BIO220 (Genomes to Ecosystems) - Lecture 3, Week 3
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
In small population the effects of genetic drift are [increased/decreased]. Describe how genetic drift affects the genetic variation and viability of subsequent offspring in a small population.
Increased. As population size is reduced, heterozygosity (i.e., genetic variation) is reduced, increasing the likelihood that members of the population will suffer from inbreeding depression.
Reduced population density enhances [blank] effects
Allee
Definition of Allee effects
Reduced population density, produces low reproductive rates (i.e., reduced population density is unable to facilitate density-dependent mating behaviours in colonial breeds)
Definition of demographic stochasticity
Variability observed of the reproductive rate in members of the population, and in survivorship in the resulting progeny producing uneven population growth overtime.
In small population the effects of demographic stochasticity are [increased/decreased].
Increased, due to a reduced effective population (Ne)
What is the genetic perspective on population extinction?
The reduction in population size and the subsequent decline of the effective population predominates extinction events.
What is the demographic perspective on population extinction?
The reduction in population size magnifies demographic stochasticity, predominating extinction events.
Predominant characteristic of the cheetah population. What is the proportion of polymorphic loci in the population?
Genetically depauperate (i.e., proportion of polymorphic loci in the population is 2-4%)
What are the three observed characteristics in the cheetah population that indicate inbreeding depression?
A low sperm count and a high susceptibility to disease were observed in captive members.
Reduced heterozygosity in the Major Histone Compatibility (MHC) locus.
What evidence, derived from field-based observations, complicated the narrative that inbreeding depression threatens cheetah populations?
Deceased cheetah specimens had no evidence of disease, or disease-induced mortality, suggesting the high disease load observed in captive cheetah species was a function of captivity.
The majority of juvenile mortality in the population is the result of predation, where low genetic variability is unlikely to influence the outcome.
What evidence, derived from genetic sequencing (i.e., MHC heterozygosity and amino acid variation, and nucleotide diversity), complicated the narrative that inbreeding depression threatens cheetah populations?
MHC heterozygosity is reduced in relative to other mammalian species; however, amino acid and nucleotide variation is similar to the variation observed in other felines.
What conclusions were derived from the field-based evidence, and genetic sequencing?
There is limited evidence to suggest reduced genetic variation in the cheetah population increases their susceptibility to disease or significantly influence their demography (i.e., no evidence for inbreeding depression)
What is the observed sex-based difference in the Florida Scrub Jay migratory behaviour?
Reproductive females migrate greater distances while males migrate shorter distances; however, most members of the population remain in one place once they sexually matured.
What are the implications on genetic diversity given the sex-based difference in migratory behaviour observed in the Florida Scrub-Jay (i.e., identity by descent and genetic variability present in sex chromosomes)
Females, particularly the W sex chromosome, have greater genetic variability within a population relative to the Z sex chromosome
Identity by descent is increasingly predominant in males in close proximity to each other; therefore evidence of identity by descent would be greater on the Z sex chromosome.
Definition of identity by descent
Identical stretch of DNA inherited from a recent, common ancestor
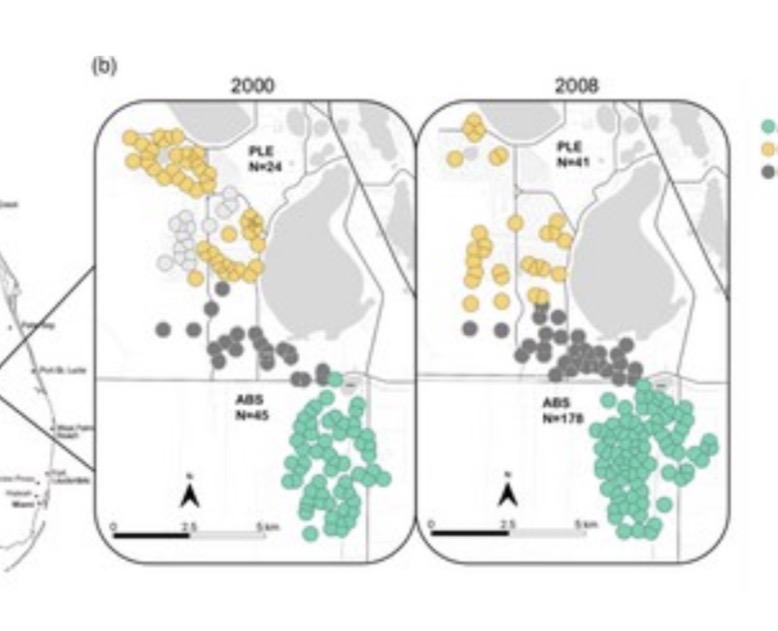
What is predicted to be observed, given the figure provided
Reduced heterozygosity and runs of homozygosity (i.e., allele fixation) in the smaller population due to inbreeding, while sustained heterozygosity in the stable population
How does inbreeding depression effect the Florida Scrub Jay population?
Reduces the viability of offspring (i.e., hatching success)