Cell Transport & Vesicle Trafficking: Golgi, Endocytosis, and Lysosomes
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
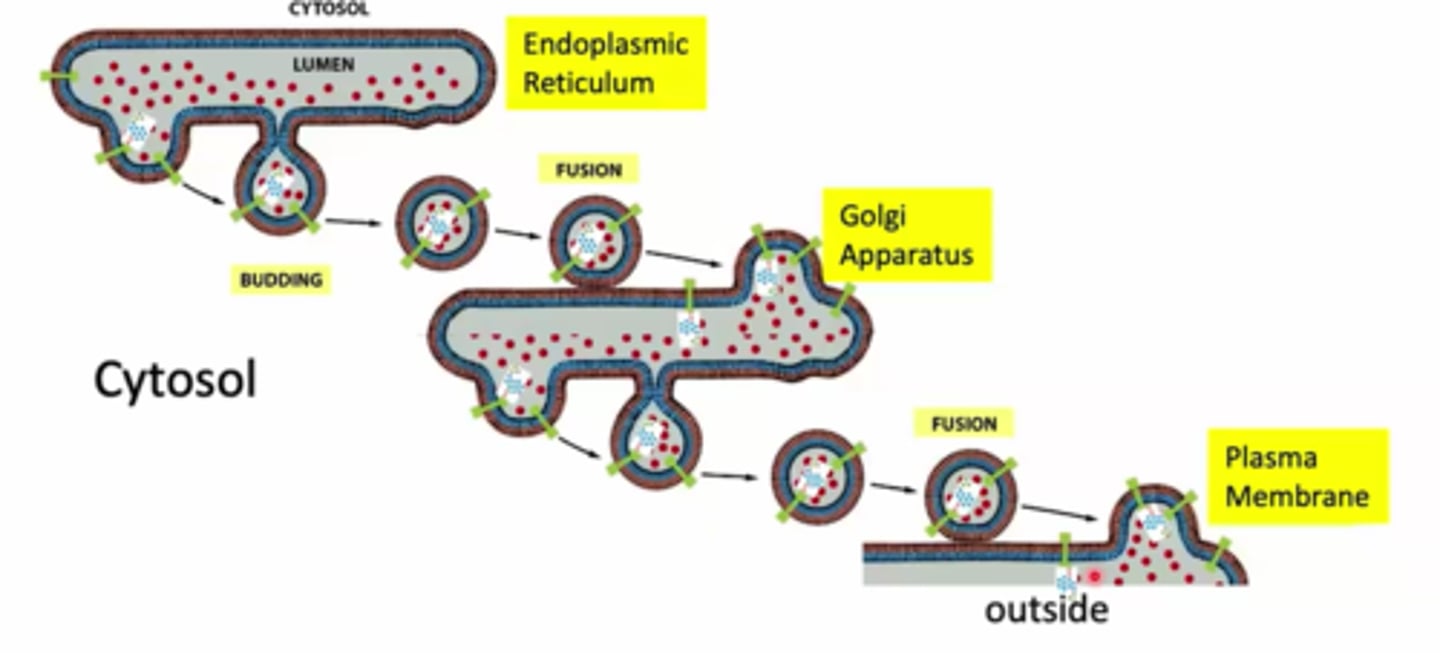
overall pathway
go from ER, sorted in golgi, released to cytosol or plasma membrane
vesicles trnasport proteisn from one ogrnalelle to antoher
vesicle traansports selectivity
only certain proteins incorporated into transport vesicles
maintain topolyg
how are the lumen or the ER of the vesicles organized
lumen of ErR, transport vesicles, golgi correspond toplogically to
how are n linked glycosylation oreinted
on the lumenal side, topologically on the "putside of the cell"
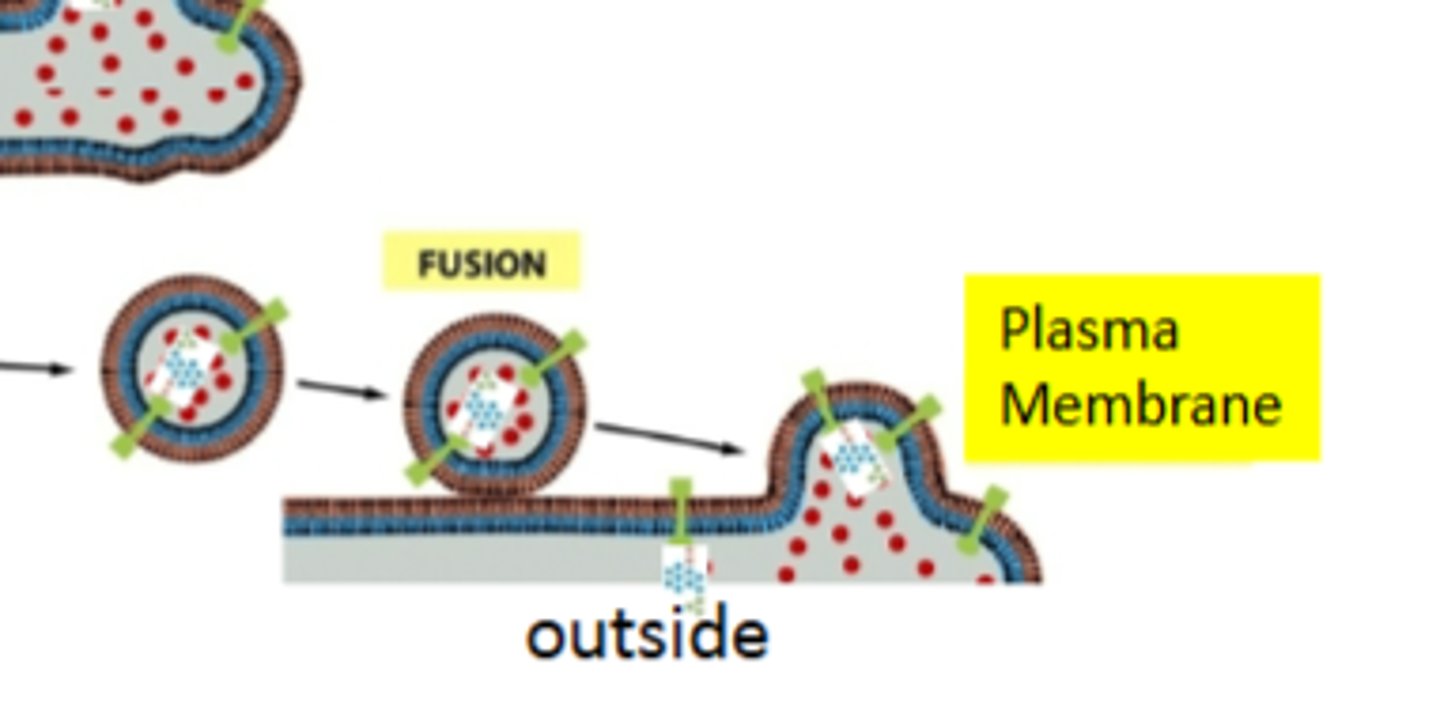
lifecycle of a transport vesicle:
budding, movement, tethering and fusion
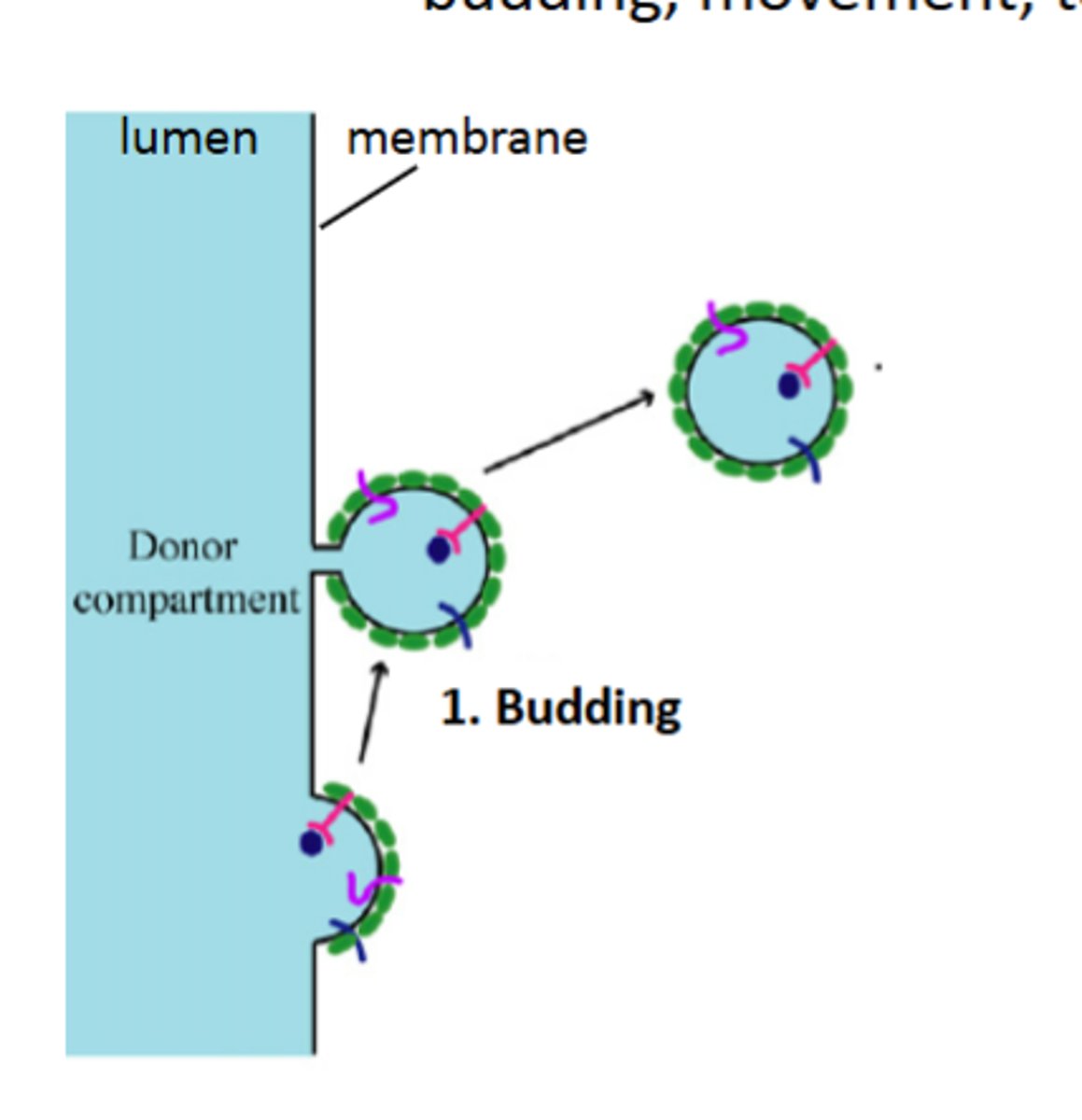
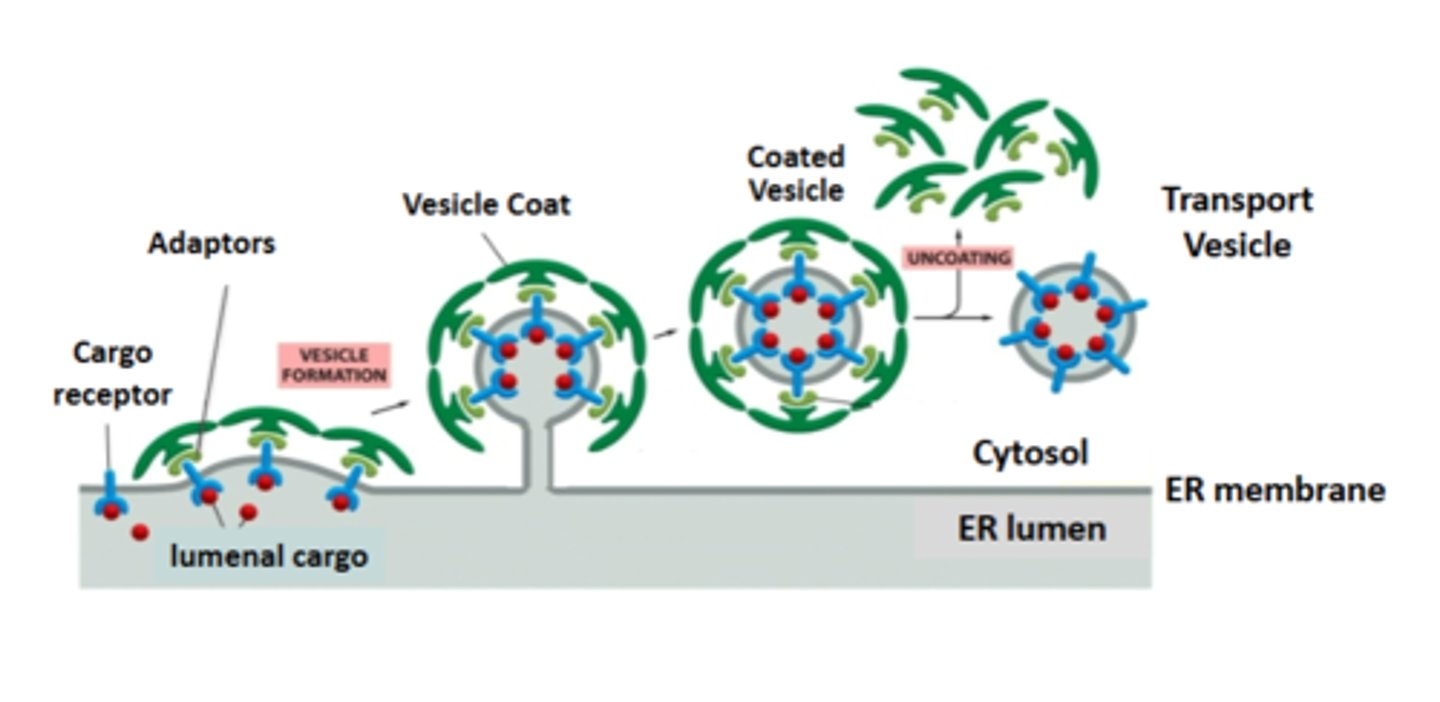
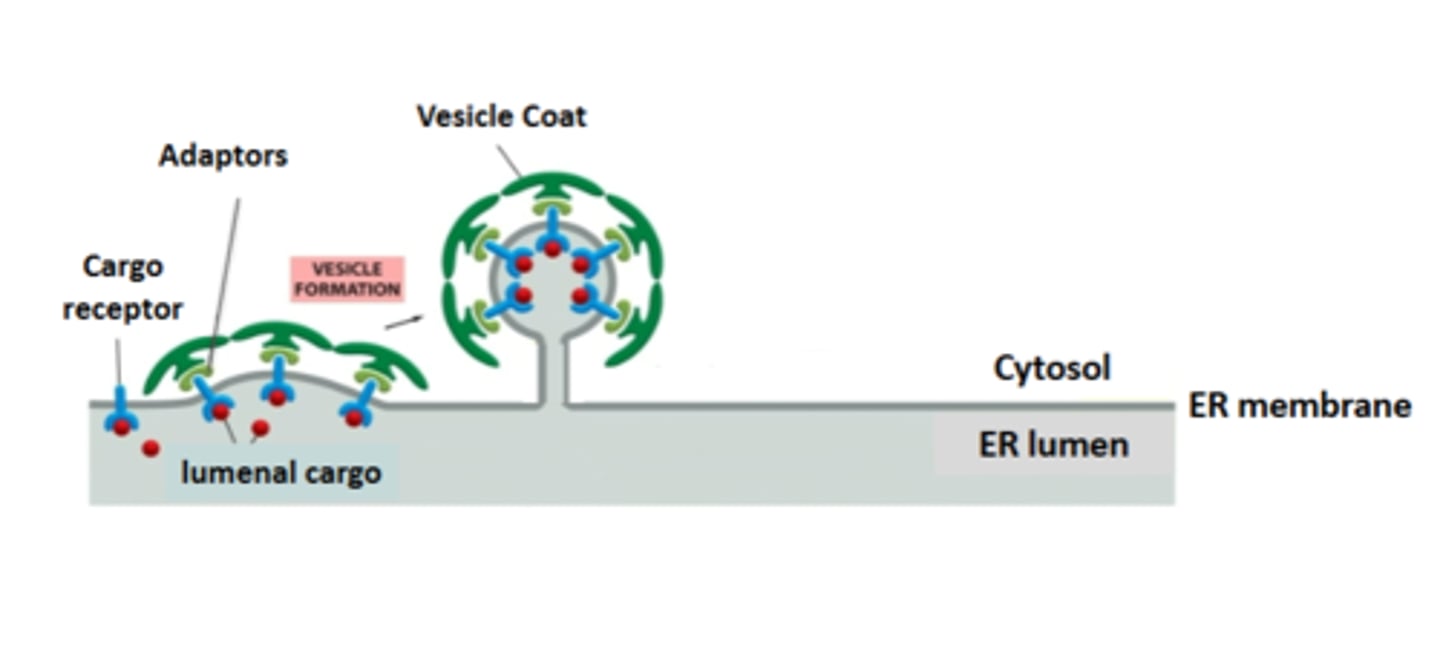
vesicle budding steps first step
1. cargo receptors bind to the lumenal protein (cargo) to be transported
2. cargo adaptors bind to the sorting signal in the cytosolic tails of the cargo receptors ( or other trasmembrane proteins transported as cargo)
3. coat proteins bind cargo adaptors shaping the membrane into a vesicle
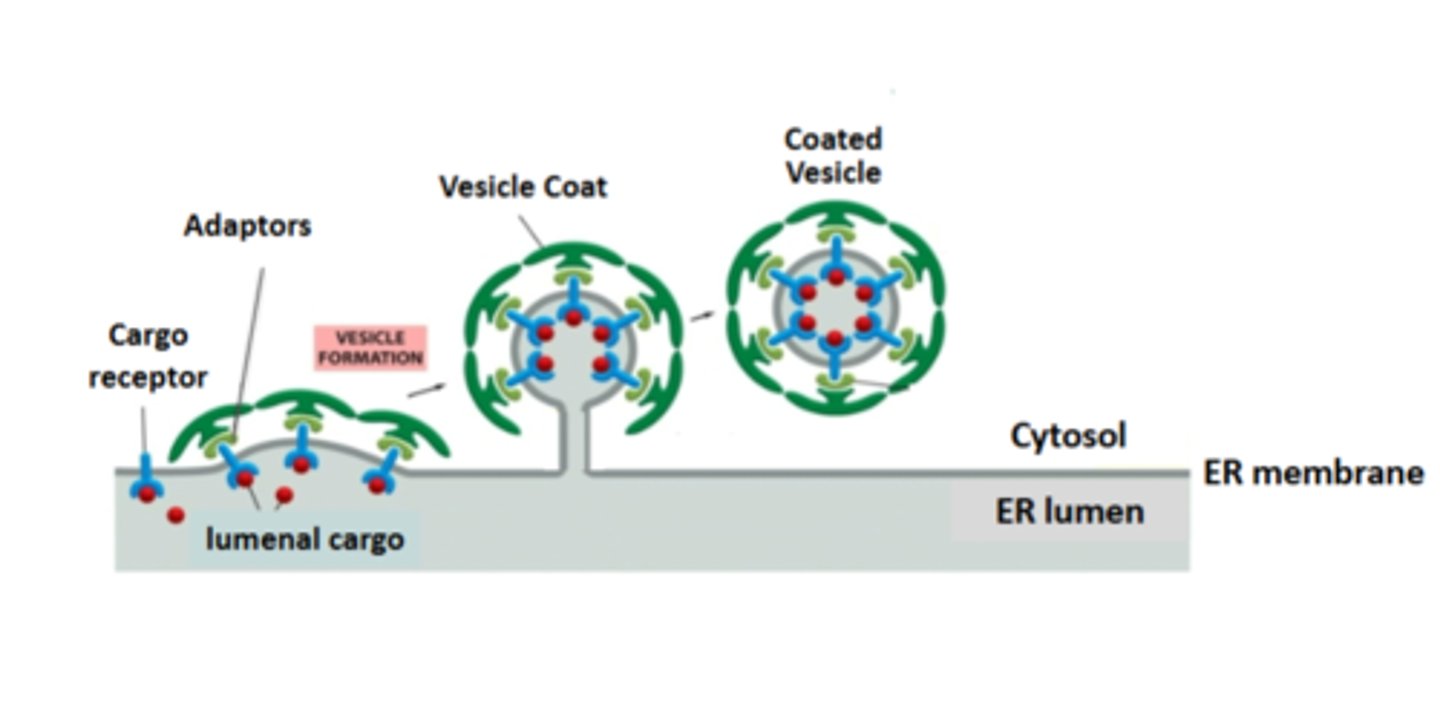
4. the fully formed cot drives the separation of the vesicle from the membrane
5. the vesicle is uncoated and ready to fuse with a target membrane
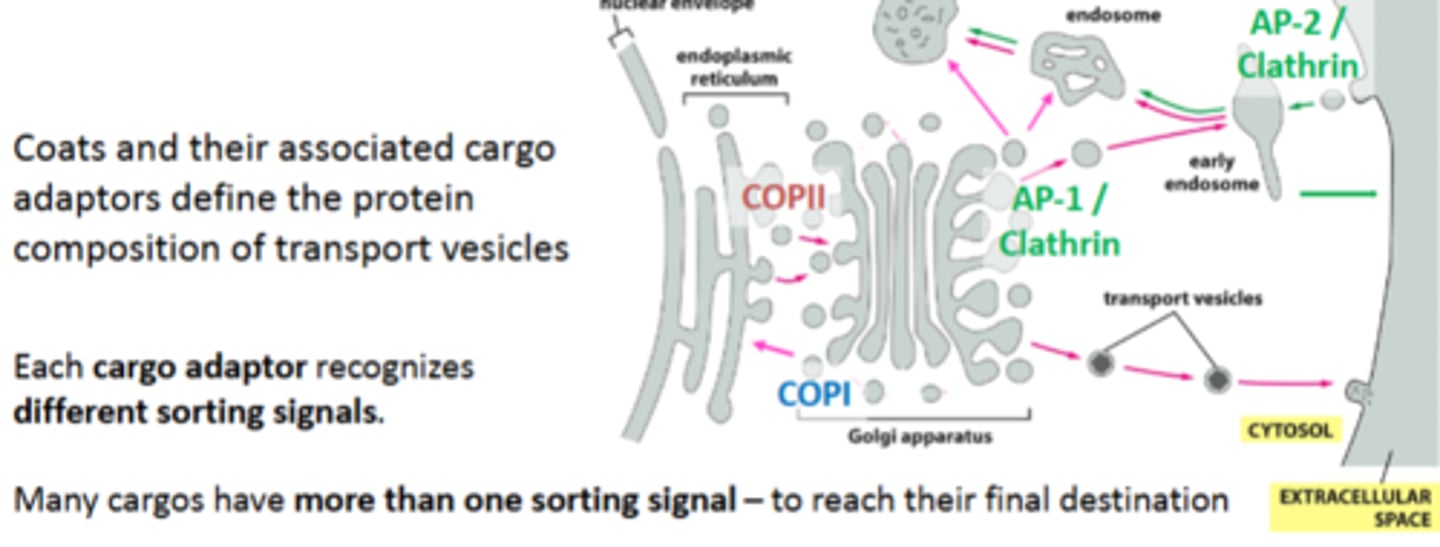
purpose of different coats / adaptors
mediate the transport of vesicles from and to different organelles
coats define the protein composition of transport vesicles
each cargo adaptor recognizes different sorting signalss
many cargos have more than 1 sorting signal, to reach their final destination
thirs step of vesicle budding
coat proteins bind cargo adaptors shaping the membrane into a vesicle
4th step of vesicle budding
the fully formed cot drives the separation of the vesicle from the membrane
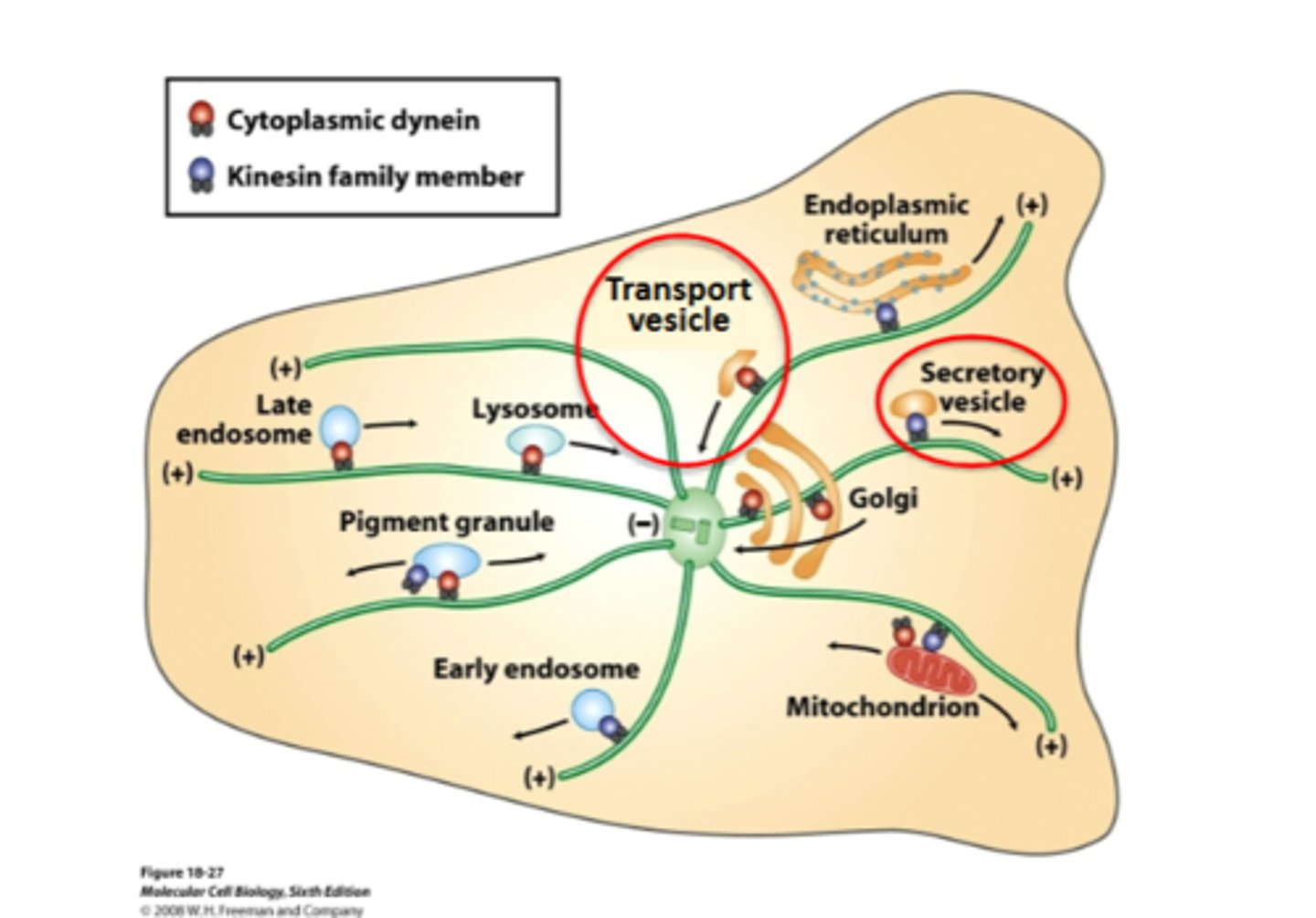
vesicle movment
many vesicles are moved along microtubules by molecular motors
Rab GTP binding proteins
many organelles and vesicles are connected to motors by them
also important for tether
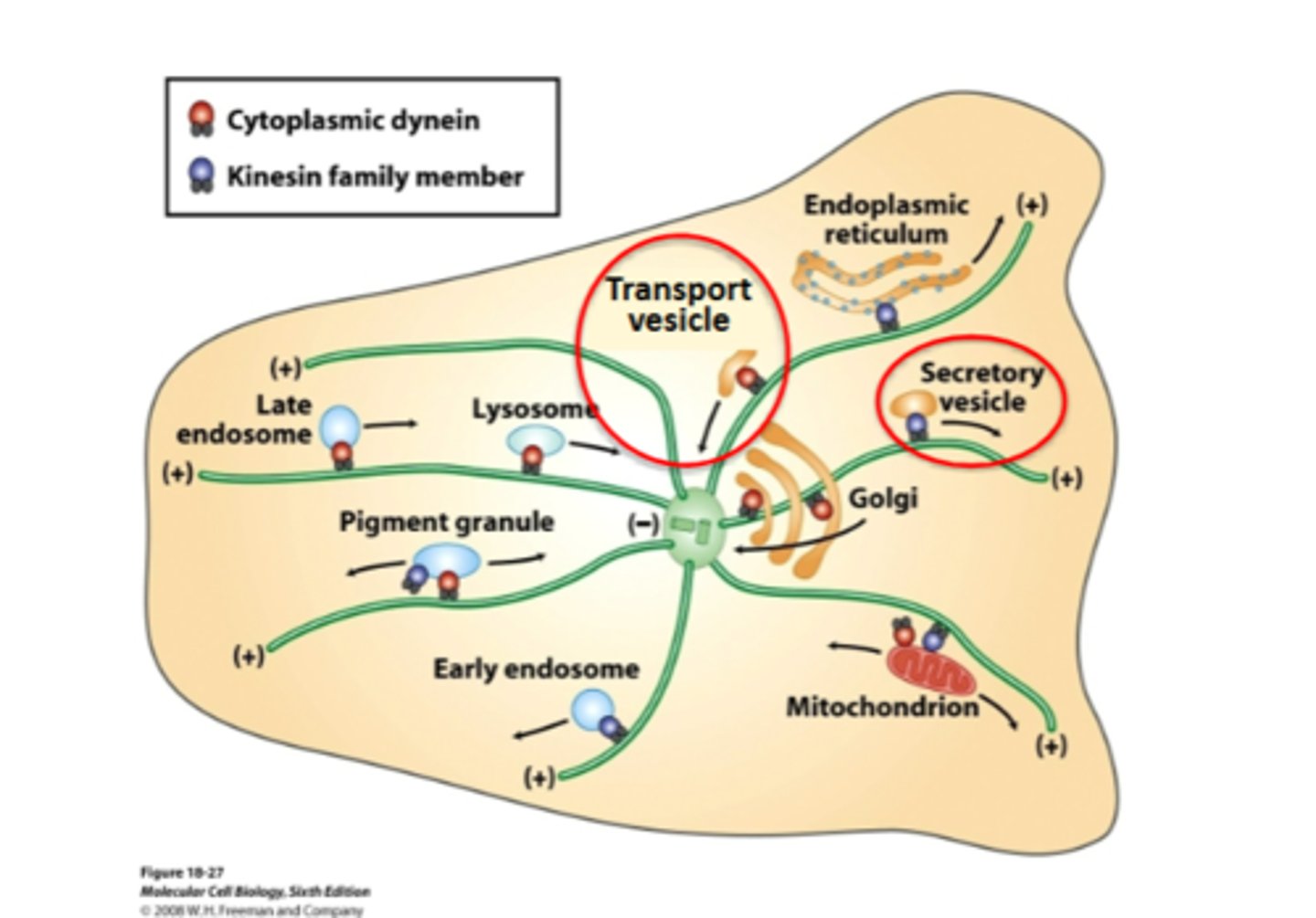
how does movment happen in the trnasport vesicle
active trasport through the cytoskeleton
tethering of vesicle steps
RAb GTPase binds to tether proteins
what happens during fusion
vesicle fusion: SNARE proteins drive the fusion of transport vesicles with their target membrane
zipper formation between t and v-snares sequeezes the vesicle into the target membrane
v and s snare have high affinity for eachother , like to bind
steps of fusion
funtions of the golgi
1. modify of the n-linked oligosaccharide chains
2. sorting proteins to multip;e destinations in the trans golgi network
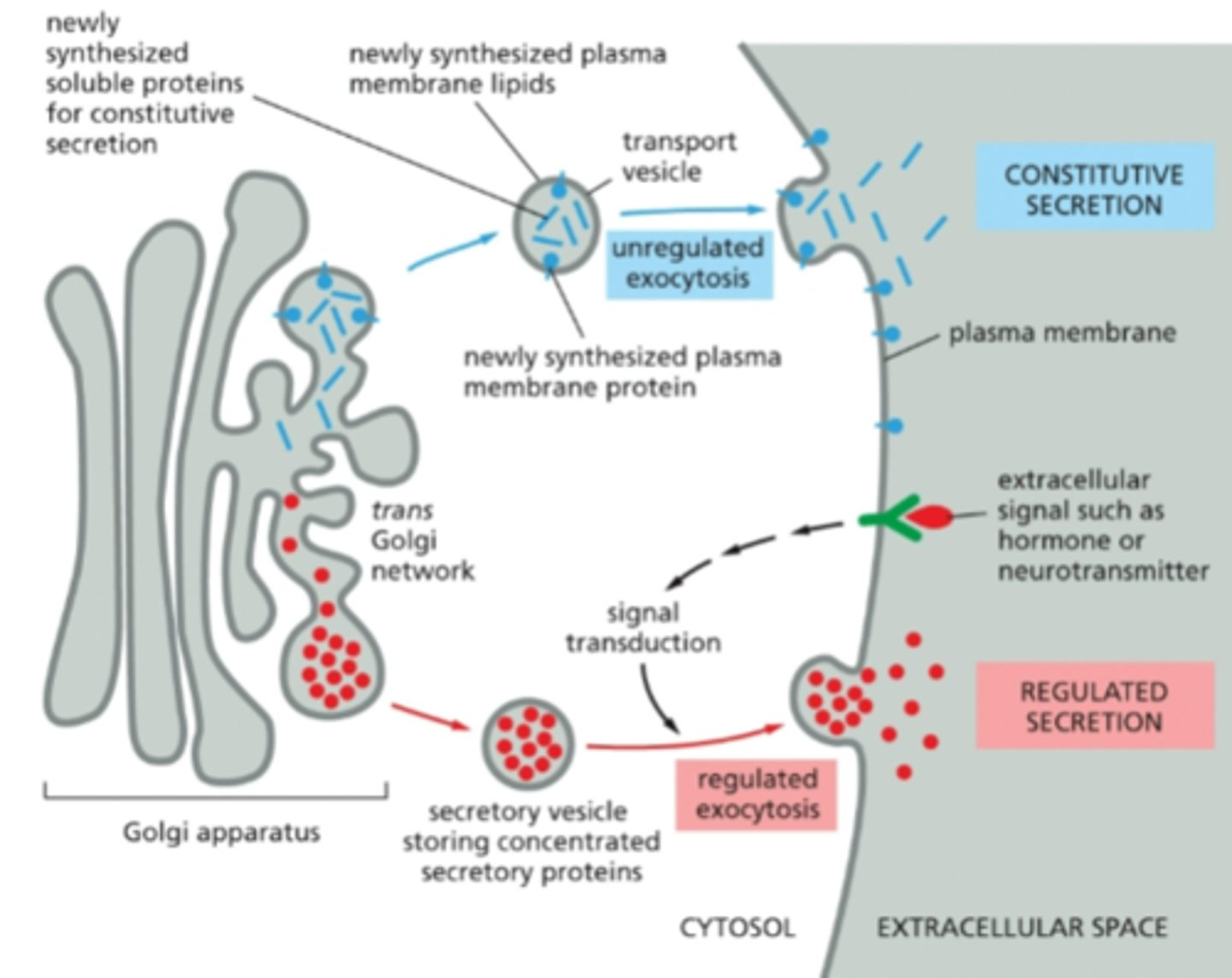
where are secretory components sorted
in the TGN for constitutive and regulated secretion (exocytosis)
unregulated secretion
consecutive secretion, continuously packed and fuse with plasma membrane and secreted by exocytosis
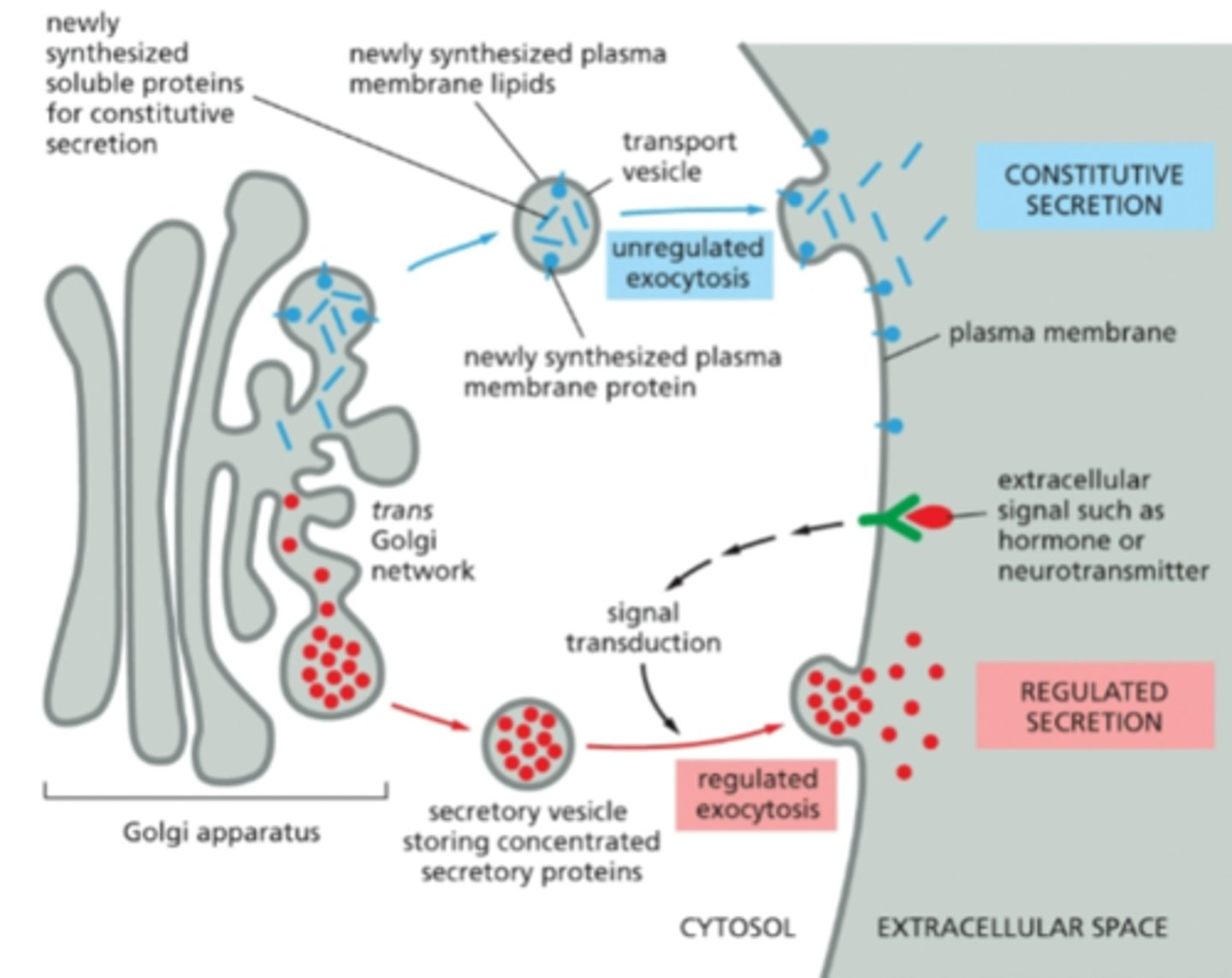
regulated secretion
also respond to signals have secretory vesicles, oly a few trasal transduction membranes, , then release when needed
selective transport to the golgi complex by what
COPII vesicles
summary of golgi journey
protein synthesis on rough ER , profetin folding and n linked hycosylation occurs
selective transport to golgi by COPII
modification sorting transport out ogf golgi
transport delivery and fusion at destination
endocytosis
the uptake of material by the invagination of the plasma membrane
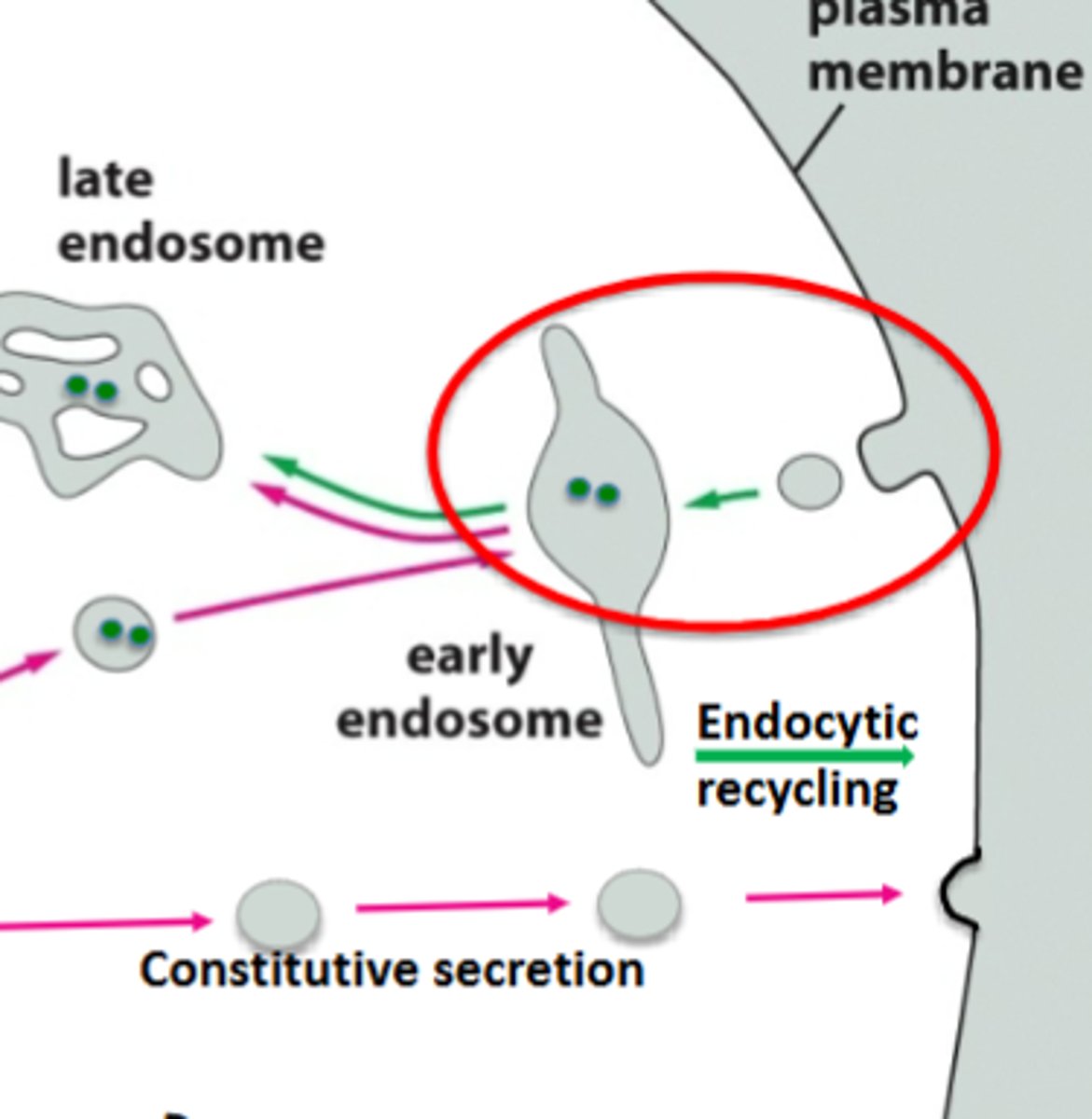
endocytosis process
the LDL receptor on the cell surface binds LDL and internalizes it through clathrin coated pits
LDLs recorgnized by AP-2 cargo adaptors and clatherin coated proteins, deform membraen , form clathrin coated vesicle
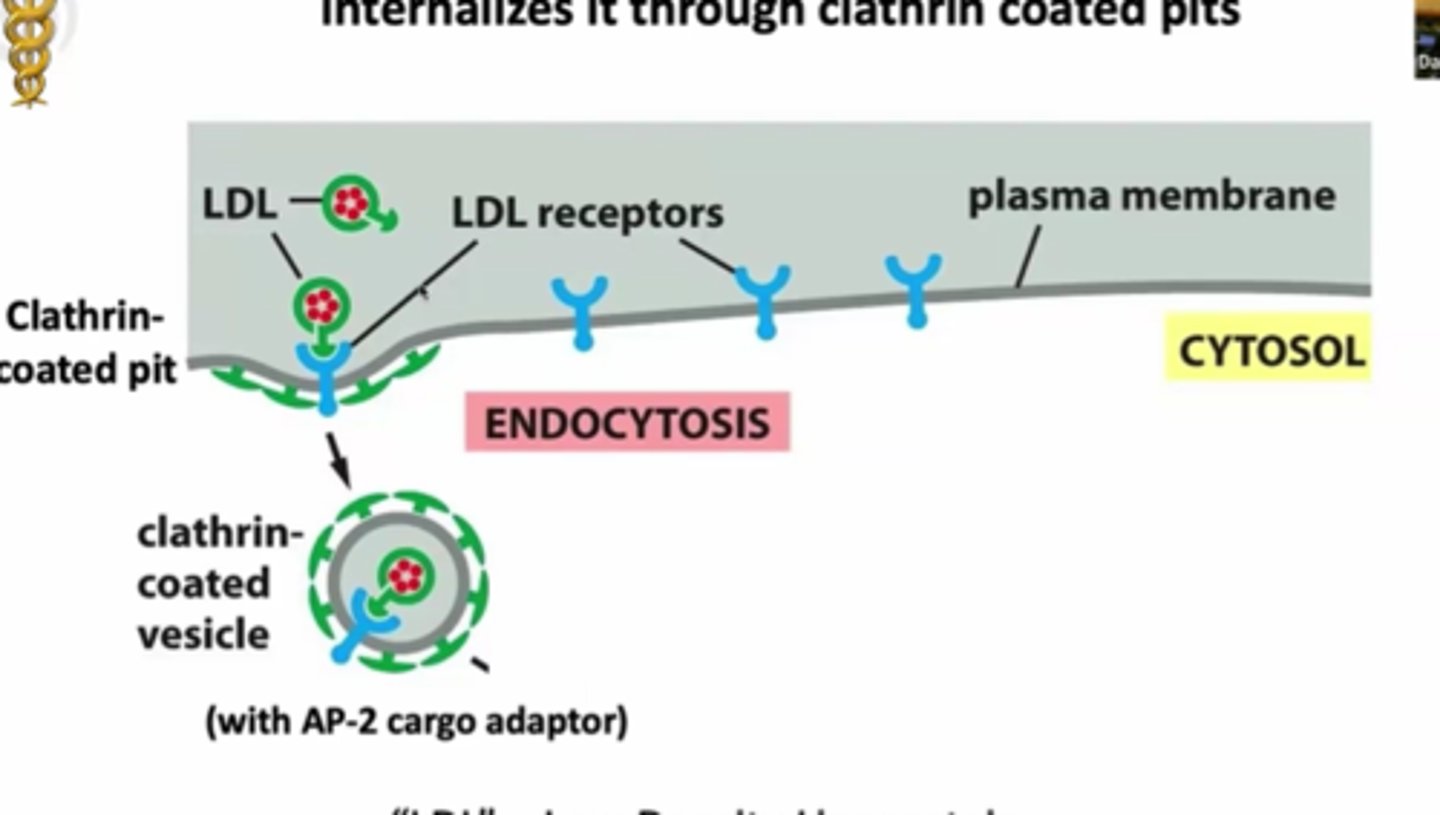
what is LDL
low desntiy lipoprotein : particle made of proteins , lipids , used by body to transport fat lipids and chloestrol through blood stream
what is LDL uptake an example of
receptor mediated endocytosis
after uncoating, can fuse with endosome, LDL particle removed from receptor, then LDL itself goes back inserted into the membrane,the LDL particle itself is then sorted into the lysosome, released and degraded, chloresterol inserted in membranes this happens at low pH anout 6
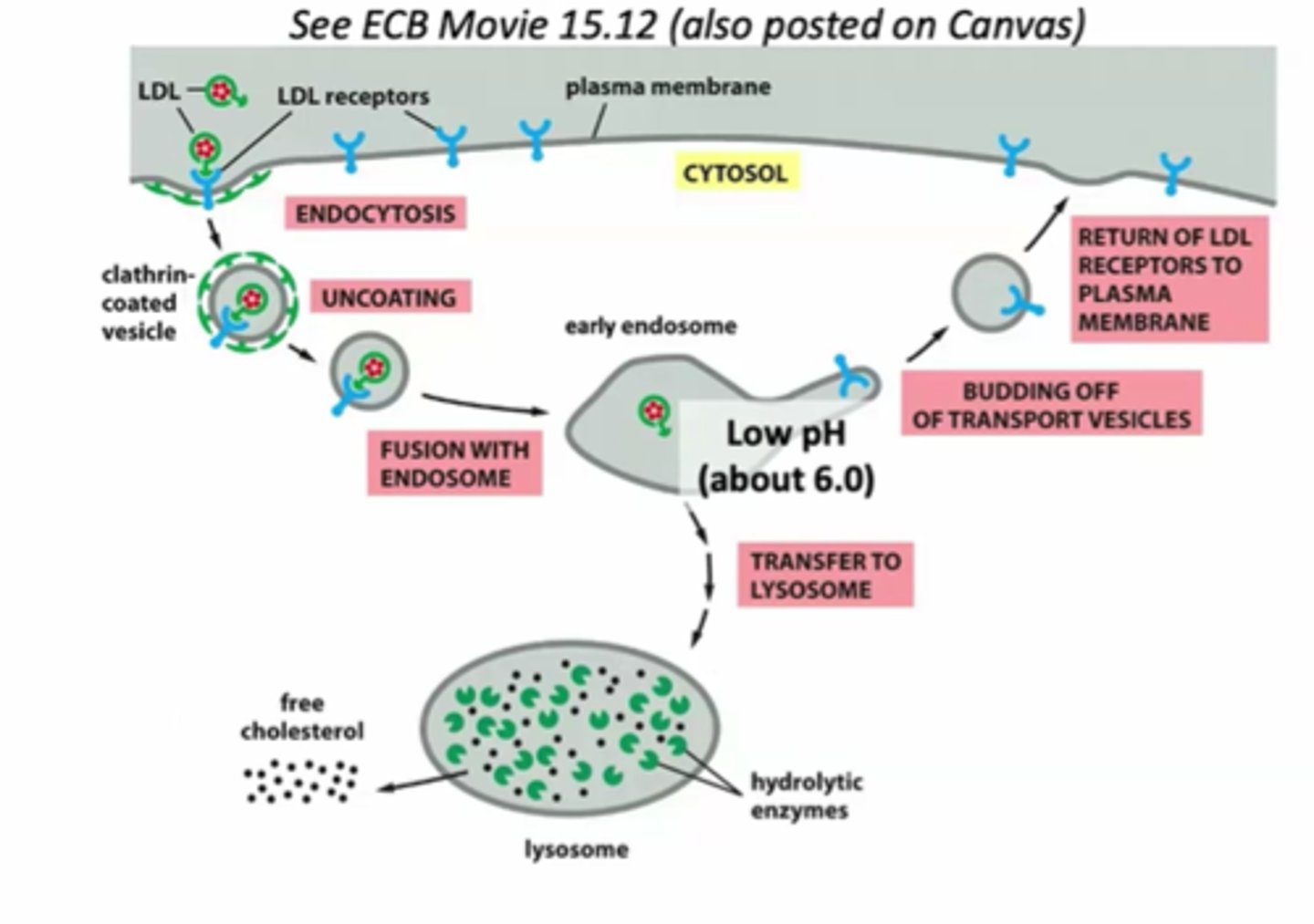
what happens when the endosome is neutralized to pH7
npth the LDL and receptor get trapped and the receptor doesn't recycle
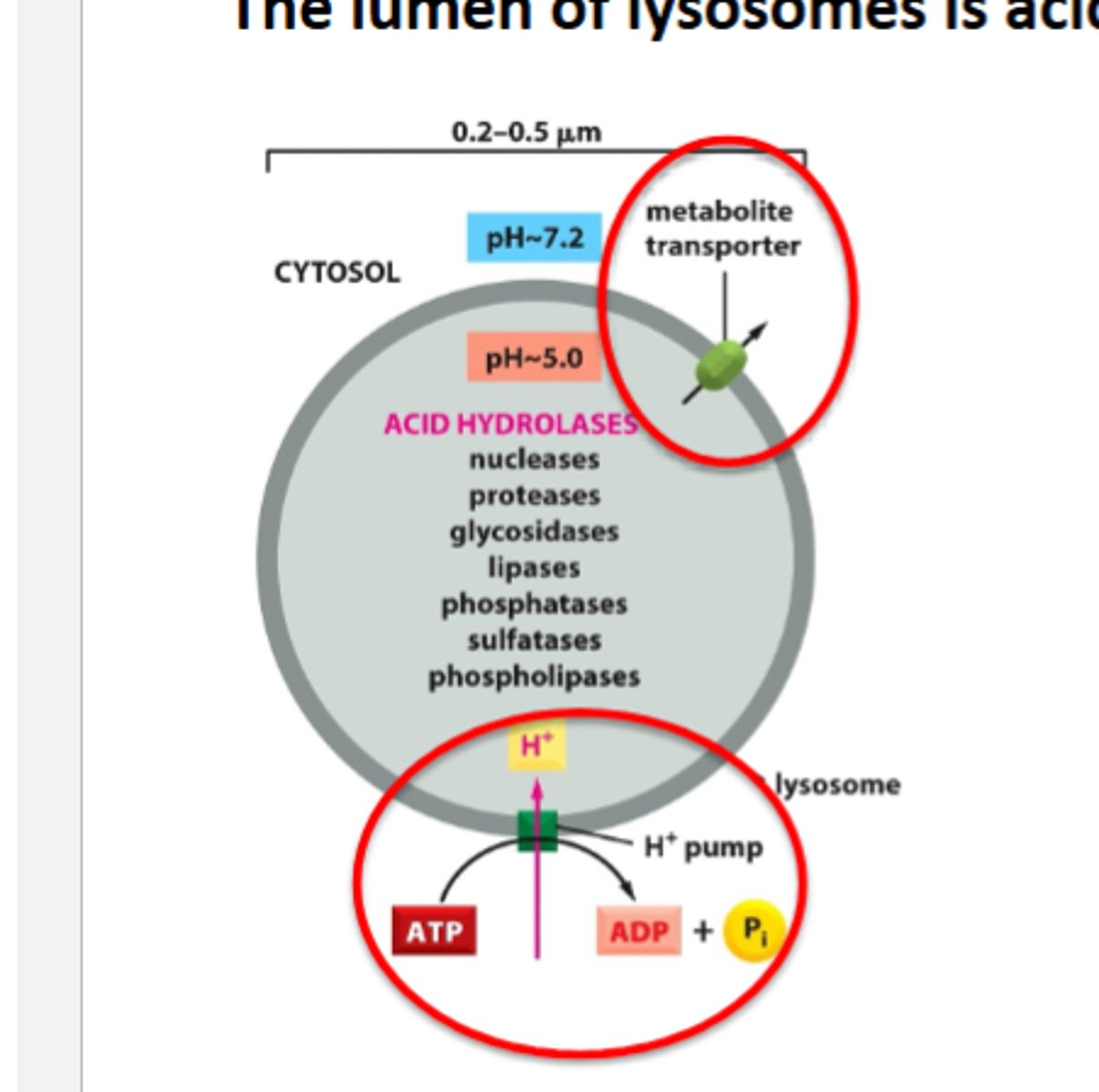
what is the lumen of lysosomes
acidic , full of hydrolytic enzymes
- lumen is acidic because of proton pum
lysosomes contan hydrilytic enzumes that can break down any bio molecules
- lysosomes enzymes funtionaround 5ph . collectively called acid hydrolases
lysosomes contain membrane transporters so that products of degredation can be used by he cell
can proteins in the lumen of the ER end up as a membrane protein on the plasma membrane ?
no, membrane proteins on the plasma membrane come from membrane proteins in the ER membrane not from the ER lumen
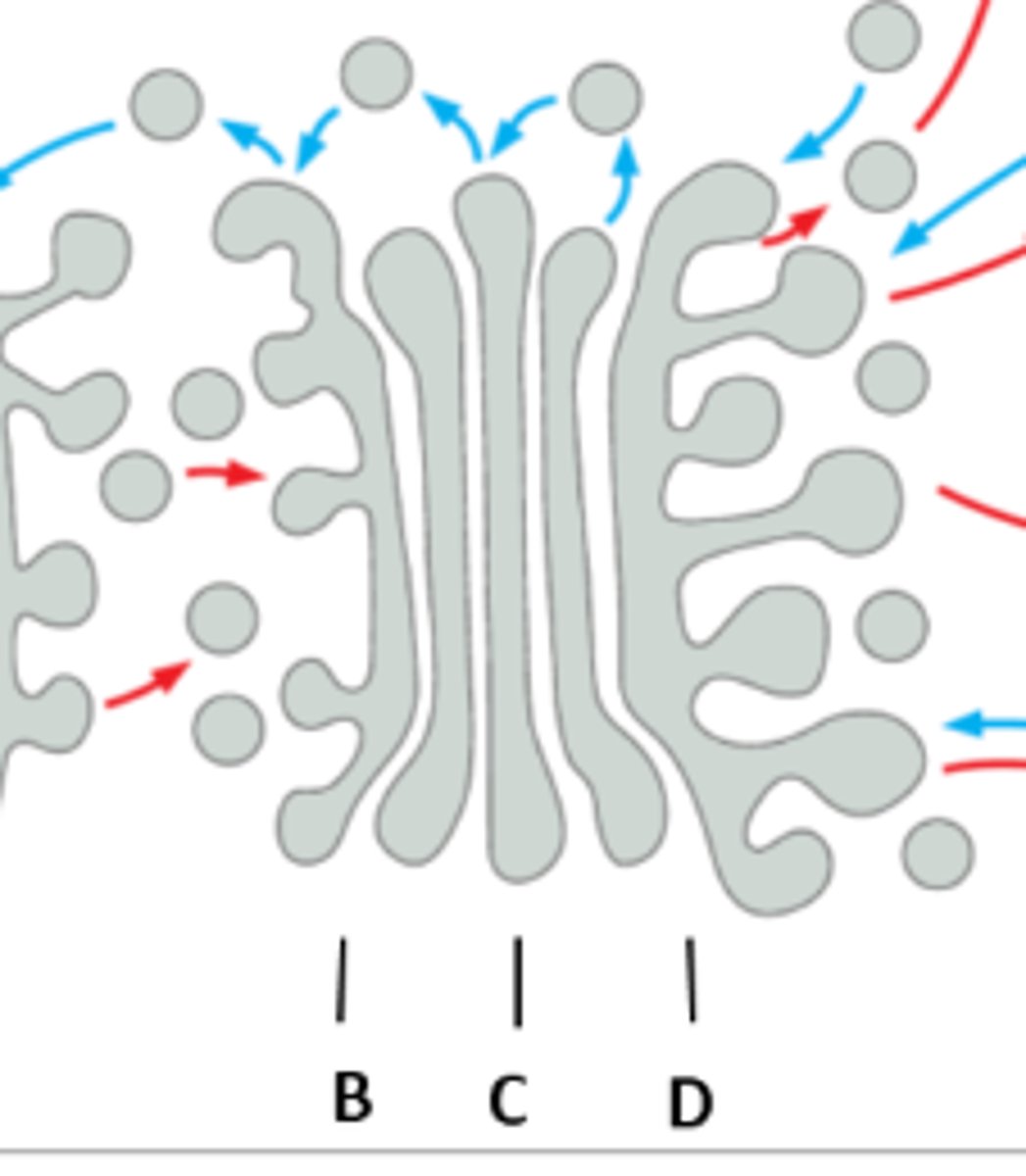
where are cis, medial, trans golgi located
b= cis
c= medial d: trans
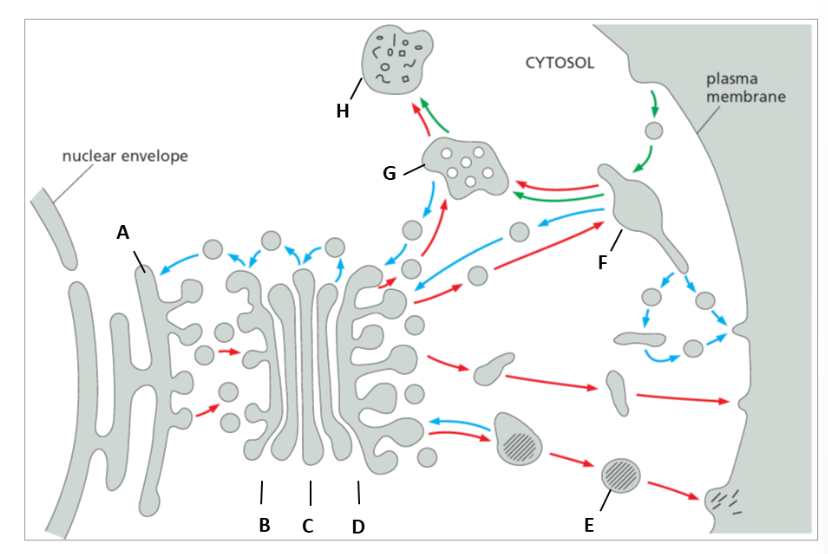
label E F G H
E: secretory vesicle
F: Early endosome
G: later endosome
H: Lysosome
what mediates transport from the ER to the cis golgi network
COPII
whats involved in receptor emdiated endocytosis
clathrin and adaptin-2 (AP-2)
involved in transport of proteins leaving the trans-golgi network that are destined for the lysosome
clathrin and adaptin (AP-1)
transport vesicles traveling from the golgi to the plasma mem move toward the ___ of microtubules using the rotein motor
plus ends , kinesin
transport vesicles traveling from the ER to the plasma mem move toward the ___ of microtubules using the rotein motor
minus ends, dyenin
does GTP hydrolysis of the RAB protein provide energy for membrane fusion
No RAB GTPase are important vesicle movmements and transport tether to the atget ( rab recruit tetherin ong the target) . RAB GTPase dont fdrive membrane fusion
v-snare for fusion needs ATP hydrolysis
WHat happens after olgiosaccharides are added to the ER protein
they are modified more
clarthin coated vesicles are involved in
uptake of extracellular molecules by receptor mediated endocytosis (RME ) and the transport of molecules from the trans golgi network to the lysosomes
during receptor mediated endocytosis , clathrin coats are bound to specific cargo recpetors by
adaptin -2 (AP-2
a cargo molecule is brought into a cell via receptor - mediated endocytosis , which of the following factors causes the receptor to release its molecules into the lumne of the ensosome
acific pH
LDL bind to what
LDL receptors on cell suraface, internalized in clathrin coated vesicles
what does acidic pH of the endosome cause
the receptor to release its cargo molecule into the lumen of the endosome
You are working in a biotech company that has discovered a small-molecule drug called H5434. H5434 binds to LDL receptors when they are bound to cholesterol. H5434 binding does not alter the conformation of the LDL receptor’s intracellular domain. Interestingly, in vitro experiments demonstrate that addition of H5434 increases the affinity of LDL for cholesterol and prevents cholesterol from dissociating from the LDL receptor even in acidic conditions. Which of the following is a reasonable prediction of what may happen when you add H5434 to cells?
D. The enzymes require the acidic pH inside lysosomes to function and are largely inactive at cytosolic pH.
enzymes require acidic pH inside lysosome to function
lumen of lysosome acidic because of proton pump
- lysosome contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down any bio molecule
- lysosomal enzymes function at 5 pH , called acid hydrolases
tf: coat proteins identify the correct target membrane for transport vesicle
false : coat proteins select speicifc cargo for transport and shape the transport vesicles from the donor compartment membrane . after budding from the donor compartment membrane, transport vesicles unocat , result in naed transport vesicles
: Rab proteins are small GTP -binding proteins that provide
initial bridge between target and vesicle membranes needed for vesicle docking and fusion