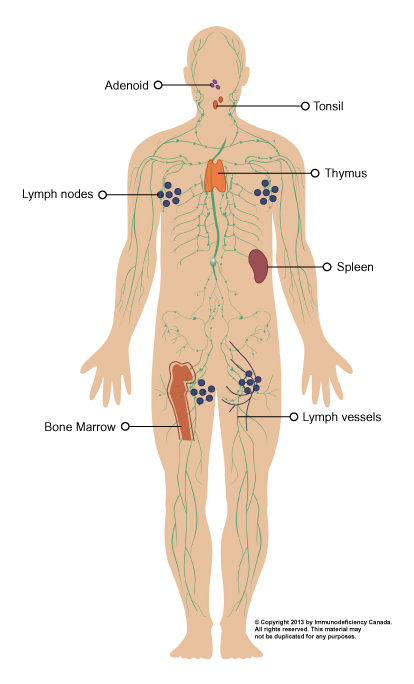
Immune System
A system that is responsible for defending the body against pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. It protects us from infectious diseases.
It includes organs such as the thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and spleen, as well as specialized cells and molecules.
Homeostasis
The maintenance of a constant internal state in a changing environment
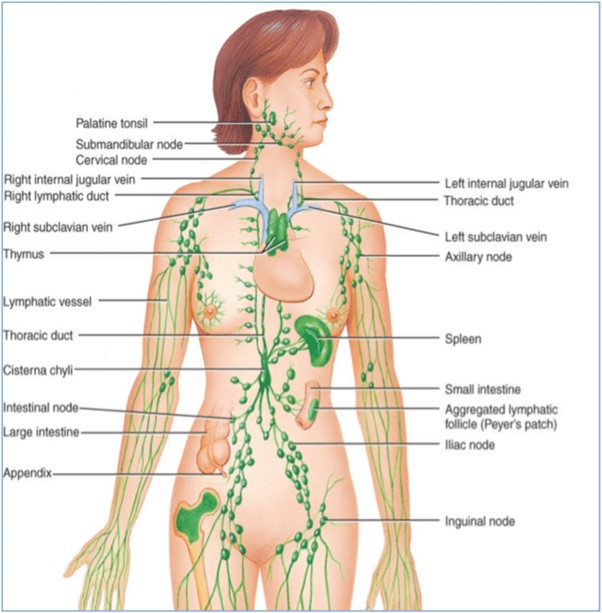
Lymphatic System
A system that is a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that helps maintain fluid balance and defend the body against infections.
It includes lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, the spleen, and the thymus gland.
Endocrine System
A system that is responsible for producing and regulating hormones, which are chemical messengers.
It includes glands such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pancreas.
The endocrine system plays a crucial role in growth, metabolism, reproduction, and response to stress.
Reproductive System
A system that is responsible for the production of offspring.
It includes organs such as the testes in males and ovaries in females.
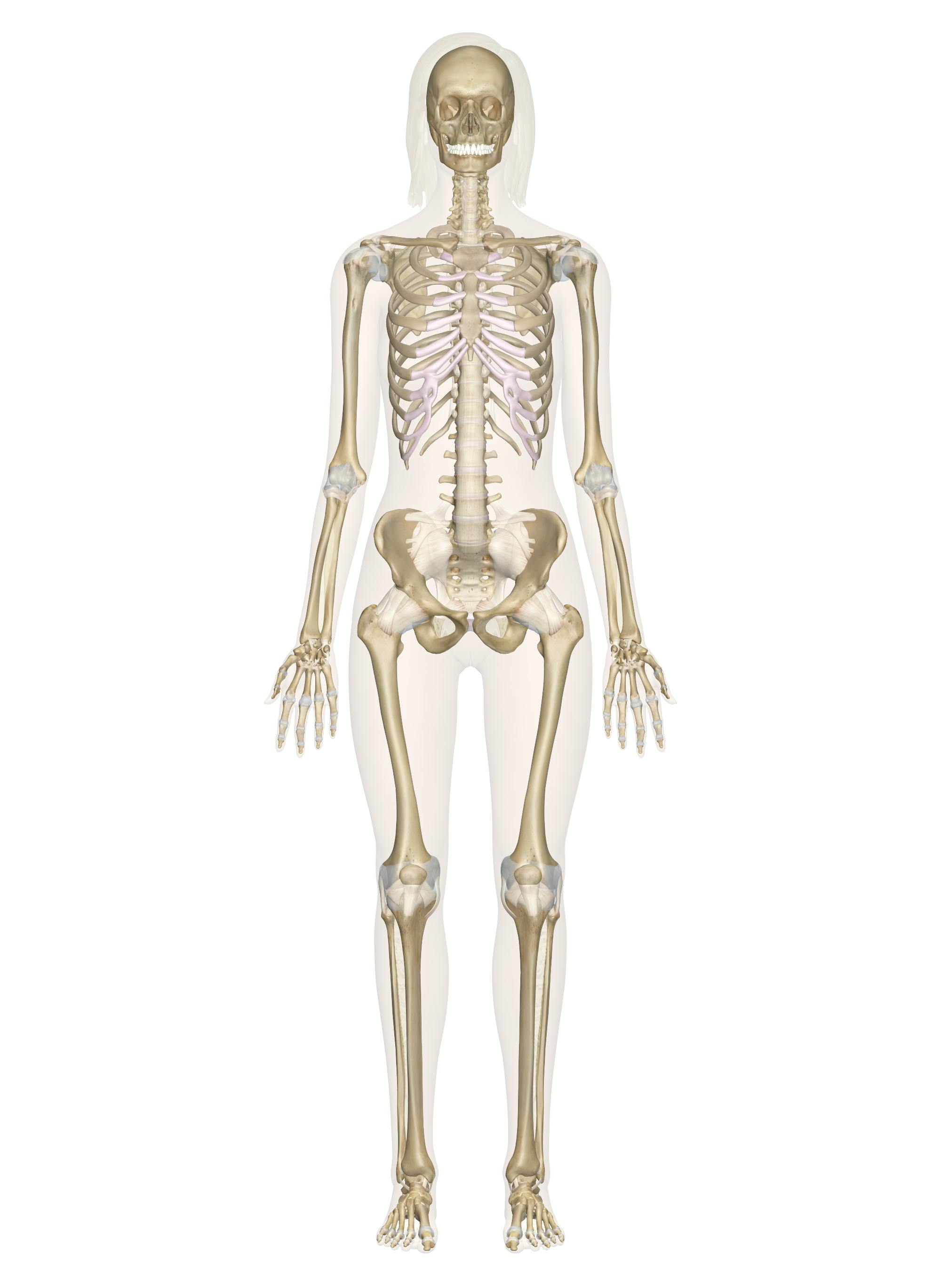
Skeletal System
A system that is responsible for providing support, protection, and movement for the body.
It is made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
The skeletal system also produces blood cells and stores minerals such as calcium and phosphorus.
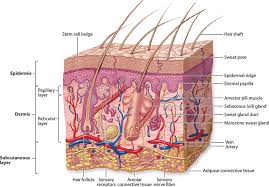
Integumentary Sytem
A system that includes the skin, hair, and nails.
It provides protection against external threats, regulates body temperature, and helps with the excretion of waste products.
The skin also contains sensory receptors that allow us to sense touch, pressure, and temperature.
Cell
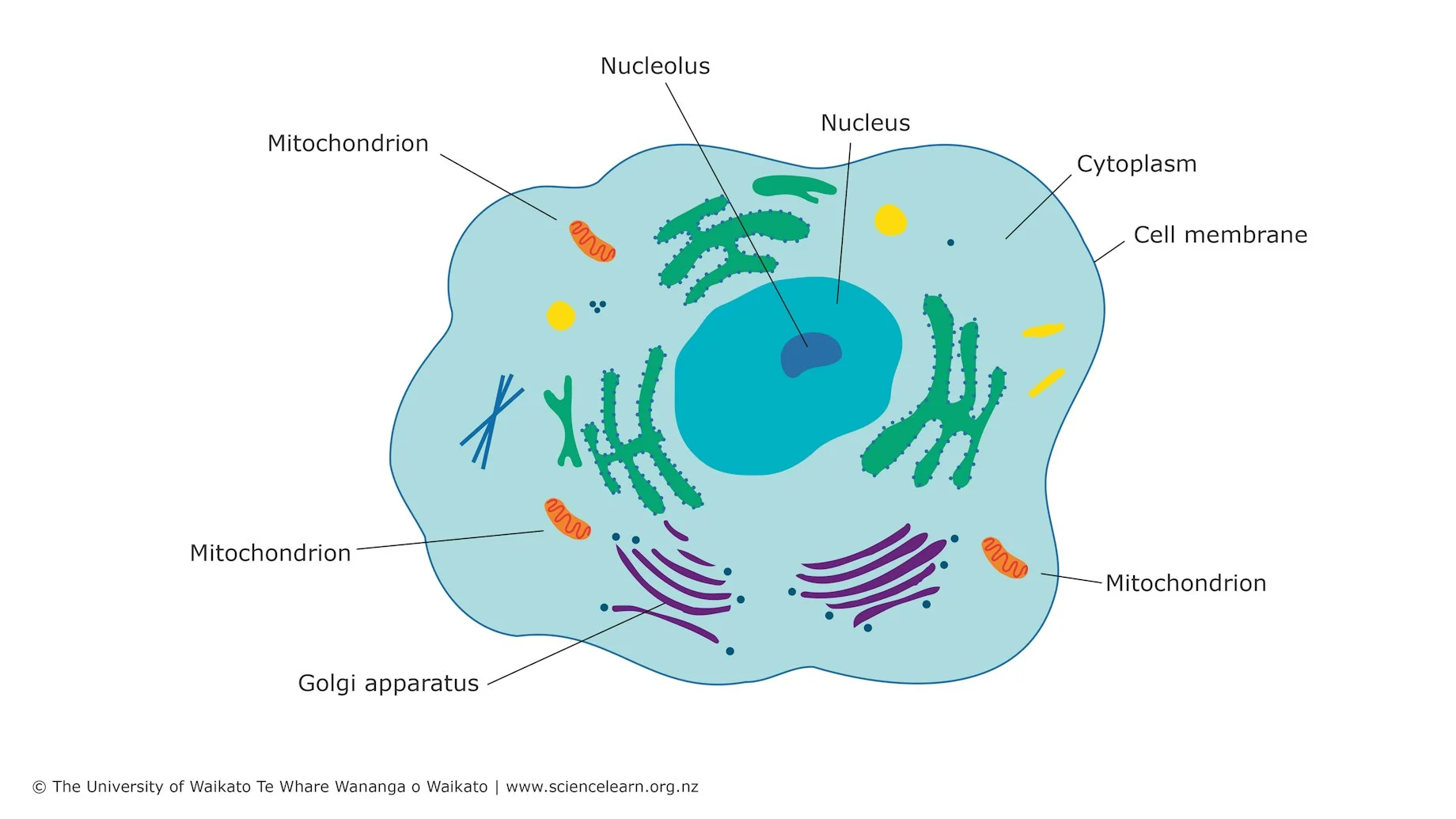
Tissue
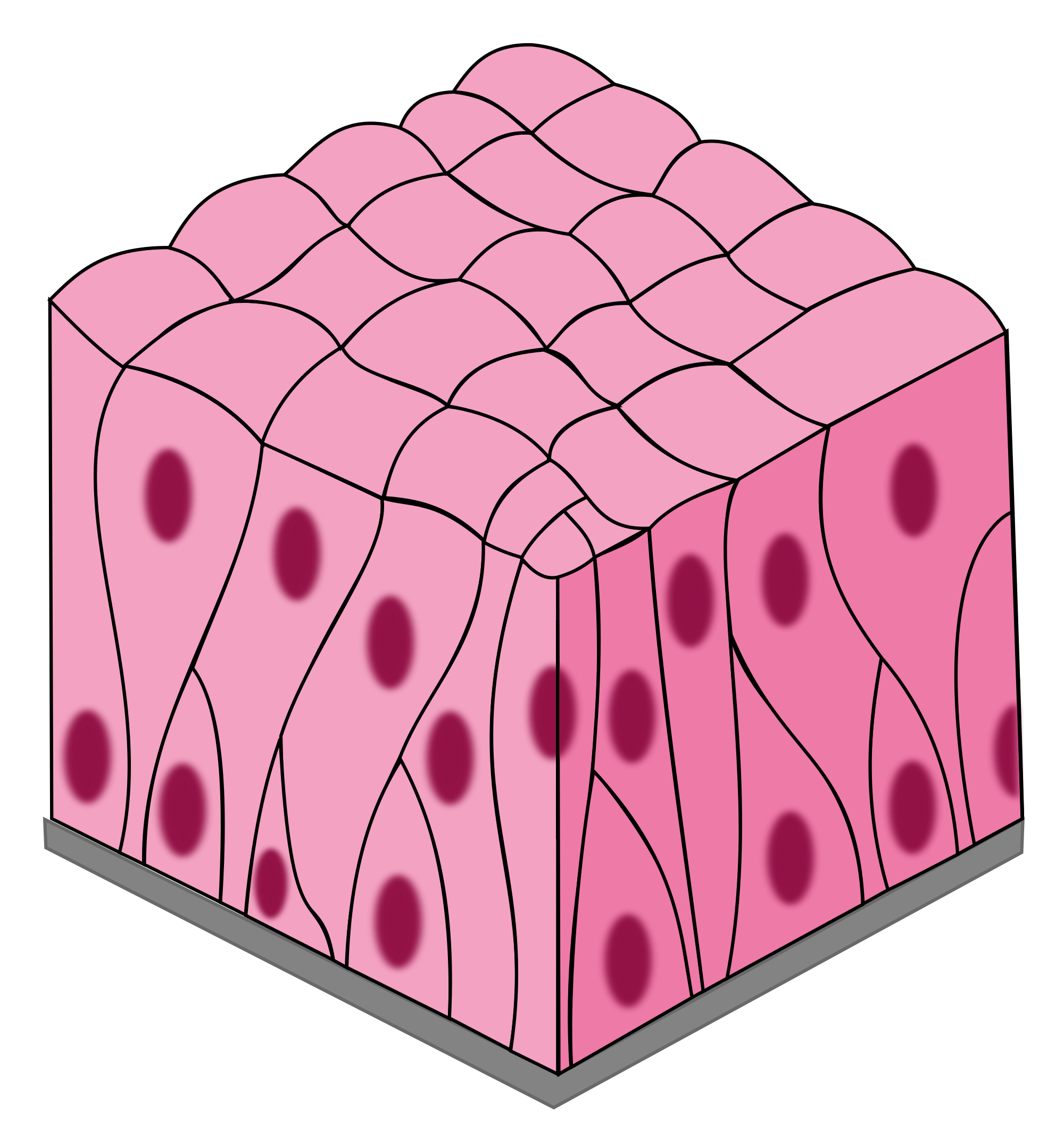
Organ
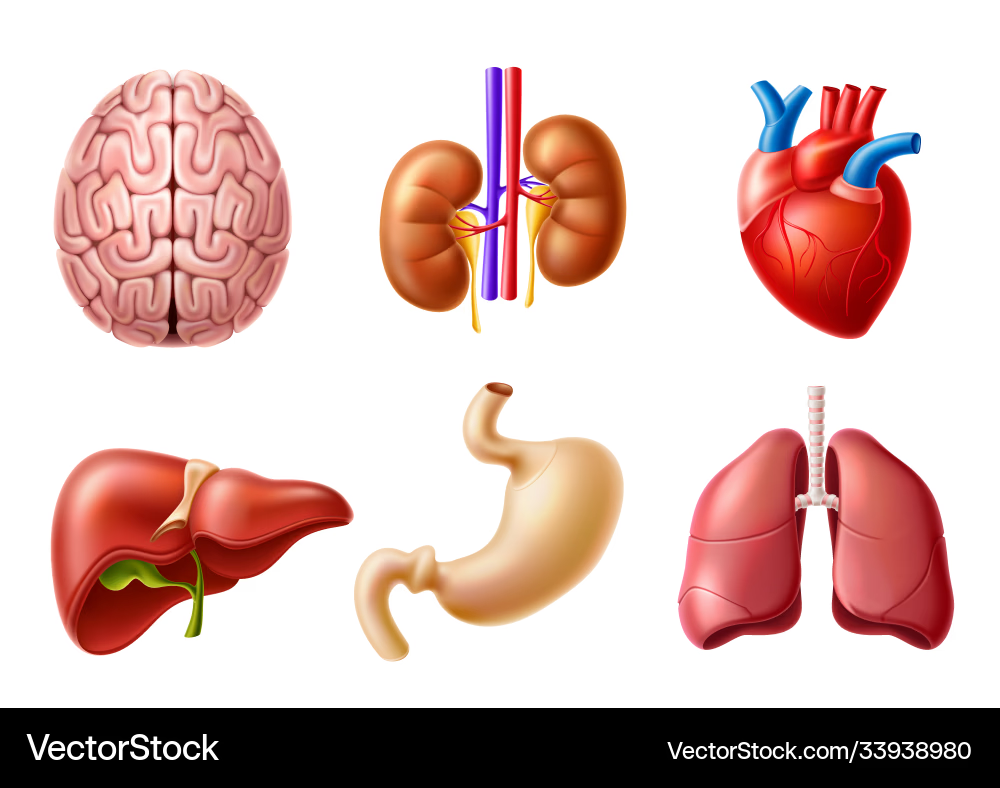
Organ System
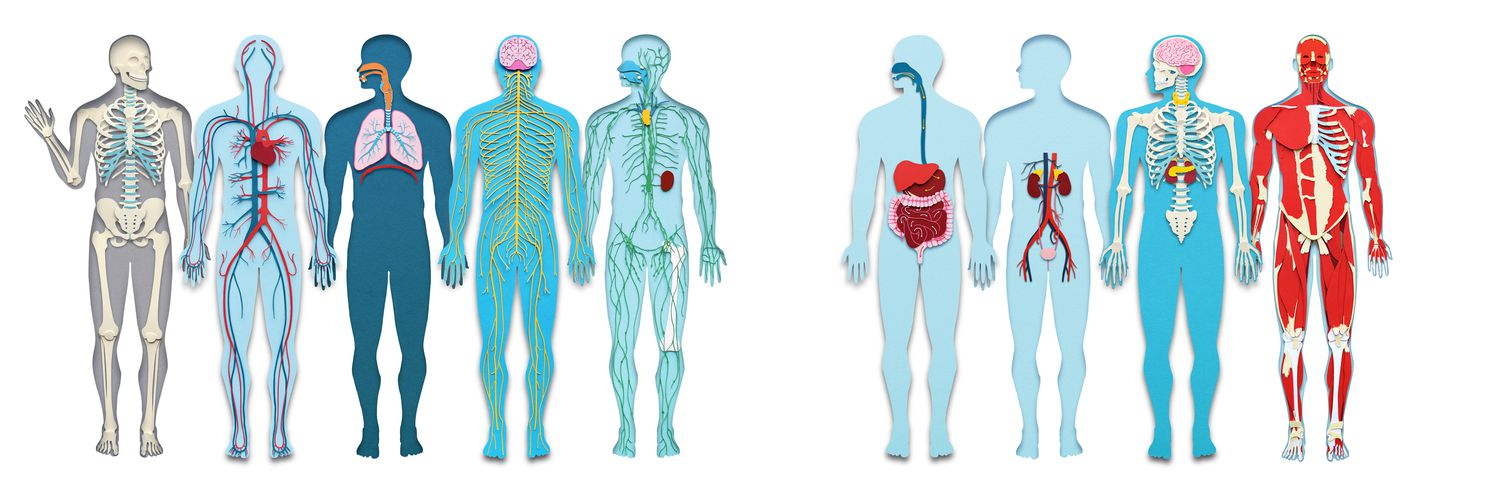
Organism

Digestive System
Nervous System
Muscular System
Excretory System
Circulatory System
Respiratory System
Immune System
Homeostasis

Lymphatic System
Endocrine System
Skeletal System
Integumentary System
What is the order of organization from smallest to largest?
Cell → Tissue → Organ → Organ System → Organism