Soil as a Natural Resource
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Soil
natural body comprised of solids (minerals and organic matter), liquid, and gases
Pedology
science dealing with the study of soils
Pedogenesis
deals with soil formation or soil origin
Importance of Soil
supports plant growth
contains nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and other bio elements
habitat for animals and microorganisms
essential for water filtration
Weathering
process that breaks down rocks and minerals into smaller pieces
Physical Weathering
mechanical breakdown of rocks without changing their chemical composition
Chemical Weathering
involved the chemical alteration of minerals within the rock
ex: Chocolate Hills, Philippines
Biological Weathering
involves the breakdown of rocks by living organisms
Soil-Forming Factors
parent material
rocks from which the soil derived
climate
temperature and rainfall impact soil formation
time/age
time of formation
topography
differences in land elevation and slipe
high elevations = dry and thin soil
biota
plants, animals, and microorganisms contribute to soil structure and nutrient cycling
Soil Horizon
distinct horizontal layers of soil
O-Horizon
top-most layer in the soil horizon
humans or organic matter
A-Horizon
second layer in the soil horizon
topsoil, rich in minerals and organic matter
B-Horizon
third layer in the soil horizon
subsoil, contains leached materials
C-Horizon
fourth layer in the soil horizon
weathered parent material
R-Horizon
fifth layer in the soil horizon
regolith, bedrock
Soil Profile
cross-sections, showing soil horizons
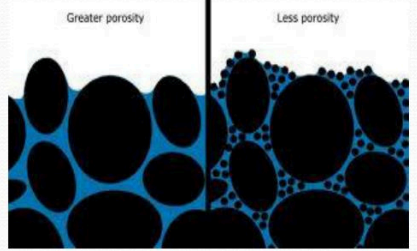
Soil Properties: Porosity
percentage of a material’s volume that is pore space
more porous = more water it can hold
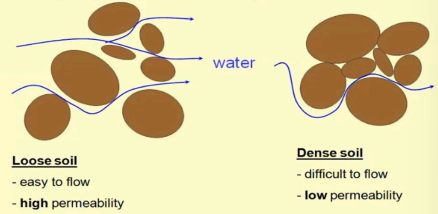
Soil Properties: Permeability
measures how easily fluids can flow through a material
Soil Properties: Color
black-brown: high organic matter
red-orange: oxidized; high iron content
yellowish-white: rich in clay minerals
gray: high moisture

Soil Properties: pH
determines the type and growth of plants that can thrive in it
solubility of some minerals needed for plant growth are pH dependent
common soils: 4 to 2
ideal pH of soil
6.5-7.5
Soil Nutrients: Nitrogen
needed by plants for cell-formation
Nitrogen Deficiency
yellowish brown colors along veins and tips of leaves, stunted growth, pale color of older leaves
Soil Nutrients: Phosphorus
essential for seed and root development
Low Phosphorus
stunted growth, late maturity of plants; weak plants with purple streaks in the stems
Soil Nutrients: Potassium
essential for strong and sturdy stems and advances root growth, resists diseases
Low Potassium
stunted growth, weak stem
Soil Degradation (Soil Problems)
decline in the quality and health of soil → loss of its ability to support healthy plant growth and perform essential ecological functions
causes
intensive farming practices (excessive tilling, overuse of chemical fertilizers)
inadequate soil conservation measures
Laterization (Soil Problems)
characterized by the intense weathering of rocks and minerals
forms laterites: high in iron and aluminum oxides but low in nutrients
cause: deforestation (exposes the soil, minerals are washed away)
Soil Erosion (Soil Problems)
removal of topsoil → leads to thinning of soil, loss of nutrients and fertility → use of more fertilizers
causes
deforestation
human mismanagement of soil
Soil Desertification (Soil Problems)
conversion of agricultural croplands to deserts (cropland abandonment)
causes
drought
deforestation
over cropping
mining
poor agricultural practices
Composting (Soil Conservation and Restoration)
decomposition of organic waste by microorganisms into CO2, water and humans
compost - good soil conditioner
Alternative Pest Control (Soil Conservation and Restoration)
crop rotation and mixed crop cultivation to distrust life cycles of pests
biological controls (ex: wasps, mantis)
biogenetics (pest-resistant plants)
use of biopesticides
Crop Rotation & Multi-Cropping: Monoculture (Soil Conservation and Restoration)
leads to soil infertility
depletes the natural nutrients of the soil faster
Multi-Cropping (Soil Conservation and Restoration)
various crops in one field
Crop Rotation (Soil Conservation and Restoration)
different crops in the same field over a period of time
Contour Plowing (Soil Conservation and Restoration)
prevent soil erosion
plowing and planting across the slope of the land, following its natural contours
Contour Plowing: Terracing (Soil Conservation and Restoration)
creating flat areas or “steps” on a slope to create level platforms for planting
Reforestation
replanting of trees in a previously forested area
Afforestation
establishing a forest in an area where there was no forest before