EESC 101 Lecture 7: Transform Boundaries
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Transform Boundaries
lateral movement of plates past each other
least common boundary type
does not create or destroy crust
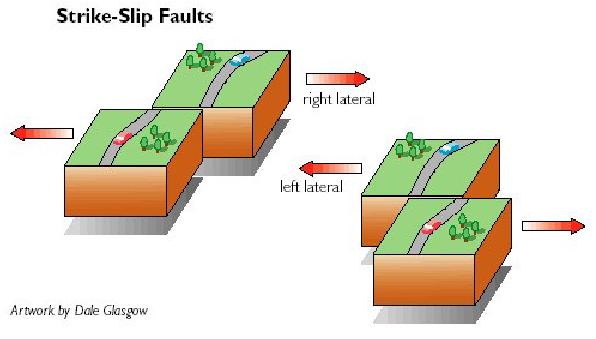
Dextral vs Sinistral
Dextral: right moving
Sinistral: left moving
determined by relative motion of one plate to another
imagine you are standing on one side of a transform fault that shifts
if the plate opposite to you moves right, its a right lateral fault
if the plate opposite to you moves left, its a left lateral fault
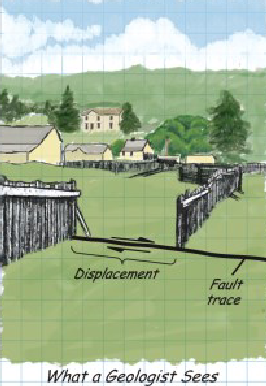
How to Spot a Transform Fault?
offset of features laterally
earthquakes common, but no volcanism
series of relatively small basins and hills
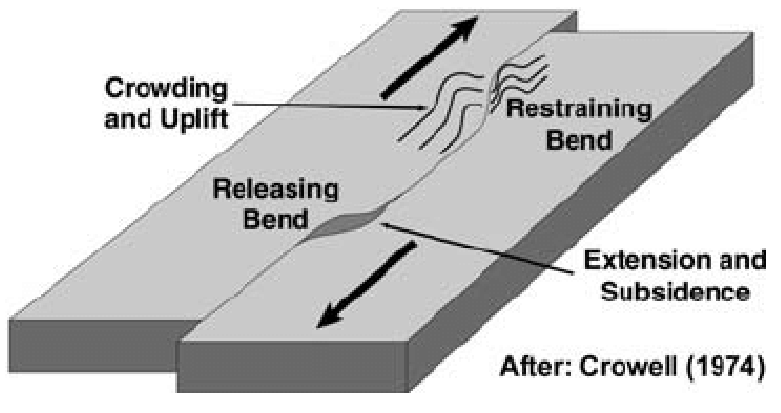
Push Up Ranges, Pull Apart Basins
whether you have a basin or a hill is determined by which way the plates move
Push Up: crust pushes together creating compressional force that builds up crust (like convergent boundary)
Pull Apart: moving away from each other creates extensional tension and normal faulting to make basin (like a continental rift)
Strike Slip Earthquakes
Locked: plates stuck together not currently moving
longer plates are locked up, more energy buildup, larger resulting earthquake
San Francisco has locked portion of San Andreas Fault
Creep: slow steady movement of plates
San Francisco Quake
1906
estimated magnitude of 7.8
similar to nuclear blast
destroyed ~80% of San Fran
killed >3,000 people
diverted economic growth and trade to Los Angeles