Biochemistry Final Module
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
In amino acid metabolism, alanine is broken down to make ___________.
pyruvate
In amino acid metabolism, glutamate and glutamine are broken down to make ___________.
a-ketoglutarate
In amino acid metabolism, aspartate is broken down to make ___________.
oxaloacetate
In amino acid metabolism, pepsin breaks down proteins in the ___________.
stomach
In amino acid metabolism, trypsin and chymotrypsin break down proteins and larger peptides in the ___________.
small intestine
In amino acid metabolism, aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase A + B break down small peptides to amino acids in the ___________.
small intestine
Small peptides are broken down into individual amino acids by ______________ and _____________.
Aminopeptidase ; carboxypeptidase A + B
Amino acid breakdown from non-dietary proteins occurs in three places:
The liver, extra-hepatic tissue, and muscle
Glutamine transports 2 units of _____________.
ammonia
The glucose-alanine cycle converts pyruvate to ________________.
alanine
Glutamate picks up 1 ____________ in the liver.
amino group
Which steps of the urea cycle use ATP and how many are used in each step?
Step 1: 2 ATP
Step 2: 1 ATP
Step 1 of the urea cycle is catalyzed by what enzyme?
ornithine transcarbamoylase
Step 2 of the urea cycle is catalyzed by what enzyme?
argininosuccinate synthetase
Step 3 of the urea cycle is catalyzed by what enzyme?
arginase
Step 4 of the urea cycle is catalyzed by what enzyme?
argininosuccinase
Triacylglycerols are __________ lipids.
storage
Phospholipids and glycolipids are __________ lipids.
membrane
Fatty acids contain how many carbon atoms (range)?
4 - 36
Saturated fatty acids have ____ C=C bond(s).
0
Monounsaturated fatty acids have ____ C=C bond(s).
1
Polyunsaturated fatty acids have ____ C=C bond(s).
2+
How would you label a fatty acid that is 18 carbons long and has a double bond on carbon 9?
18: 1Δ9
How would you label a fatty acid that is 18 carbons long and has double bonds on carbons 9 and 12?
18: 2Δ9, 12
When numbering double bonds on fatty acids, start numbering from the __________ end.
carboxylic acid
What are triacylglycerols made of?
Three fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule
What determines the surface properties of membrane lipids?
Head group substituents
What are membrane lipids made of?
Fatty acid chains, a glycerol molecule, and a phosphate group (varying substituents)
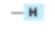
What membrane lipid has this head group?
Phosphatidic acid

What membrane lipid has this head group?
Phosphatidylethanolamine
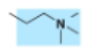
What membrane lipid has this head group?
Phosphatidylcholine
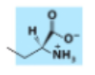
What membrane lipid has this head group?
Phosphatidylserine
Cerebrosides contain ______ carbohydrate(s), while gangliosides contain ______ carbohydrate(s).
1 ; 2-4
What kind of lipid contains blood group determinants?
Glycosphingolipids
What kind of lipid is always made up of ring structures?
Sterols
What kind of fatty acid has a very high melting point?
Trans fatty acids
What kind of fatty acids are able to pack tightly together?
Saturated fatty acids
What kind of fatty acids are not able to pack together tightly and are usually kinked?
Unsaturated fatty acids
Do saturated or unsaturated fatty acids have a higher melting point?
Saturated
What is transbilayer diffusion?
When a lipid moves from one side of the membrane to the other
What is lateral diffusion?
What a lipid moves from one location to another on the same side of the membrane
What is the fluid mosaic model in membranes?
Proteins + lipids embedded in the membrane are free to move laterally within the plane of the membrane
What is oxidation of fatty acids and what does it provide?
“Burning” of fatty acids to provide energy
Why is fat good for energy?
Fatty acids have a lot of carbons that are reduced (electrons) and carry more energy
What molecules are used for short-term energy needs?
Glucose and glycogen
What molecules are used for long-term energy needs?
Fats
What does epinephrine release signal?
The body needs energy immediately
What does glucagon release signal?
The body is out of glucose
Where does B-oxidation of fatty acids occur?
The mitochondria
Can fatty acids diffuse freely across mitochondrial membranes?
Yes, if they are small (<12 carbons)
How are large fatty acids transported across mitochondrial membranes?
The carnitine transporter
How are fatty acids activated for transport?
By adding a good leaving group using fatty acyl-CoA synthetase
Adding Acyl-CoA to a fatty acids makes:
An activated fatty acid
Activated fatty acids are trans-esterified to _____________.
acyl carnitine
What is both the committed step and the rate-limiting step in B-oxidation?
Carnitine-mediated import
The carnitine shuttle links two pools of ___________ and ___________.
acyl-CoA and CoA
B-oxidation consists of _____ reactions per round.
4
What is removed with each round of B-oxidation?
One acetyl group (2C) as acetyl-CoA
In the 4 steps of one round of B-oxidation, what four kinds of enzymes are used in order?
1) Dehydrogenase, 2) hydratase, 3) dehydrogenase, 4) acetyltransferase
B-oxidation processes fatty acids that are at least _____ carbons long.
12
The number of acetyl-CoA molecules produced from fatty acid metabolism will always be ______ the amount of starting carbons.
half
There will always be ______ less rounds of fatty acid metabolism than the number of acetyl-CoA molecules produced.
one
7 rounds of fatty acid metabolism would result in _______ NADH and ______ FADH2.
7 ; 7
What must occur for monounsaturated fatty acids before they can undergo B-oxidation?
Cis C=C bond must be converted into a trans C=C bond through isomerization reaction
What must occur for polyunsaturated fatty acids before they can undergo B-oxidation?
They must be reduced and then undergo an isomerization reaction
Odd-numbered fatty acids have what molecule leftover after the last acetyl-CoA is removed?
Propionyl-CoA
Burning fat makes acetyl-CoA which is ultimately recycled to make ________.
ATP
When the body is starved, the liver turns on the process of _______________.
gluconeogenesis
Why is glucose necessary in the body?
For the brain to run all of its processes
The process of gluconeogenesis depletes _____________.
oxaloacetate
What cycle cannot be run without oxaloacetate?
The citric acid cycle
What molecule builds up when the citric acid cycle is not run?
acetyl-CoA
When there is a build-up of acetyl-CoA, __________ runs out.
free CoA
When there is no free CoA for the body to use, what process cannot be run?
B-oxidation
What can the liver produce to replenish CoA pools?
Ketone bodies
____________ is the first ketone body molecule made.
Acetoacetate
The presence of ___________ in the breath occurs with the creation of ketone bodies.
acetone
What molecule is the building block for fatty acid synthesis?
Malonyl CoA
Where does fatty acid synthesis take place?
In the cytosol (high NADPH concentration)
What does breakdown of ketone bodies create?
Molecules such as succinate, acetyl CoA, etc. that can be used in the citric acid cycle to create ATP
Fatty acid synthesis is a __________ reaction, whereas fatty acid breakdown is a ___________ reaction.
anabolic ; catabolic
The 4 reactions that happen in fatty acid degradation are:
Oxidation → Hydration → Oxidation → Cleavage
The 4 reactions that happen in fatty acid synthesis are:
Condensation → Reduction → Dehydration → Reduction
Acetyl-CoA + CO2 → ___________
Malonyl CoA
What regulates the rate limiting step in the formation of Malonyl CoA?
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Biotin acts as the carrier of ________.
CO2 (can be transferred to Acetyl CoA)
What is the active group in fatty acid synthesis?
A thiol
The fatty acid synthase enzyme involves ______ protein(s) and ______ active site(s).
1 ; 7
What protein will swing into each active site in fatty acid synthase?
The acyl carrier protein (ACP)
Fatty acid synthesis terminates at how many carbons?
16C
How many ATP are made during the synthesis of 1 fatty acid?
~106
How many ATP are used during the synthesis of 1 fatty acid?
~30
What inactivates fatty acid synthesis?
Phosphorylation
What allosterically activates fatty acid synthesis?
Citrate