Vocab
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Law of definite proportions
Different samples of the same compound always contain its constituent elements in the same proportions by mass.
Law of multiple Proportions
If two elements can combine to form more than one type of compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in ratios of small whole numbers.
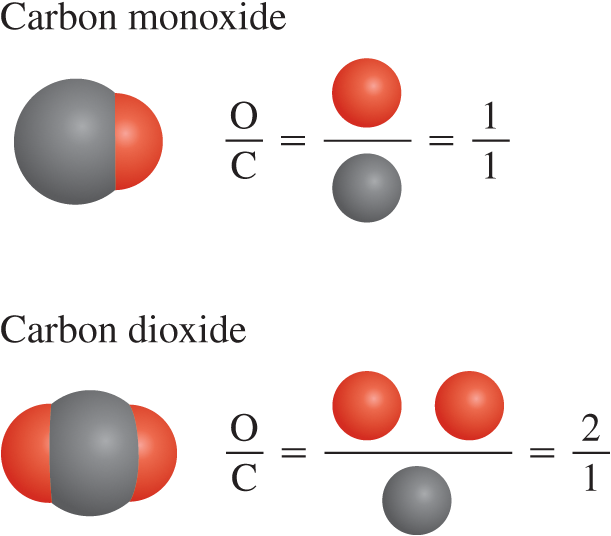
Law of conservation of mass
Hypothesis stating that matter can be neither created nor destroyed.
Atom
The basic unit of an element that can enter into chemical combination.
Radiation
The emission and transmission of energy through space in the form of particles and/or waves.
Electrons
A subatomic particle that has a very low mass and carries a single negative electric charge.
Radioactivity
The spontaneous breakdown of an atom by emission of particles and/or radiation.
alpha (α) rays/ alpha particles
Helium ions with a positive charge of +2.
beta (β) rays/beta particles
electrons
gamma (γ) rays
High-energy radiation
Nucleus
The central core of an atom
Protons
A subatomic particle having a single positive electric charge. The mass of a proton is about 1840 times that of an electron.
Neutrons
A subatomic particle that bears no net electric charge. Its mass is slightly greater than a proton’s mass.
Atomic number (Z)
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Mass number (A)
The total number of neutrons and protons present in the nucleus of an atom.
Isotopes
Atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Periodic table
A tabular arrangement of the elements.
period
A horizontal row of the periodic table.
Group/Families
The elements in a vertical column of the periodic table.
Metal
Elements that are good conductors of heat and electricity and have the tendency to form positive ions in ionic compounds.
Nonmetals
Elements that are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Metalloid
An element with properties intermediate between those of metals and nonmetals.
Alkali Metals
The Group 1 elements (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, and Fr).
Alkaline Earth Metals
The Group 2 elements (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Ra).
Halogens
The nonmetallic elements in Group 17 (F, Cl, Br, I, and At).
Noble gases
Nonmetallic elements in Group 18 (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn).
Molecule
An aggregate of at least two atoms in a definite arrangement held together by special forces.
Diatomic molecule
A molecule that consists of two atoms.
Polyatomic molecule
A molecule that consists of more than two atoms.
Ion
An atom or a group of atoms that has a net positive or negative charge.
Cation
An ion with a net positive charge.
Anion
An ion with a net negative charge
Ionic compound
Any neutral compound containing cations and anions.
Monatomic Ion
An ion that contains only one atom.
Polyatomic Ion
AN ion that contains more than one atom
Chemical Formula
An expression showing the chemical composition of a compound in terms of the symbols for the atoms of the elements involved.
Molecular formula
An expression showing the exact numbers of atoms of each element in a molecule.
Allotrope
Two or more forms of the same element that differ significantly in chemical and physical properties.
Structural Formula
A chemical formula that shows how atoms are bonded to one another in a molecule.
Empirical formula
An expression showing the types of elements present and the simplest ratios of the different kinds of atoms.
Organic Compound
Compounds that contain carbon, usually in combination with elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur.
Inorganic compounds
Compounds other than organic compound
Binary Compounds
Compounds formed from just two elements.
ternary compounds
Compounds consisting of three elements.
Acid
A substance that yields hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
Oxoacids
An acid containing hydrogen, oxygen, and another element (the central element).
Oxoanions
An anion derived from an oxoacid
Hydrates
Compounds that have a specific number of water molecules attached to them.