AS 313 Exam 3 Small Ruminants
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
When were sheep domesticated
after dogs
Where in the United States is there the least amount of sheep and why
South east - too humid - parasite issues
Resistance to dewormers
What is happened to the amount of sheep from 2001 to 2024
Declining
Why is there a disclaimer for the rare wool breeds
manage customer expectations
What happened from the late 1880’s- 1900’s
Range wars - Cattle vs Sheep
50,000-100,000 Sheep diet
Over grazing land and many shepherds were immigrants- fighting because people were different
Reasons to keep sheep
Meat - many dual purpose
Lamb feeding
Hair sheep
Wool
Milk (A2)
Vegetation control
Ram where do they clean
penis
Why is there a decrease in shearers
Too expensive
Crutch
Before lambing shear around vulva, udder for teat
A1 Milk
Causes lactose intolerance because of the beta casein
A2 milk
Lactose intolerant people can consume
Leafy Spurge
Weed
Yellow flower- open sap
Cows wont eat, but sheep love it
**Sheep instead of herbicides
Methods of wool
Commercial and handspinning
Sheep vision
360 except directly in front and back
Sheep knee
Can replace a person’s knee
What time were sheep domestication
10,000 BC - Fertile Crescent
Sheep brains
Large brains - used in neurological studies
Not stupid, emotional, used in cognitive function
Emotional support- depression, anxiety
Recognize faces
Used to study Huntington Disease - neurological model
Havy many neural, mental, and emotional disorders
Alzheimers and Parkinsons
Flight zones
Depends on:
type - range, farm, show
Dam vs. bottle raised (no flight zone imprinted)
Routine- timing (know what time to feed
Breed differences
When sheep babies are young
Play , pure joy, procking
When do baby sheep have their morning/night run
When mom is busy/ eating
to play
Dehorning
First week of life
Hot iron- over buds
if you mess up it will overheat the brain straight into sinus cavity
Band over horn - horn will slowly come off
Fencing for sheep
Make sure no heads are stuck
3-4 inch space between
5 ft height
hot wire at top- no cats /people
Cast
Long fleece - wet and cold
Upside. down and cant get up
sheep can suffocate
If the coat melts its too heavy
2009 Dr. Irlbeck first sheep
Put them in portahuts for hogs with guard llama
burnt their lungs
advanced ammonia
urine dissolved limestone and made ammonia
What do you do when housing sheep and fleeces
Out of wind and dry
What are the preferences of goats
Dont like wet
need dry area
vocal complainers
What caused fatal penumonia
BActerium called Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae
Domestic sheep resistance
not same as wild sheep
top predator of sheep
Coyotes - go for the throat
Dogs - indiscriminate killers - kill to kill
Mountain lions
Llamas
Guardian
Sheep attach and recognize as safety
Females without babies are the best
No intact male - break sheeps backs
Burrows
Put with rams - she cannot beat them up
Goats are quicker than sheep
Guardian dogs
Great puranies
Like to travel at night
How you feed
Feed costs are on average 70% of the cost of producing sheep and other food production species
How you feed - factors
Year, environment, region, management, #animals, range (need oversile)/farm flock, breeds , feed availability
What do Rumen papilla absorb
VFA’s - Need Cobalt - Vit B12
What do you need in their homes
Water - clean and avaliable
Drop tarps - snowstorms
Heated water
Forages
Carbohydrates
Energy
> Chewing
Buffering
Rumen health
Long stem hay for ruminants
Scratch Factor
Does Feeding Onions To Ewes Increase Lambing Rate?
No, makes pastures smell
First cutting alfalfa
Thick Stems
• Few Leaves (nutrients)
• ~15-18% CP
• Calcium
• Too Much Waste
Third cutting alfalfa
Thin Stems
• MANY Leaves (nutrients)
• ~ over 20% CP
• MUCH Calcium
• Too rich…can cause bloat…
• Use Creep feed babies
Which cutting is just right for alfalfa
Second
Feeding alfalfa
diarrhea
too much nitrogen
Pizzle Rot with long fleeces
burns Penis
Alfalfa
high N
when feeding alfalfa
Mix grass and legume hay
except during late pregnancy, early lactation, and creep feeding
Timothy hay

Alfalfa Hay

teeth
Used to estimate age
older ewes cant eat as well - cost more to keep than young animals
Feed according to
Physiological status
When feeding dont
Overfeed
In their diets sheep need
rough forage - straw / cornstalks/ mature hay
What do sheep do on their own in terms of feeding
Balance their diets themselves
What determines what is fed
Economica
Are sheep and goats utilized to their full potential
No
Mature range with supplement
Protein and Vitamin A + energy (later in season)
Green grass
No Beta Carotene
Protein for sheep
Forages
Alfalfa
Immature grass hay
Grazing
Evaluate energy source (grain)
Use by-products
Soybean meal
Canola meal
Cull lentils, peas, garbonzos (pulses)
Remember they are ruminants - microbial protein
Corn and SBM
corn low in lysine
SBM high in lysine
High P in sheep
urinary calculi (water belly) in male sheep and can lead to bone lesions and hypocalcemia
Carbohydrates
Starch - grains - energy
low protein
high energy
To pass stones in males
Cut off penis
Sheep chew
Very fine
No need to process grain
Coarse grind

Fine Grind

Too much grain
Acidosis
Water belly
Urinary Calculi
Unable to urinate
Inverse Ca:P
Feedlot Lambs
Feed acidifiers
Ammonium Chloride
Alfalfa Fixes - high in Ca & Limestone (add molasses)
Enterotoxemia
change diets
Clostridium Perfringes
Physiological status and which have highest nutrient requirement
Growth
Neonate vs Early vs Late
Flushing
Gestation - last 1/3
Lactation - Early vs Late
Maintenance
Dry period for ewes
5 months
Gestation length for ewe
150 days
Gleaners
small ruminants
eat lowest quality
they are cleaners
clean with prehensile lips
Maintence to lactation
increasing nutrients
BCS
Do not want them to fat - deposit fat in udder - destroy alveoli - milk cells - lowers milk production
BCS chart
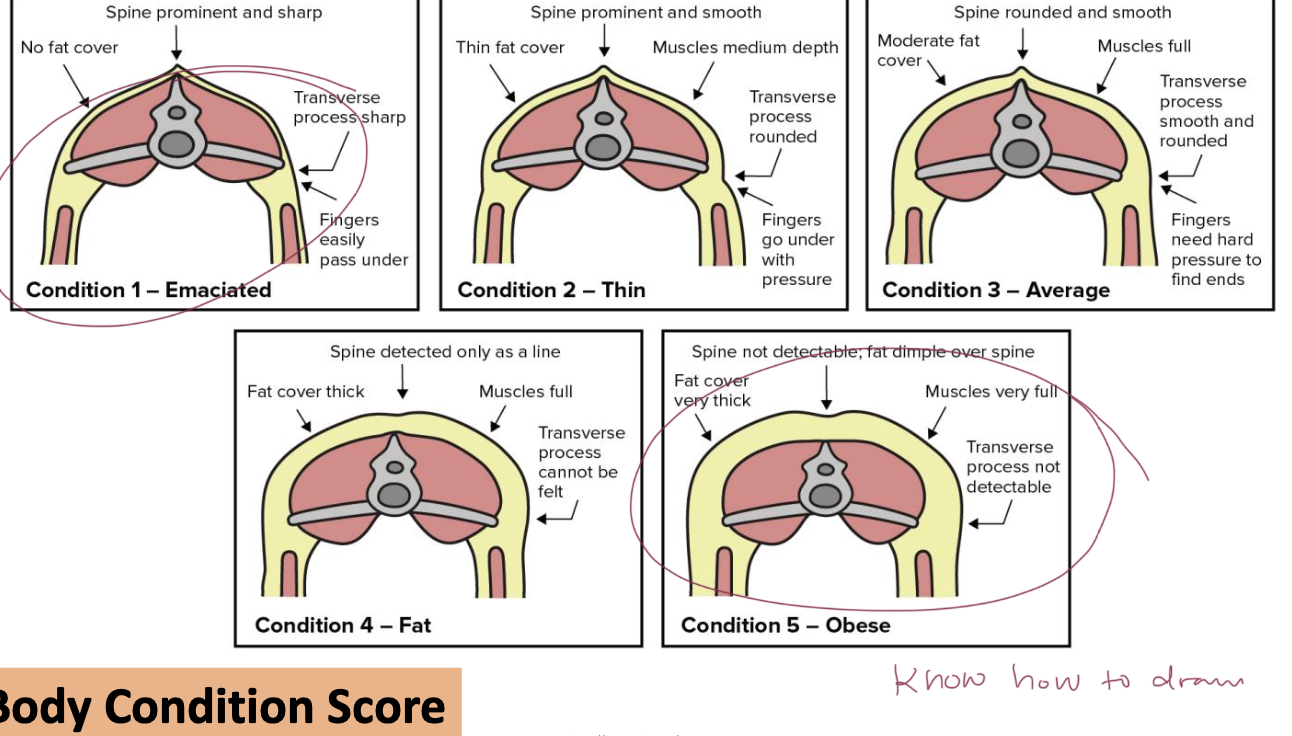
To keep BCS down
Give water on a hill, eat at pasture
otherwise dystocia- difficult giving birth
Hyperphagia
eat all the time, prone to obesity, lambs of obese ewe for 2 generations are fat
Flushing
Increase Ovulation Rate
Increase Number Born Live
Improvement of Animal Health
Only works if limit energy - not proteins/vitamins/ minerals
Scur
Short horns
break horns - goes to sinus cavity - brain damage
Beat rams with sticks
first scream at them
then beat them with a stick
third chance theyre gone
Rams back up
then go full speed forward
rams smell
Strong, know when ewes are in heat
Laproscopic
Laparoscopic insemination: Semen is inserted directly into the uterus using a laparoscope.
Heat synchronization:
Ewes receive a CIDR that releases progesterone to block heat.
After 12–14 days, the CIDR is removed and Novermon (PMSG) is injected to trigger ovulation in about 2 days.
Insemination:
Ewes are mildly sedated and a small abdominal incision is made.
Semen is placed into each uterine horn under laparoscopic view.
Recovery:
Ewes rest while minor cuts heal.
Third trimester
90% fetal growth
Metabolic conerns in late gestation
Hypocalcium
Milk fever - give calcioum glutonate
Pregnancy Toxemia
ketosis
break down of fat in the body and ketones in the body is increased
Once an animal prolapses
She will always prolapse
Edema out
Swelling
Ringwob
ewe's cervix does not dilate completely, preventing the birth of a lamb
Sheeps and c section
dont do well
Uterine Torsine
Twin horns
Big single
baby gets active
twists horn
twisted gut
C-section
Multifeeders
Cold milk/ice
lambs drink slow
no enterotoxemia
Bose injection
Within 24 hours of birth in palouse
3rd cutting leafy alfalfa
Start babies on solid food
Wean
3-8 weeks
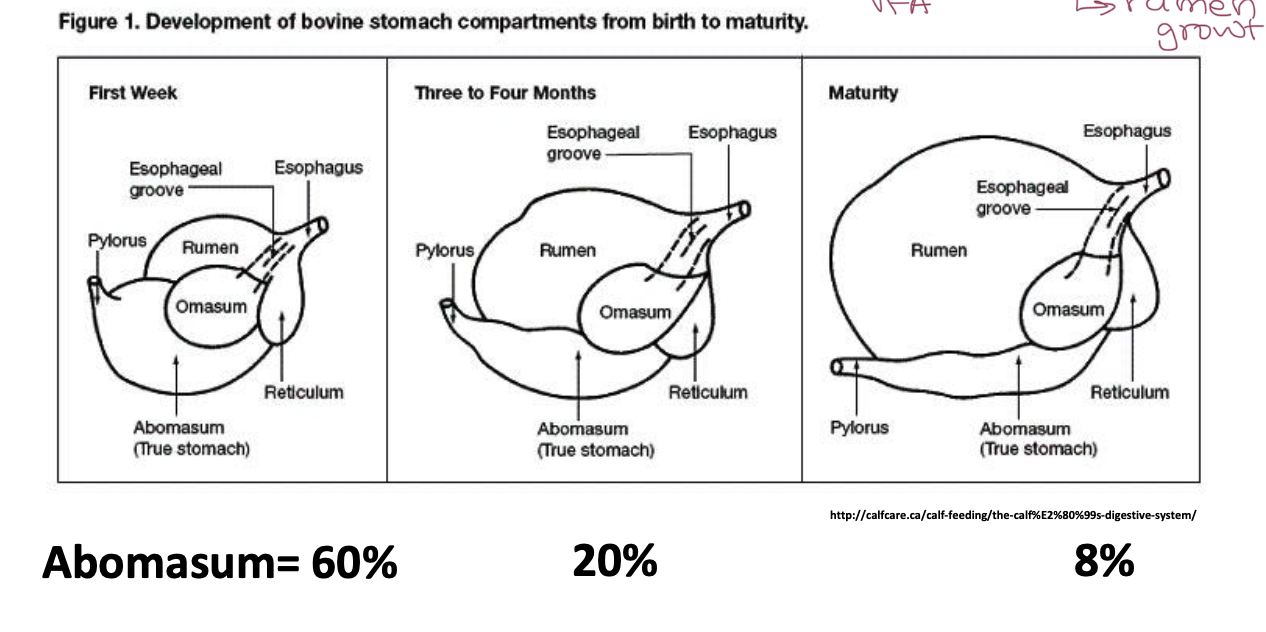
Development of rumen
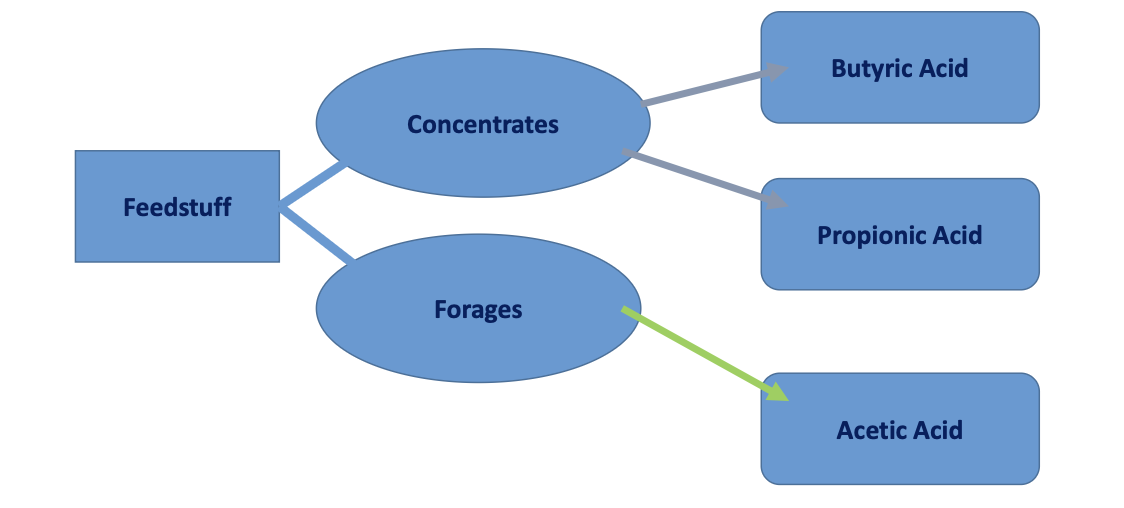
Butyrate Stimulates
Rumen Growth
energy source for rumen wall growth
Propionate and acetate
Energy source for lamb growth
Feedstuff
Rumen Development
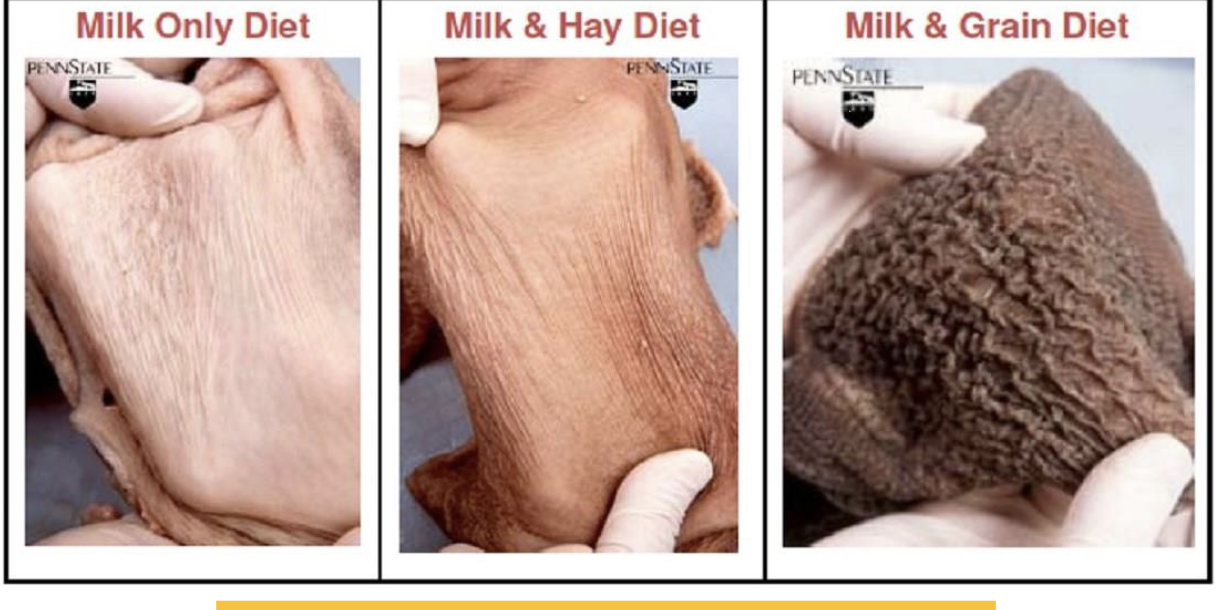
Early weaning - 6 weeks of age
Milk, milk and hay, milk and grain only diets