immunology quiz 4
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Ig structure
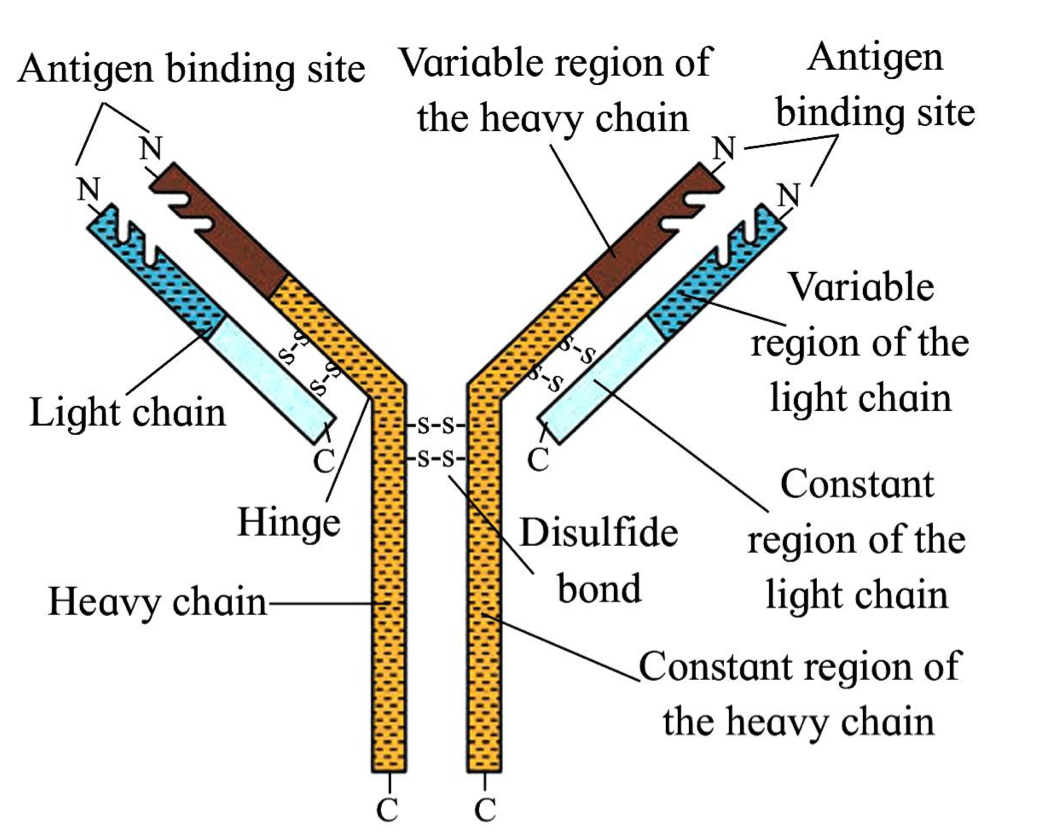
IgM
main antibody of primary response
B-cell receptor
immune system memory
compliment system
PENTAMERIC
IgG
binds to phagocytes
main blood antibody for secondary response
crosses placenta
MONOMER (one Y)
IgD
B-cell receptor
stimulates release of IgM
not soluble in blood
MONOMER
IgE
binds to mast cells —> release granulocytes and histamines
allergies and antiparasitic activity
MONOMER
IgA
mucosal membrane, saliva, tears
tags pathogens for destruction
DIMER
Dreyer and Bennett somatic recombination
wanted to know how polypeptide sequences can have stable constant regions AND have so much diversity in variable regions
proposed that DNA encoding heavy or light chain is divided into constant and variable segments. there are few constant segments and LOTS of variable. mixing and matching these creates diversity in the Ag binding region while keeping the rest of the molecule intact
somatic variation theory
have few Ig genes but in each B cell the Ig genes undergo rearrangement at the DNA level in a way that creates new sequences and thus diversity
good theory! probably true!
Tonegawas experiment
supported dreyer and bennett theory
hypothesized that gene rearrangement of Ig occurs and may be linked to B cell development
used mice embryonic and myeloma cells from different stages of B cell development
isolated DNA from these cells and ran a digest with BamHI
ran gel and it showed that germ cell DNA (embryonic) had several smaller segments compared to developed cells (myelomic)
conclusions: a segment specifying the V region and a segment specifying the C region became joined during B cell development
kappa light chain
chromosome 2
30 V segments, 5 J segments, and 1 C segment
VJ recombination
lambda light chain
chromosome 22
30 V segments, 4 J segments, and 4 C segments
VJ recombination
somatic recombination
happens to B cells
occurs in BONE MARROW
heavy chain
chromosome 14
40 V segments, 23 D segments, 6 J segments, and 9 C segments
VDJ recombination
D and J join first
leader signal peptide
address label for the light chain peptide to the ER where it’ll get modified and assembled with heavy chain
cleaved prior to final assembly of heavy and light chain
basically just a postage stamp for light chain stuff
recombination process
germline config: V(D)J regions line up
somatic recombination: happens to DNA, RAG pulls up and binds to recombinement signal sequence (RSS). RAG then pulls the sequences together which makes that little loop guy
RAG cleaves unwanted piece of DNA
remaining segments joined by lipase
RSS sequences
recombinement signal sequence
where RAG binds on DNA during recombination
TWO KINDS
one turn (12 bp)
two turn (23 bp)
one turn binds with two turn, OPPOSITES ATTRACT
RAG complex and junctional diversity
generation of junctional diversity: a one turn and two turn segment line up
RAG cleaves the heptamer RSS from these segments which yields DNA hairpins
RAG opens up these hairpins, creating palindromic P-nucleotides
TdT (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase) adds random nucleotides to these segments
not all the nucleotides line up and match, so some are removed via exonuclease
DNA ligase fills in gaps in chain with matching nucleotides —> coding joint formed
junctional diversity complete great job team now the D and J segments can join together with even more diversity woooooo
flow cytometry
analyzes cells by identifying the types of cels present
lymph nodes
lymphocytes introduced to pathogens and activated
spleen
this is where T cells get activated and T cells activate B cells which make antibodies so this is kinda a big deal