Bio module 3-cells
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Cytology
the study of cellular function and structure
Plasma membrane
forms a cells surface boundary sh. forms cells shape
Cytoplasm
the material between the plasma membrane and nucleus
parts:
cytoskeleton
organelles
inclusions
cytosol
Cytoskeleton
network of protein filaments and tubules in cytoplasm that structurally support cell
What are the main components of the cytoskeleton?
microfilaments
intermediate filaments
microtubules
What function does the cytoskeleton serve?
determines cell shape
contributes to cell movements
gives cell structural support
organizes content
Organelles
diverse structures that perform tasks for the cell
Inclusions
A nonessential cell component with no membrane that contains accumulated cell products like fats and pigments as well as viruses and bacteria
Cytosol
clear gel containing enzymes and other proteins that embeds the cell components sh. the fluid in the cell
What are the functions of the plasma membrane?
governs interactions with other cells
defines the boundary of the cell
maintains chemical difference between ECF and ICF
contributes to movement of cell components
What is the plasma membrane made up of?
a two layered lipid film with embedded proteins
Phospholipids
make up 75% of membrane lipids
Cholesterol
make up 20% of membrane lipids
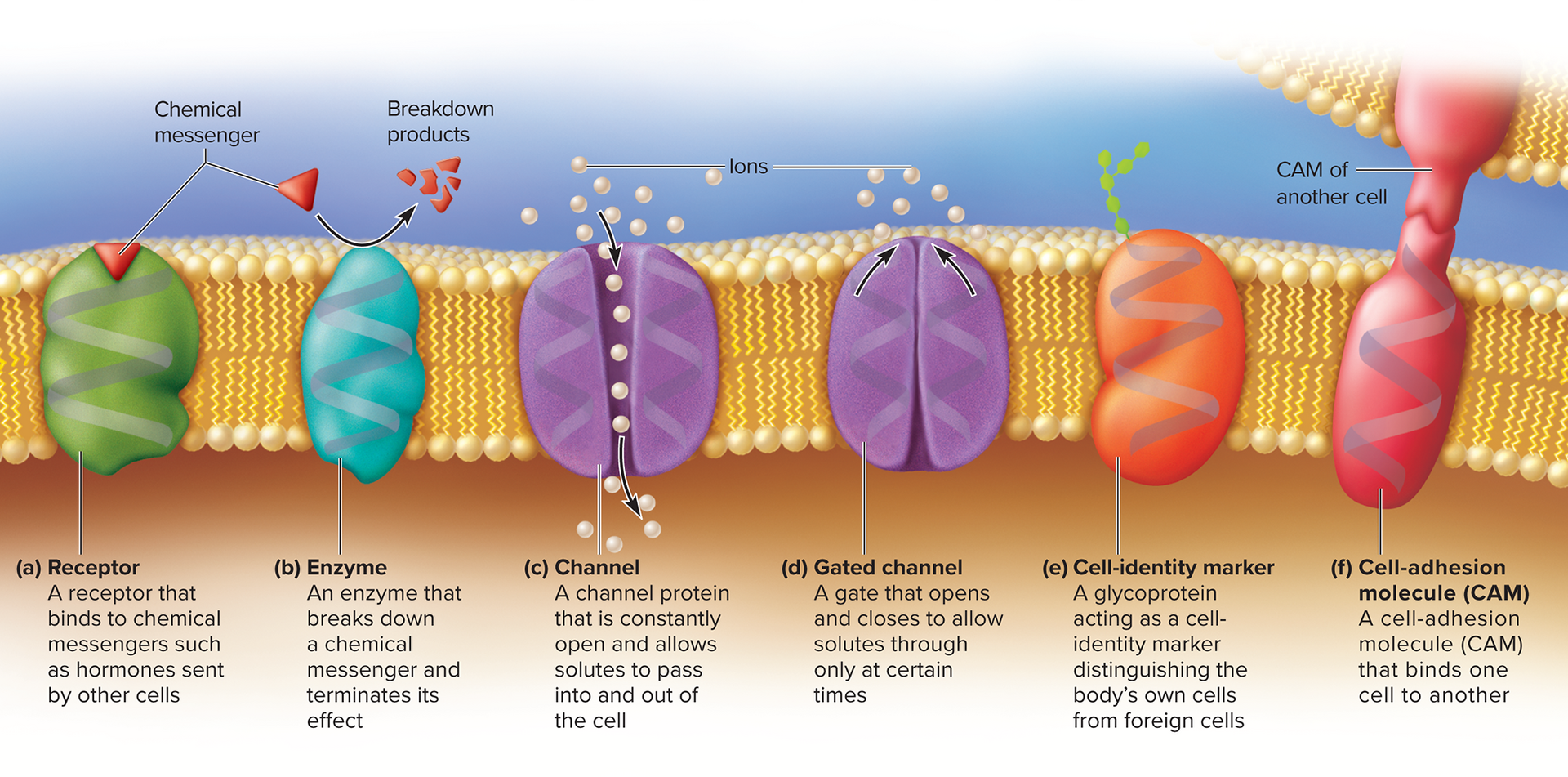
Functions of membrane proteins
receptor
channel
enzyme
gated channel
cell identifier marker
cell adhesion molecule
Glycocalyz
a fuzzy carbohydrate coat covering cells that is made up of the sugar chains glycolipids and glycoproteins
What are the functions of the glycocalyx?
cell adhesive
determines blood types
protects plasma membrane
identifies self-cells from foreign cells
identifies healthy cells from diseased cells
What are the four cell surface extension types?
microvili
cilia
flagellum
pseudopods
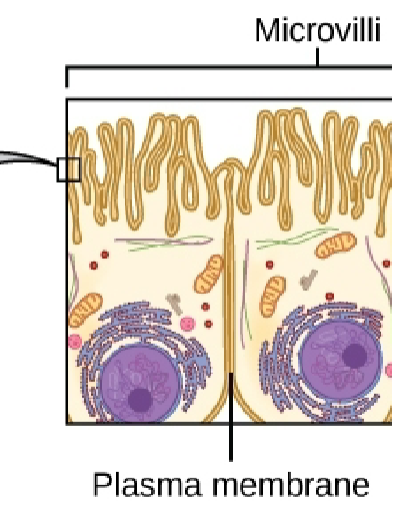
Microvilli
extension with finger shaped projections of the plasma membrane
functions: increases surface area for absorption and secretion
sometimes called a brush border
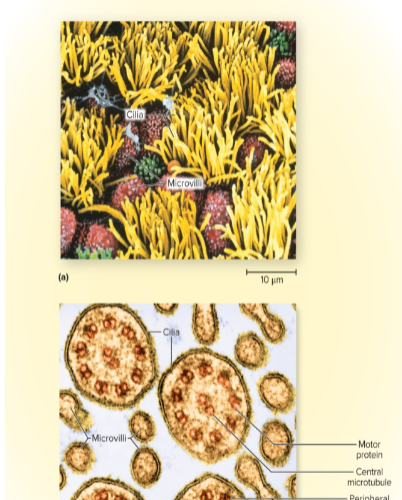
Cilia
hairlike extensions of the plasma membrane that are found in the mucous membranes of respiratory tract and uterine tubes
functions: helps move things like mucus
ex. move mucus from lungs up to throat
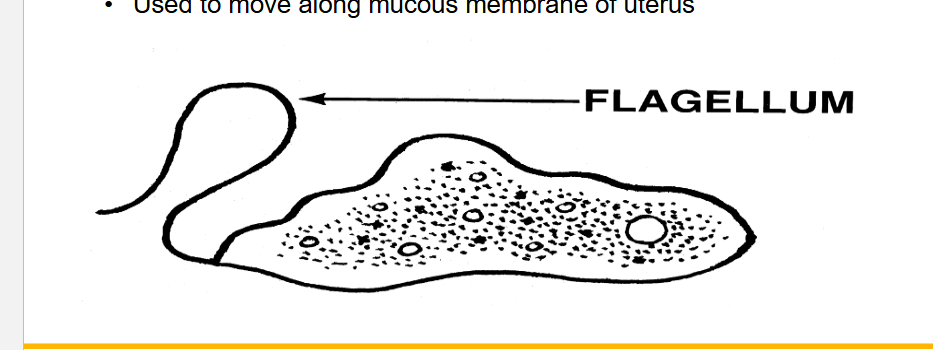
Flagellum
extensions that resemble a long and solitary cilium
sh. essentially a tail attached to a cell
function: helps cell move
Pseudopods
cytoplasm filled extensions of a cell that change shape continually
function: form fake arms that play a role in movement and help cells to eat
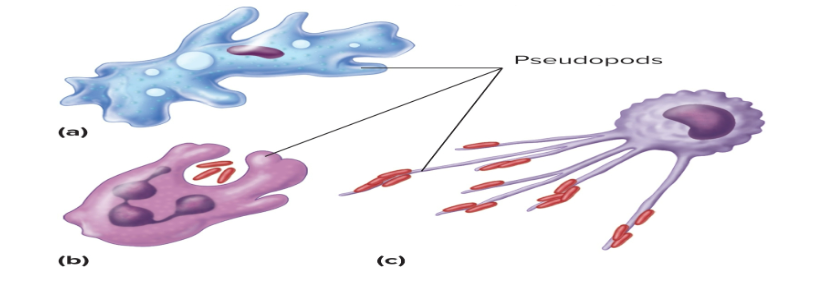
What are the functions of extensions?
absorption
movement
sensory processes
phagocytosis
Macrophages
white blood cells that use pseudopods to engulf bacteria
What are the functions of cell junctions?
link cells together
attach cells to extracellular material
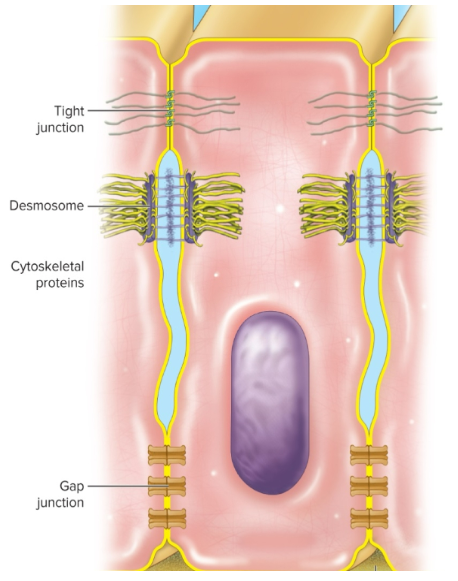
Tight junctions
these junctions fully encircle epithelial cells near upper end and join them securely to adjacent cells making it difficult for substances to leak between
ex. ensures absorbed nutrients pass through digestive system cells and not around them
Desmosomes
holds cells together at a specific point and keeps them from pulling apart. enables tissues to resist mechanical stress.
ex. common in skin and cardiac muscles
Gap junctions
formed by ring of proteins that surround a channel and is used for the diffusion of ions, glucose, and other solutes.
Filteration
A process in which external pressure forces fluid through a selectively permeable barrier and holds back large particles while allowing water and small particles to pass through.
sh. the passage of fluid
Simple diffusion
the net movement of particles from high to low concentration with random motion of molecules providing energy for diffusion.
ex. simple diffusion seeks to achieve balance
ex. how oxygen and steroid hormones reach cells
Osmosis
the net movement of water from lower to higher solute concentration (water follows solutes)
Tonicity
the ability of a solution to change intracellular pressure and the volume and shape of a cell
Isotonic
extracellular fluid has an equal concentration of solutes as the intracellular fluid
cells gain and lose water by an equal rate sh. cell does not change shape
Hypertonic
extracellular has a higher concentration of solutes than intracellular fluid
draws water out of cell and cell shrinks
Hypotonic
extracellular fluid has a lower concentration of solutes than intracellular
water enters cell and cell swells
Active transport
like facilitated diffusion, is a carrier mediated transport
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
Active transport requires ATP (energy) while passive transport does not
Vesicular transport
substances move through membranes in vesicles (resemble bubbles or sacs)
Endocytosis
brings matter into cell
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis that is “cell eating” and uses pseudopods to reach out and surround particles, enzymatically degrading it
occurs especially in macrophages (white blood cells)
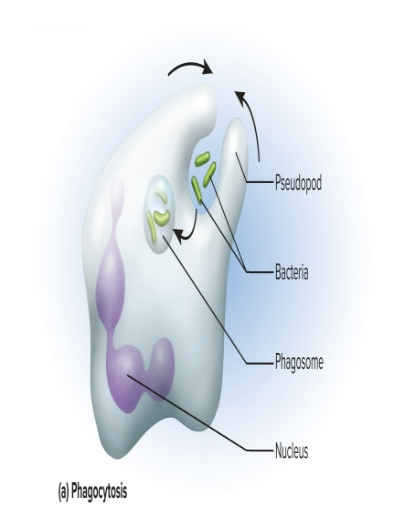
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis that is “cell drinking” that starts off with the formation of dimples that cave in and pinch off as vesicles
Receptor mediated
This type of endocytosis is more selective, and the cell can take in specific molecules from the ECF through receptor proteins on plasma membrane
ex. absorption of insulin from blood
Exocytosis
exports matter from cell
How does exocytosis occur?
cell vesicle migrates to surface, fuses with plasma membrane and ruptures, releasing products from the cell
Facilitated diffusion
a carrier mediated transport that employs carrier proteins to move solutes down a concentration gradient
Nucleus
the largest and most important organelle that stores chromosomes and DNA and gives out orders to maintain organization within the cell
Nuclear envelope
two parallel membranes, perforated by nuclear pores, that surround the nucleus
Nucleoli
dense masses within the nucleus where subunits of ribosomes are made
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
a system of interconnected channels called cisternae that is enclosed by a membrane
functions: synthesizes steroids and other lipids, manufactures cell membranes, and produces proteins
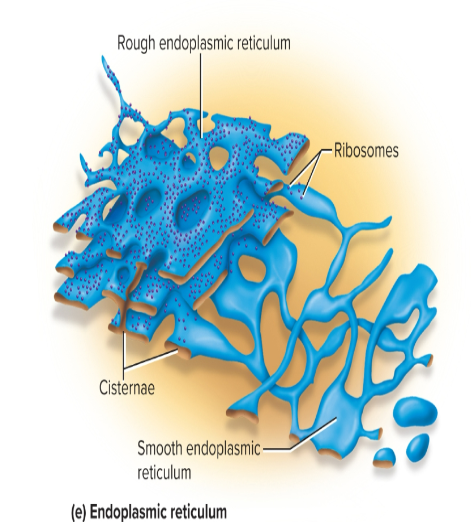
Rough ER (RER)
cisternae is covered with ribosomes
abundant in cells producing proteins
function: the synthesis of proteins
Smooth ER (SER)
lack ribosomes
continuous with rough ER
abundant in cells that synthesize steroid hormones like testes, ovaries
function: helps with detoxification and stores calcium
Ribosomes
small granules of protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA) that read the genetic code from the nucleus and assemble amino acids into proteins
function: the synthesis of proteins
location: nuclear envelope, rough ER, and free in cytoplasm
Golgi complex
A small cluster of cisterns that synthesize carbohydrates and put the finishing touches on protein and glycoprotein synthesis
sh. reshapes or changes proteins sent from ER
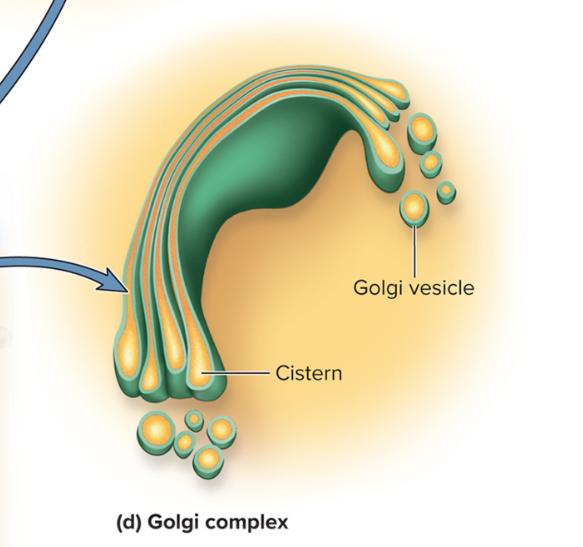
Golgi vesicle
membranous sacs
filled with secretory product
some become part of plasma membrane
others become secretory vesicles that store products released by exocytosis
sh. allow cisternae to receive and release proteins
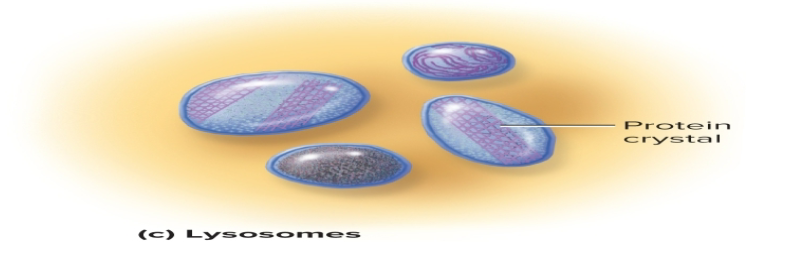
Lysosomes
packages or sacs of enzymes enclosed within a membrane that store “good” products and help carry out apoptosis (programmed cell death)
Mitochondria
A double membrane organelle that synthesizes ATP and has its own DNA while its inner membranes cristae (folds) synthesize enzymes
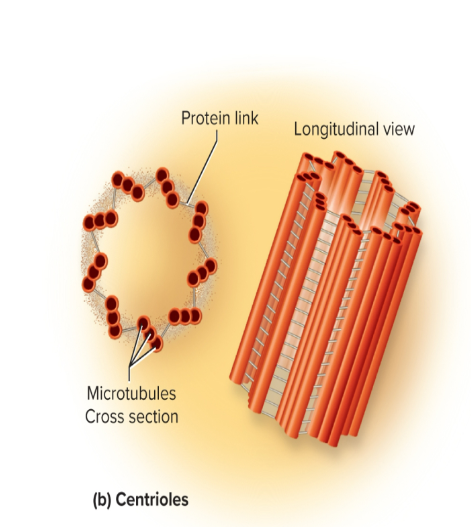
Centrioles
an organelle with a short cylindrical assembly of microtubles
function: plays a key role in cell division
What are the two types of cells?
somatic cells
sex cells
Mitochondrial matrix
the space between the cristae that contain enzymes, ribosomes, and mitochondrial DNA
Centrosome
area of cytoplasm near nucleus that contains a pair of centrioles
True or false: all cells arise from existing cells and divide giving us new cells
true
What are the four phases and functions of processes within the life cycle?
G1 first gap phase
interval between cell division and DNA replication that prepares for new division by synthesizing proteins and packing itself with nutrients for DNA replication
Synthesis phase
where DNA replication occurs
G2 second gap phase
interval between cell division and DNA replication where centriole replication finishes along with the synthesis of enzymes that control cell division
Mitotic (M) phase
where the nucleus replicates and mitosis occurs
What are the four phases of the Mitosis?
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
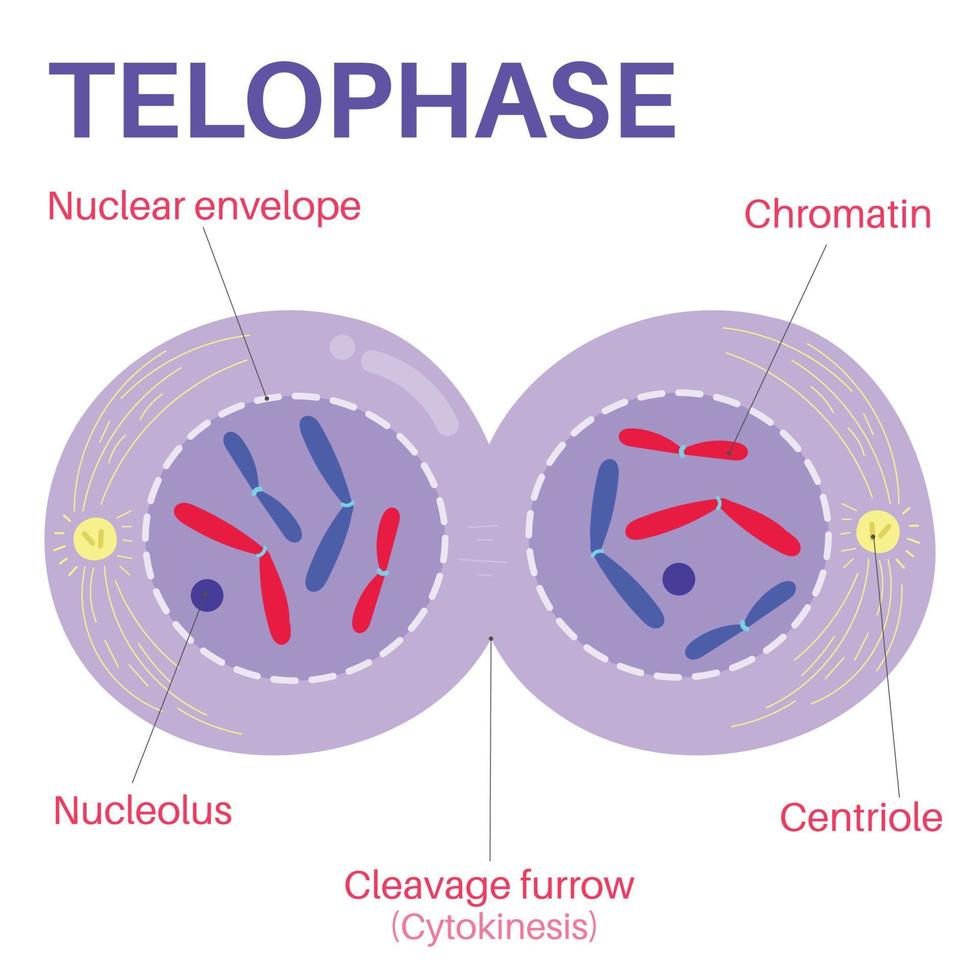
telophase
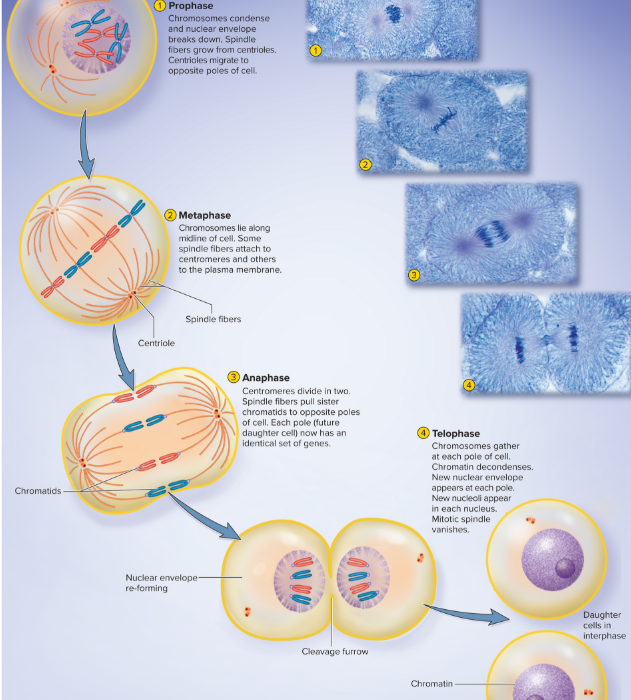
Cytokinesis
when the cytoplasm divides and the cell divides forming two genetically identical daughter cells
ex. occurs during telophase
telophase:
chromosomes gather at each pole of cell
chromatin decondenses
new nuclear envelope appears at each pole
new nucleoli appear in each nucleus
mitotic spindle vanishes
What is mitosis cell division used for?
growth
fertilized egg into individual'
continues growth of organs after birth
repairs damaged tissues