Orgo exam 3 flash cards
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
carbonyl reduction
is a chemical reaction that involves the conversion of a carbonyl group (C=O) into an alcohol (C-OH). This process is typically achieved using reducing agents such as sodium borohydride or lithium aluminum hydride.
LiAlH4
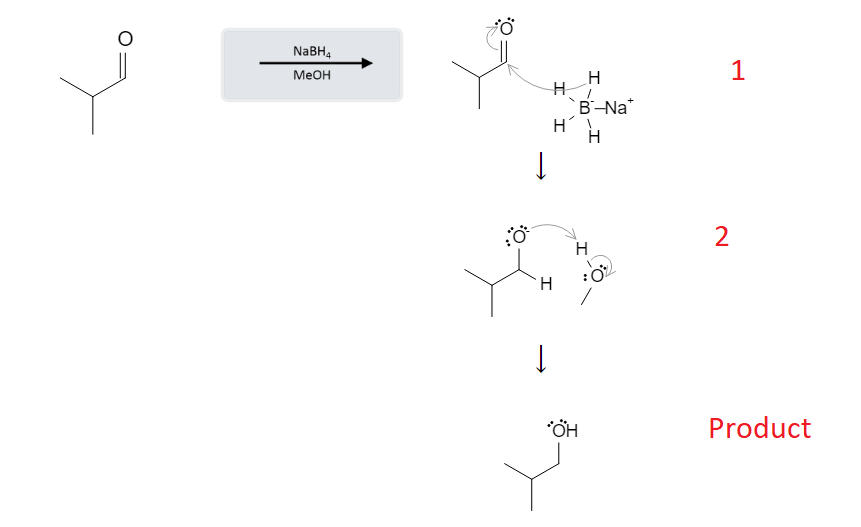
NaBH4
lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4)
reacts with aldehydes
ketone to form alcohols through reduction.
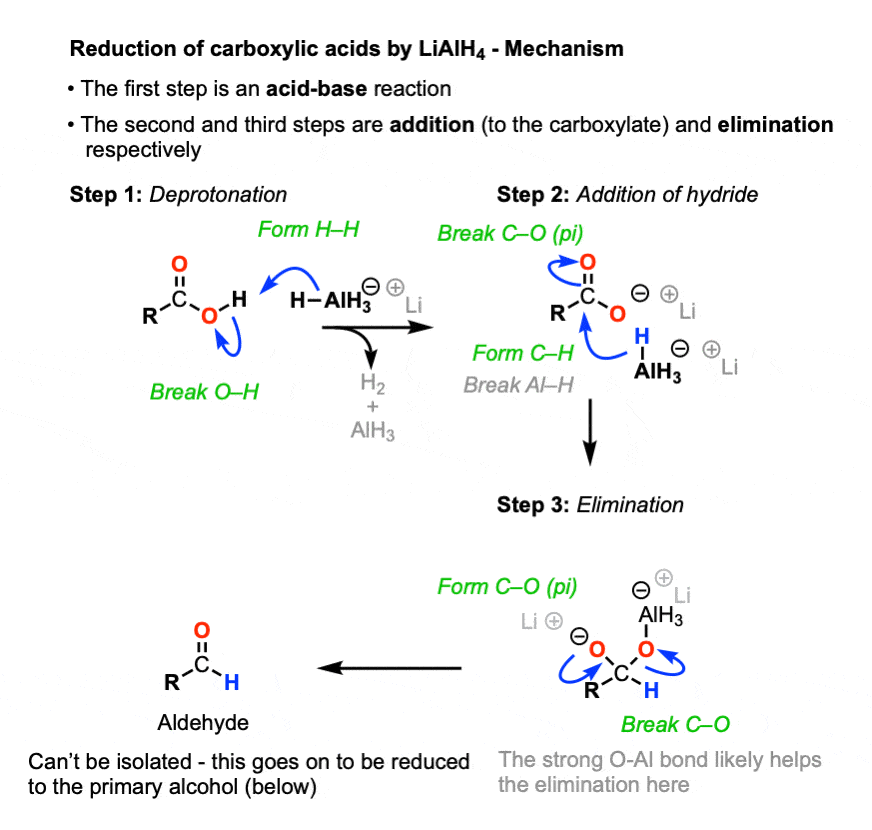
sodium borohydride (NaBH4)
reacts with ester amides aldehydes and ketones
elimination of alcohol
1- E2
2+3- E1
reagent for - H2SO4
TSOH
POCl3
H2SO4
1- E2
2+3- E1
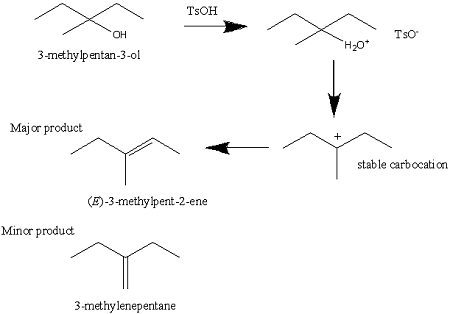
reagent used to dehydrate alcohols
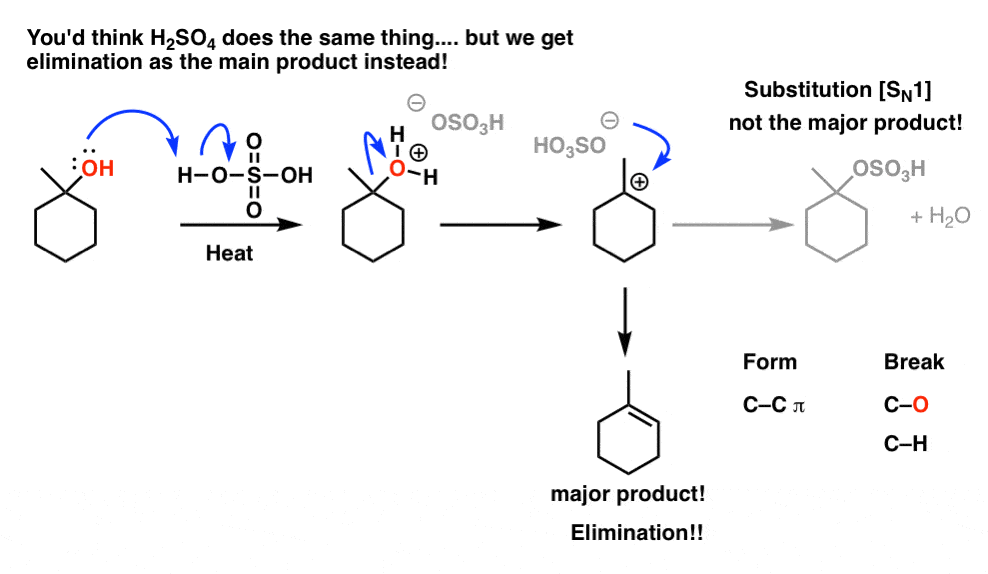
TSOH
A strong acid used as a reagent in dehydration reactions and promoting E1 and E2 eliminations of alcohols.
POCl3
A reagent used for the dehydration of alcohols, typically yielding alkenes through elimination reactions.
Only does E2 can do 1,2,3
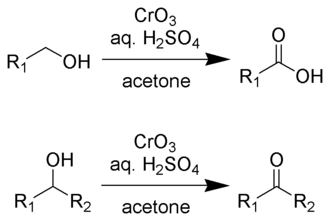
oxidation of alcohols
The process where alcohols are converted into carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes or ketones via oxidizing agents.
3 - tertiary carbons yield no reactions must have hydrogen
common reagents
CrO3/H2So4 - stronger
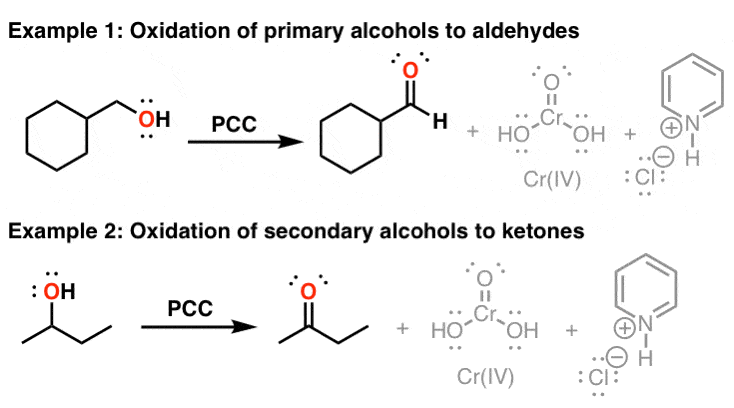
Pcc (Pyridinium Chlorochromate) - milder

CrO3/H2So4 - stronger
makes carboxylic acid at 1 - primary carbon
Pcc (Pyridinium Chlorochromate) - milder
makes aldehyde at 1 - primary carbon
protecting groups for alcohol
TMSCl/et3Ni
tbdmscl
removing protecting groups from alcohol
H3O+ ,TBAF
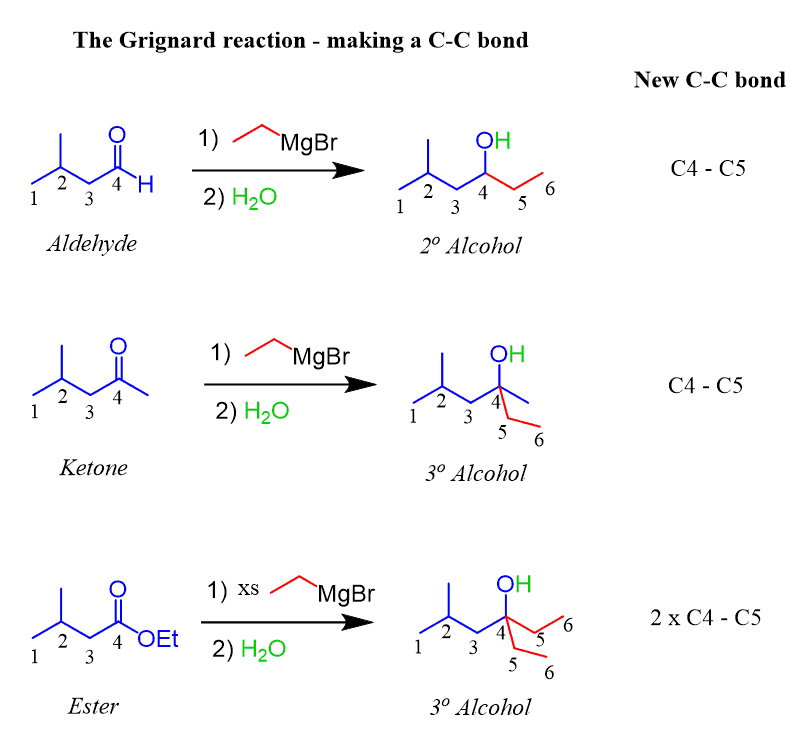
Grignard reagents
R-MgBr /H30 +
can be used to add things must be double bonded to oxygen removes all hydrogens and removes any addtional oxygens
substitution of alcohols
1- primary HX - SN2
2+3- secondary or tertiary—does SN1 HX
only SN2 and no-tertiary
SoCl2
PBr3
TSCl/ pyridine
make a good leaving group for SN2
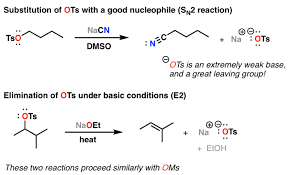
ether creation
NaH deprotnates alchol then leaving group gets booted out
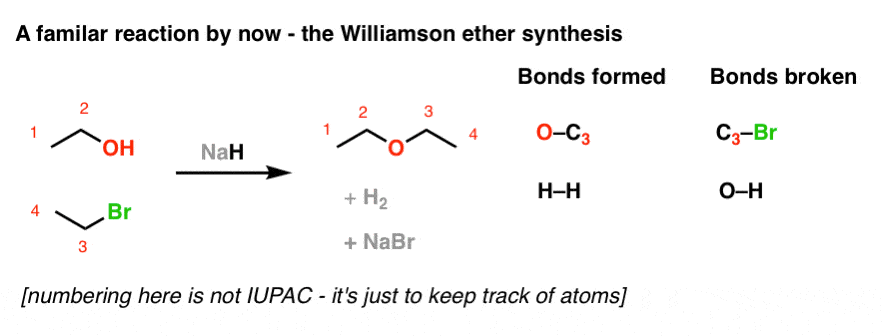
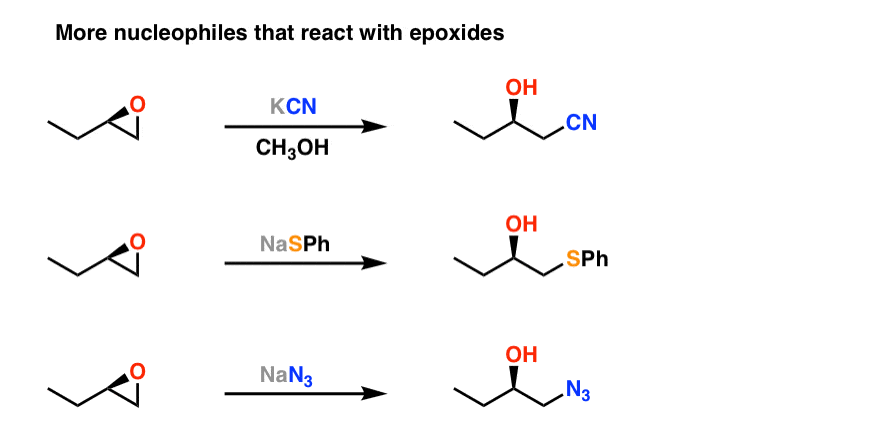
epoxidation with acid
OH goes to least substitution.
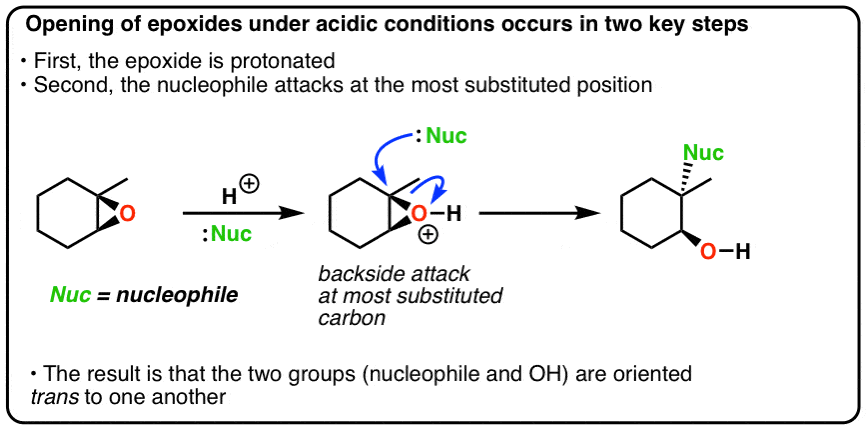
epoxidation with base
OH goes to most substitution.