Protein Structure and Function 1
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Describe bonding in alpha - helices.
A hydrogen bond forms between every fourth peptide bond, linking C=O of one peptide bond to the N-H of another.
Describe bonding in beta- sheets.
The hydrogen bond forms between peptides in different strands.
Explain the different types of bonds that determine the tertiary structure of a protein.
Secondary and tertiary structures are stabilised by multiple weak non-covalent interactions and forces, and by the covalent bonds in the polypeptide backbone.
Where is the primary structure formed?
During translation in the cell cytoplasm.
After protein synthesis, amino acids can…
contain altered and modified amino acid residues.
Desmosine
Found in elastine.
Ornithine + citrulline
Key intermediates of the biosynthesis of arginine and in the urea cycle.
Adding what to amino acids can increase or decrease their activity? and are also reversible?
Phosphoryl, methyl, acetyl, adenylyl, ADP-ribosyl.
How are α-carbons of adjacent amino acids connected in a polypeptide?
They are separated by three covalent bonds, arranged as Cα-C-N-Cα.
What does X-ray diffraction show about the peptide group?
The six atoms (Cα-C-N-Cα + O & H) lie in a single plane due to partial double-bond character.
Why is the peptide bond rigid and planar?
The partial double bond character of the C-N bonds prevents free rotation.
What dipole is created within the peptide bond?
The oxygen has a partial negative charge and the nitrogen has a partial positive charge.
What defines peptide conformation (spatial arrangement)
Three dihedral angles: Φ (Phi), Ψ (Psi), and Ω (Omega), reflecting rotation around backbone bonds.
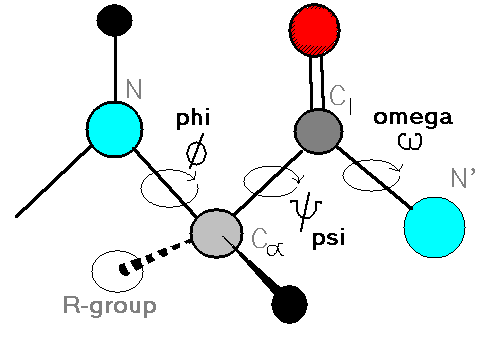
What is a dihedral angle?
It is the angle of intersection between two planes in the peptide backbone.
Frederick Sanger
Worked out the sequence of amino acid residues in the polypeptide chains of the hormone insulin, using the Edman degradation technique.
Dorothy Hodgkin
Used X-ray crystallography to solve the structure of penicillin, vitamin B12 and insulin.
How is protein sequencing obtained?
By matrix assisted laser desorption/ ionization- mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS)
The secondary structure of a protein folds the peptide chains into?
α helices, β sheet and β turns.
How is an alpha helix generated?
When a single polypeptide chain twists around on itself to form a rigid cylinder.
What gives polarity to an alpha helix?
All the N-H groups point up whereas the C=O point down.
How many turns every residues in an alpha helix?
3.6
Where are alpha helixes abundant?
In proteins located in the cell membrane due to the hydrophilic polypeptide backbone, where the hydrogen is bonded to itself and shielded from the hydrophobic lipid membrane.
What amino acids destabilise the structure due to its charged properties?
Asp, Glu (-ve) and Lys, Arg (+ve)
What amino acids destabilise the structure due to its shape and polar uncharged nature?
Asn, Glm, Ser, Thr and Cys
What amino acid has the greatest tendency to form alpha helices?
Alanine
What amino acid has a destablising kink?
Proline
In the beta sheet adjacent peptide chains runs in which direction?
Antiparallel and parallel directions.
Why is hydrogen bonding stronger in antiparallel beta sheets?
The C=O and N-H groups are better aligned
Why are beta turns common in globular proteins?
The structure allows some amino acid residues to form turns and loops and have a compact structure.
What are beta turns?
They are the connecting elements that link successive runs of alpha helix or a beta conformation.
Why does Gly residues often occur in beta turns?
It is small and flexible.
Why does Pro residues occur in beta turns?
Peptide bonds involving the imino nitrogen of proline can assume readily the right configuration.
Circular dichroism spectroscopy
Measurement of differences in absorption of polarized light of structural asymmetry in a molecule.