GRAVITATIONAL FIELDS TO REMEMBER
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Gravitational field
The force field around a mass is a gravitational field. A force field is a region where a body will experience a non contact force.
Gravitational field line
The direction, and relative magnitude, of force on a small mass placed in the gravitational field of a large mass.
Gravitational field strength
The gravitational field strength at a point is the force per unit mass on a small mass at that point. (The gravitational field strength is equal to the negative of the potential gradient.)
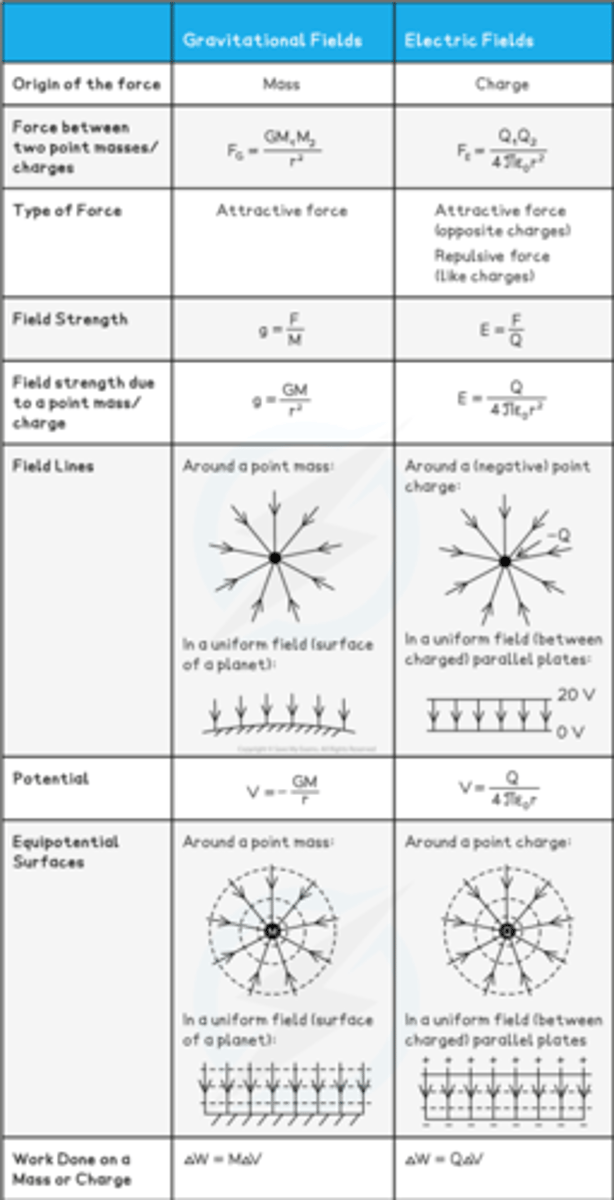
Similarities between gravitational and electrostatic forces
1. Both forces follow inverse square law relationships with distance
2. The field lines in uniform gravitational and electric fields are identical
3. Both gravitational potential and electric potential both follow an inverse (1/r) relationship with distance
4. The equipotential surfaces are spherical around a point mass or charge and equally spaced parallel lines in uniform fields
5. The work done by either field is equal to the product of the mass or charge and change in potential
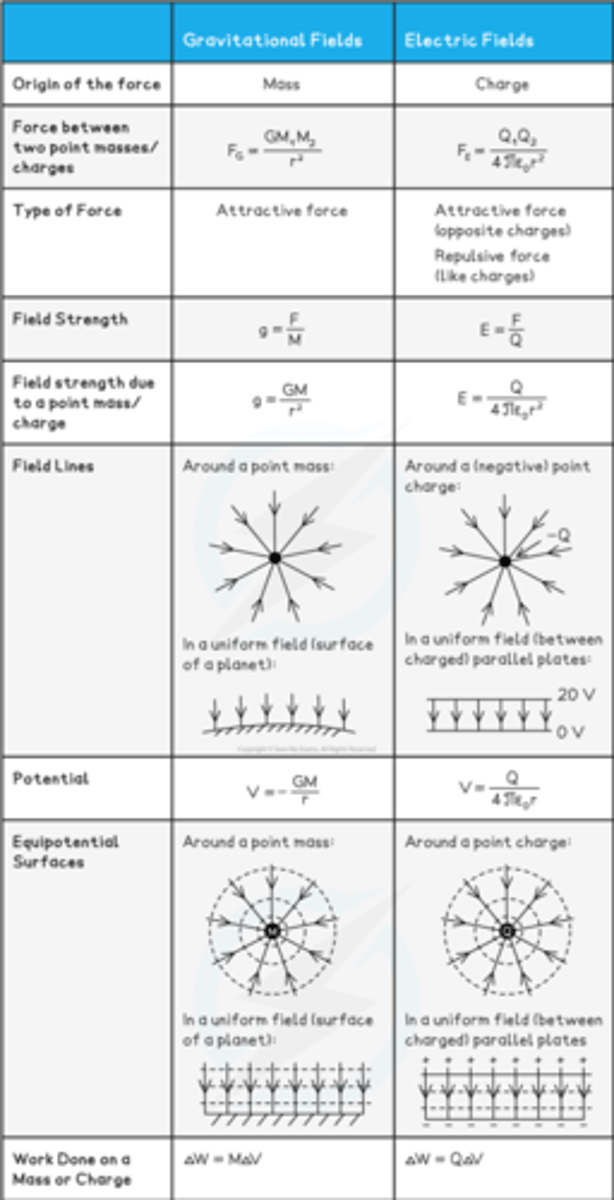
Differences between gravitational and electrostatic forces
1. The gravitational force acts on particles with mass whilst the electrostatic force acts on particles with charge
2. The gravitational force is always attractive whilst the electrostatic force can be attractive or repulsive
3. The gravitational potential is always negative whilst the electric potential can be either negative or positive
4. Gravitational fields are relatively weak compared to electric fields as the gravitational constant G is much smaller than the Coulomb constant k
Newton's law of Gravitation
The force of attraction between two masses is directly proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional to the square of their separation.
Gravitational potential energy
The energy of an object due to its position in a gravitational field (position for zero g.p.e. is at infinity).
Gravitational potential
The work done per unit mass in moving a small object from infinity to that point (i.e. the gravitational potential energy per unit mass)
Gravity
Defined as force per unit mass
- universal attractive force acting between all matter
Equipotential
A 2-dimensional surface of constant potential. No work needs to be done to move along an equipotential surface.
Potential gradient
The potential gradient at a point in a gravitational field is the change of potential per metre at that point
Uniform
Gravitational field strength is the same everywhere. Field lines are parallel and equally spaced
Radial field
Due to a point mass or uniform spherical mass. Gravitational field strength follows inverse square law
Magnitude of g in radial field
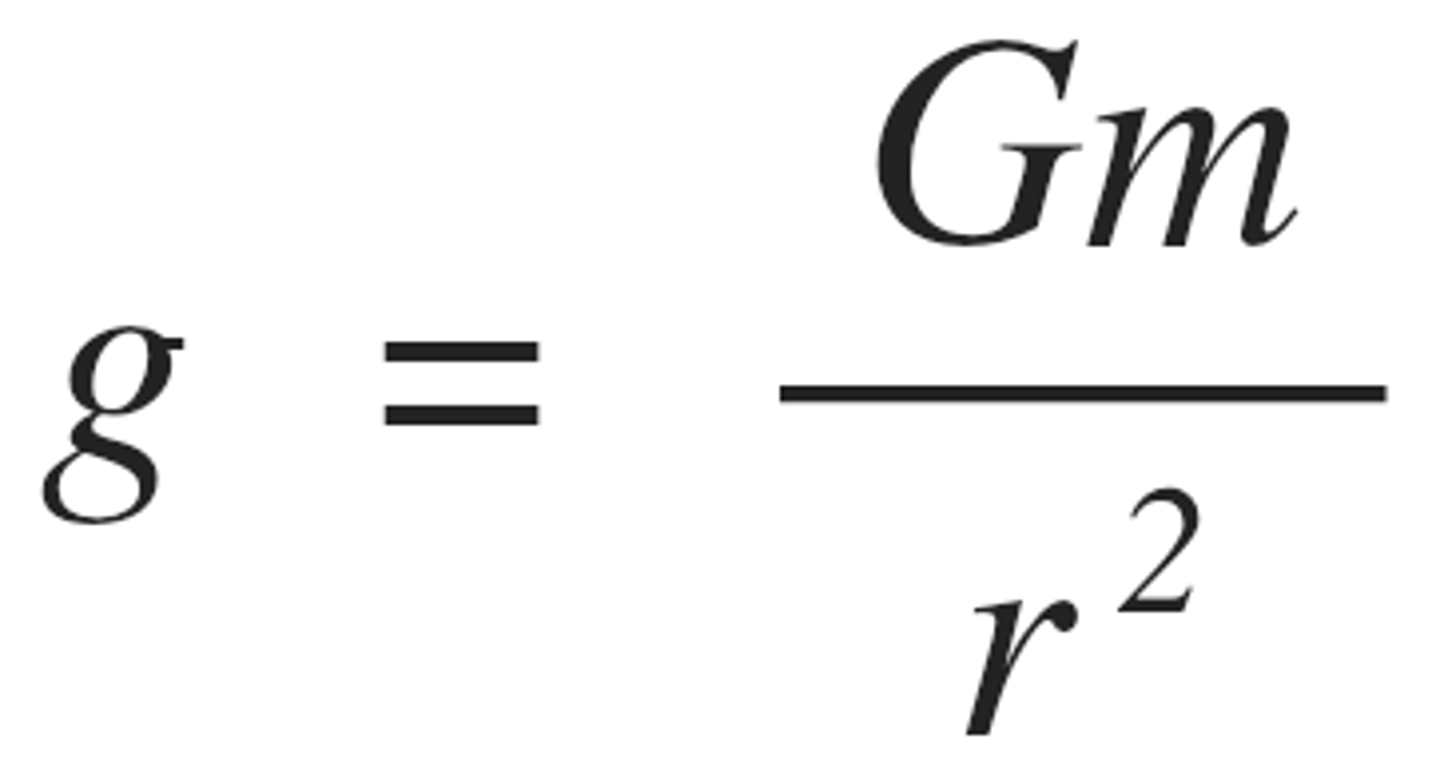
Escape velocity
The minimum velocity an object must be given to escape from a large mass (e.g. planet) when projected vertically from the surface
Geostationary satellite
A satellite which orbits the Earth directly above the equator and has a time period of exactly 24 hours.
(Note that a geosynchronous orbit is a 24 hour orbit inclined to the equator.)
Why are gravitational potential energy (Eₚ) values negative (2 marks)
(1) Eₚ is defined as zero at infinity
(2) Because work is done by the field moving the object from infinity
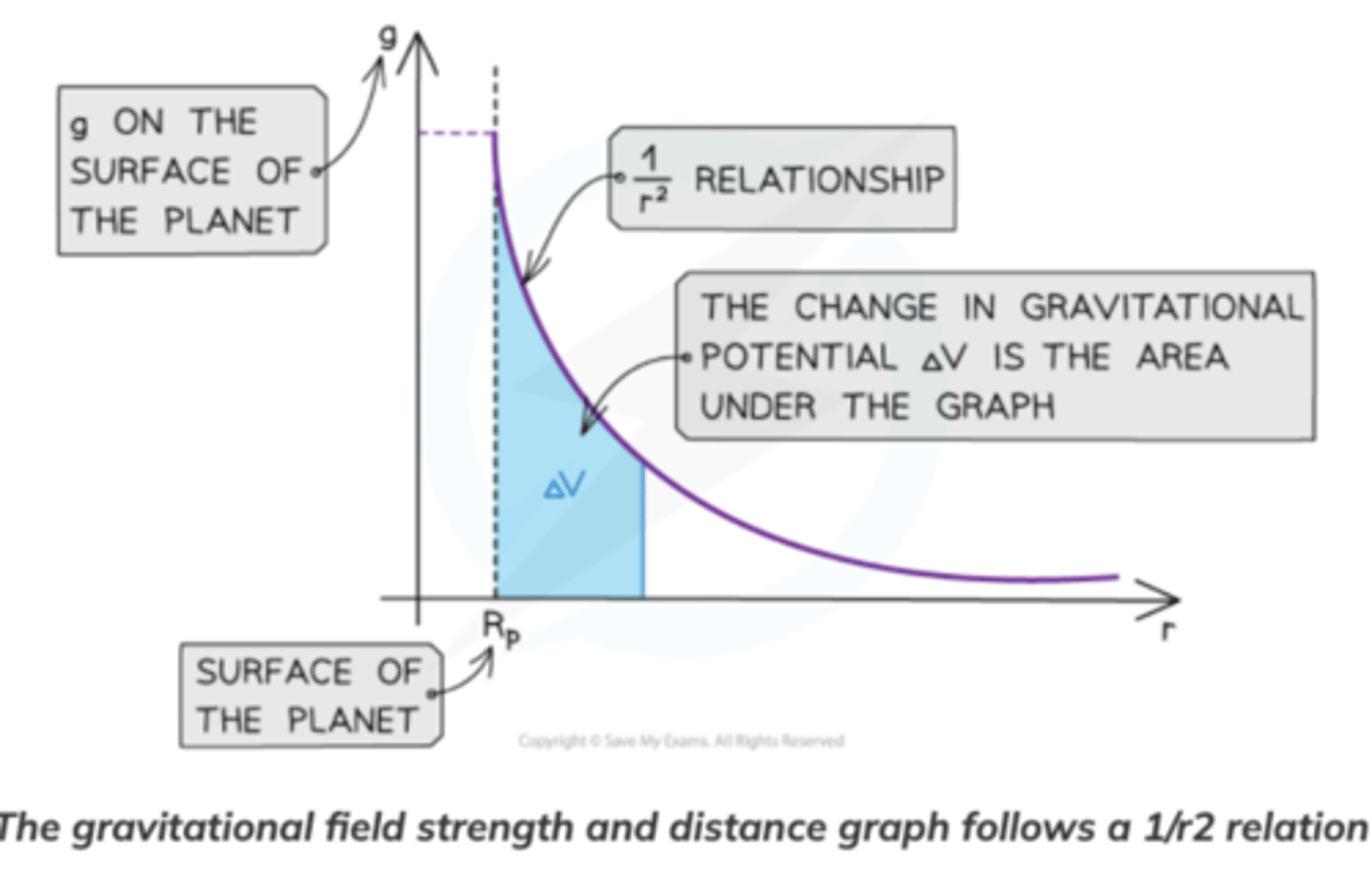
What is the area under a graph of g against r
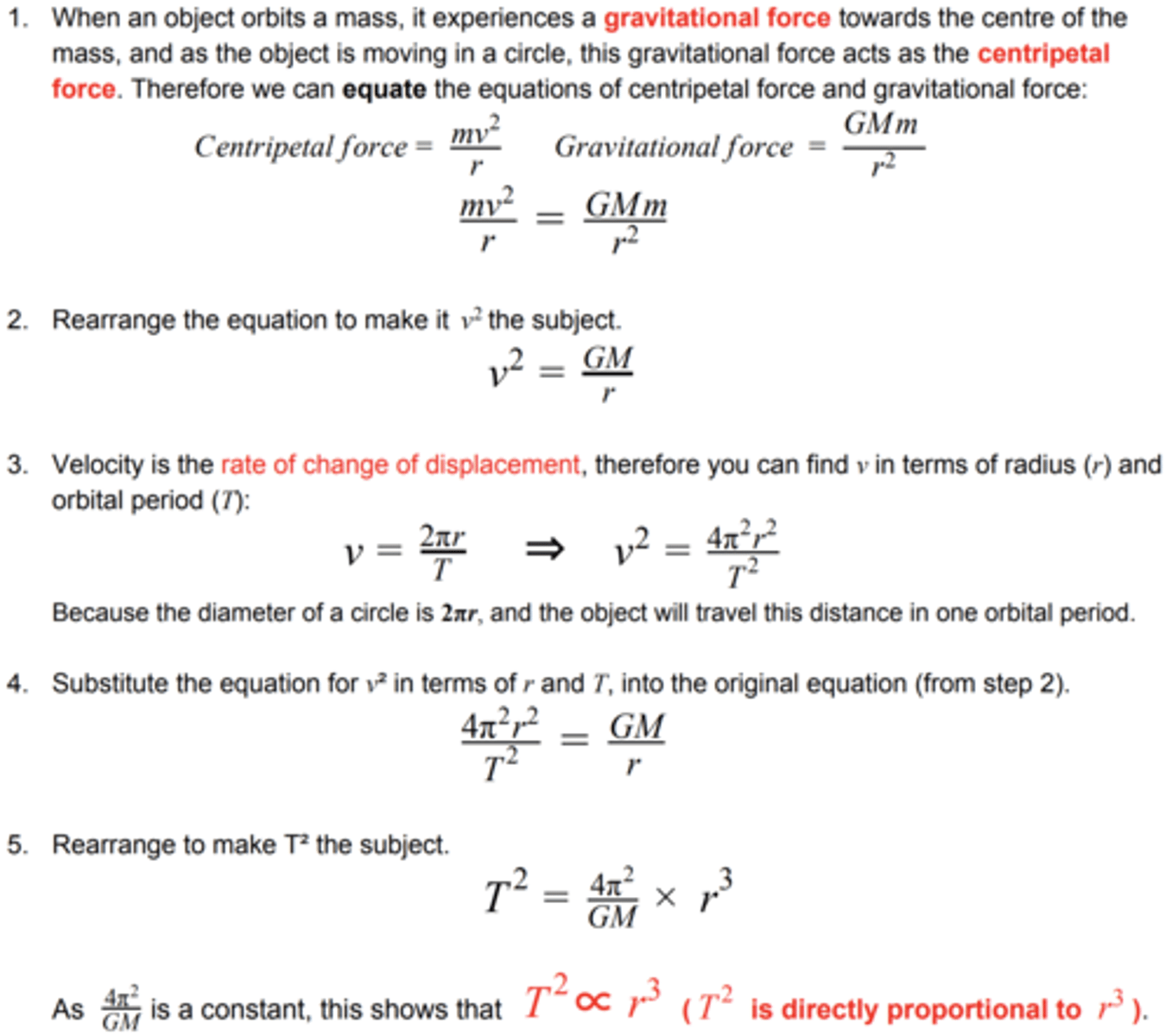
Derivation of Kepler's Third Law
Derivation of escape velocity
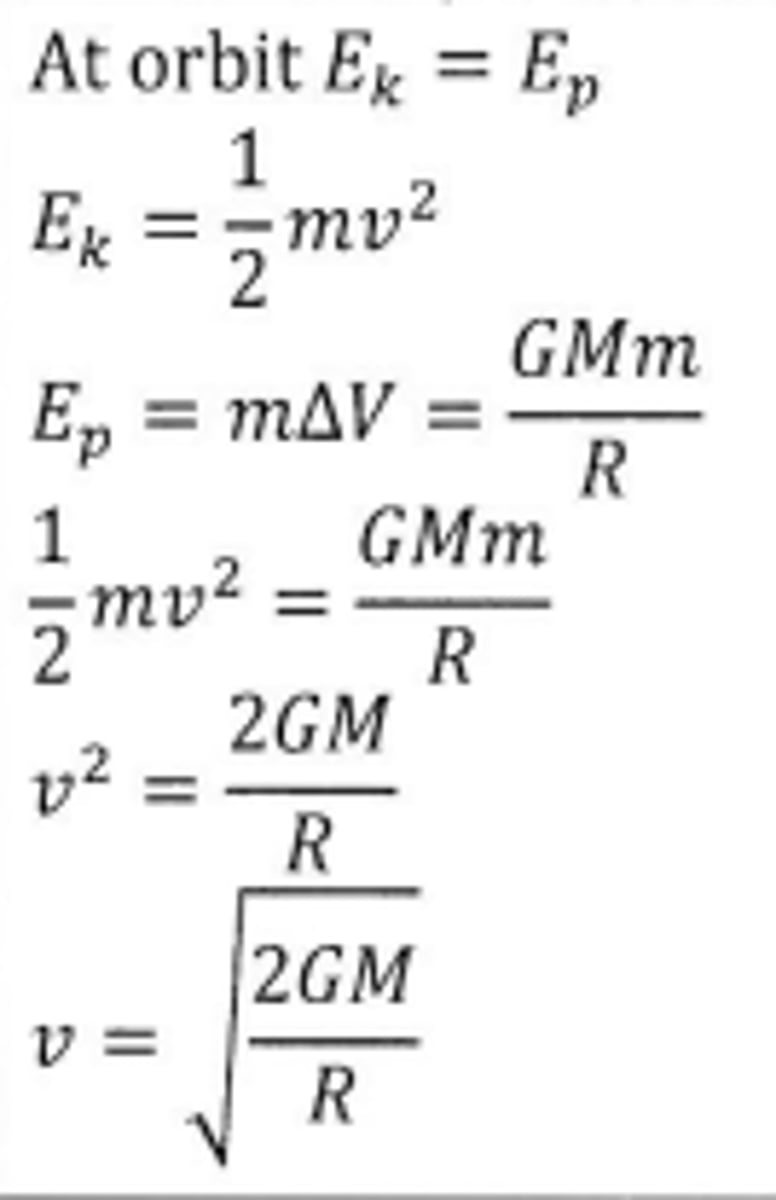
Derivation of orbital speed
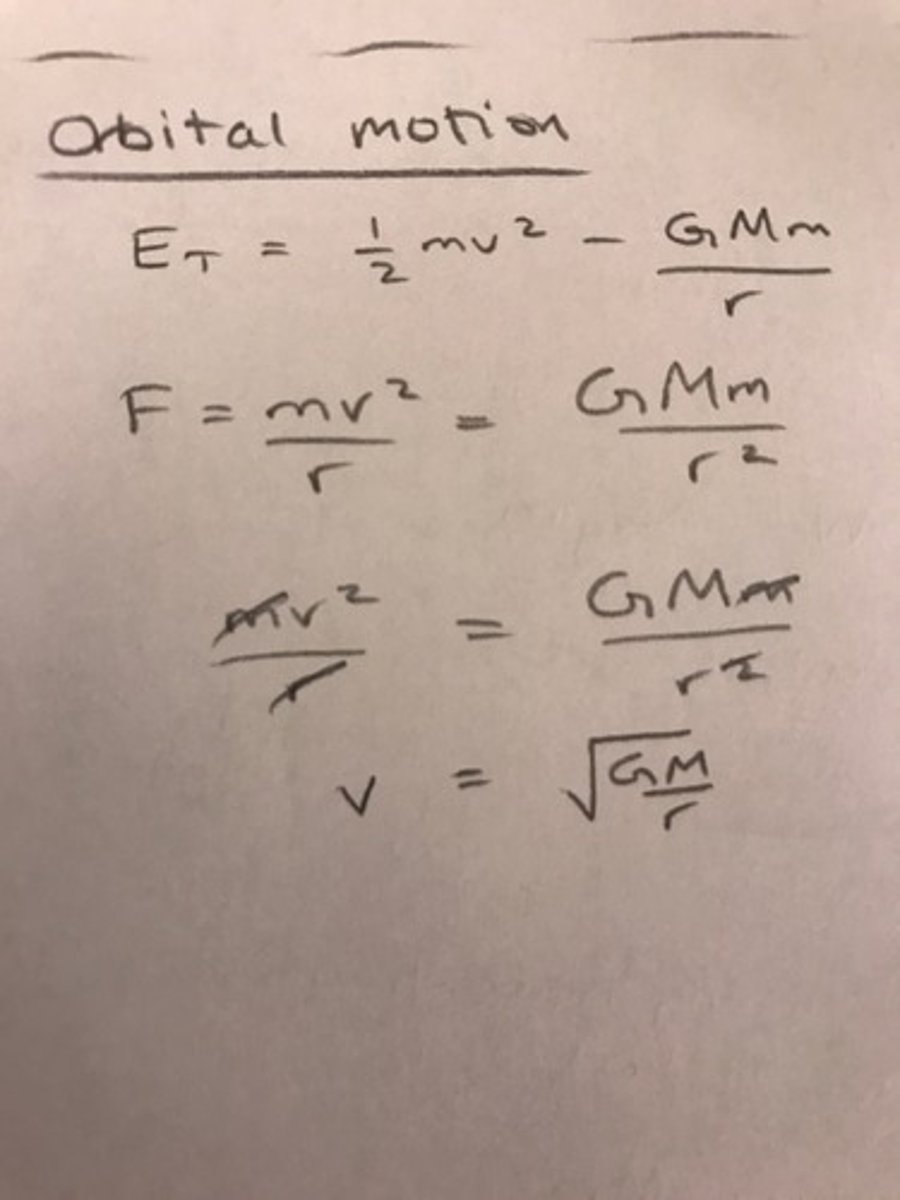
Graph of kinetic, potential and total energy of a satellite with the radius of orbit
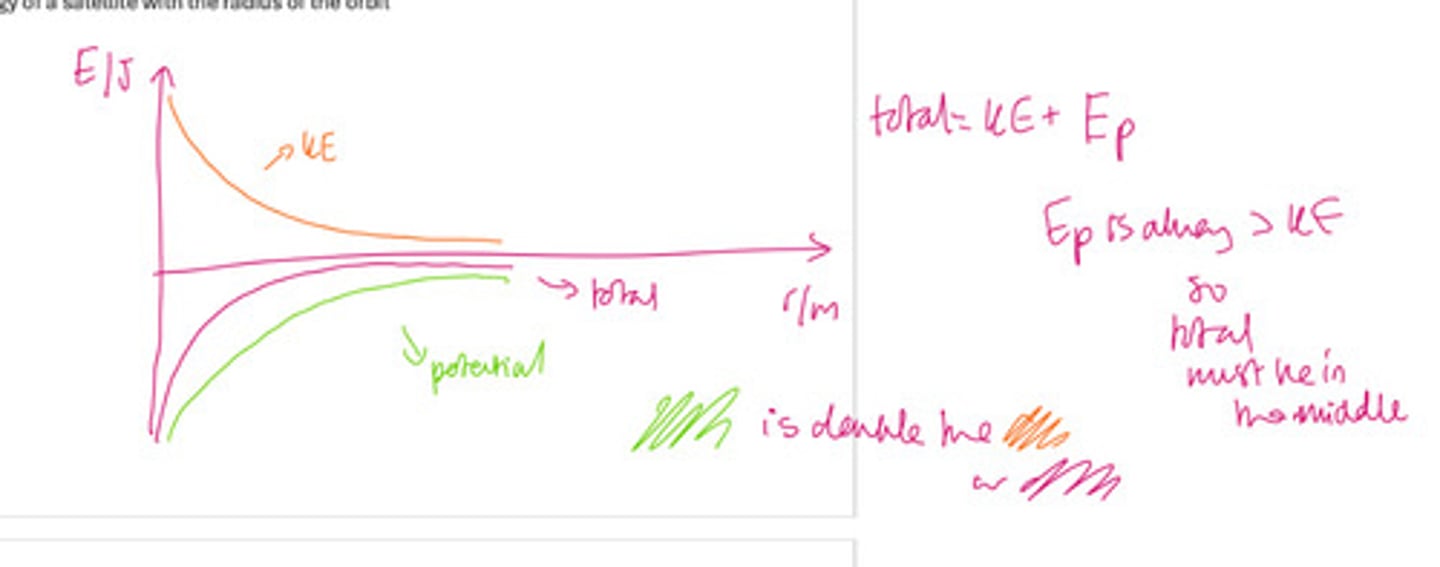
Total energy =
Kinetic energy + Gravitational potential energy
Synchronous orbit
When an orbiting body has a time period equal to that of the body being orbited and in the same direction of rotation as that body
Uses of low orbit satellites
Weather
Military applications
Uses of geostationary satellites
Telecommunication transmissions (e.g. radio) and television broadcast
Kepler's third law
For planets or satellites in a circular orbit about the same central body, the square of the time period is proportional to the cube of the radius of the orbit