Specimen Collection- Part 2 W6:L2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
New
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
The Clotting Process:
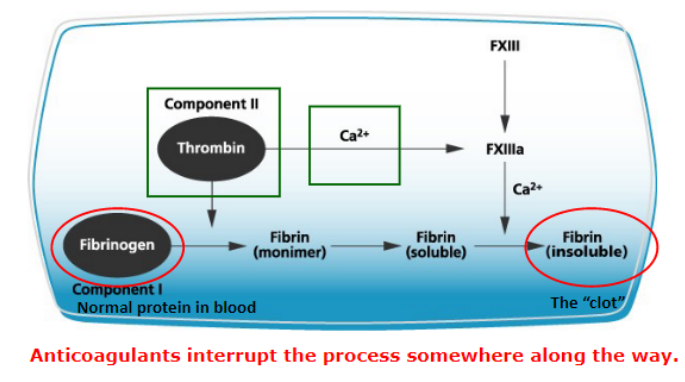
2
New cards
WHOLE BLOOD: PURPLE (LAVENDER, MAUVE) TOP TUBE
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CONTAINS ANTICOAGULANT: EDTA-PREVENTS BLOOD FROM CLOTTING
-CELLS REMAIN FREE IN THE TUBE.
EDTA PRESERVES CELLS SO THEY CAN BE IDENTIFIED BY
HOW THEY LOOK (MORPHOLOGY) WHEN USING
PARTICULAR STAINS.
anticoagulant of choice for blood cell counting
and sizing, because EDTA produces less shrinkage
of RBCs and less of an increase in cell volume on
standing.
-CELLS REMAIN FREE IN THE TUBE.
EDTA PRESERVES CELLS SO THEY CAN BE IDENTIFIED BY
HOW THEY LOOK (MORPHOLOGY) WHEN USING
PARTICULAR STAINS.
anticoagulant of choice for blood cell counting
and sizing, because EDTA produces less shrinkage
of RBCs and less of an increase in cell volume on
standing.
3
New cards
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid :
CHELATES calcium
•Prevents formation of fibrin
•Comes in di-sodium, di-potassium, or tri-potassium salt forms
•Most often used in hematology but
also used in Biochemistry (A1c, RFOL), Molecular
•Prevents formation of fibrin
•Comes in di-sodium, di-potassium, or tri-potassium salt forms
•Most often used in hematology but
also used in Biochemistry (A1c, RFOL), Molecular
4
New cards
CHELATION:
The process by which organic molecules bind to multiple metals and remove them from tissue (blood)
5
New cards
Chelate:
Greek for claw (EDTA grabs onto calcium and removes it from the blood)
6
New cards
PLASMA: LIGHT BLUE TOP TUBE
CONTAINS ANTICOAGULANT: 3.2% SODIUM CITRATE
PRESERVES MORE OF THE CLOTTING FACTORS.
IF TUBE IS CENTRIFUGED, LIQUID ON TOP IS FREE OF
CELLS BUT STILL CONTAINS FIBRINOGEN
THIS TUBE IS USED TO EVALUATE THE ABILITY OF
THE BLOOD TO CLOT
(COAGULATION/HEMOSTASIS STUDIES).
PRESERVES MORE OF THE CLOTTING FACTORS.
IF TUBE IS CENTRIFUGED, LIQUID ON TOP IS FREE OF
CELLS BUT STILL CONTAINS FIBRINOGEN
THIS TUBE IS USED TO EVALUATE THE ABILITY OF
THE BLOOD TO CLOT
(COAGULATION/HEMOSTASIS STUDIES).
7
New cards
Sodium Citrate:
•Chelates calcium but binding is reversible by adding
calcium back to the plasma
•Used for Coagulation (PT, PTT, INR) studies
•Requires 1 part NaCitrate to 9 parts blood!!!! (1:9 RATIO)
Inhibits ALT, AST, ALP
calcium back to the plasma
•Used for Coagulation (PT, PTT, INR) studies
•Requires 1 part NaCitrate to 9 parts blood!!!! (1:9 RATIO)
Inhibits ALT, AST, ALP
8
New cards
Fill volume extremely important!! Why?
THE RATIO OF anticoagulated TO BLOOD HAS TO BE EXACT, IF RATIO IS OFF, THEN ALL STUDIES ARE OFF
Test is to access how quickly a patient's blood can clot, not an accurate representation if the ratio is off
reject sample is fill volume is incorrect
Test is to access how quickly a patient's blood can clot, not an accurate representation if the ratio is off
reject sample is fill volume is incorrect
9
New cards
What chemistry test could you NOT test for if the sample is collected in a blue top tube??
You could NOT test for the ALT,AST, ALP and SODIUM because we are going to expect very high sodium levels because its in the anticoagulant
10
New cards
Green top tube PLASMA
contains the anticoagulant HEPARIN
If tube is centrifuged, liquid on top is free of cells but contains fibrinogen
This tube is most commonly used for Biochemistry tests because heparin has the least biochemical interferences
only anticoagulant that should be used in a blood collection device for the determination of pH, blood gases, electrolytes, and ionized calcium
If tube is centrifuged, liquid on top is free of cells but contains fibrinogen
This tube is most commonly used for Biochemistry tests because heparin has the least biochemical interferences
only anticoagulant that should be used in a blood collection device for the determination of pH, blood gases, electrolytes, and ionized calcium
11
New cards
Heparin:
Accelerates the action of antithrombin III, which neutralizes thrombin and prevents formation of fibrin from fibrinogen
Available as Na+, K+, lithium and ammonium
heparin
•All are green top tubes
Should not be used in hematology as it disrupts
cellular morphology
Available as Na+, K+, lithium and ammonium
heparin
•All are green top tubes
Should not be used in hematology as it disrupts
cellular morphology
12
New cards
Why is the type of heparin tube used extremely important in biochemistry testing?
Lithium heparin is the recommend because it’s the least likely to interfere with tests for other ions because its free of extraneous ions
It allows us to run potassium, sodium, ammonium except lithium
It allows us to run potassium, sodium, ammonium except lithium
13
New cards
RED TOP TUBE SERUM:
-EITHER CONTAINS NOTHING (NO ANTICOAGULANT)
-OR AN ADDITIVE TO ACTIVATE THE FORMATION
OF A CLOT
UPON CENTRIFUGATION, LIQUID PORTION IS CALLED
SERUM BECAUSE IT NO LONGER CONTAINS
FIBRINOGEN (REMOVED DURING THE CLOTTING
PROCESS)
USED MOST FREQUENTLY IN CHEMISTRY,
BUT ALSO IN SEROLOGY.
-OR AN ADDITIVE TO ACTIVATE THE FORMATION
OF A CLOT
UPON CENTRIFUGATION, LIQUID PORTION IS CALLED
SERUM BECAUSE IT NO LONGER CONTAINS
FIBRINOGEN (REMOVED DURING THE CLOTTING
PROCESS)
USED MOST FREQUENTLY IN CHEMISTRY,
BUT ALSO IN SEROLOGY.
14
New cards
Clot Activators:
•Promote coagulation
•Reduces clotting times
•Reduces clotting times
15
New cards
Types of Activators:
•Thrombin: part of coagulation system, can reduce clotting
time to 5 min. OFTEN USED FOR STATS
•Glass or Silica: provide more surface area for platelet
activation to occur
•Activators often are adhered to the side of the tube
•Hard to see
•Requires minimim 5 inversions to allow blood to come in
contact with activator
time to 5 min. OFTEN USED FOR STATS
•Glass or Silica: provide more surface area for platelet
activation to occur
•Activators often are adhered to the side of the tube
•Hard to see
•Requires minimim 5 inversions to allow blood to come in
contact with activator
16
New cards
Sodium Fluoride* GRAY:
-Antiglycolytic agent: substance that prevents glycolysis
•preserves glucose for 3d by preventing cellular
breakdown
•usually combined with Potassium Oxalate
•anticoagulant that precipitates calcium
•Commonly used for glucose when transportation
is required
•*some gray top tubes contain Iodoacetate
(preserves glucose for 24h)
•preserves glucose for 3d by preventing cellular
breakdown
•usually combined with Potassium Oxalate
•anticoagulant that precipitates calcium
•Commonly used for glucose when transportation
is required
•*some gray top tubes contain Iodoacetate
(preserves glucose for 24h)
17
New cards
Separator Tubes:
•SST: Serum separator tube
•PST: Plasma separator tube
Contain thixotropic gel (inert synthetic substance) that
when centrifuged will rise to a position in the tube between the
red cells and the plasma/serum
•PST: Plasma separator tube
Contain thixotropic gel (inert synthetic substance) that
when centrifuged will rise to a position in the tube between the
red cells and the plasma/serum
18
New cards
THIXOTROPIC gel:
During centrifugation, THIXOTROPIC gel becomes
“liquefied” and moves between cell layer and upper
serum or plasma layer
Forms a BARRIER between cells and fluid portion of the blood
Prevents “contamination” from cells
Allows for easy separation of the serum or plasma from the cells
“liquefied” and moves between cell layer and upper
serum or plasma layer
Forms a BARRIER between cells and fluid portion of the blood
Prevents “contamination” from cells
Allows for easy separation of the serum or plasma from the cells
19
New cards
Other factors Associated w/ETS:
-Ambient (room) Temperature
-Humidity
-Humidity
20
New cards
Ambient (room) Temperature:
•At low temperature, pressure of gas inside the tube will
decrease leading to an increase in draw volume for the
evacuated tube.
•At higher temperatures increased pressure could cause
decreased draw volume
decrease leading to an increase in draw volume for the
evacuated tube.
•At higher temperatures increased pressure could cause
decreased draw volume
21
New cards
Humidity:
Storage under different humidity conditions affects plastic
evacuated tubes due to greater permeability to water vapor
relative to glass.
•Addition of moisture (for powdered additives) or removal
of moisture (for liquid additives) in the tube can affect
accuracy of test results
evacuated tubes due to greater permeability to water vapor
relative to glass.
•Addition of moisture (for powdered additives) or removal
of moisture (for liquid additives) in the tube can affect
accuracy of test results
22
New cards
Proper Mixing is imperative:
Must “invert” appropriate number of times to mix
anticoagulant with blood or fibrin clots will form
anticoagulant with blood or fibrin clots will form
23
New cards
Order of Draw:
•1st: blood culture tube or vials
•2nd: coagulation tube BLUE
•3rd: serum tube (w or w/o SST/activator) RED
•4th: Heparin tube (w or w/o PST) GREEN
•5th: EDTA LAVENDER
•6th: glycolytic inhibitor GRAY
•2nd: coagulation tube BLUE
•3rd: serum tube (w or w/o SST/activator) RED
•4th: Heparin tube (w or w/o PST) GREEN
•5th: EDTA LAVENDER
•6th: glycolytic inhibitor GRAY
24
New cards
Why is this so important? drawing an EDTA tube prior to a serum or heparin tube for chemistry testing.
The potential cross contamination of K2 or K3 EDTA on
the needle from the lavender top tube into the
chemistry tube can lead to a FALSELY elevated
potassium result
can require recollection of the sample or
•possible misdiagnosis or treatment of the patient
the needle from the lavender top tube into the
chemistry tube can lead to a FALSELY elevated
potassium result
can require recollection of the sample or
•possible misdiagnosis or treatment of the patient
25
New cards
Hematoma (bruising):
•Due to leakage of blood into the tissue
•Needle inserted too far
•Needle not inserted completely into vein
•Needle inserted too far
•Needle not inserted completely into vein
26
New cards
Most common causes of hematoma:
•Excessive probing w/needle
•Needle not inserted far enough into the
vein
•Needle goes through the vein
•Failure to remove the tourniquet before
removing the needle
•Inadequate pressure on the site after
removing the needle
•Bending the elbow while applying pressure
•Needle not inserted far enough into the
vein
•Needle goes through the vein
•Failure to remove the tourniquet before
removing the needle
•Inadequate pressure on the site after
removing the needle
•Bending the elbow while applying pressure
27
New cards
Causes of Hemolysis During Collection:
•Mixing additive tubes too vigorously or using rough handling
during transport, prior to centrifugation
•Drawing blood from a vein that has a hematoma
•Pulling back the plunger on a syringe too quickly
•Using a needle with too small of a bore for the venipuncture
•Using too large a tube when using a small diameter needle
•Forcing the blood from a syringe into an evacuated tube
•Excessive fist clinching
•Leaving the tourniquet on for longer than one minute
•Exposing sample to cold/ice
•Adding water to sample
•Not allowing alcohol to dry during blood collection
during transport, prior to centrifugation
•Drawing blood from a vein that has a hematoma
•Pulling back the plunger on a syringe too quickly
•Using a needle with too small of a bore for the venipuncture
•Using too large a tube when using a small diameter needle
•Forcing the blood from a syringe into an evacuated tube
•Excessive fist clinching
•Leaving the tourniquet on for longer than one minute
•Exposing sample to cold/ice
•Adding water to sample
•Not allowing alcohol to dry during blood collection
28
New cards
How to Avoid Hemolysis
•For routine collections, use a 20- to 22-gauge needle
•If there is air leakage around the needle or loss of vacuum in the
tube, replace the vacuum tube
•Collect blood in room temperature containers unless the specimen requirement specifies otherwise.
•If there is air leakage around the needle or loss of vacuum in the
tube, replace the vacuum tube
•Collect blood in room temperature containers unless the specimen requirement specifies otherwise.
29
New cards
Venipuncture: Reflux
To prevent reflux, the client’s arm should be kept in a downward
position so that the tube is below the venipuncture site and fills from the bottom up
reflux may cause a reaction to the tube additive
position so that the tube is below the venipuncture site and fills from the bottom up
reflux may cause a reaction to the tube additive
30
New cards
Labeling the tube- Required on the vacutainer tube:
•Patient Name
•Patient unique number (admission
number)
•Date collected
•Time collected (must be in 24h
clock format)
•Initials of person collecting the
sample
•Patient unique number (admission
number)
•Date collected
•Time collected (must be in 24h
clock format)
•Initials of person collecting the
sample
31
New cards
Specimen Collection guidelines:
•CLSI H3-A5 (2003) Guidelines:
•Discard collection device w/o disassembly
(NO re-capping needles) = disposable
vacutainer holders!
•Outpatient phlebotomy chairs: 2 arms to prevent falls after
syncope
•Ammonia inhalants NOT recommended (asthmatics)
•ID bracelet must be attached to
patient
•Gloves not required until just prior to site preparation (allowed to find veins w/fingers!!)
•Must inquire if patient has latex sensitivity
•Discard collection device w/o disassembly
(NO re-capping needles) = disposable
vacutainer holders!
•Outpatient phlebotomy chairs: 2 arms to prevent falls after
syncope
•Ammonia inhalants NOT recommended (asthmatics)
•ID bracelet must be attached to
patient
•Gloves not required until just prior to site preparation (allowed to find veins w/fingers!!)
•Must inquire if patient has latex sensitivity
32
New cards
CLSI (NCCLS) H3-A5 (2003):
•Tourniquet now required unless interferes w/test results (lactate)
•Hemostasis must be completed before bandaging
•Wake sleeping patients prior to collection
•Discontinuation of sharp tapping of collection site to make veins more prominent
•Hemostasis must be completed before bandaging
•Wake sleeping patients prior to collection
•Discontinuation of sharp tapping of collection site to make veins more prominent
33
New cards
Capillary Puncture:
Dermal (Skin) puncture using a lancing device
•lancet: a small, broad, two-edged surgical knife
or blade with a sharp point
•lancet: a small, broad, two-edged surgical knife
or blade with a sharp point
34
New cards
When is a capillary puncture recommended? middle finger and ring finger
•Severely burned patients
•Obese patients
•Patients with thrombotic tendencies
•Elderly patients or others in whom superficial veins are
very fragile or inaccessible
•Patients performing self-testing
•Point-of-care testing
•Newborn testing
•Patients on chemotherapy
•Patients who have a paralyzing fear of needles
•No accessible veins (ex. in casts)
•Obese patients
•Patients with thrombotic tendencies
•Elderly patients or others in whom superficial veins are
very fragile or inaccessible
•Patients performing self-testing
•Point-of-care testing
•Newborn testing
•Patients on chemotherapy
•Patients who have a paralyzing fear of needles
•No accessible veins (ex. in casts)
35
New cards
Capillary Collections:
Lancing device must be retractable
•Depth of incision in adults must be less than 3.0mm to avoid contact with bone
•For heel puncture must be less than 2.0mm (calcaneus bone lies close to the surface)
•Less than 0.85mm in premature babies
•Depth of incision in adults must be less than 3.0mm to avoid contact with bone
•For heel puncture must be less than 2.0mm (calcaneus bone lies close to the surface)
•Less than 0.85mm in premature babies
36
New cards
First drop of blood always wiped off WHY??
Removes any alcohol any tissue fluid that is contained right under the surface of the skin in that first drop
-eliminate any tissue fluid contaminants
-eliminate any tissue fluid contaminants
37
New cards
Capillary Collections:
Blood is collected into a microcontainer (or capillary tube)
•Preparation includes warming the area (massaging NOT
recommended) and cleaning w/alcohol (air dry) or soap &
water
•Preparation includes warming the area (massaging NOT
recommended) and cleaning w/alcohol (air dry) or soap &
water
38
New cards
CLSI (2003) Guidelines:
•Retractable lancing devices required (no scalpels or wire lancets).
•Plastic capillary tubes recommended (required by CAP)
•Avoid excessive milking of puncture site (hemolysis)
•Elimination of the great toe as a puncture site
•Elimination of punctures/incisions from same side of a mastectomy as a collection site
•Plastic capillary tubes recommended (required by CAP)
•Avoid excessive milking of puncture site (hemolysis)
•Elimination of the great toe as a puncture site
•Elimination of punctures/incisions from same side of a mastectomy as a collection site