a) To oxidise phenylmethanol (benzyl alcohol) to benzoic acid with potassium manganate (VII) in alkaline conditions
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Theory
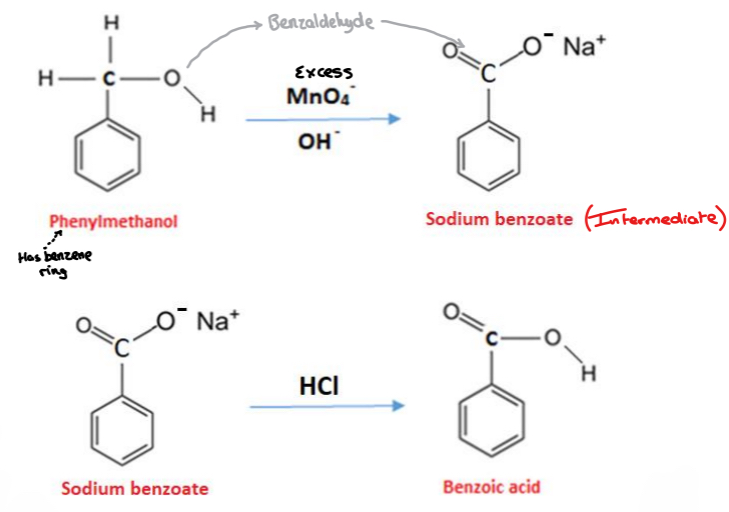
Phenylmethanol (Benzyl alcohol) – (C6H5CH2OH) is a primary alcohol that can be oxidised to benzoic acid using excess potassium manganate (KMnO4) in the presence of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3)
Reaction
3C6H5CH2OH + 4KMnO4 —Alkaline conditions→ 3C6H5COOH + 4MnO2 + H2O + 4KOH
Phenylmethanol + potassium manganate→ Benzoic acid +Manganese dioxide + Water + Potassium hydroxide
Limiting agent + excess agent
Notice: As the potassium manganate is in excess, the phenylmethanol is the limiting reagent
The molar ratio between phenylmethanol and benzoic acid is 3 : 3
This can be used to calculate the yield of benzoic acid obtained
The formation of benzoic acid
i. The formation of a sodium benzoate intermediate in alkaline conditions
ii. The formation of benzoic acid in acidic conditions
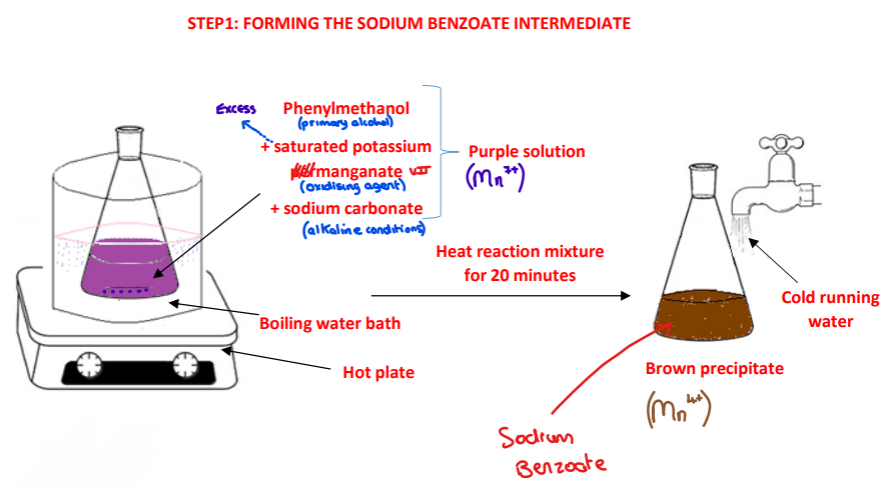
Procedure: step 1
➢ Using a graduated dropper, a small known volume of phenylmethanol is added to a conical flask
➢ A saturated solution a saturated solution of potassium manganate and a solution of sodium carbonate are added
➢ The reactants are heated in a boiling water bath using a hot plate for 20 minutes
➢ The conical flask is cooled under cold running water
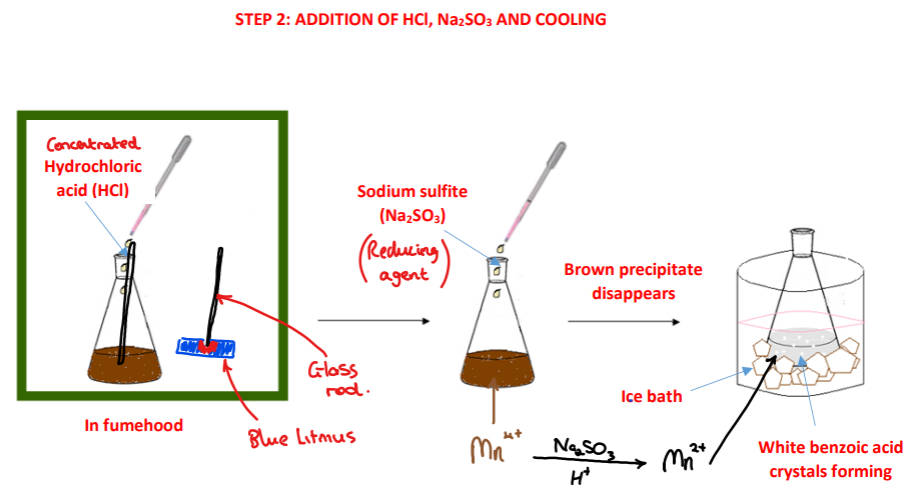
Procedure: step 2
➢ In a fumehood, concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to the conical flask using a dropper
➢ Sodium sulfite solution (Na2SO3) is added to the conical flask using a dropper and the conical flask is continuously swirled until the brown precipitate disappears
➢ The conical flask is placed in an ice bath
➢ White crystals of benzoic acid are observed crystallising out of solution
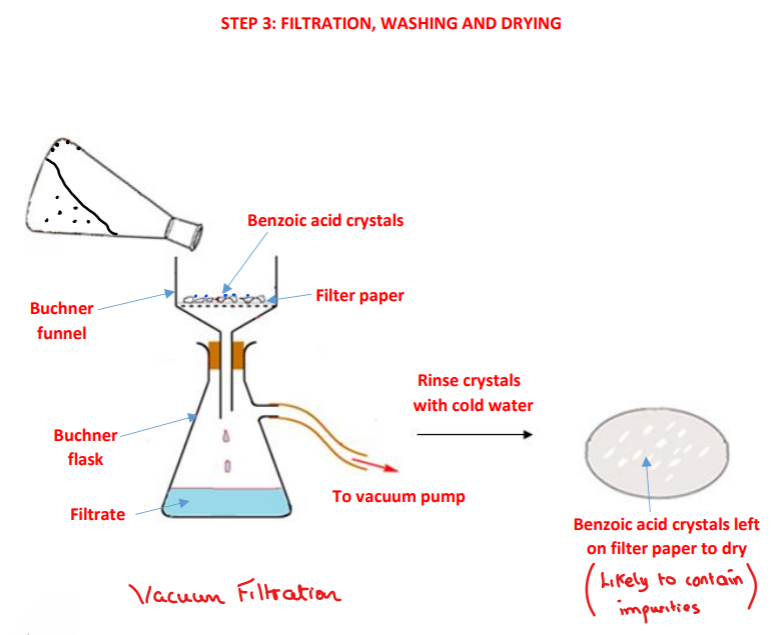
Procedure: step 3
➢ The benzoic acid crystals are filtered using vacuum/suction filtration using filter paper, a Buchner funnel and a Buncher flask
➢ The conical flask is rinsed with the filtrate from the Buchner flask and is re-filtered to ensure maximum yield of benzoic acid crystals are obtained
➢ The benzoic acid crystals are washed with cold water remove any soluble impurities present on the filter paper or on the crystals
➢ The benzoic acid crystals are left to air dry on the filter paper in a warm place or placed in a desiccator
Describe the appearance of phenylmethanol at room temperature
Phenylmethanol is a colourless liquid at room temperature
Name a suitable piece of apparatus to measure a precise small volume of the phenylmethanol
Graduated dropper
Why is a saturated solution of potassium permanganate used?
• Potassium manganate (VII) is an oxidising agent. A saturated solution is used to ensure that it is in excess
• This will mean sufficient is present to oxidise ALL of the phenylmethanol to benzoic acid
Note: The small volume of phenylmethanol also ensures it is all oxidised
Why is sodium carbonate required?
• To create alkaline/basic conditions
• The oxidation of phenymethonal to benzoic acid works best and faster at an alkaline pH
Identity the source of a smell of almonds during the heating phase
• The formation of benzaldehyde
Remember: Primary alcohols are oxidised first to aldehydes and then to carboxylic acids
What is observed in the conical flask as the reaction mixture of phenylmethanol, potassium manganate (VII) and sodium carbonate is heated ? Explain this observation
The purple solution turns to a brown precipitate
Explanation:
• The Mn7+ ions in KMnO4 are reduced to Mn4+ ions in MnO2 in the alkaline conditions
• Mn4+ ions cause a brown colour
• MnO2 is not soluble in water hence a precipitate forms
What intermediate organic compound is formed in the conical flask?
Sodium benzoate – an intermediate compound formed
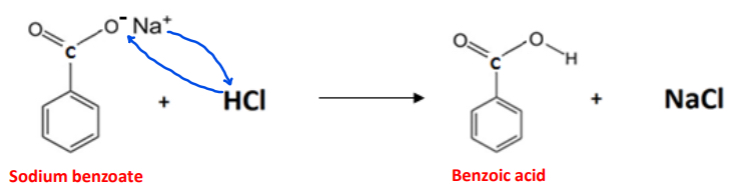
Give three reasons why concentrated hydrochloric acid is added to the conical flask?
(1) To convert the sodium benzoate intermediate into benzoic acid
(2) To neutralise any excess sodium carbonate and potassium hydroxide present
(3) To create an acidic environment for Mn4+ ions to be reduced to Mn2+ ions
How can the solution be tested for that enough acid has been added to the conical flask?
A glass rod is dipped into the solution and is then touched against a piece of damp blue litmus paper – if the blue litmus turns red, enough acid has been added
Why is sodium sulfite (Na2SO3) added to the conical flask?
• Sodium sulfite is a reducing agent
• It is added to reduce the insoluble Mn4+ ions present to soluble Mn2+ ions
• If present the insoluble Mn4+ ions would contaminate the benzoic acid crystals formed
What is observed upon addition of the sodium sulfite and shaking of the conical flask?
• The brown precipitate decolourises as Mn4+ ions are reduced to Mn2+ ions
• White crystals of benzoic acid become visible
State the changes in the oxidation number of manganese during the experiment
Mn7+ → Mn4+ —Na2SO3→ Mn2+
(KMnO4) → (MnO2)
Purple → Brown → Colourless
Oxidation number: +7 +4 +2
Why is the conical flask placed in an ice bath? *
• Benzoic acid is very soluble in hot water but only slightly soluble in cold water
• Placing the conical flask in an ice bath helps to ensure crystallisation of the benzoic acid crystals out of solution is complete and maximises the yield of benzoic acid crystals
How are the benzoic acid crystals isolated/obtained after they have crystallised?
• By vacuum/suction filtration using filter paper, a Buchner funnel and a Buncher flask
• The conical flask is rinsed with the filtrate from the Buchner flask and is re-filtered to ensure maximum yield of benzoic acid crystals are obtained
Why is vacuum filtration performed in preference to gravity filtration?
a) To speed up the filtration process – faster than using regular filter paper
b) To help dry the crystals
Why are the crystals washed with cold water?
• To remove any soluble impurities present on the filter paper or on the crystals. Water is cold to avoid the benzoic acid redissolving
Note: The mass of the crystals is then found, compared to the mass of the original impure crystals and the percentage yield of benzoic acid is obtained
How are the benzoic acid crystals further dried?
Allowed to air dry on the filter paper in a warm place