Lecture 4 - Lab Test Stewardship
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
why might a pharmacist need to order a laboratory test
ensure drug and dose are appropriate
monitor patient response to therapy
monitor for adverse effects and ensure patient safety
screen patients with preliminary indicators for untreated disease
what does a pharmacist need to do to order a laboratory test
register with the laboratory (Alberta Precision Laboratories) - receive a code
be familiar with the standards and responsibilities
plan for receiving/interpreting results (need 24/7 contact info in case of critical results)
things to consider when ordering a lab test
is it appropriate
is the cost of test worth the information it generates
logistical issues for the patient (e.g. fasting, collect and deliver samples)
what should a pharmacist always do before initiating lab requests and POCT
check patient’s netcare
what is informed consent for laboratory tests
patients must be provided with the name of the test, the reason for testing, the risks and benefits of the test, and what the plan for follow up is
what are general principles when interpreting lab results
accuracy and precision
test performance
reference range
critical value
units
what is accuracy
how close is a measurement to its true value
measurements are never absolute
influence of both random and systematic error
what is precision
represents degree of arrangement between multiple measurements of the same sample when repeatedly measured under same conditions
what is sensitivity of a lab test
related to error
The ability of a test to correctly identify people who have a disease/condition
what does it mean if a lab test has high sensitivity
high possibility of a true positive
low possibility of a false negative
someone with a negative result does not have disease/condition
what does it mean if a lab test has low sensitivity
a negative result could lead to missing a case of disease
what is specificity of a lab test
ability of a test to correctly identify people who truly do not have a given condition
what does it mean if a test has high specificity
low possibility of false positive
high possibility of true negative results
high confidence someone with positive result has the condition/disease
what does it mean if a test has low specificity
a positive result could lead to unnecessary additional tests/over treatment
what if a test is too sensitive
increase the chance of getting false positive results
what if a test is too specific
increase the chance of false negative results
what are predictive values
provides more clinically meaningful information for individual patient care
What is a positive predictive value
percent of positive results that are truly positive
if the test is positive, what is the probability the patient actually has the disease
what is negative predictive value
percent of negative results that are truly negative
if the test is negative what is the probability the patient does not actually have the disease
what is the formula for sensitivity using a 2×2 table
true positive / patients with disease
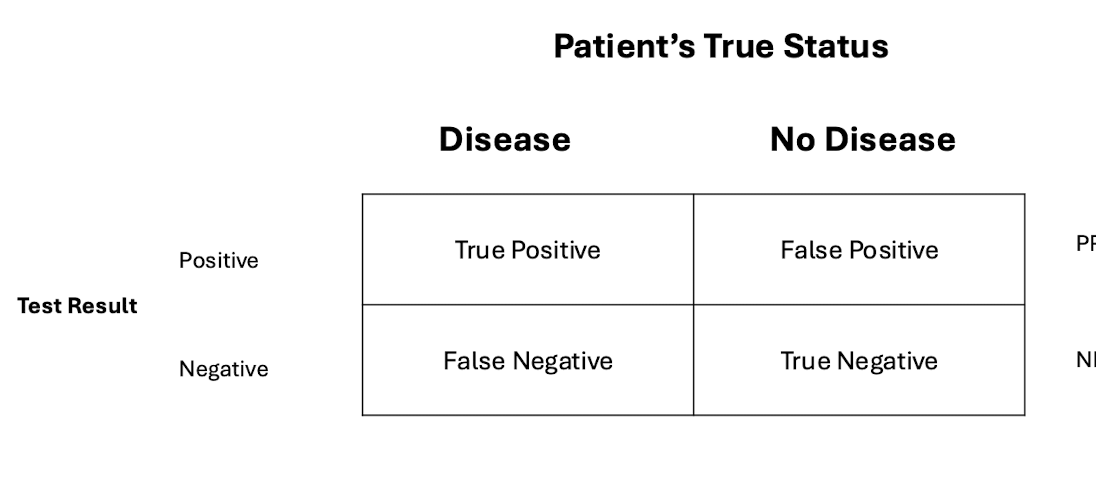
what is the formula for specificity using a 2×2 table
true negative / patients without disease
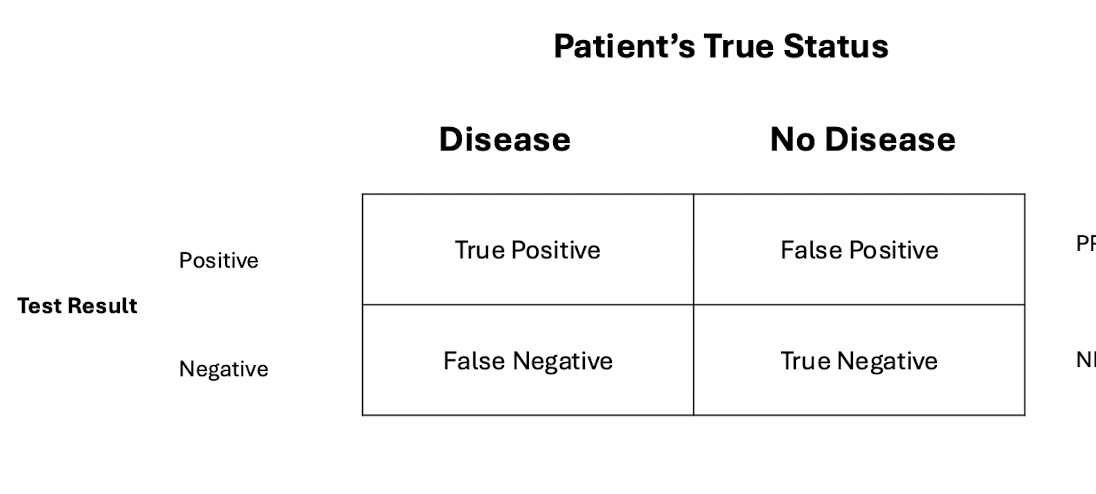
what is the formula for PPV (positive predictive value) using a 2×2 table
true positive / all positive test results
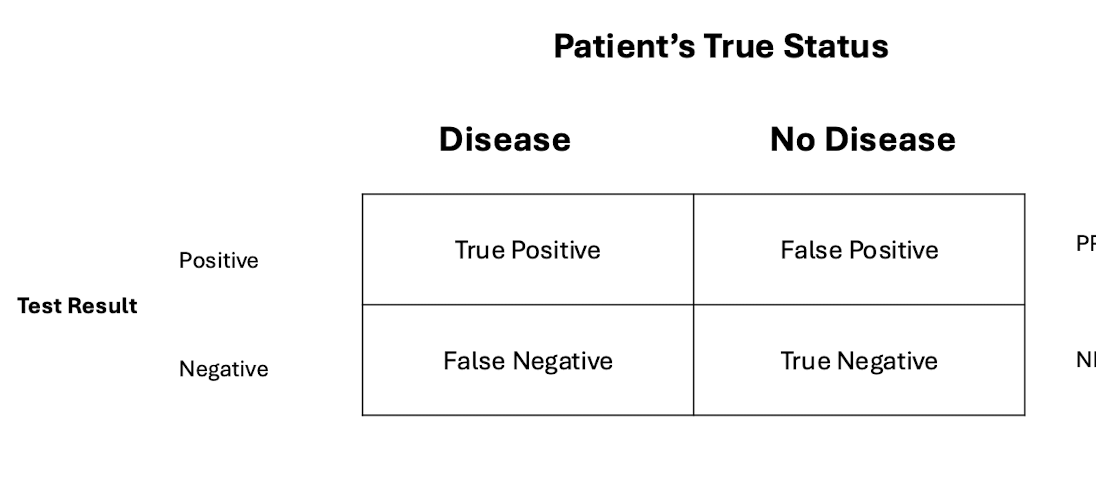
what is the formula for NPV (negative predictive value) using a 2×2 table
true negative / all negative test results
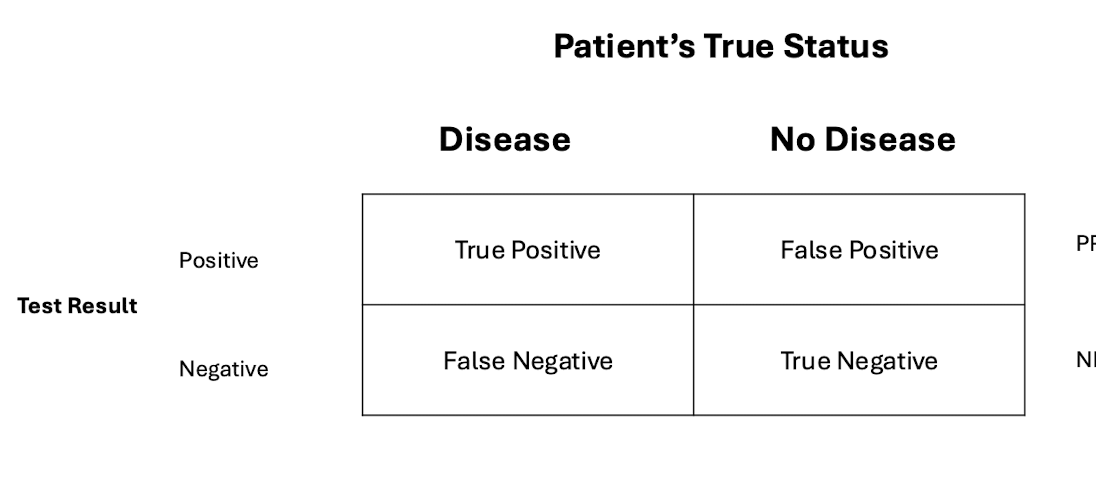
what is a reference range
range of values obtained from testing a large sample of health individuals
range will contain 95% of the values
reference range may vary from lab to lab
what are critical values
test result is outside of the reference range and requires immediate attention
first: possibility of error?
how far is critical value beyond reference range, are patient symptoms consistent with the lab value
what units are used for lab tests
Canada: SI (international units)
mmol/L, mEq/L
what are the steps to follow when interpreting lab tests
gather patient information
look at netcare for relevant lab results
if not available → request/order lab test
compare the lab result with reference range
assess lab result with patient symptoms, medical conditions, other influential factors
determine if action is required