Degradable Polymers
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
3 ways to make progress in waste
use monomers derived from biomass to make biodegradable polymers
introduce small amt of monomer into traditional polymers causing chain cleavage
use polymers that can depolymerize when treated with acid or base
why are biodegradable polymers expected to break down more quickly in environment?
they can be hydrolyzed
unlike C-C bonds of polyolefins
oftentimes, biodegradable polymers include __________ bonds in the polymer backbone
polar C-O or C-N
such as esters, carbonates, amides, phosphoesters
biodegradable polymers are often ________ and have __________ applications
nontoxic / biomedical
degradation studies in labs have not been __________ and thus are hard to _________ to environmental conditions
standardized / translate
most common biodegradable polymer
poly(lactide)
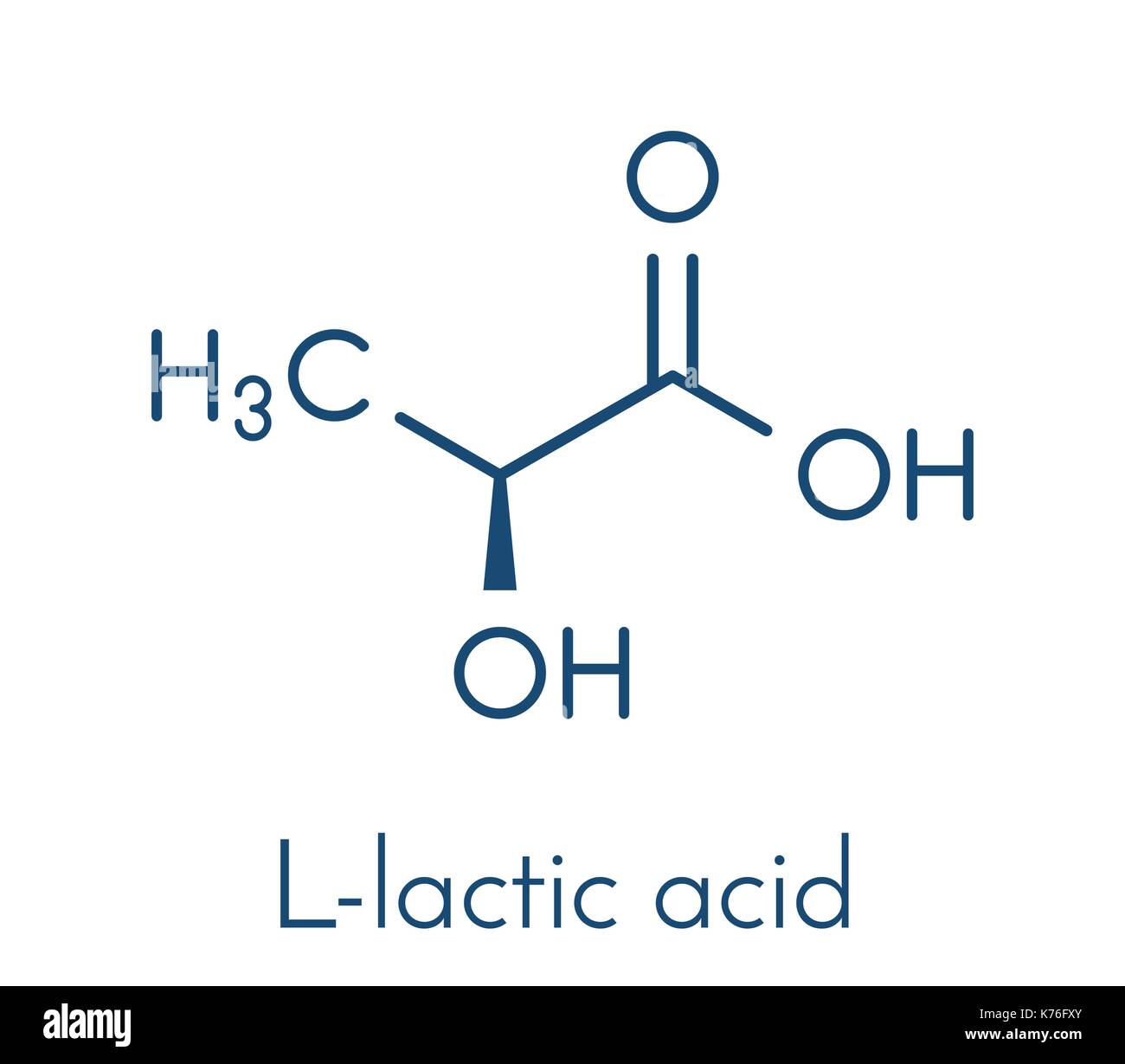
how is L-lactic acid produced?
from biomass: fermented plant starch (corn, sugar starch)
how is poly(L-lactide) turned into corn cups?
thermoforming
how are dissolvable stitches made from poly(L-lactide)
spinning
L-lactide structure
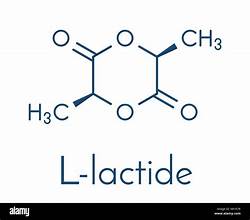
L-lactic acid structure
will poly(lactide) ever be able to replace polyolefins? why/why not?
no — has inferior material properties even for high MW samples
low Tm
polyolefins
high MW hydrocarbons
polyethylene
polypropylene
how long does it take poly(lactide) to degrade fully in body?
b/w 6 months and 2 years
do poly(lactides) degrade/compost well in landfills?
no
what temp is required for poly(lactides) to degrade?
above 55 C or 130 F
why are such high temps required to degrade poly(lactide)?
need to kick off hydrolysis
there is concern that wide-scale use of poly(lactide) will cut into _______ supply
food (corn)
biodegradable polymers are _________ to match commercial polymer properties
unlikely
thionolactones
promising monomer → can be radically polymerized with olefins like styrene & methyl acrylate
triggered degradation
add small amount of monomer that degrades easily, causing chain cleavage/scission at special monomer site more rapidly due to weak bond
thionolactone product with desirable properties produced in article via computational chem predictions
POT
benefits of POT
reactivity ratios
styrene
acrylate derivatives
RAFT copolymerization
once POT was synthesized, what was the additive?
5% of polymerized styrene & methyl acrylate
describe steps of example triggered degradation
synthesize POT
use Lawesson’s reagent to replace ester =O with =S
add radical growing polymer chain
C-S bond formation (b/w radical C and =S)
ring opens
stabilized radical reacts with more olefin
degrade poly(styrene) using TBD in THF for hydrolysis
degrade poly(methyl acrylate) using KOH and iPrNH2 in water for hydrolysis
overall, triggered degradation likely requires _________ of used polyolefins & hydrolysis to break the thionolactone links
dissolution
what does triggered degradation degrade into?
oligomers
could still lead to microplastics
does depolymerization take it back to monomers?
no - oligomers
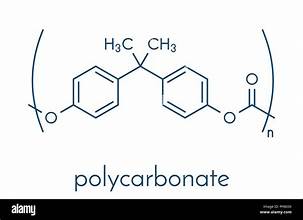
poly(carbonates)
can be synthesized from epoxides (oil-based) and CO2 (from atm)
requirements for depolymerization
high pressure
catalyst
products of depolymerization depolymerize fully into ____________
cyclic carbonates
mechanism used in depolymerization
back-biting
depolymerization is especially fast with a ________ but not with the metal catalyst used in the paper
base
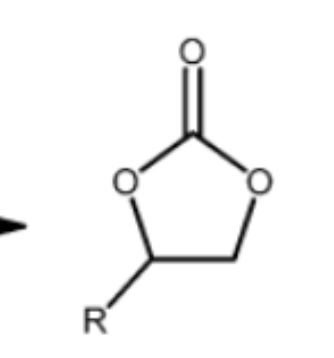
5-membered cyclic carbonates are very _________ due to _____________
stable / bond angles
depolymerization is driven by __________
thermodynamics
it is very hard to _________ a 5-membered cyclic carbonate
repolymerize
are 5-membered cyclic carbonates toxic?
no
ok as waste
describe which R groups in depolymerization led to fastest yield of cyclic carbonate from fastest to slowest
Ph and Me (tied)
CH2Cl
cyclic carbonate structure
polycarbonate structure