Cancer Care
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is cancer?
Uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body that can invade other tissues.
Can cancer be genetic? Hereditary?
Genetic: Yes
Hereditary: Not always, less common
Benign vs Malignant tumors
Benign: Non-cancerous tumors that don’t spread to other tissues.
Malignant: Cancerous and can invade surrounding tissue or metastasize to other organs/ tissues

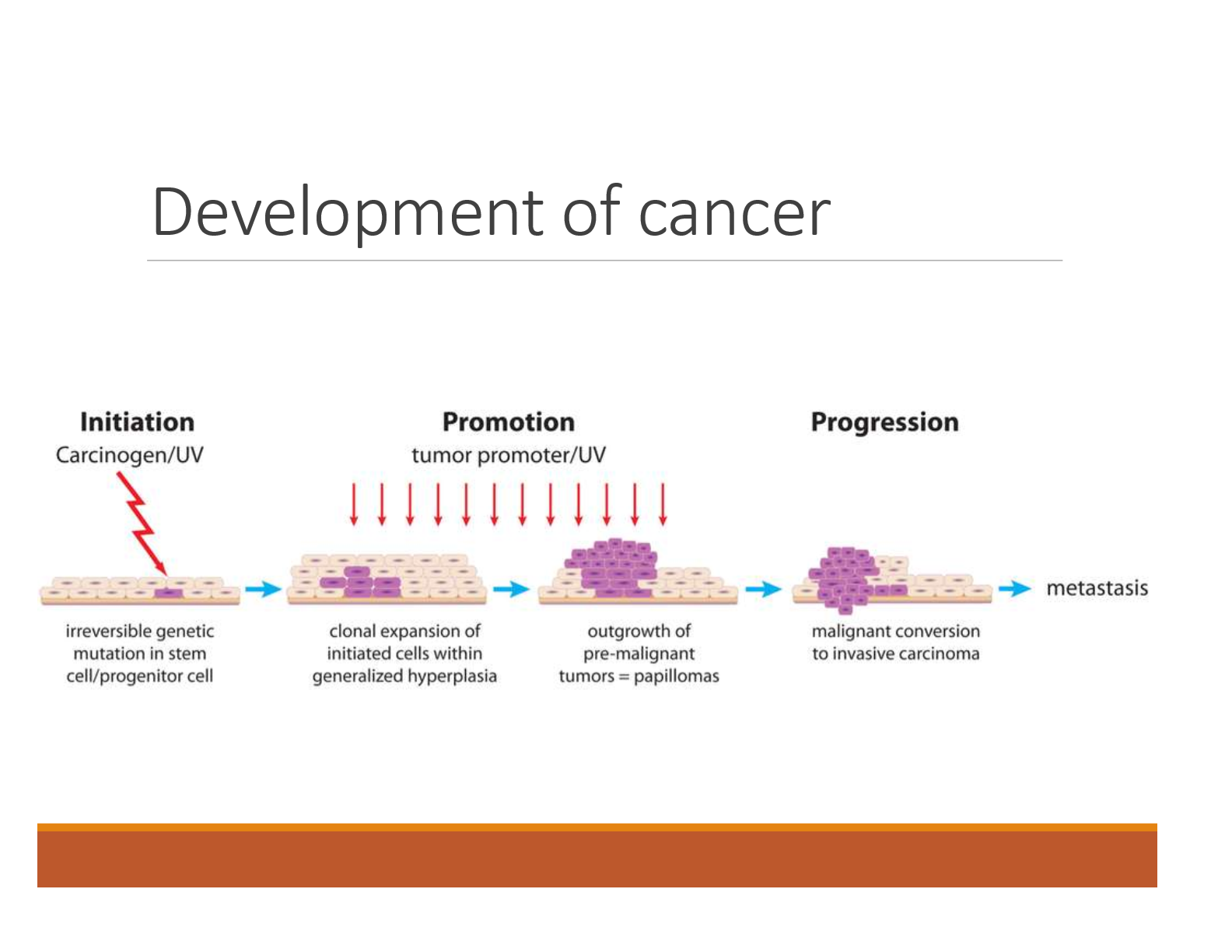
How does cancer develop
Initiation: Carcinogen/UV
Irreversible genetic mutation in stem cell/progenitor cell
Promotion: Tumor promoter/ UV
Clonal expansion of initiated cells within generalized hyperplasia
Outgrowth of pre-malignant tumors = papillomas
Progression:
Malignant conversion to invasive carcinoma
Metastasis
What are carcinogens that influence the initiation phase of cancer development
Group 1: Carcinogenic to humans
Smoking, exposure to solar radiation, alcoholic beverages, and processed meats
Group 2A: Probably carcinogenic to humans
Emissions from high temp, frying, steroids, exposures working in hairdressing, red meat
Group 2B: Possibly carcinogenic to humans
Coffee, gasoline & exhaust, welding fumes, pickled veggies
Group 3: Carcinogenicity not classifiable
Tea, static, magnetic fields, fluorescent lighting, polyethene
Group 4: Probably not carcinogenic
Caprolactam, use in the manufacture of synthetic fibers.
What makes the promotion phase of cancer development worse
Alcohol, tobacco, diet
What is immunologic surveillance
Some cancer cells present altered cell-surface antigens: TAAS (tumor associated antigens)
Constant monitoring of normal tissues by NK cells, cytotoxic T cells, macrophages, and B cells
Cancer cells may go unnoticed because they arise from normal human cells (immunologic escape)
What can cause cancer to progress faster
Additional genetic alterations
Inflammation and oxidative stress

What is cancer cachexia
Wasting syndrome that results in weakness and involuntary weight loss
What is metastasis? Where are the most common sites?
Spread of cancer to a distant site.
Most common sites: Liver, bone, lungs
Some cancers have an affinity for specific tissue:
Colon → liver
Breast → bones
What does CAUTION stand for in the 7 warning signs of cancer
C: Change in bowel/bladder habits
A: A sore that does not heal
U: Unusual bleeding or discharge
T: Thickening or lump
I: Indigestion or difficulty swallowing
O: Obvious change in wart or mole
N: Nagging cough or hoarseness
Diagnostic studies
Computed tomography (CT) scan
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
Breast MRI
X-rays and other radiographic tests
Mammography
Nuclear medicine scans
Ultrasound
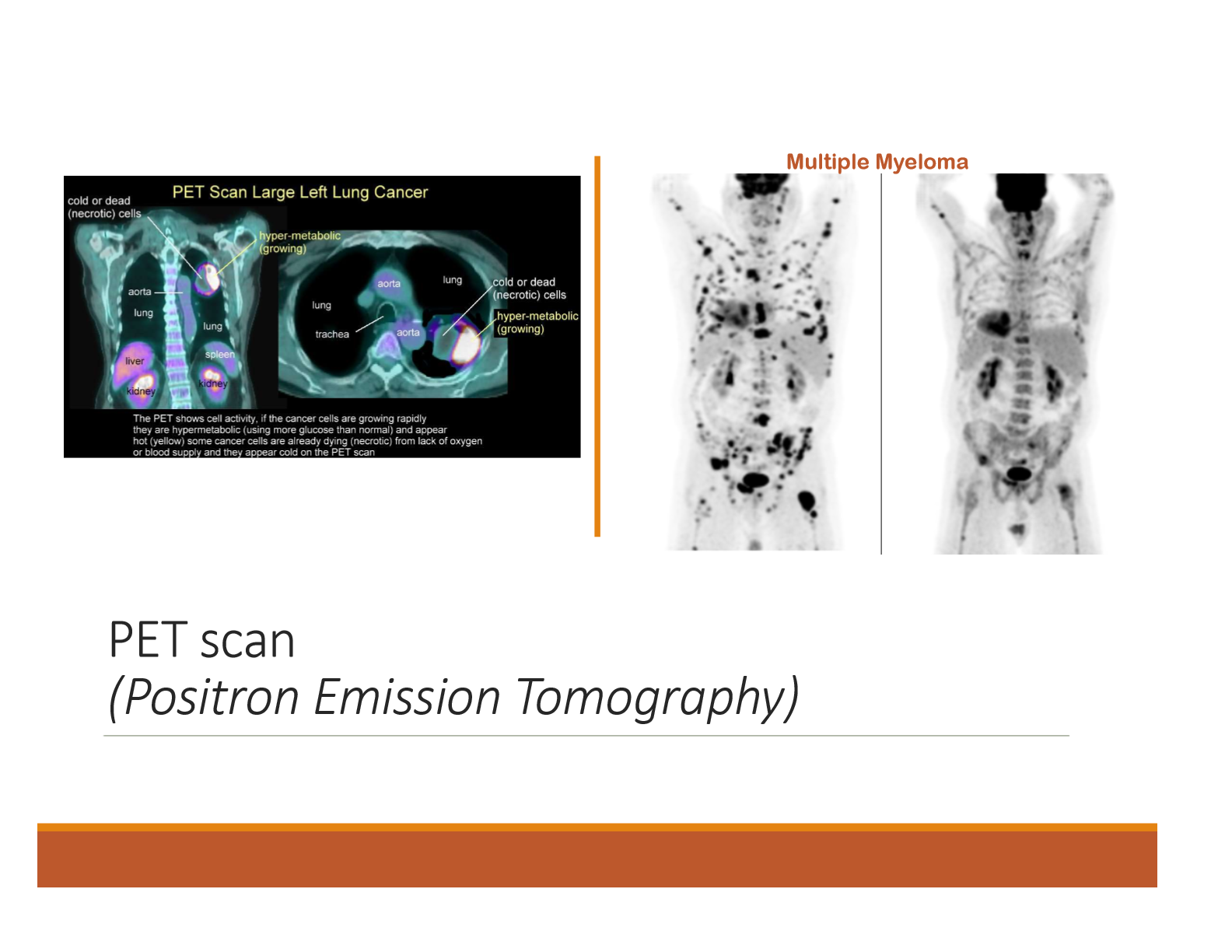
What is a PET scan (Positron Emission Tomography)
Imaging test that uses a small amount of radioactive material (radiotracer) to visualize how tissues and organs are functioning.
Define these types of cancer: Carcinoma, sarcoma, lymphoma, glioma, and leukemia
Carcinoma: epithelial tissue that line or cover internal organs (breast, prostate, colon, stomach, lung)
Sarcoma: connective or supportive tissue (bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels)
Lymphoma: lymphatic system
Glioma: Nerve cells
Leukemia: blood-forming tissue (bone marrow)
What is histological classification
Grading of tumor- appearance of cells and degree of differentiation
What are the different grades of histologic classification
Grade I: Low grade
Well differentiated (closer to appearance to the normal tissue of origin)
Grade II: Intermediate grade
Grade III: High grade
Grade IV: High grade
Poorly differentiated (undifferentiated)
Grade X: Cannot be graded
What does TNM stand for and what does it measure (breast cancer)
Measures the extent of disease classification.
LN= lymph nodes
IM= internal mammary
T: Tumor size
T1: Tumor size <2 cm
T2: Tumor size 2-5 cm
T3: Tumor size >5 cm
T4: Tumor extends to skin or chest wall
N: Lymph nodes
N0: No lymph node metastasis
N1: Metastasis to ipsilateral, movable, axillary LN’s
N2: Metastasis to ipsilateral fixed axillary, or IM LN’s
N3: Metastasis to infraclavicular/ supraclavicular LN or to axillary and IM LN’s
M: Metastasis
M0: No distant metastasis
M1: Distant metastasis
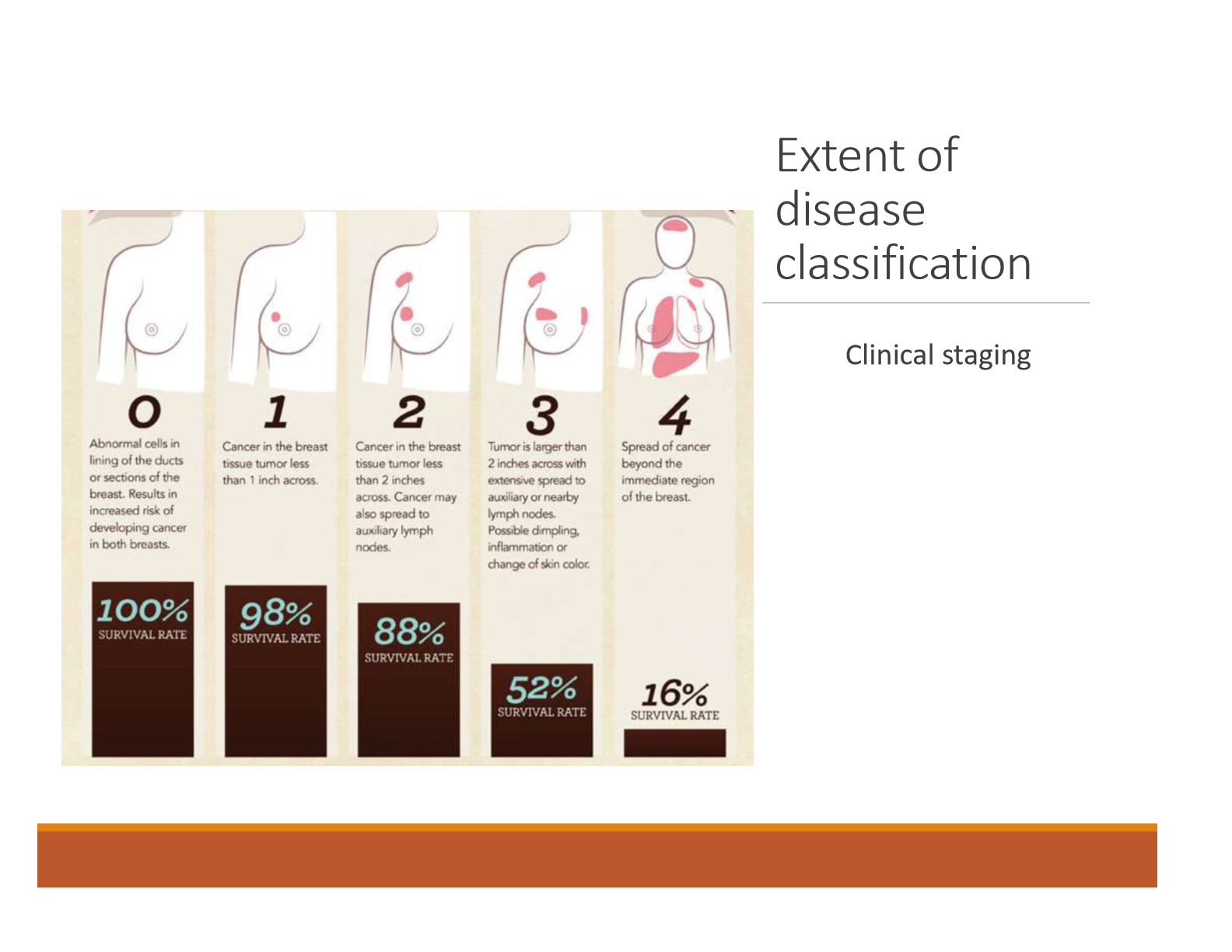
Define clinical staging 0-4 with breast cancer
0: Abnormal cells in lining of the ducts or secretions of the breast. Results in increased risk of developing breast cancer in both breasts. 100% survival rate
1: Cancer in the breast tissue, tumor < 1 inch across. 98% survival rate
2: Cancer in the breast tissue, tumor < 2 inches across. Cancer may also spread to auxiliary lymph nodes. 88% survival rate.
3: Tumor is larger than 2 inches across with excessive spread to auxiliary or nearby lymph nodes. Possible dimpling, inflammation, or change in color of the skin. 53% survival rate.
4: Spread of cancer beyond the immediate region of the breast. 16% survival rate.
What are the breast cancer screening guidelines for women with average risk
Age 40: Talk with doctor about when to begin screening, women should have the opportunity to begin screening if they choose.
Age 45: Being yearly mammograms.
Age 55: Transition to mammograms to every other year or continue with annual.
Age 55+: Continue regular mammograms if you’re in good health
Is there a standard or routine screening for prostate cancer? What are the tests for prostate cancer?
No, there is no standard or routing screening test.
Tests include:
Digital rectal exam
Prostate-specific antigen test
Prostate cancer gene 3 (PCA3) RNA
When do colorectal cancer screenings start for both men and women
Begins at age 50, continues to at least age 75
What tests find polyps and colorectal cancers
Flexible sigmoidoscopy q 5 yrs
Colonoscopy q 10 yrs
CT colonography q 5 yrs
Double contrast barium enema q 5 yrs
What tests mainly find colorectal cancer
FOBT yearly: guaiac (gFOBT) and immunochemical tests (or FIT)
Stool DNA tests (q 3 yrs)
What are the screening guidelines for cervical cancer
<21: No screening recommended
21-29: Cytology (pap smear) every 3 years. Abnormal pap may be followed up with HPV testing
30-65: Cytology + HPV testing every 5 years or cytology every 3 years
>65: No cervical cancer screening required if woman has had regular screening in the previous 10 years and no serous precancers in the last 20 years or continue testing if an abnormality was found in the last 20 years
What are the ABCDEs of screening for skin cancer
A: Asymmetry
B: Border
C: Color
D:Diameter
E: Evolving
What are standard therapies for cancer treatment
Surgery
Chemotherapy
Radiation
Biologic response modifiers
Hematopoietic stem cell transplant
Watchful waiting