Evidence based veterinary medicine
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is evidence based medicine
The process of systematically reviewing, appraising and using clinical research findings to aid the delivery of optimum clinical care to patients
How should EBM be approached
Ask a specific question
Search for the best information
Critically appraise information
Apply it to a clinical situation
Review and update as required
What specific questions should be asked
Define patient and condition
define drug and procedure
Active control or placebo
Define clinical response
Where should you search for the best information
Anecdote or expert opinion
Textbooks
Continuing professional development
Journals
Databases
Internet and news media
What should you critically appraise evidence on
Amount and depth of evidence
Quality of evidence
Balance of evidence
What is the hierarchy of evidence
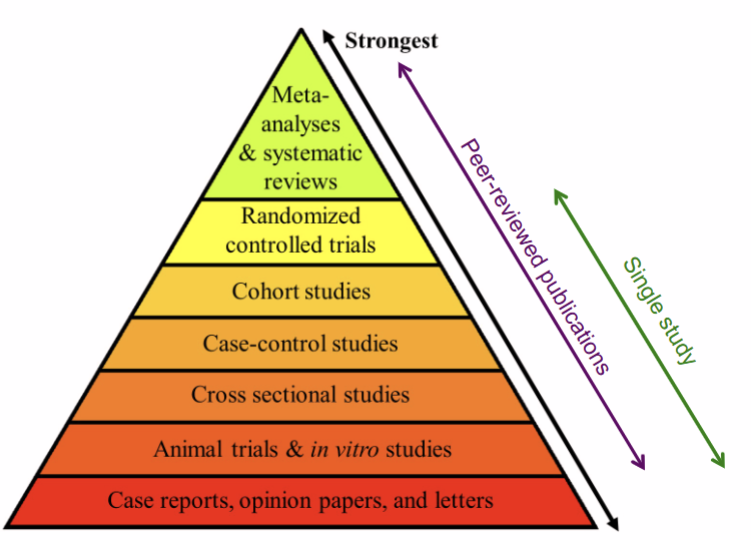
What are the features of a case control study
Compare cases with a group of controls
Usually retrospective
Not blinded or randomised
What are the features of a cohort study
Follow cases to see what happens to them
Can assess different treatments
Not blinded or randomised
What are the features of a randomised controlled trial
Compare treatment to a control
Control can be a placebo or another treatment
Always prospective
Randomised and often blinded
Designed to eliminate bias
Why should controls be included
Placebo effect
May be an actual physiological response
The effect can be marked
What are the features of a systematic review
Review of all published research in a field
Critical appraisal
Quality of evidence
What are the features of meta-analysis
A systematic review
Uses stats to integrate results of different studies
What is publication bias
Trials are more likely to be published if they have positive findings
Positive results at 3-4x more likely to be published
Negative results often not published at all
Sponsored trials more likely to be positive