Psy 120 exam 1 self made v2
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
empirical method
gaining knowledge through the OBSERVATION OF EVENTS, the collection of data, and logical reasoning
Wilhelm Wundt
German physiologist who founded psychology as a formal science
Introspection
A method of self-observation in which participants report their thoughts and feelings (Wilhelm Wundt)
Structuralism
reported their conscious sensations and feelings in response to stimuli (Beach) (Wilhelm Wundt)
Titchener's 3 ElementaryStates of Consciousness
sensations, images, and feelings (building blocks of all perceptions)
Functionalism
He emphasized the "function" or purpose of the mind (e.g., consciousness as a continuous stream) rather than its structure, as opposed to structuralism
Psychoanalytic Theory
focus on the role of the unconscious in affecting conscious behavior (Sigmund Freud)
Behaviorism
the science of behavior that focuses on observable behavior only
John Watson and B.F. Skinner
founders of behaviorism
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events (Ivan Pavlov) (Pavlov's Dog)
operant conditioning
Learning based on the consequences of responding. (B.F. Skinner)
Humanism
A perspective that emphasizes looking at the whole person, and the uniqueness of each individual (Abraham Maslow)
Hierarchy of needs
Maslow's theory of the most important motivations people have (pyramid of needs)
Carl Rogers
Developed "client-centered" therapy
WEIRD populations
Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, Democratic
Multicultural psychologists
focuses on understanding the psychological experiences within diverse societies, especially minority groups, emphasizing how race, ethnicity, and culture interact in a single context
cross-cultural psychology
compares psychological traits across different cultures to find universal patterns
Biopsychology
study of how biology influences behavior
Evolutionary Psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
Cognitive Psychology
the scientific study of all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Developmental psychology
the study of continuity and change across the life span
Personality Psychology
the study of an individual's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting
Social Psychology
the study of the causes and consequences of sociality
Industrial-Organizational Psychology
the application of psychological concepts and methods to optimizing human behavior in workplaces
Clinical and Counseling Psychology
diagnose and treat people with psychological problems
Careers in Psychology
-academic(34%)
-clinical(24%)
-private practice(22%)
difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist
Psychiatrists = medication
psychologists = behavioral intervention
4 occupations for graduates with a bachelor's degree in psychology
- Mid and Top - Level Management (executive,administrator) - Sales
- Social Work
- Human resources (personnel, training)
Deductive vs. Inductive Reasoning
Deductive: general to specific
Inductive: specific to general
How are hypotheses related to theories?
Theories are used to form hypotheses.
cross-sectional study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another
longitudinal study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
correlational study
a research project designed to discover the degree to which two variables are related to each other
illusory correlation
the perception of a relationship where none exists (ice cream to robberies)
confounding variable
in an experiment, a factor other than the independent variable that might produce an effect
experimenter bias
researcher expectations skew the results of the study
quasi-experimental
an experimental design that lacks random assignment
Reliability vs. Validity
reliability (consistency) and validity (accuracy)
IRB (Institutional Review Board)
any academic research needs to be proposed to their IRB, review for ethical violations and/or procedural errors
4 components of informed consent
disclosure, comprehension, competency, and voluntariness
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
Alleles
alternative versions of a gene
Dominant vs. Recessive Alleles
Dominant: will always display in offspring- even heterozygous
Recessive: only displayed when homozygous recessive
single gene inheritance
Characteristics or traits inherited by the participation of a single gene
Polygenic inheritance
occurs when multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
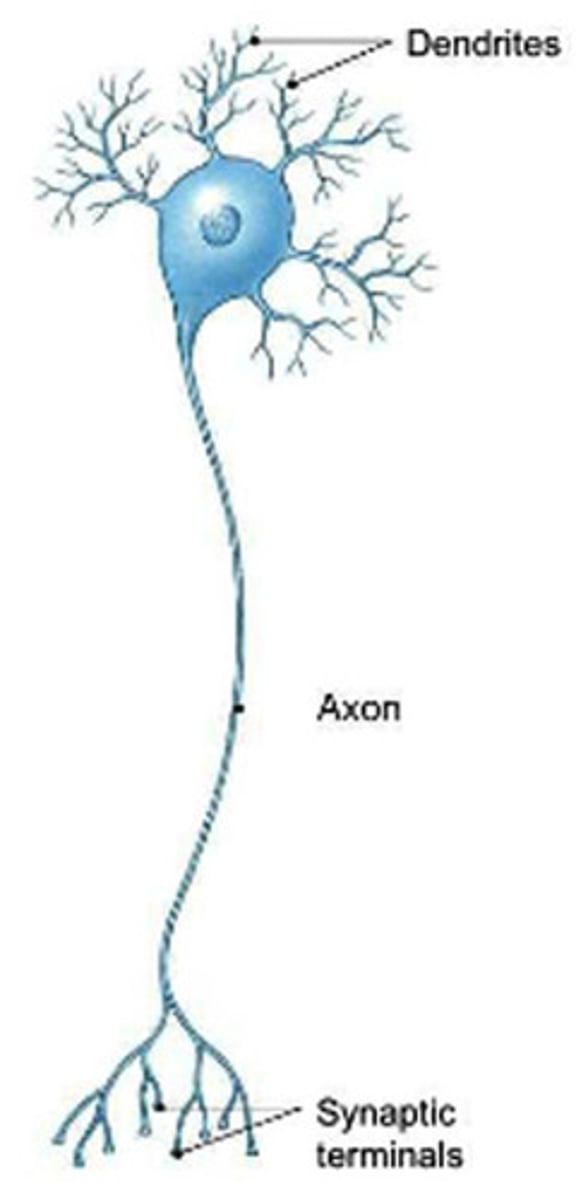
Soma
cell body of a neuron
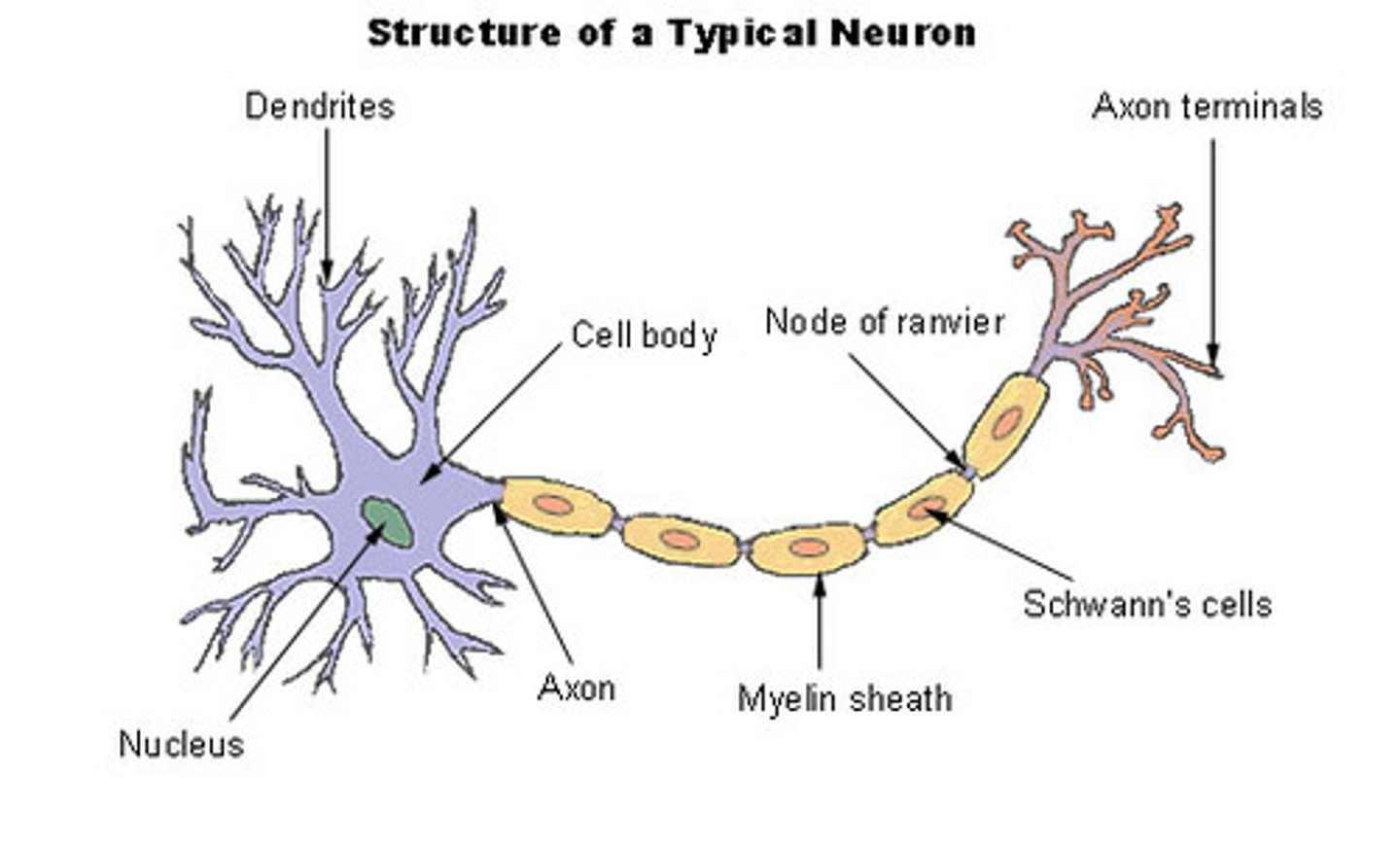
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
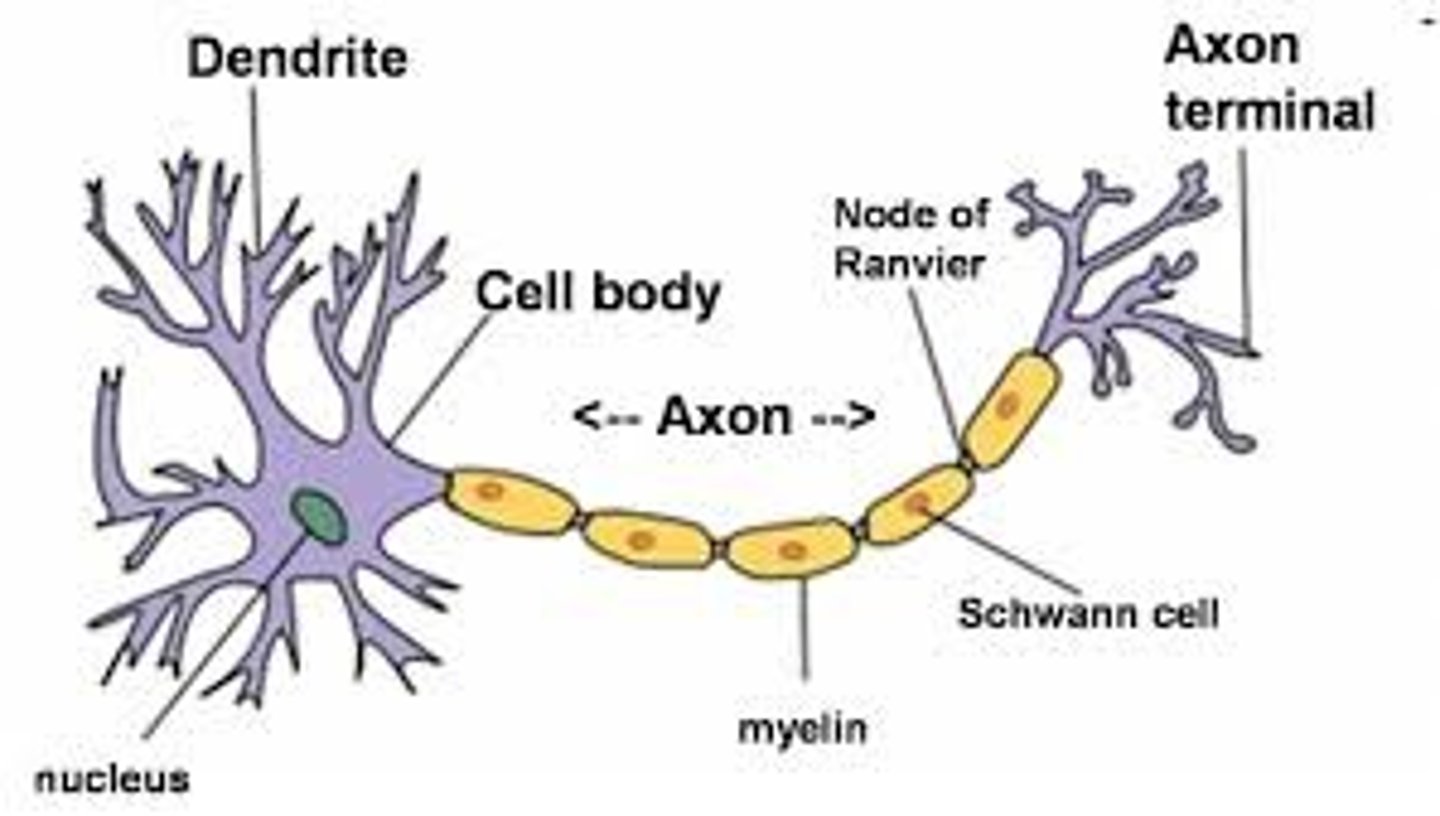
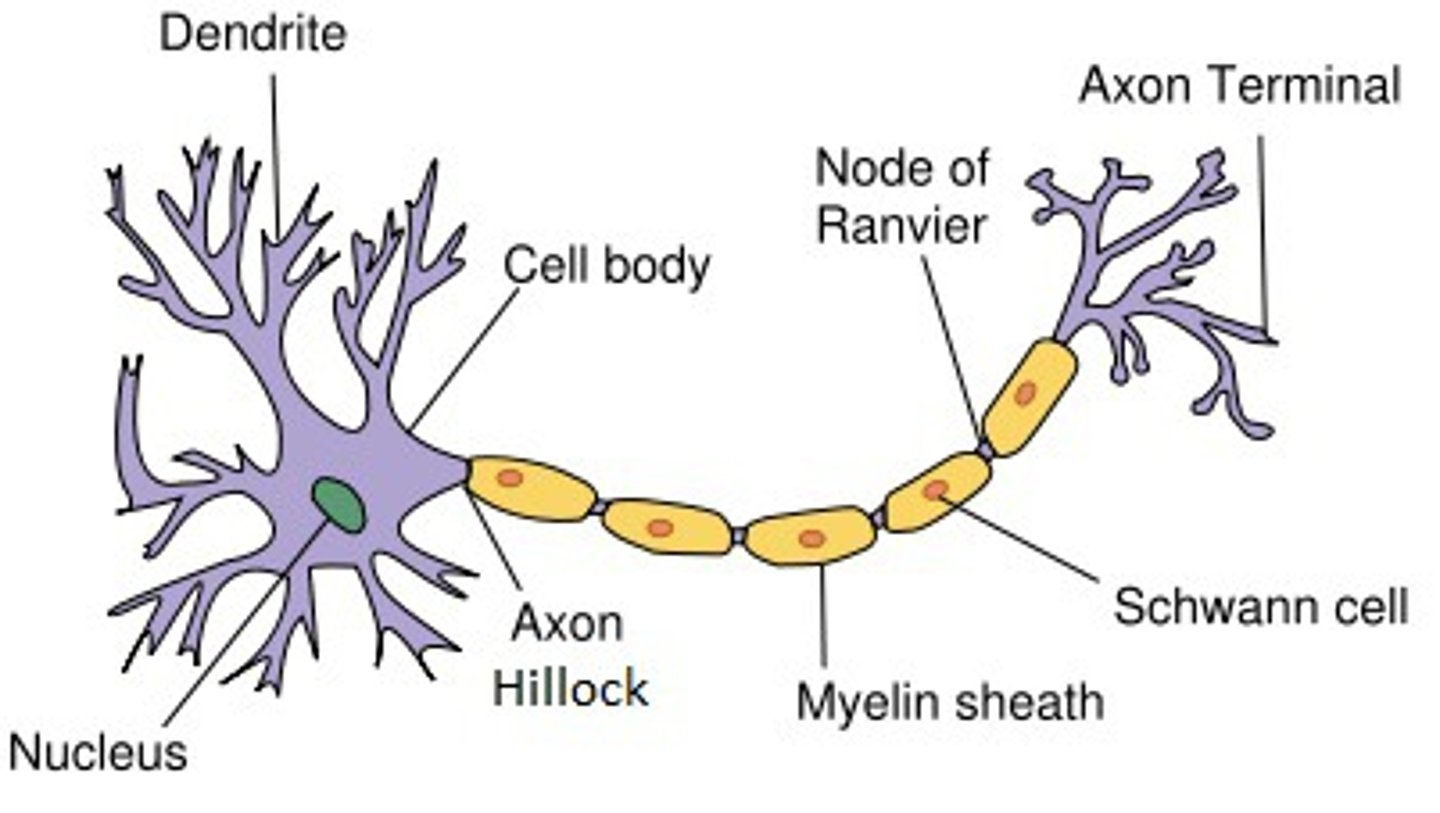
Axon
the neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
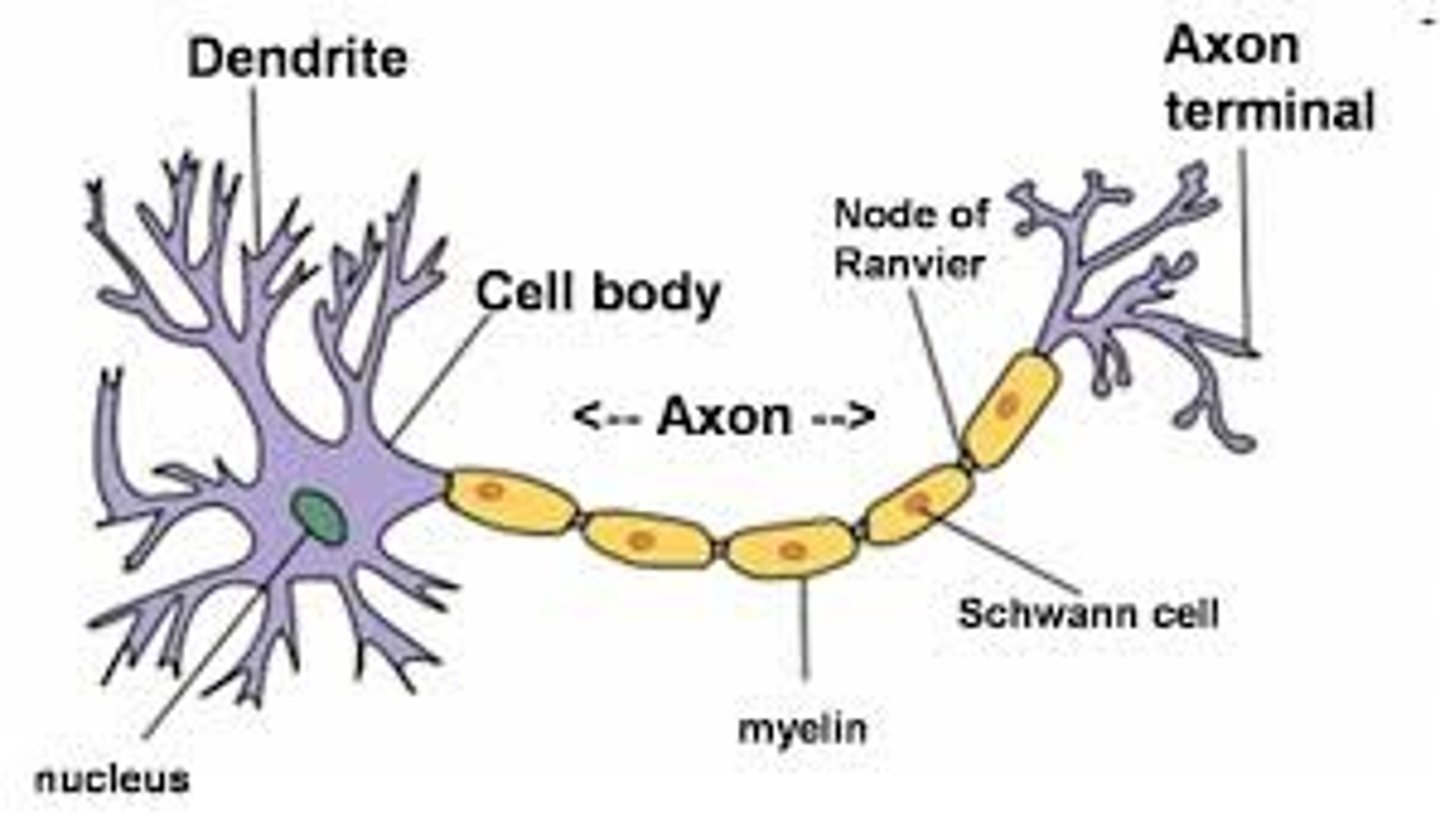
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
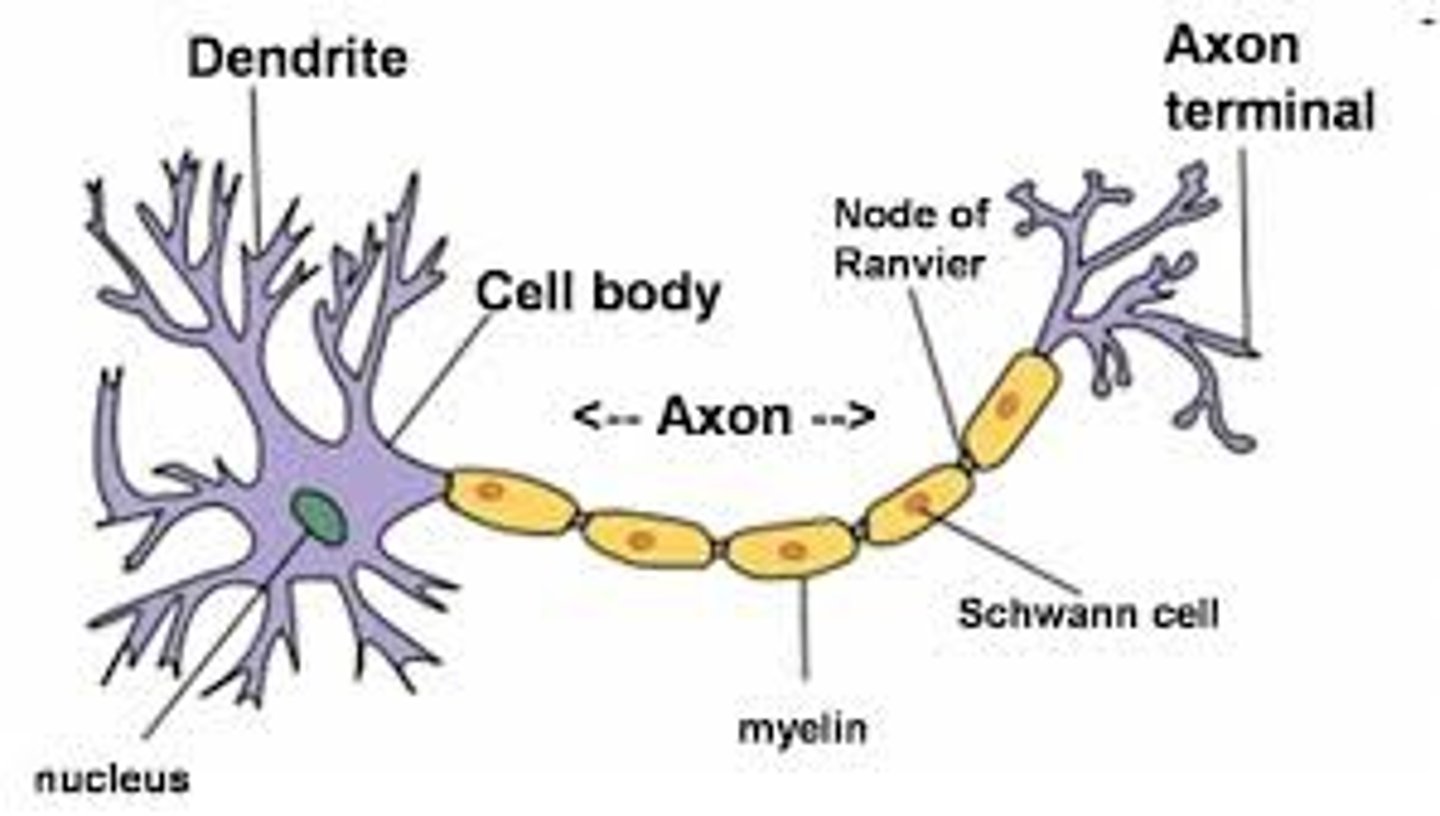
terminal buttons
Small knobs at the end of axons that secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
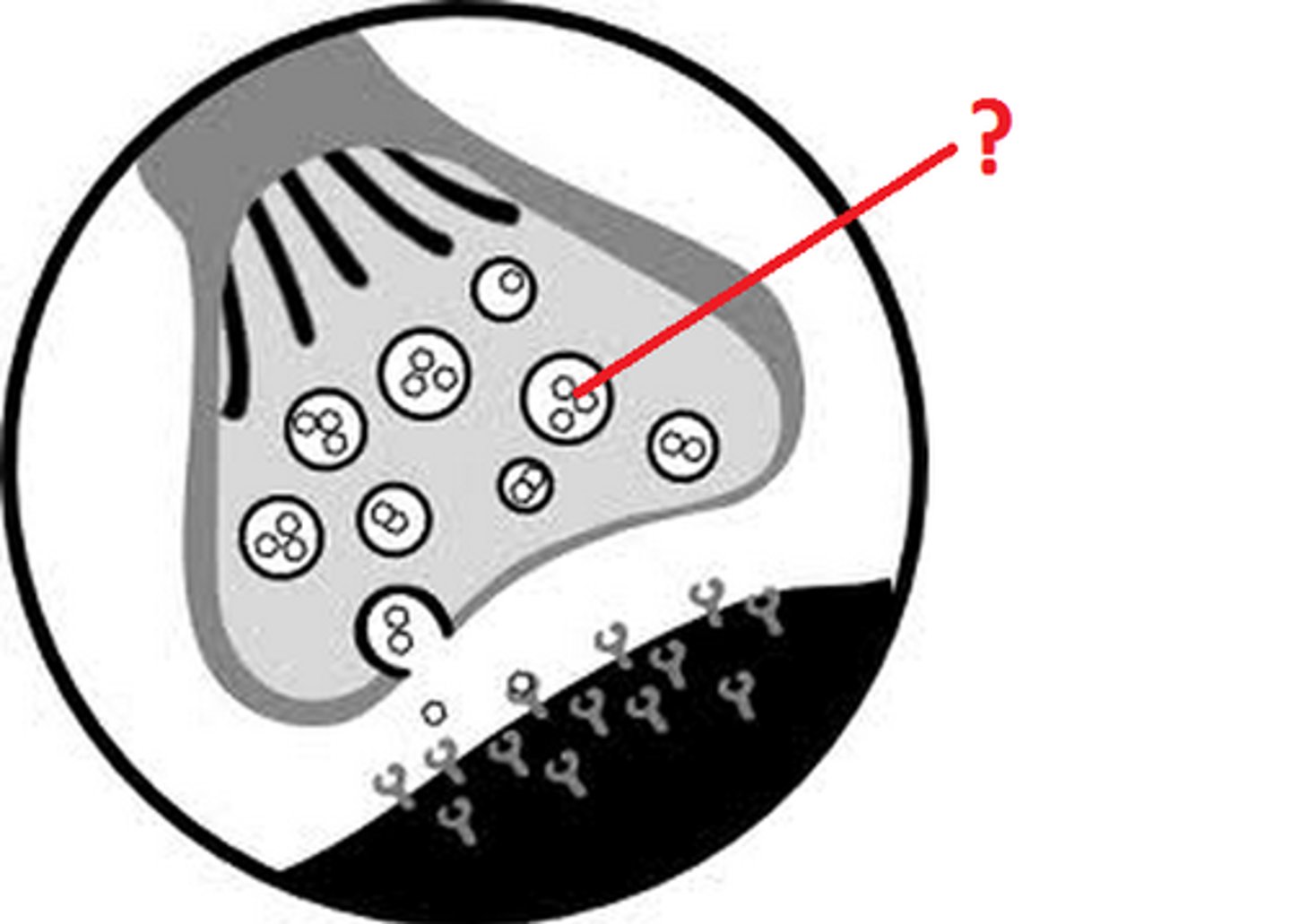
synaptic vesicles
Tiny pouches or sacs in the axon terminals that contain chemicals called neurotransmitters.
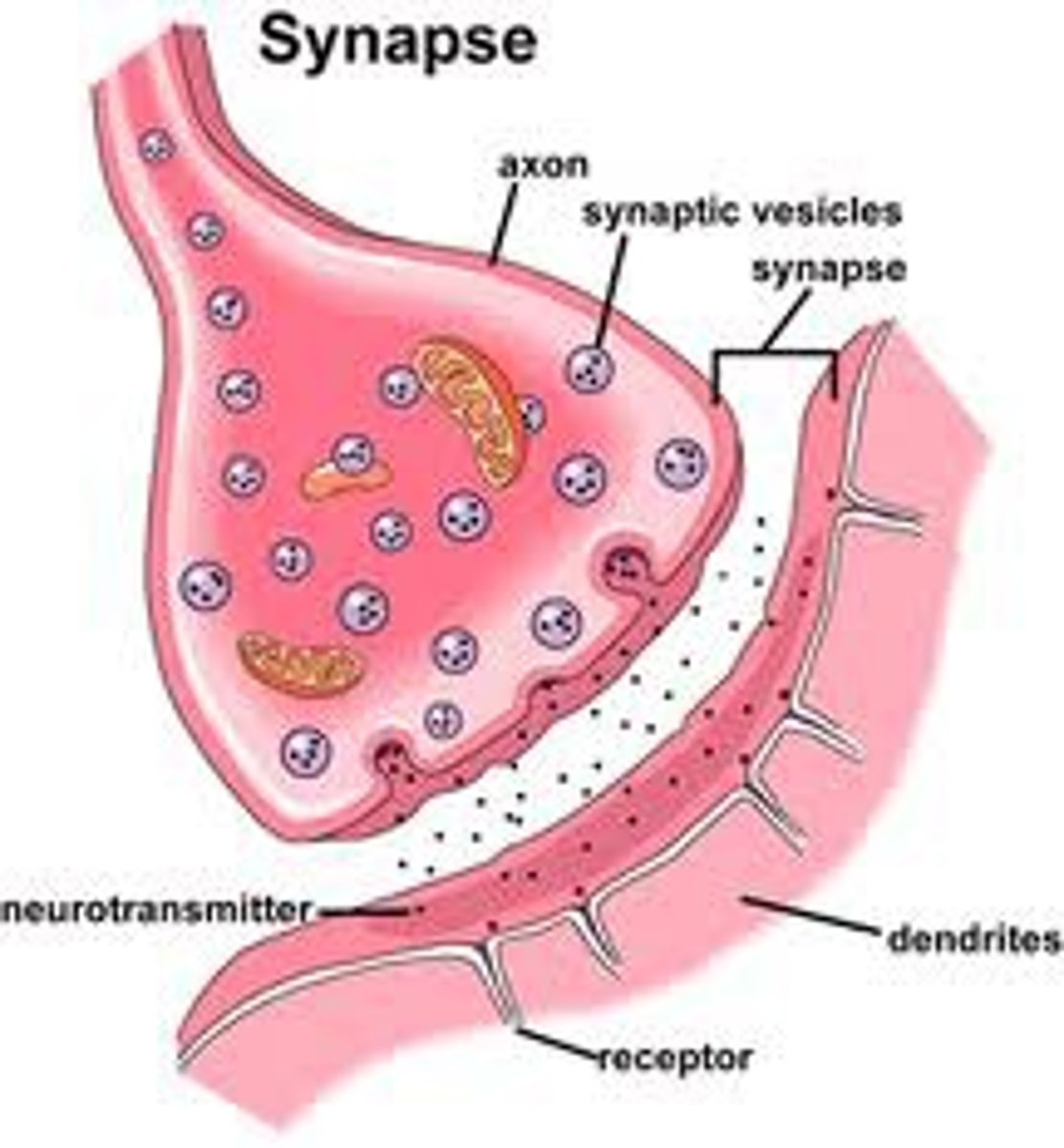
Synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
Threshold of Excitation
the level an impulse must exceed to cause a neuron to fire
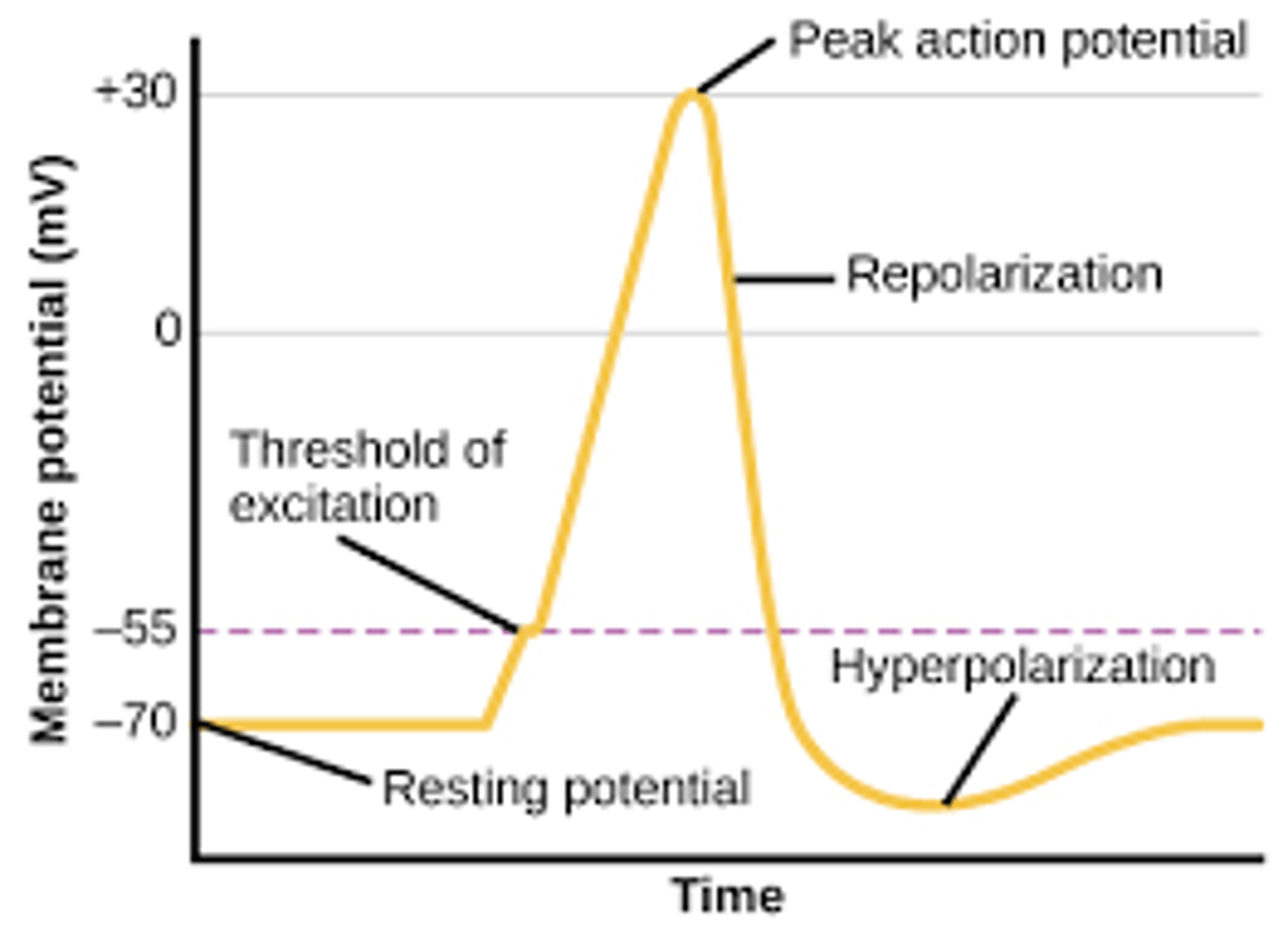
Action Potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
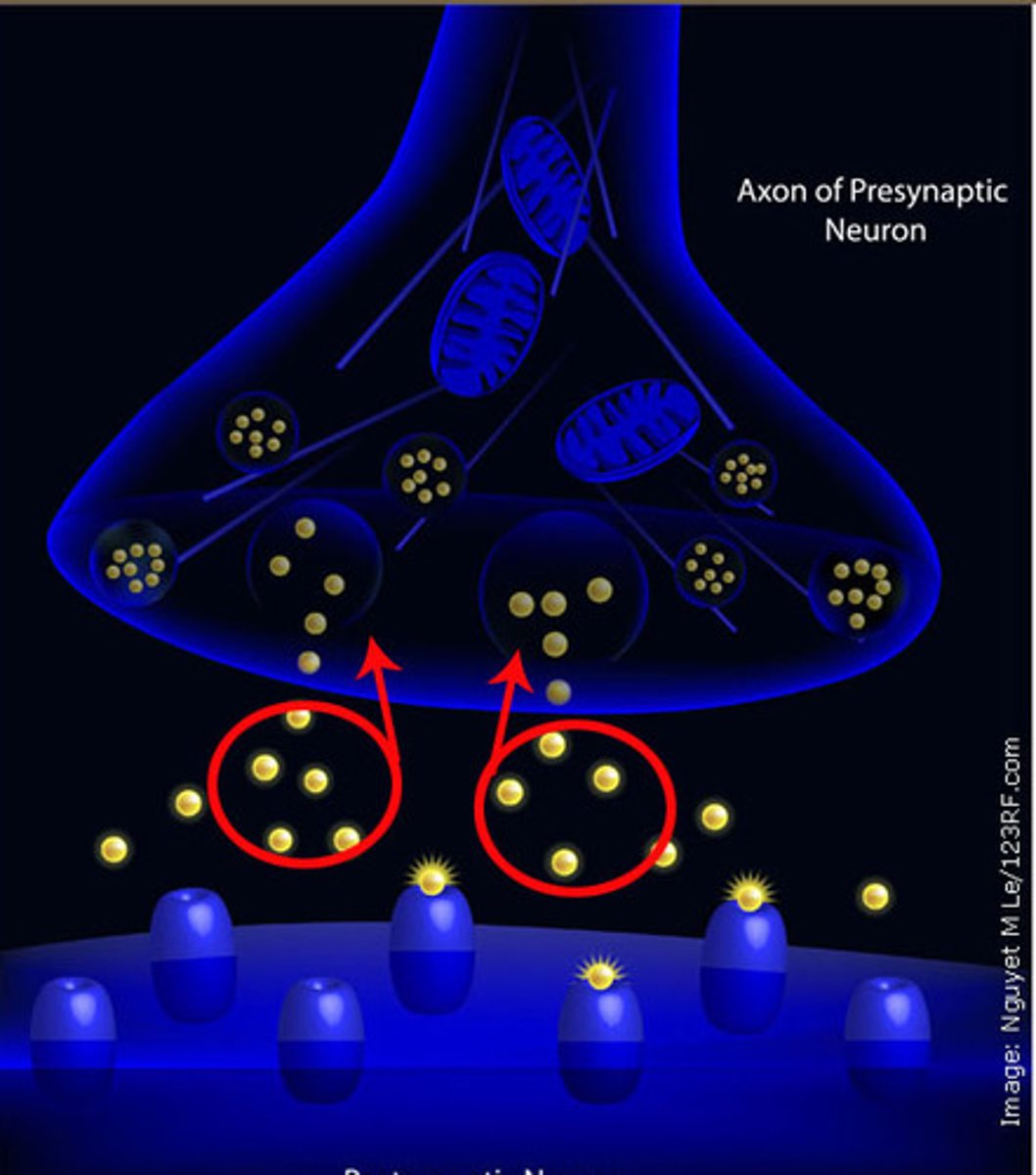
Major neurotransmitters
Acetlycholine, GABA, Dopamine, Nitric oxide
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter (blocking signals and slowing brain activity)
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system.
Norepinephrine
A neurotransmitter involved in arousal, as well as in learning and mood regulation
Agonists vs. Antagonists
Agonists enhance the activity of neurotransmitters
Antagonists inhibit the activity of neurotransmitters
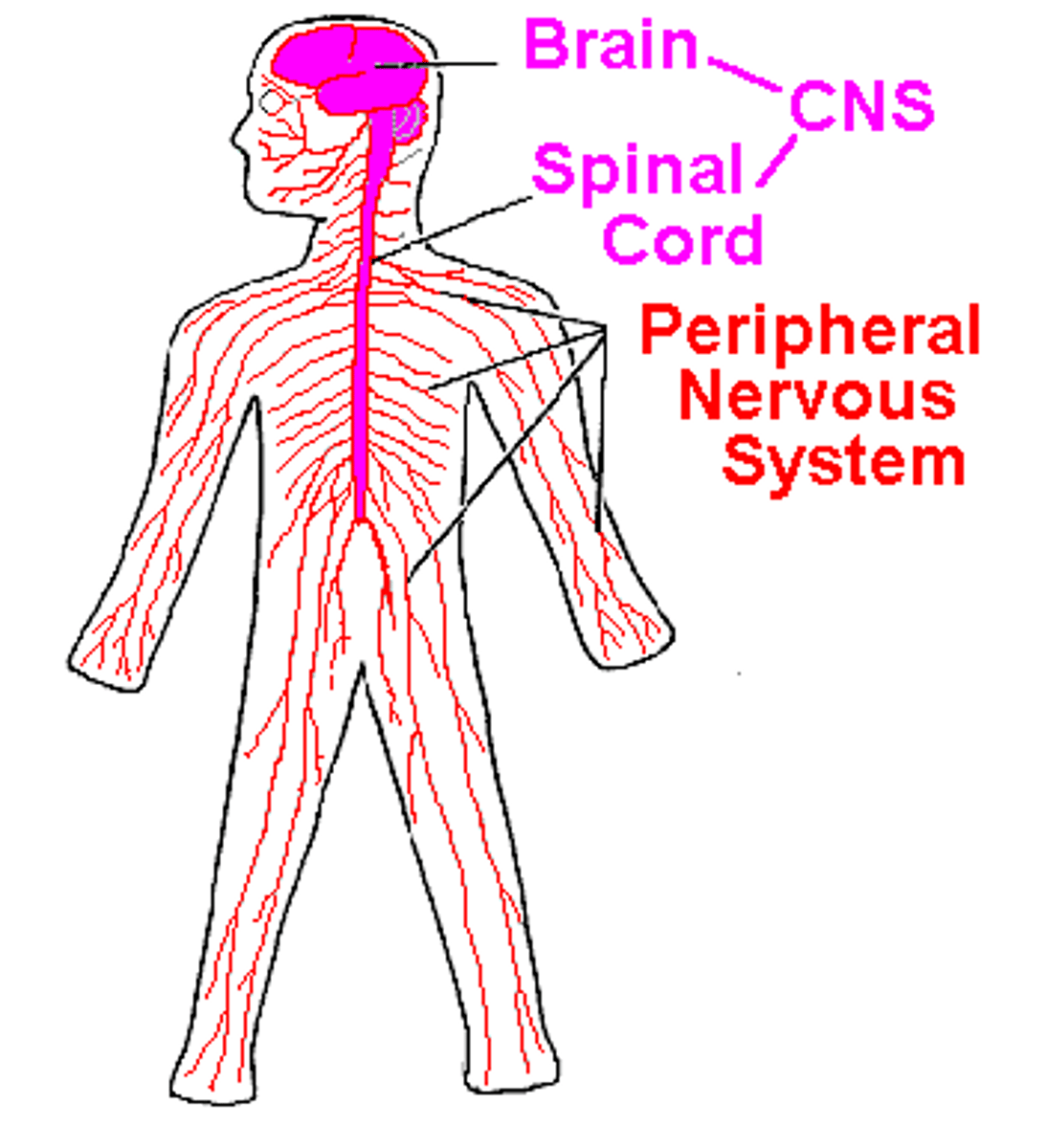
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
A division of the nervous system consisting of all nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord.
somatic nervous system
Division of the PNS that controls the body's skeletal muscles.
autonomic nervous system controls
involuntary functions of the internal organs
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
left hemisphere of brain
controls right side of the body and is logical, contains mathamatics, lauguage, & speech
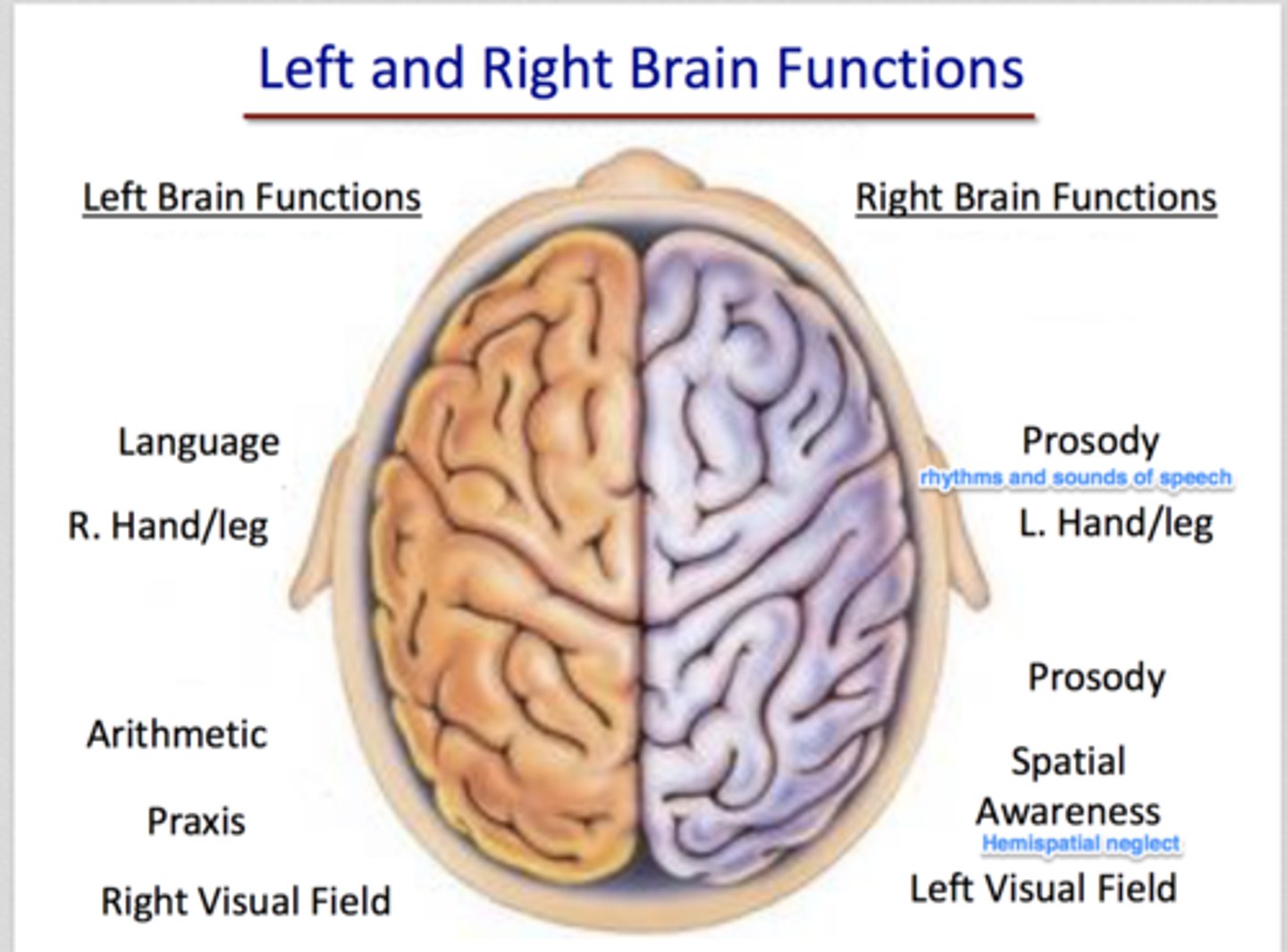
right hemisphere of brain
controls left side of the body and contains creativity and the arts
Corpus Callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
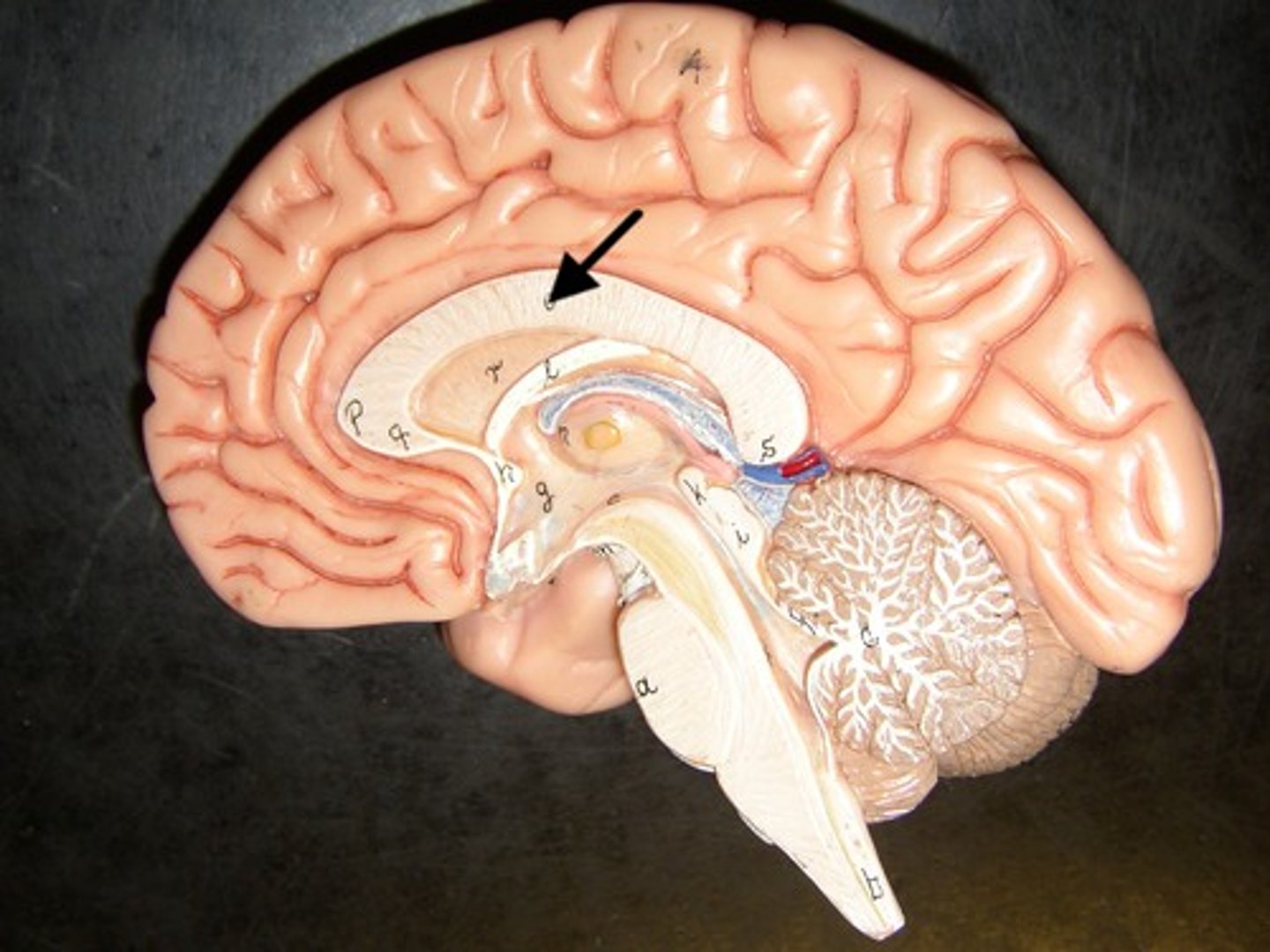
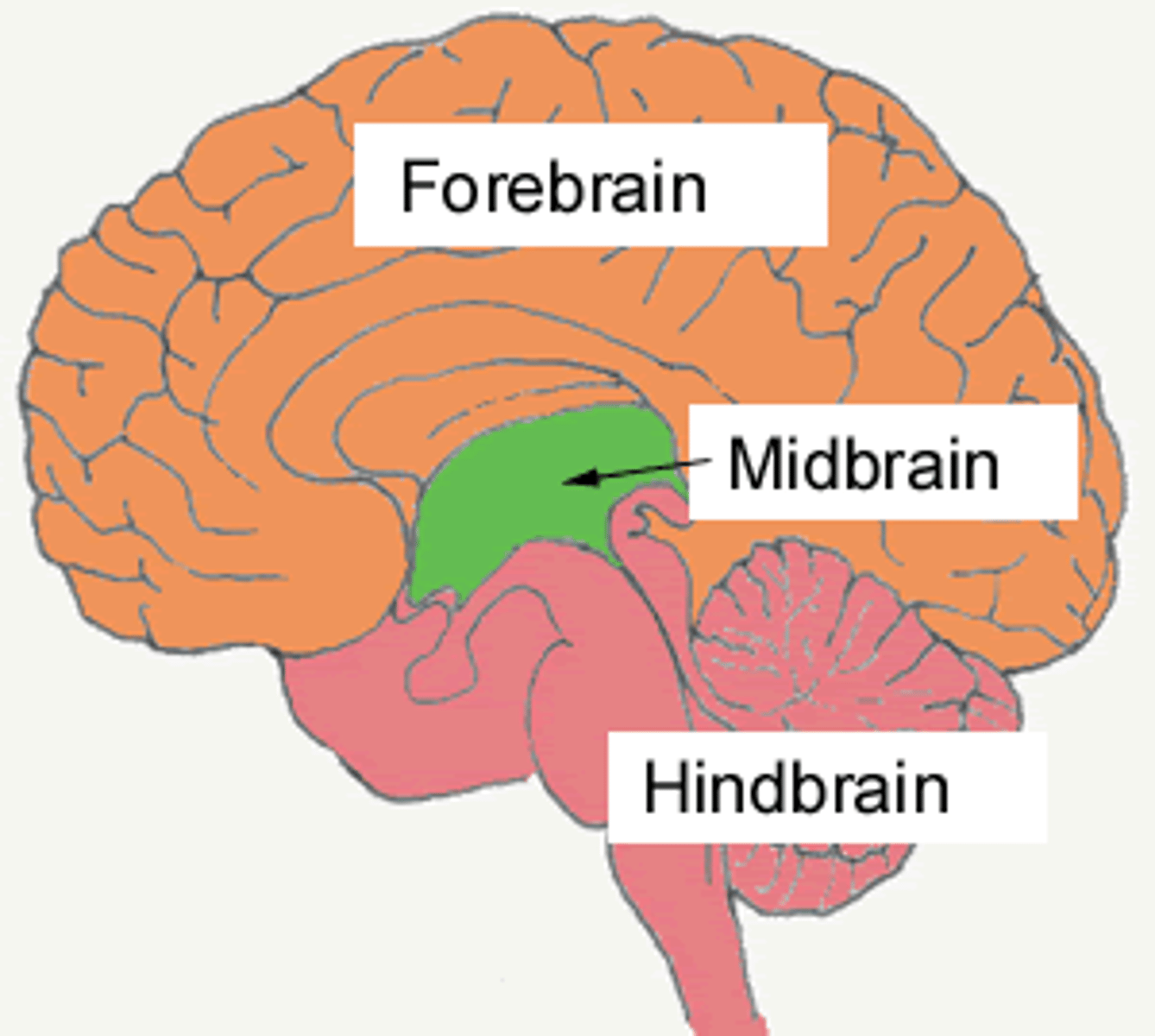
forebrain (cerebrum)
forward part of the brain that allows advanced intellectual abilities
cerebral cortex
Outer layer "grey matter" "wrinkled" and does higher level processes
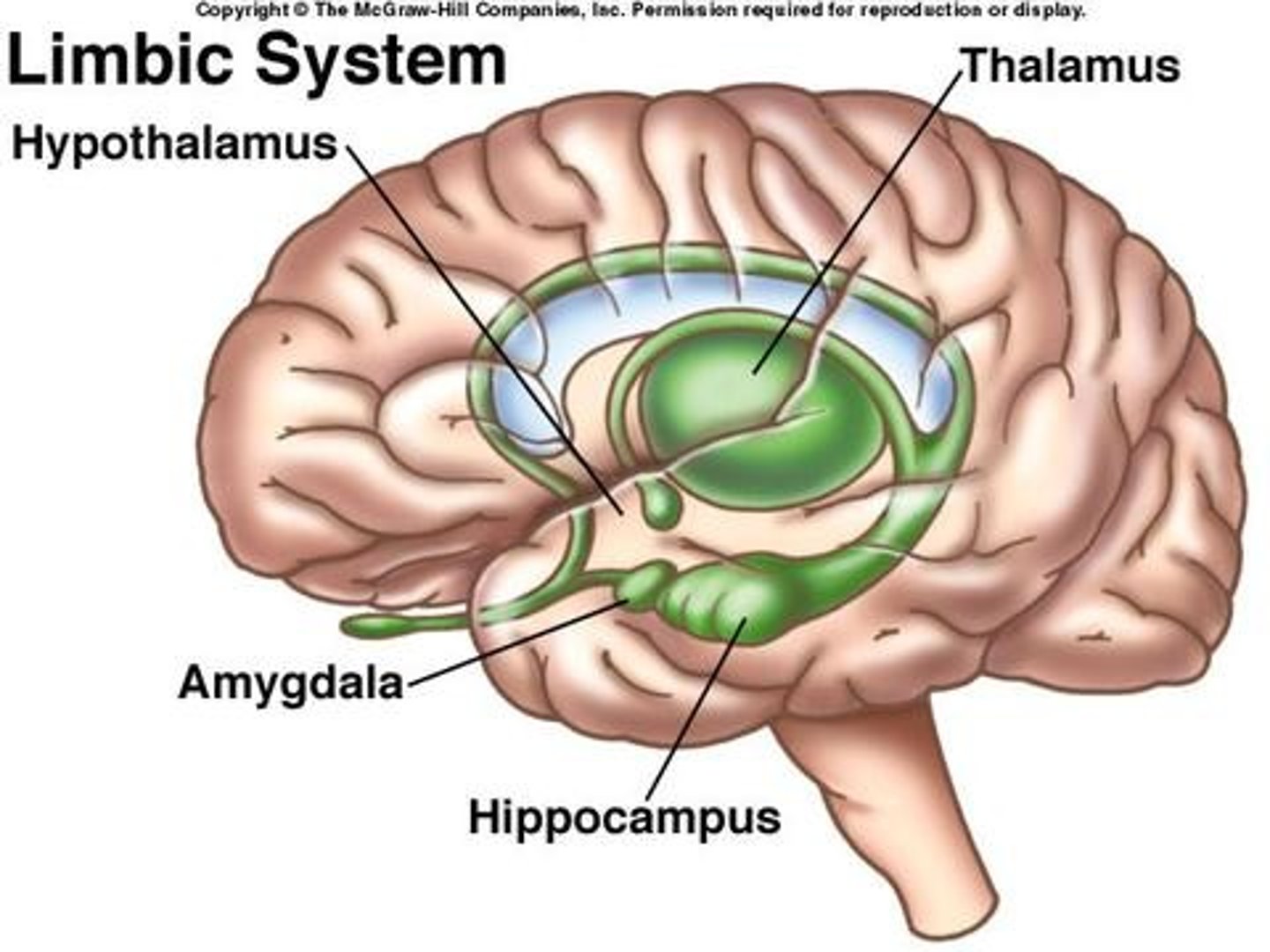
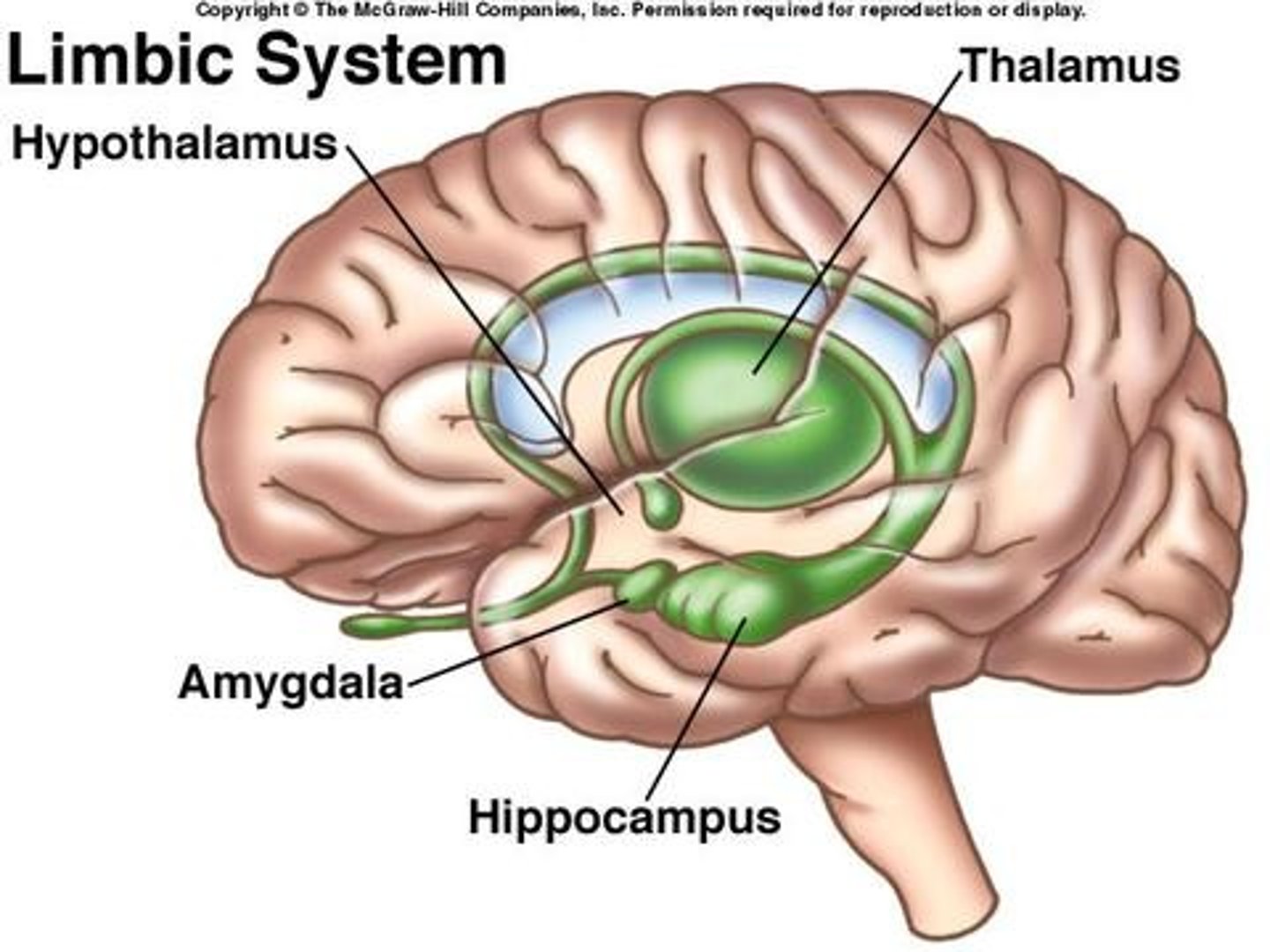
Thalamus
sensory relay controls most senses (excluding smell)
Hypothalamus
links the nervous system and endocrine system by controlling the pituitary gland
Also
regulates homeostatic processes including body temperature, appetite and blood pressure (sleep too)
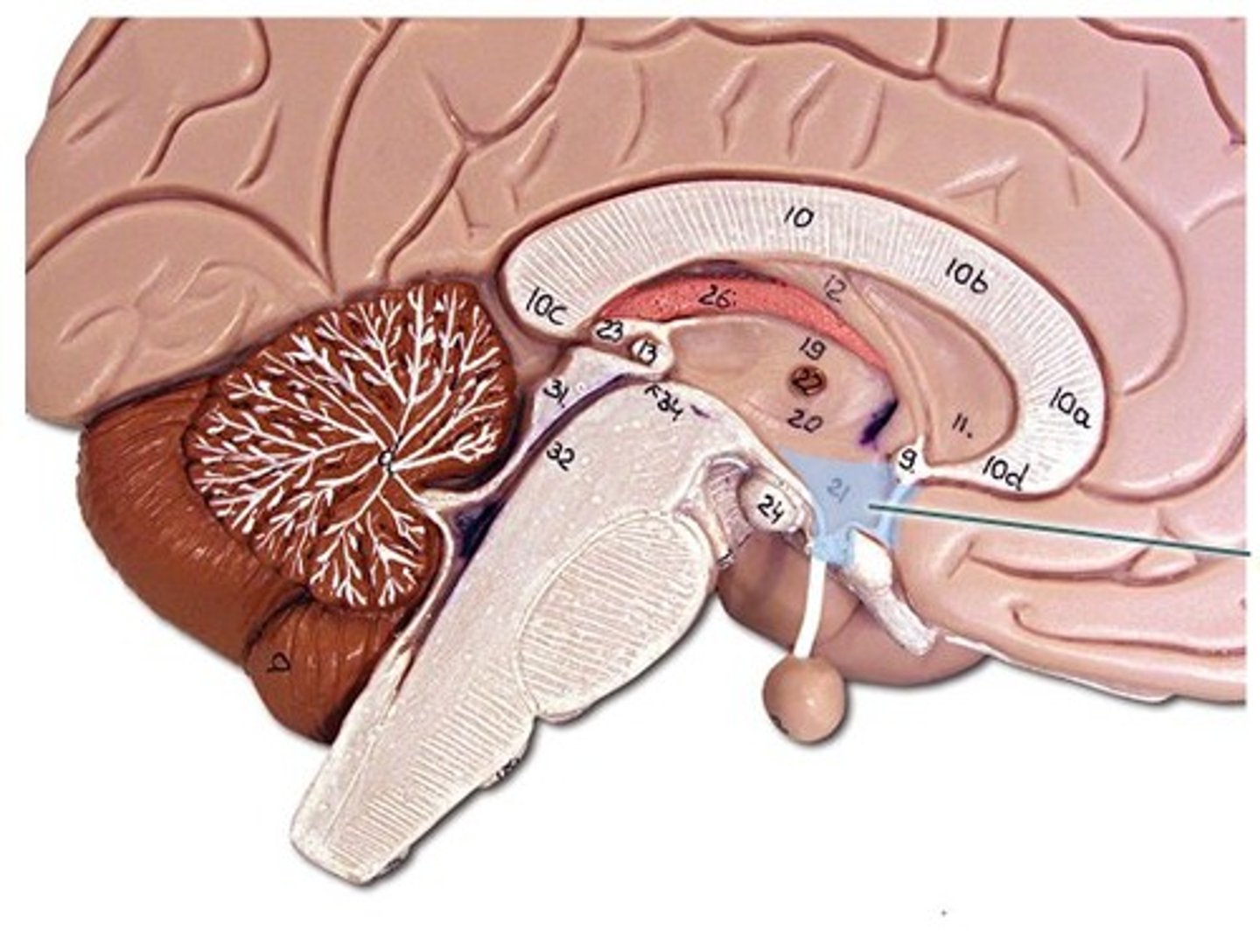
pituitary gland
serves as the master gland,controlling the secretions of all other glands (sleep too)
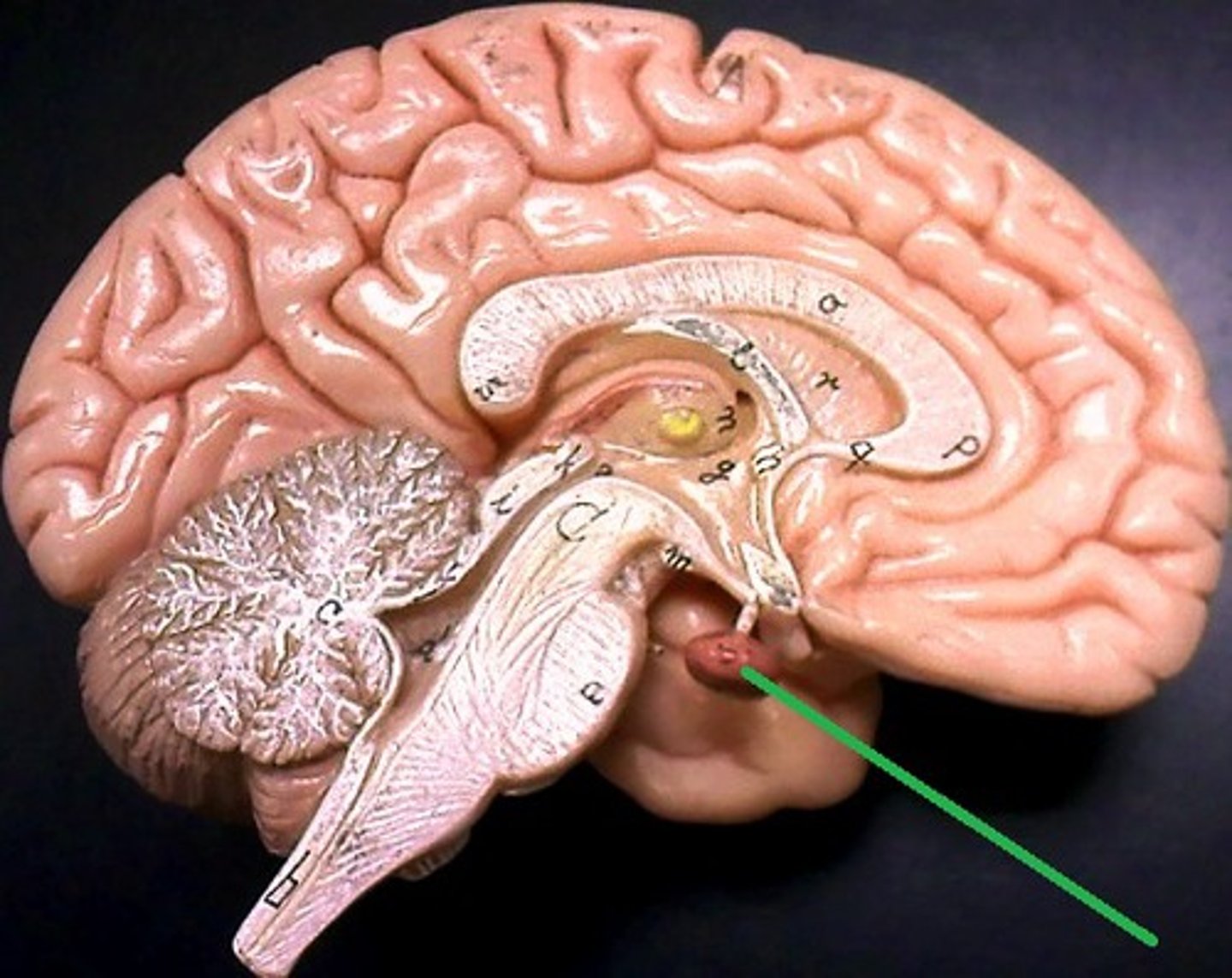
limbic system
Circular and regulates emotion and memory circuit
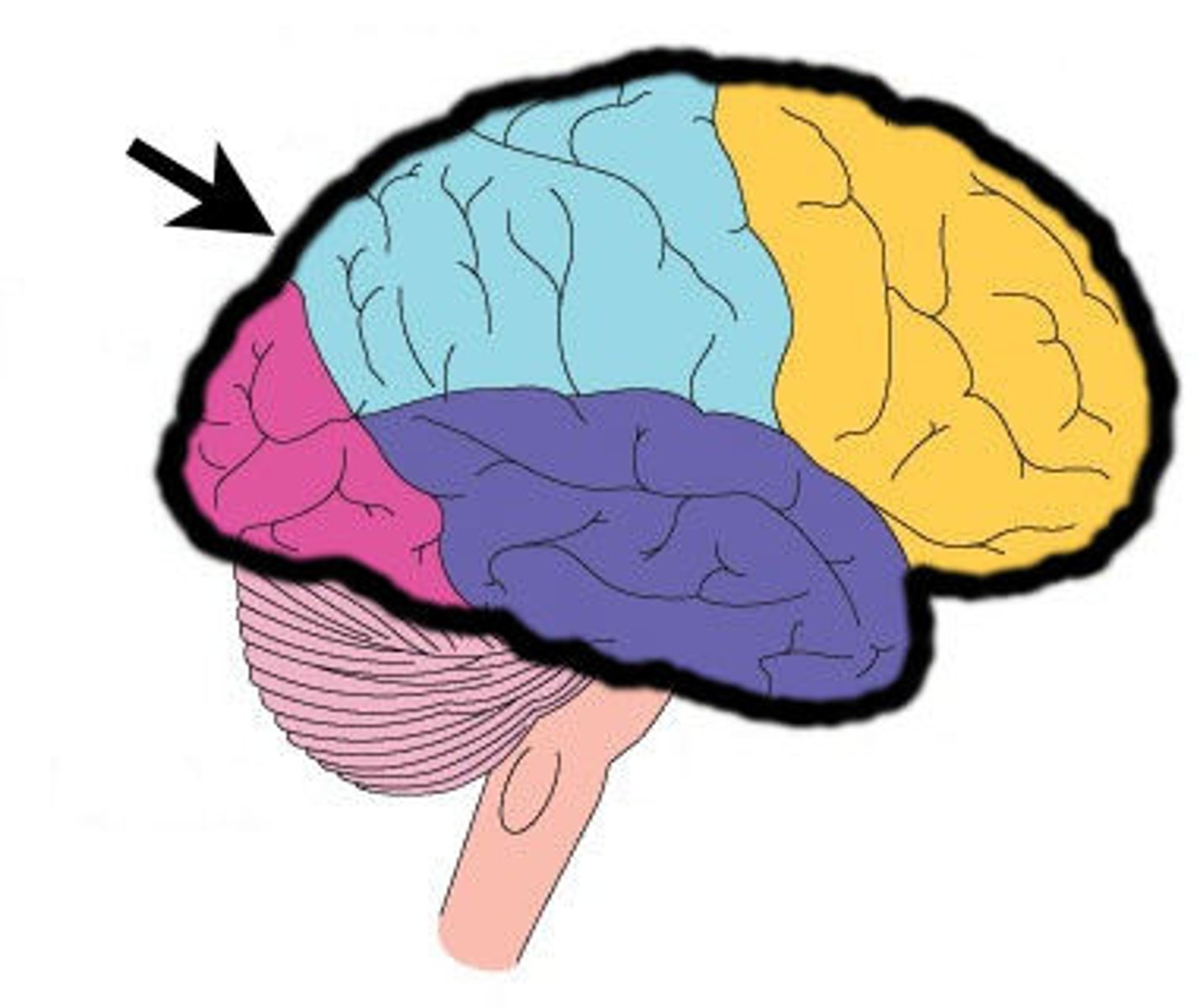
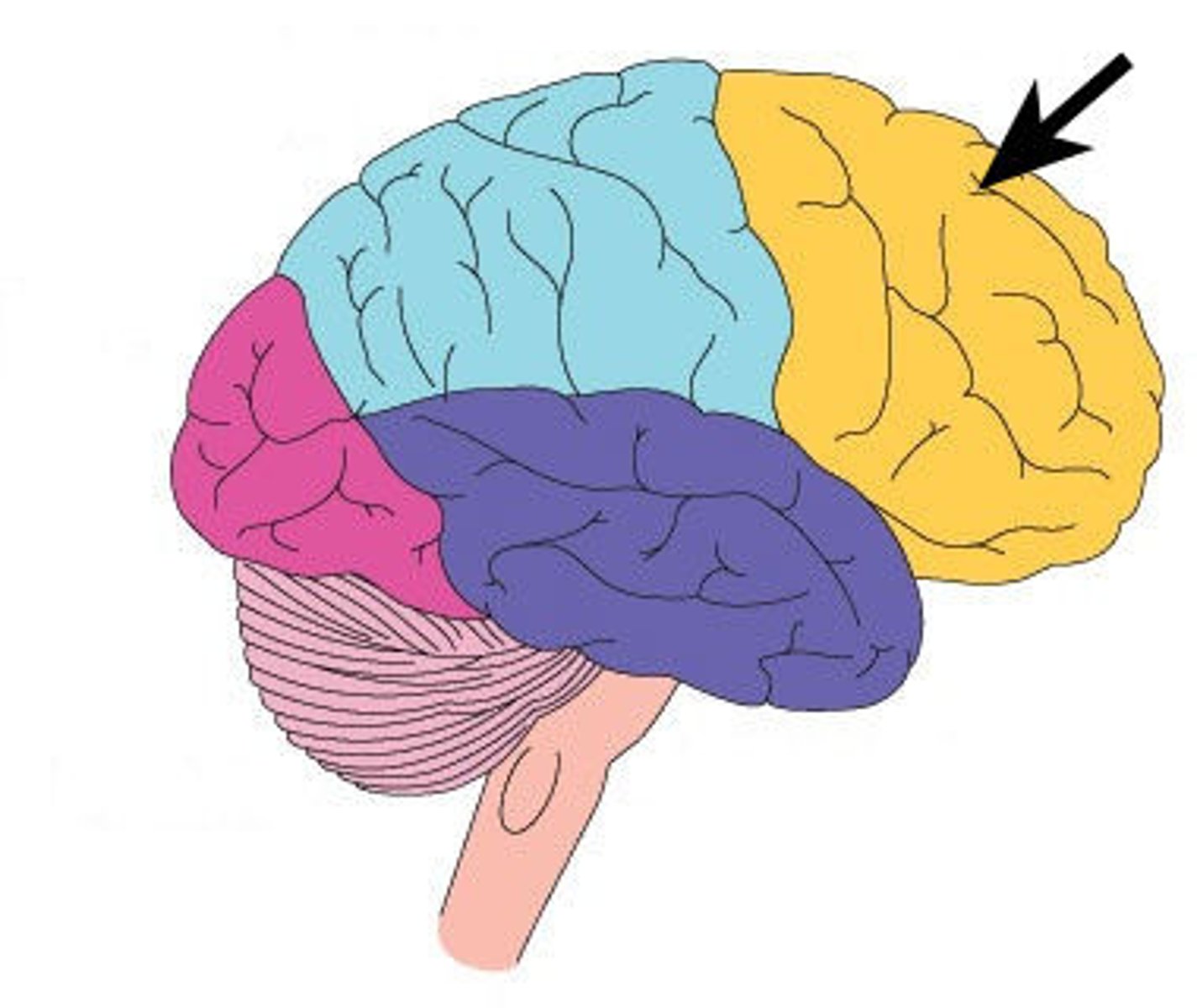
Cerebral cortex's frontal lobe
associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving
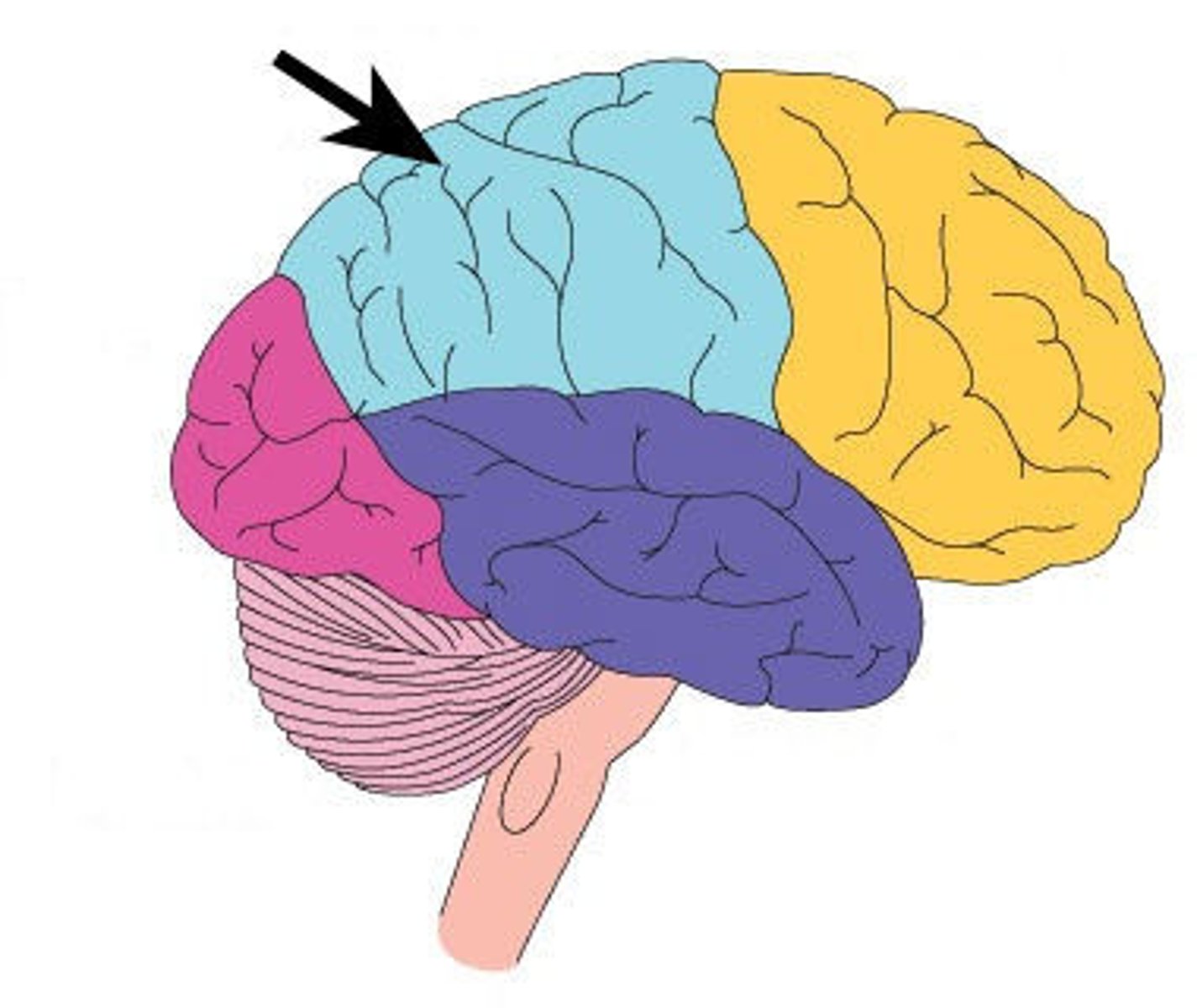
Cerebral cortex's parietal lobe
receives sensory input for touch and body position
Cerebral cortex's occipital lobe
visual processing
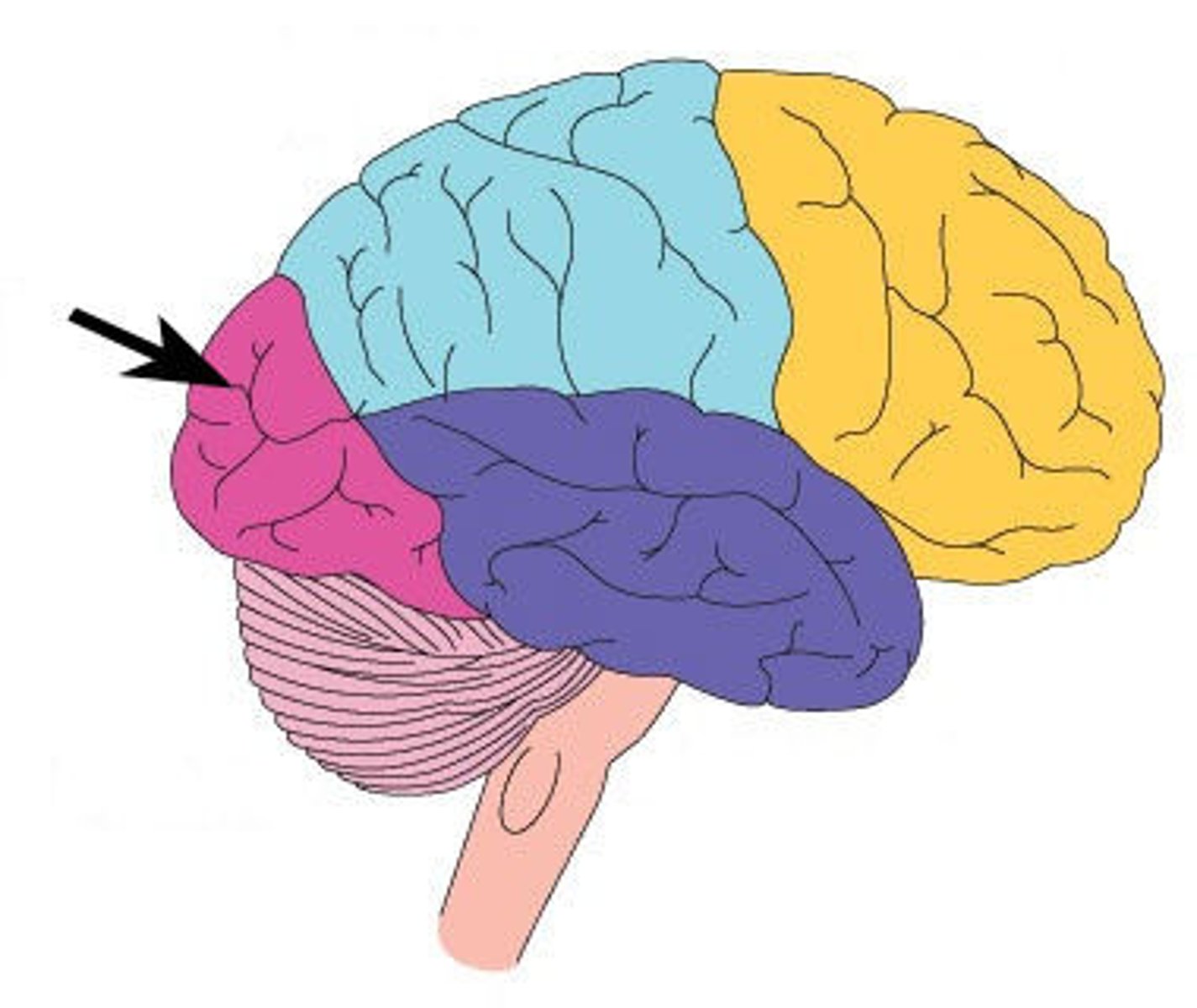
Cerebral cortex's temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
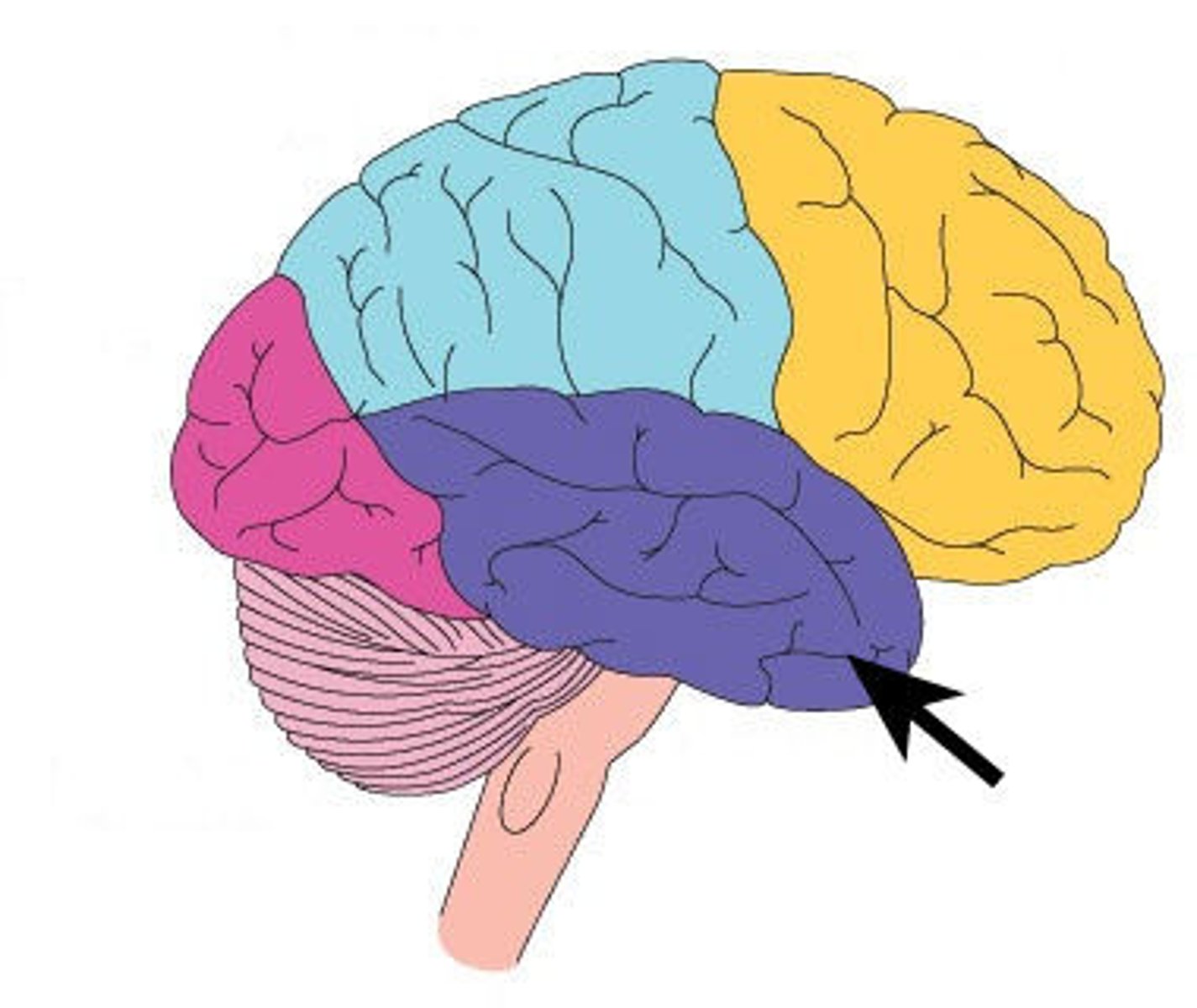
Thalamus
relays messages between lower brain centers and cerebral cortex (sleep
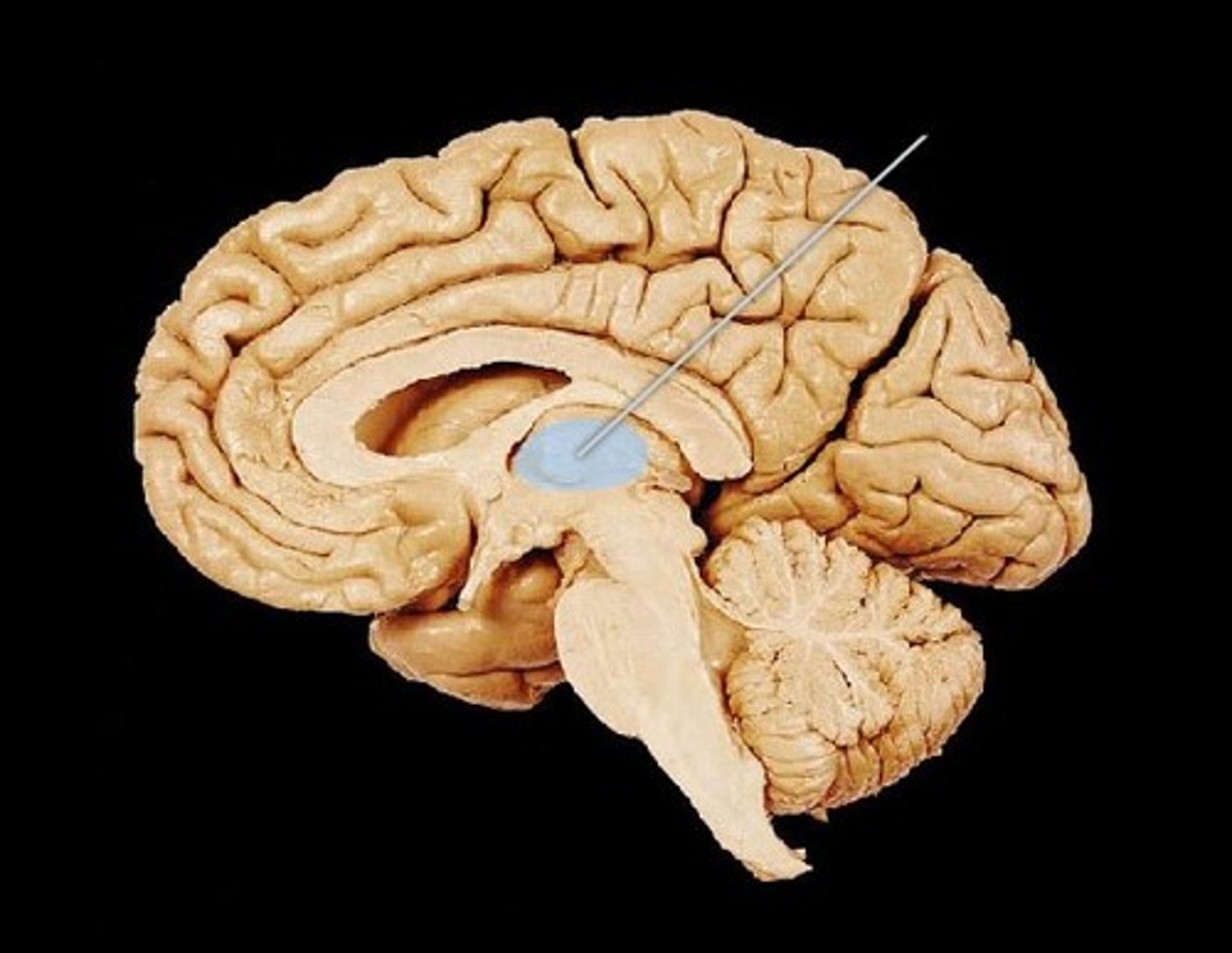
Amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression.
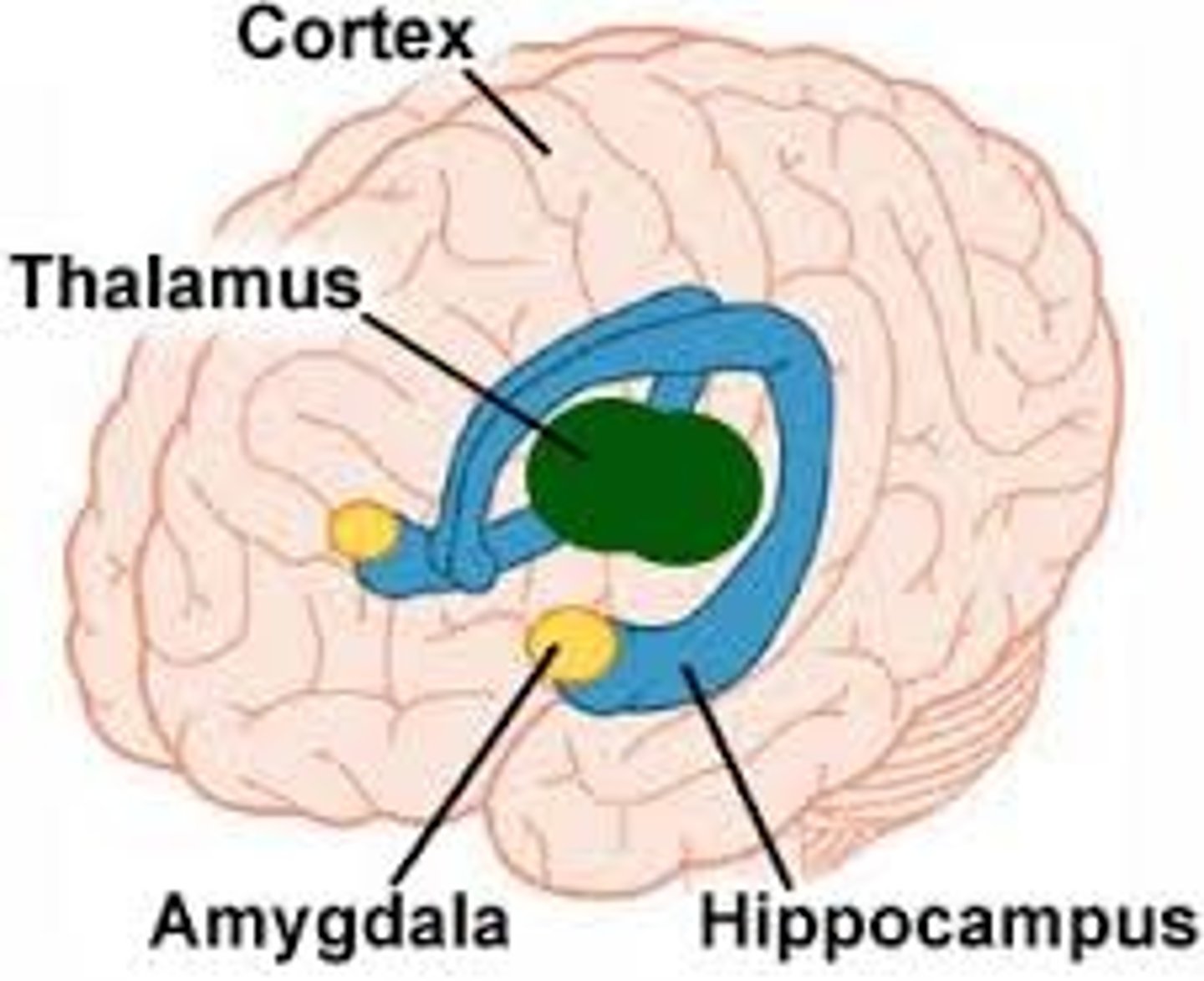
Hippocampus
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
Midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
Reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal (Midbrain)
substantia nigra
An area of the midbrain that is involved in motor control and contains a large concentration of dopamine-producing neurons
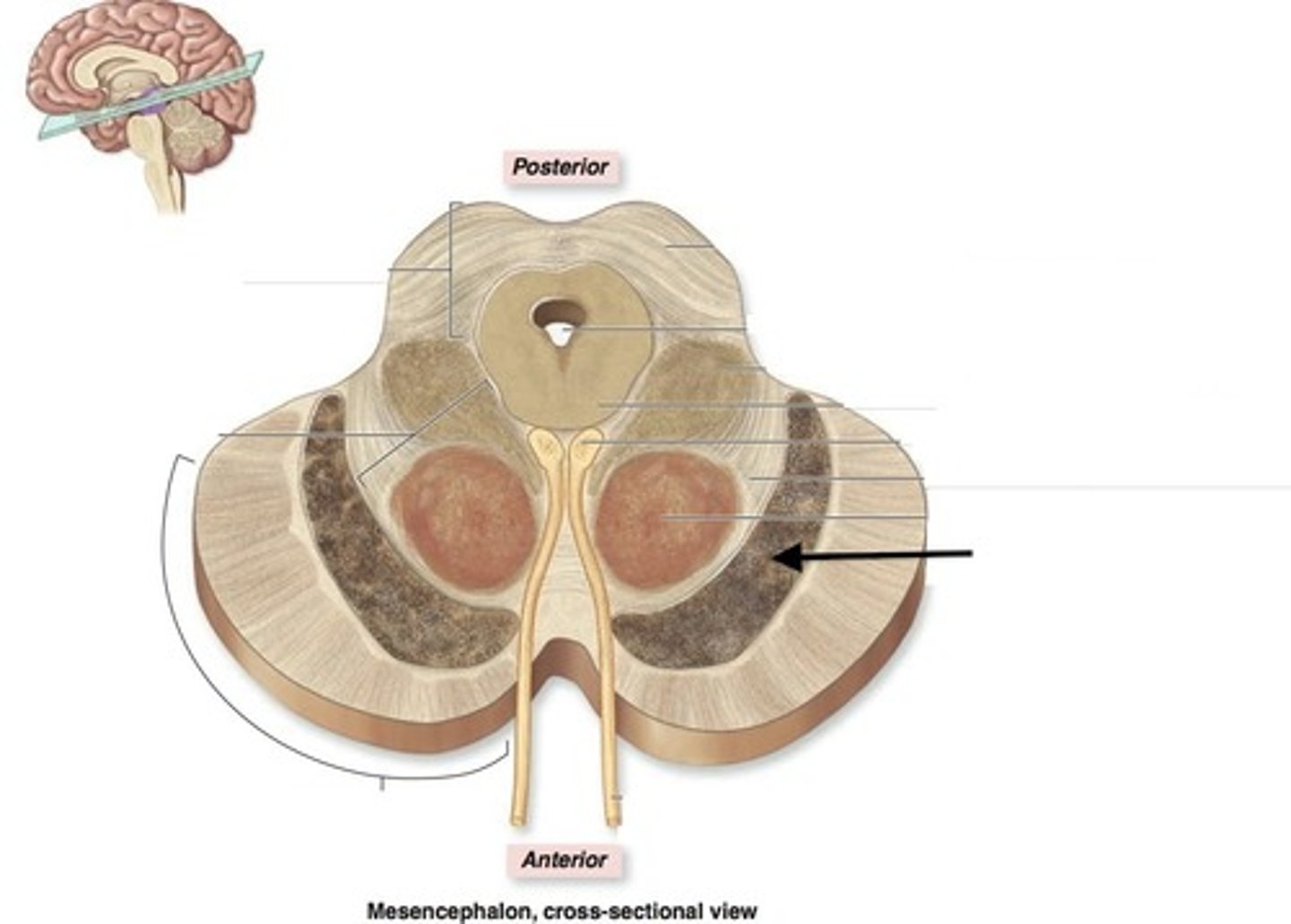
Ventral Tegmental Area
where dopamine is produced; associated with mood, reward, and addiction. (when triggered rats use it until they starve)
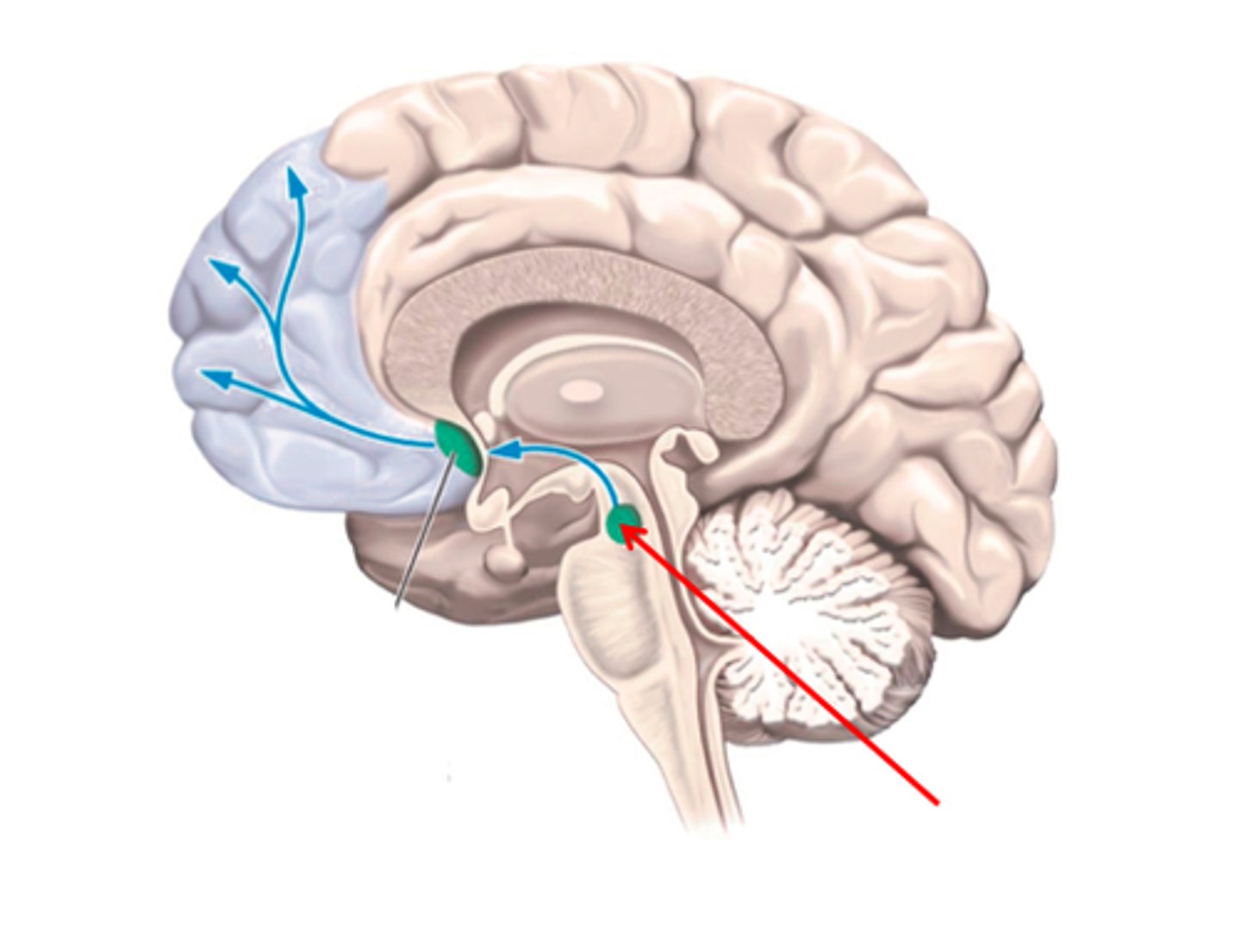
Hindbrain
medulla, pons, cerebellum (oldest part of the brain)
Medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing (Hindbrain)
Pons
connects the brain and the spinal cord involved in regulating brain activity during sleep (Hindbrain)
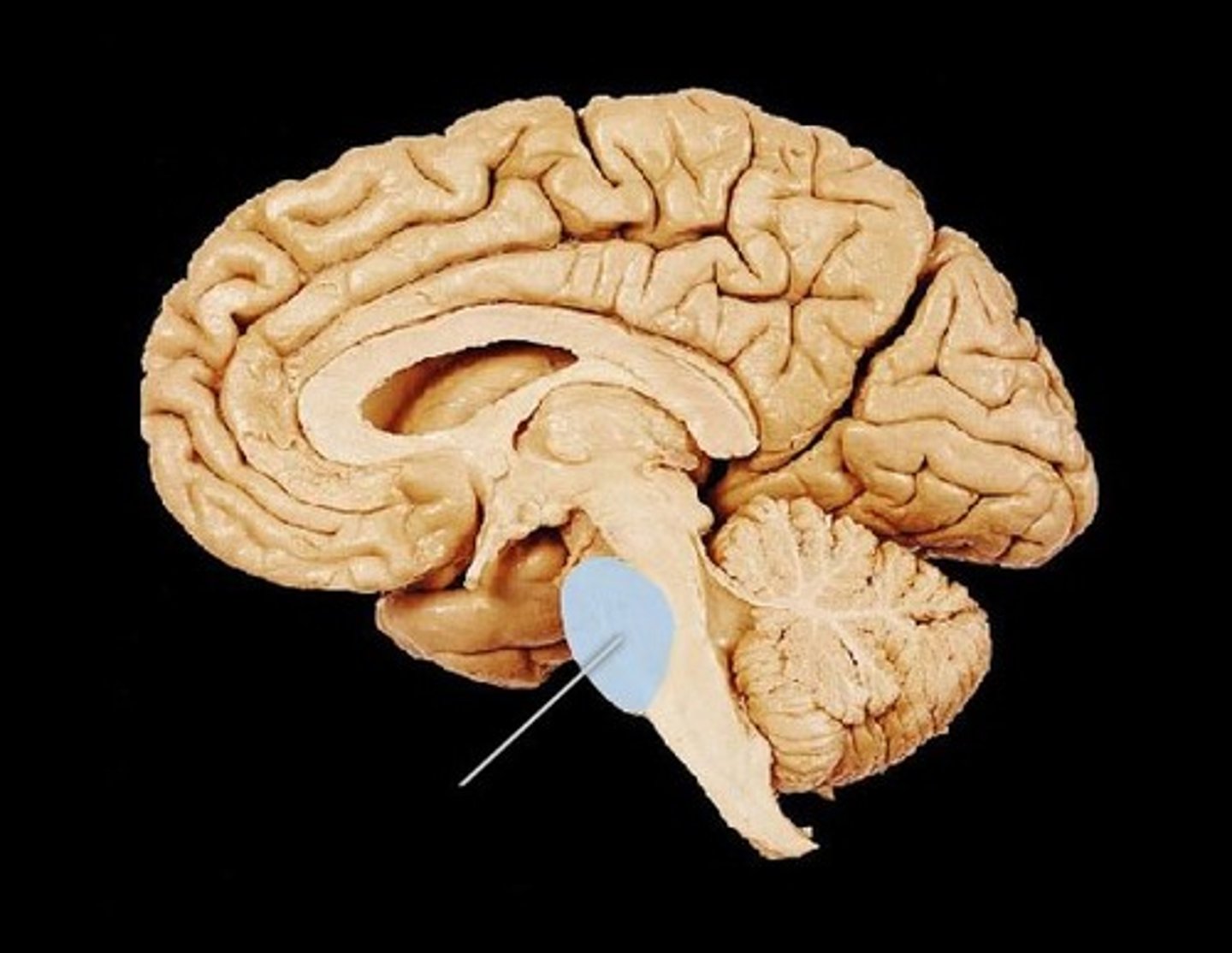
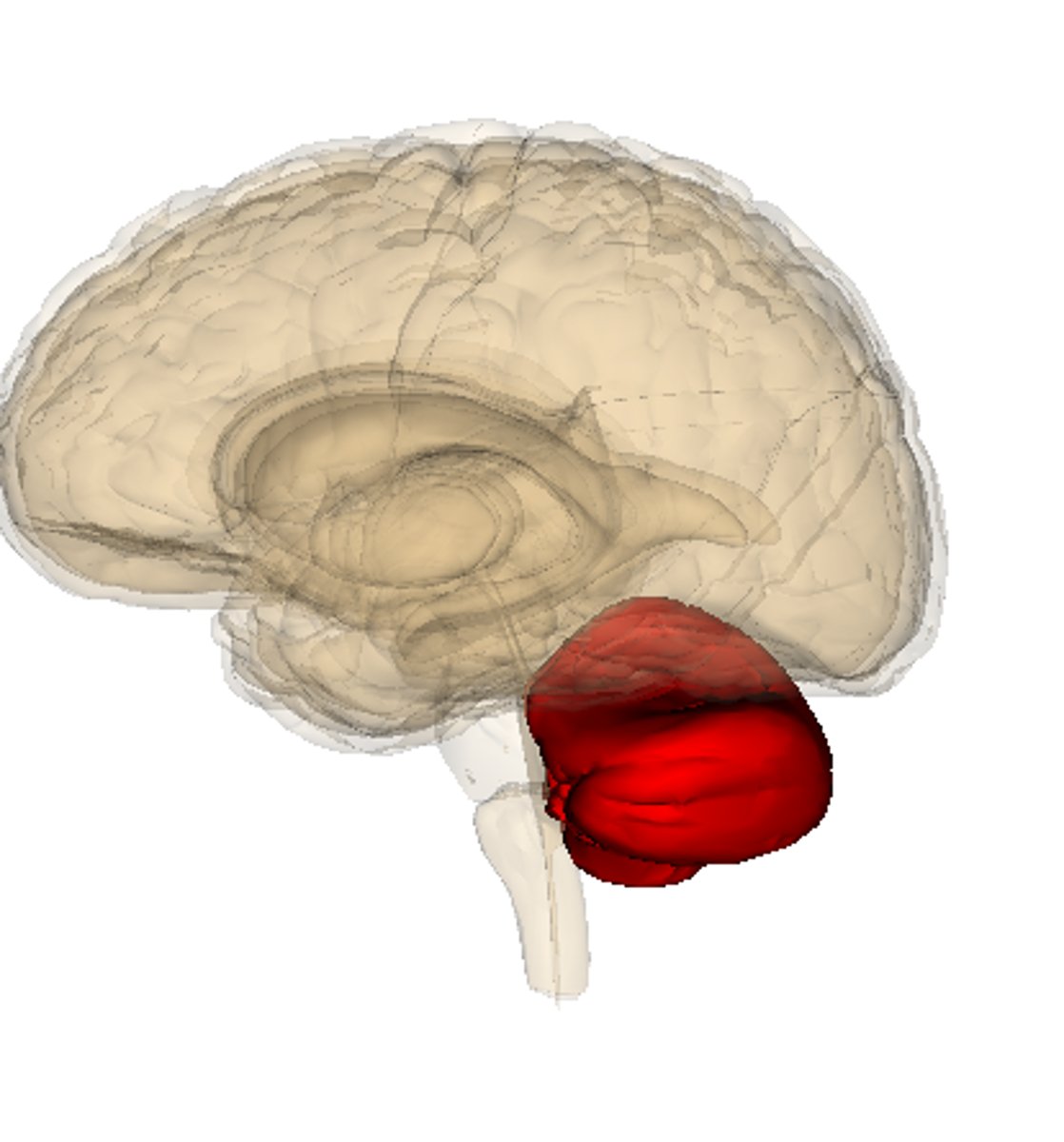
Cerebellum
controls our balance, coordination,movement, and motor skills, and it is thought to be important in processing some types of memory (Hindbrain)
PET scan
a visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task
CT scan
a series of x-ray photographs taken from different angles and combined by computer into a composite representation of a slice through the body
MRI vs fMRI
MRI studies brain anatomy
fMRI studies brain function
EEG
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
endocrine system
A series of glands that produce hormones to regulate normal body functions.
Thyroid
regulates metabolism