Biological Molecules
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Benedict's solution contains Cu2+ ions [copper(II) sulfate] that are blue. reducing sugars react with the copper ions reducing them to Cu+ ions [copper(I) sulfate] that are orange/red. the more reducing sugar present, the more precipitate formed meaning there are less Cu2+ in the solution therefore the precipitate is more brick red
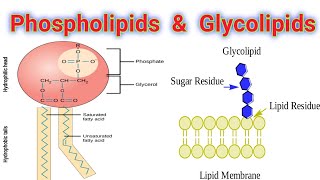
glycolipid is a molecule made of a lipid with a carbohydrate chain attached, found on the outer surface of the cell membrane. function = cell stability and function, cell surface receptors, cell-to-cell recognition, play role in immune response
roughly spherical. compact. hydrophobic r groups move to centre and hydrophilic r groups move to water, the amino acids twists due to this interaction. soluble. roles - transport, hormones, enzymes. contain prosthetic groups - are conjugated proteins. Examples: insulin, catalase, haemoglobin
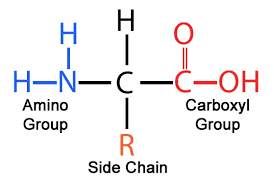
amino acid general structure
amine group, hydrogen, carboxyl group, alpha carbon, r-group
secondary structure
oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen atoms of aa interact to form hydrogen bonds (not include R-group). location of hydrogen bond depend on aa sequence. forms alpha helix or beta-pleated sheet
primary structure
sequence of amino acids - polypeptide chain. number and order of aa determines the function of the protein
tertiary structure
coils and pleats fold. held together by hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds - stronger than hydrogen bond, disulphide bridges - covalent bonds bw r groups, hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions - weak interactions bw polar and non-polar r groups.
quaternary structure
interaction of 2 or more individual proteins/polypeptide chains/subunits. chains do not have to be the same.
alpha helix
chain of aa coils into alpha helix - due to hydrogen bonds formed between oxygen from carboxyl group and hydrogen in amine group on an aa 4 aa ahead in the chain
beta pleated sheet
polypeptide chains lie parallel and are joined by hydrogen bonds. form sheet like structure. hydrogen bonds are strong enough to maintain shape but are easily broken by increase in temperature or change in pH
how is tertiary structure affected by heat
increase kinetic energy. bonds holding globular protein together break (not covalent bonds). complex shape of protein unravels. tertiary structure defines the active site of enzymes.
the breakdown of dipeptides and polypeptides
hydrolysis reaction breaks peptide bond