Series circuits
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
What is a series circuit?
the different components are connected in aline, end to end (except the voltmeters which are always connected in parallel)
What are the rules of a series circuit?
potential difference is shared
Current is the same everywhere
Resistance adds up
Cell potential differences add up
How is the potential difference shared in a series circuit?
The total potential difference of the supply is shared between the various components, so the potential difference around a series circuit will always add up to equal the source potential difference
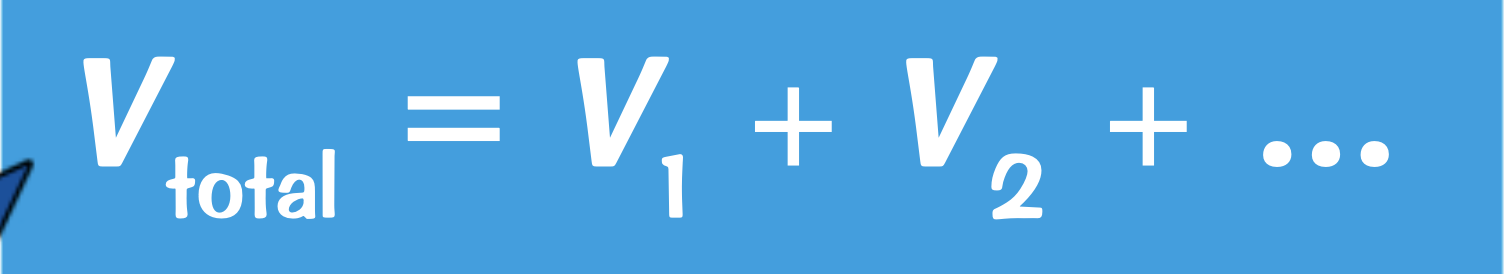
How is the current the same everywhere in a series circuit?
The same current flows through all the components
The size of the current is determined by the total potential difference of the cells and the total resistance of the circuit (I=V/R)
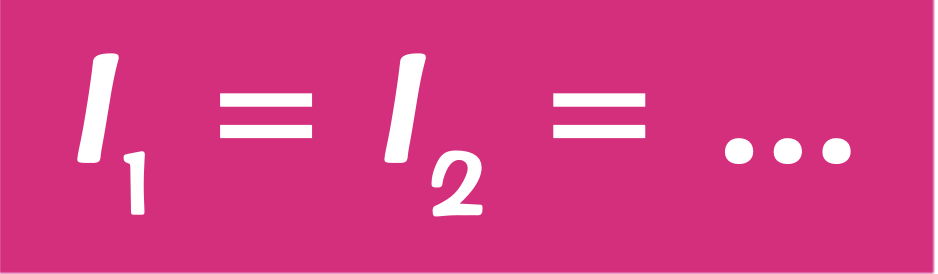
How does the resistance add up in a series circuit?
The total resistance of 2 components is the sum of their resistances
This is because by adding a resistor in series, the 2 resistors have to share the total potential difference
The potential difference across each resistor is lower, so the current through is resistor is also lower.
In a series circuit, the current is the same everywhere so the total current in the circuit is reduced when a resistor is added. This means that the total resistance of the circuit increases
The bigger a components resistance, the bigger its share of total potential difference
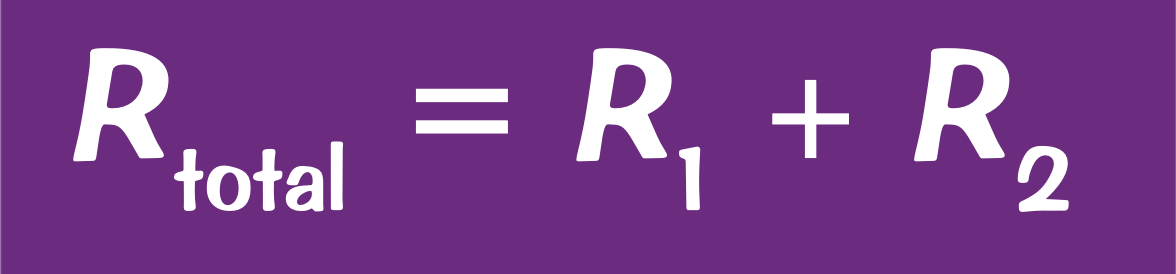
How do cell potential differences add up in a series cell?
There is a bigger potential difference when more cells are in a series, if they are all connected the same way