Nutrients, Biogeochemical Cycles, and Climate Change in Oceanography
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What are nutrients?
Inorganic compounds used by bacteria and plants to build organic material.
List some examples of essential nutrients.
Inorganic carbon (TCO2), phosphate (PO4), nitrogen (NH3 or NO3), silicon (H4SiO4), essential metals (Fe, Mg, Cu, V, Mo, etc.).

How do nutrients enter organic molecules?
Through biochemical processes like photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy = C6H12O6 + O2.
What is the equation for respiration?
C6H12O6 + O2 = 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy.
What is a limiting nutrient?
The nutrient that is least abundant in proportion to demand, limiting growth.
What nutrients limit phytoplankton growth in the ocean?
Fixed nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), silicon (Si), and iron (Fe), depending on location.
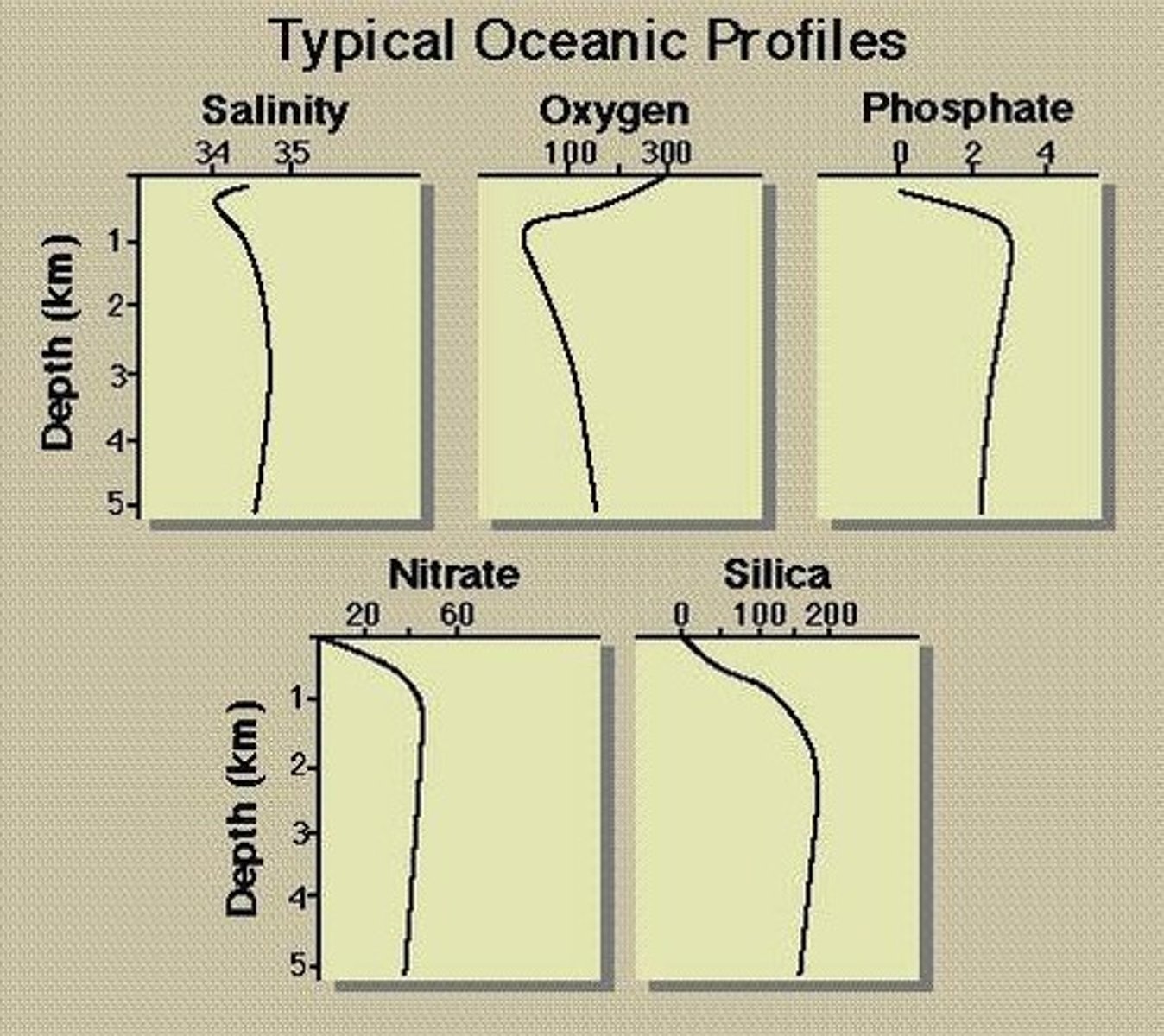
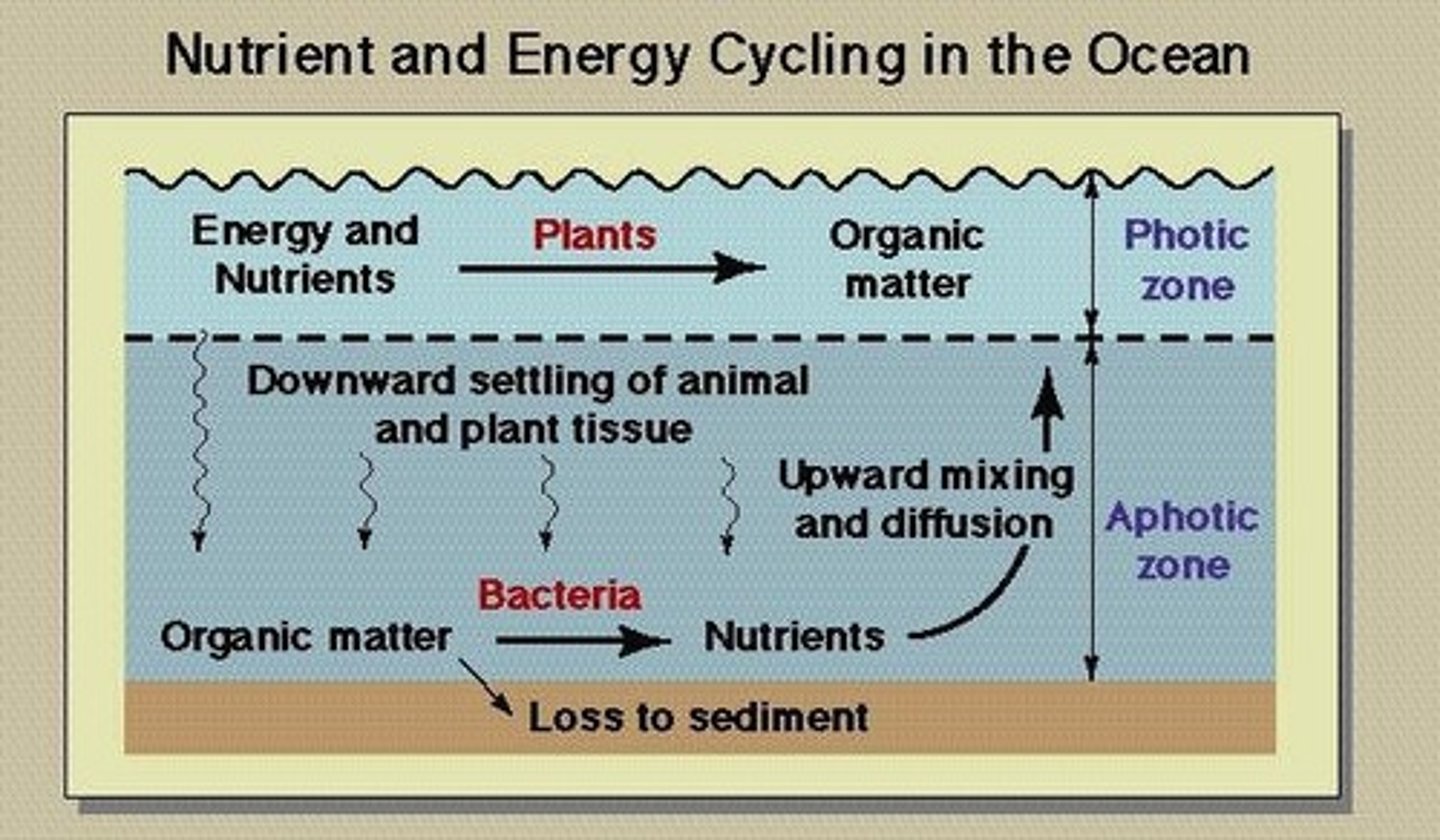
What is the photic zone?
The upper layer of the ocean where sunlight penetrates and photosynthesis occurs.
What happens to nutrients in the aphotic zone?
Phytoplankton decomposes, releasing nitrate as particles settle.
Why is nutrient content low in the surface ocean?
Due to phytoplankton uptake and particle settling.
What is the difference in nutrient content between Pacific and Atlantic deep water?
They differ due to vertical cycles and horizontal flow of deep water.
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The process where nitrogen occurs in various compounds (N2, NO3, NH3) and is recycled in ecosystems.
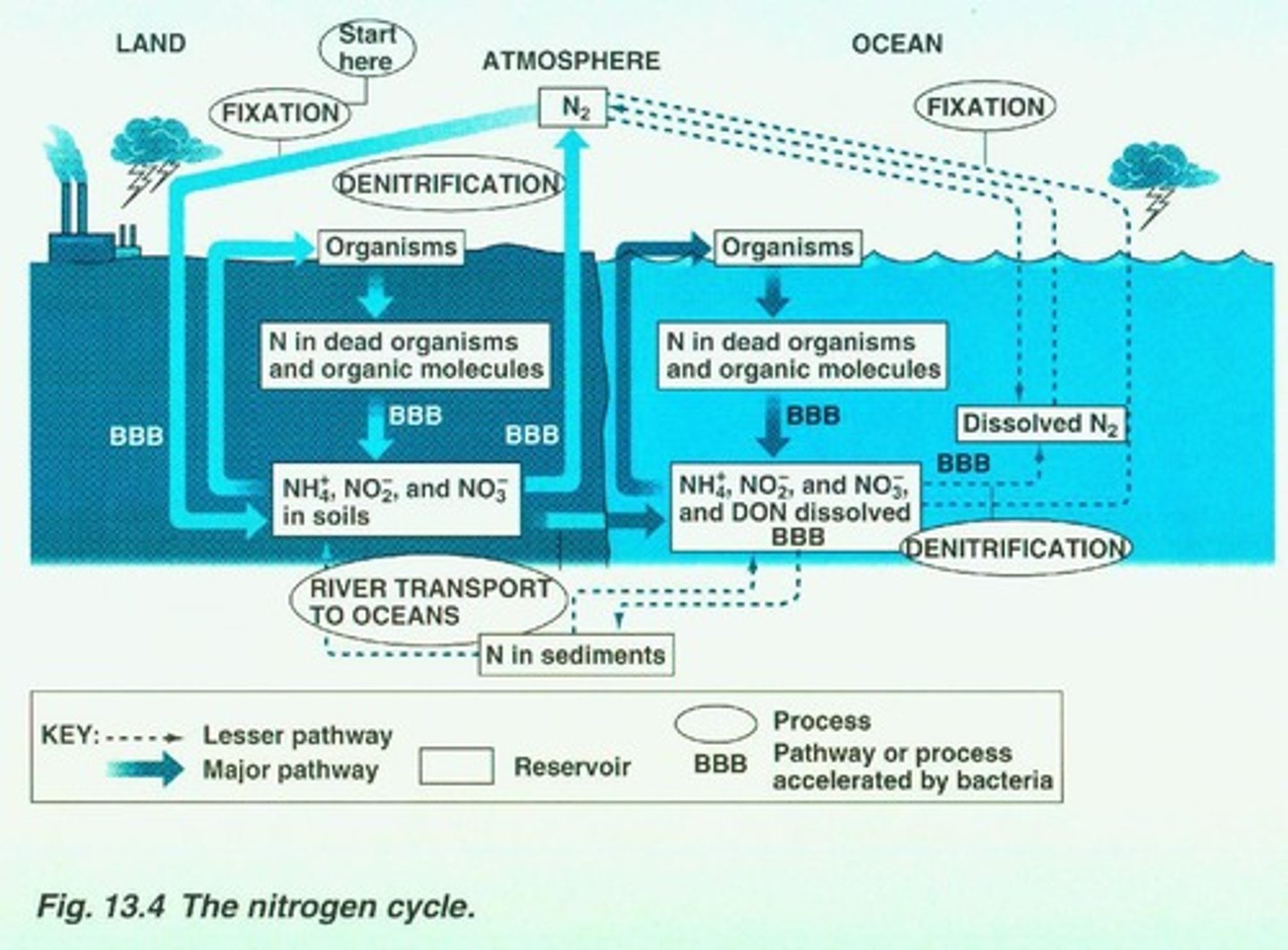
How do nitrates and nitrogen gas enter the oceans?
From the atmosphere and rivers.
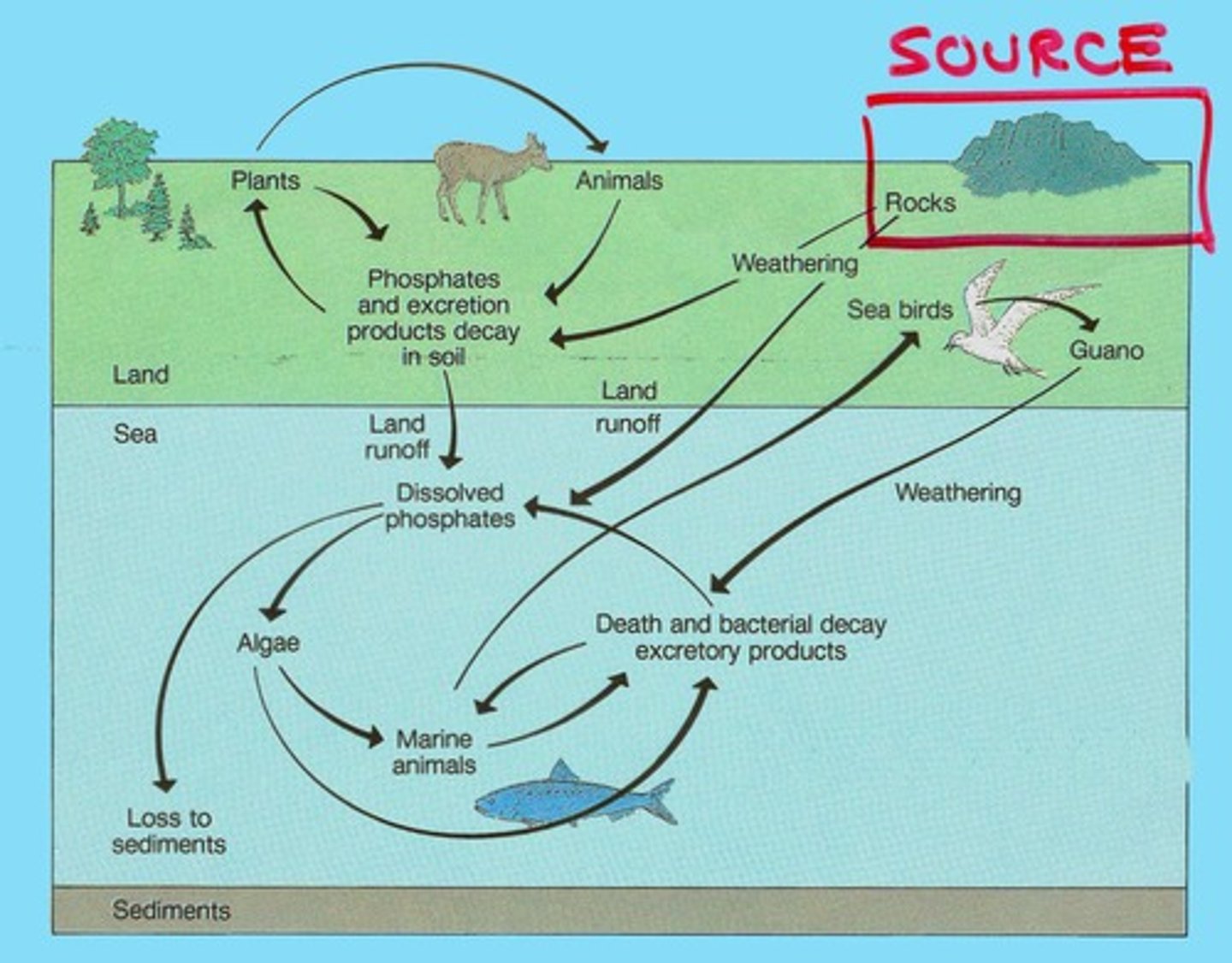
What is the phosphorus cycle?
The cycle where phosphorus is input, recycled, and lost in ecosystems.
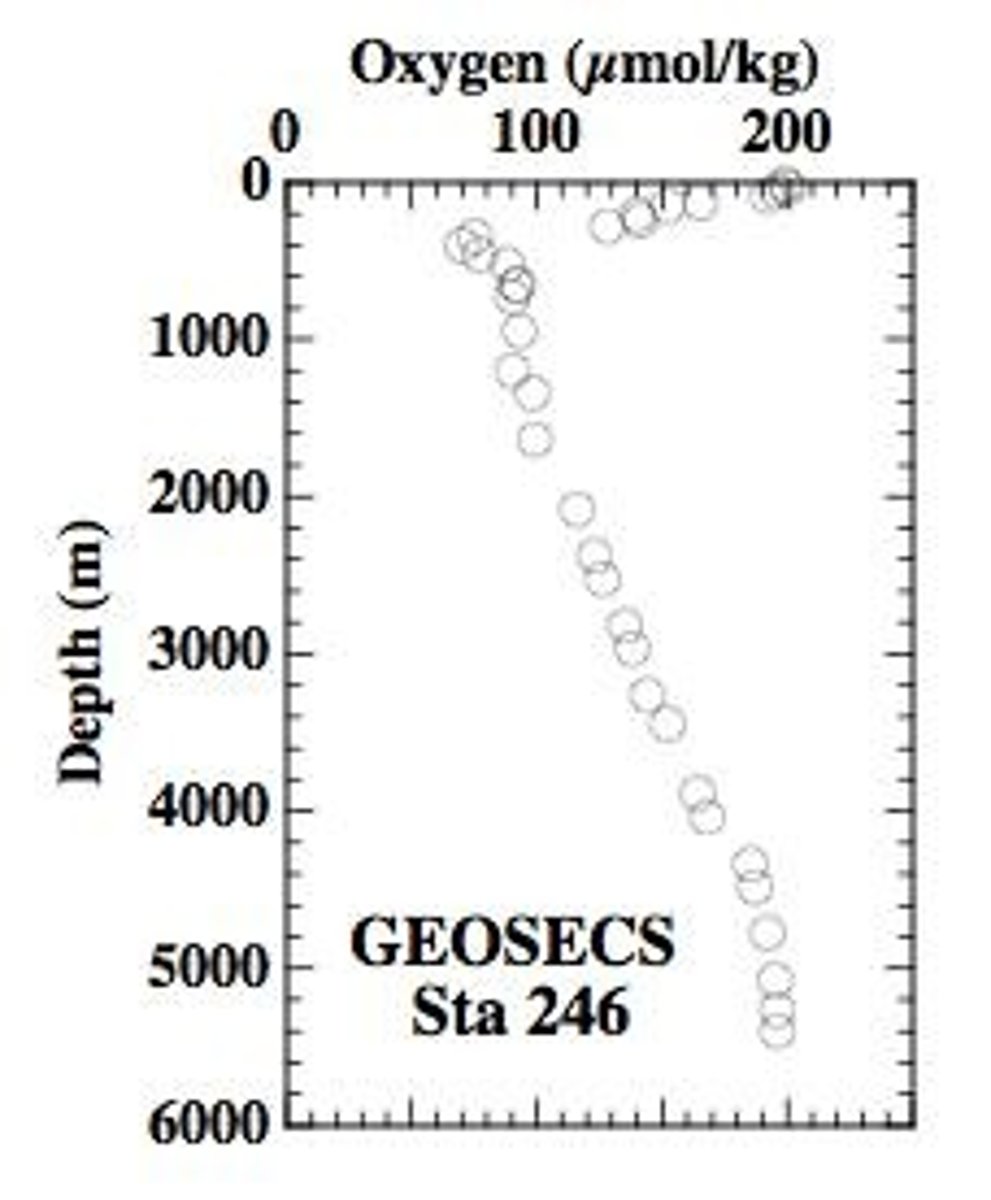
What is an oxygen minimum zone?
A layer below the photic zone where oxygen levels are low, affecting organism survival.
What causes eutrophication in lakes and coastal zones?
Nutrient input leads to algal blooms, which degrade and cause anoxia, killing fish.
What is the role of upwelling in nutrient supply?
Upwelling brings nutrients from the deep ocean to the surface, enhancing productivity.
What is the significance of chlorophyll reflectance data?
It helps identify ocean productivity and upwelling patterns over time.
What is the relationship between nutrient concentration and seasons?
Nutrient levels increase in winter due to upwelling and decrease in spring due to high productivity.
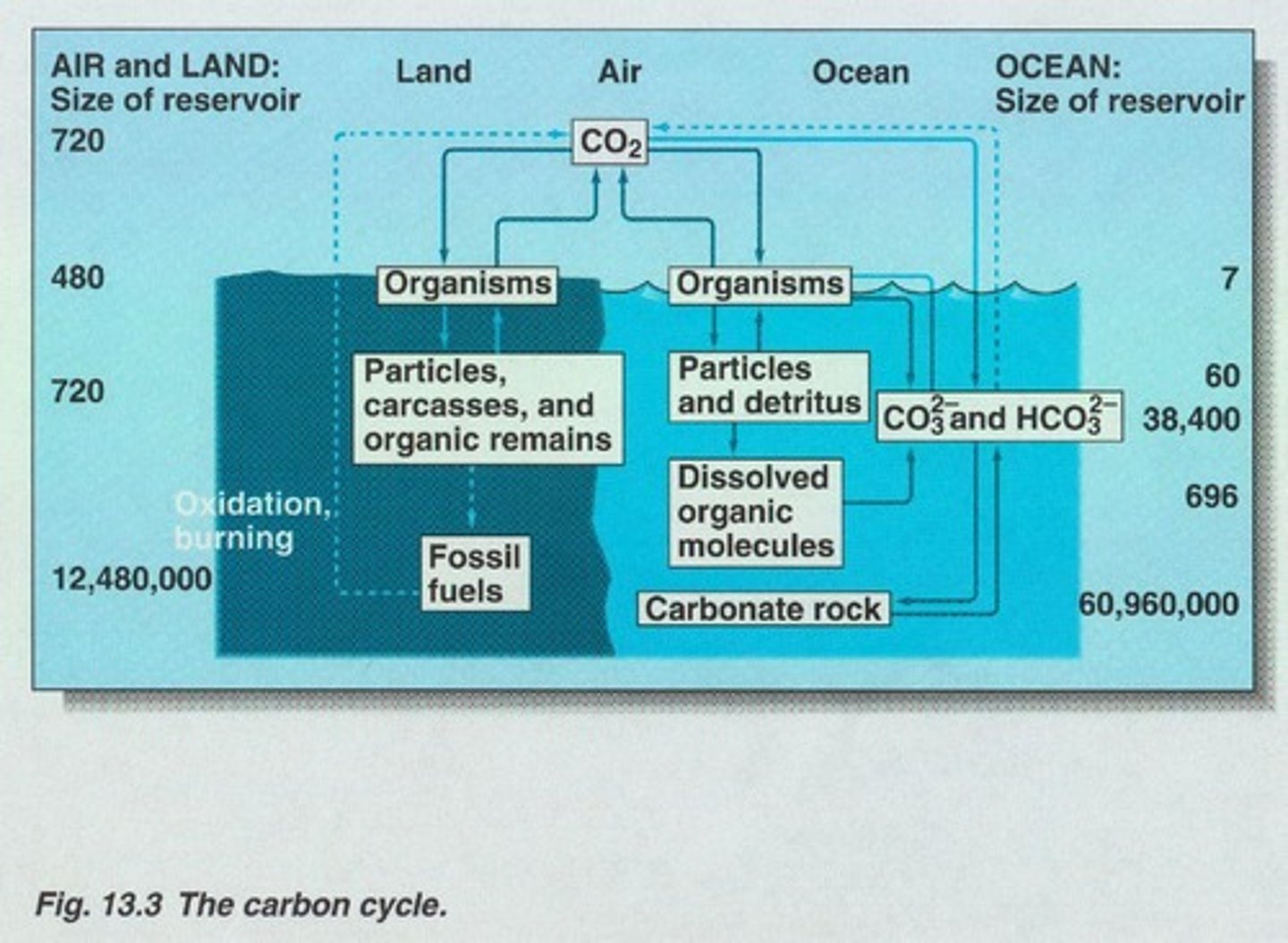
What are carbon inventories in the ocean?
The total amounts of carbon stored in various reservoirs like the atmosphere, living plants, and deep ocean.
What is biogeochemical cycling?
The movement of nutrients through the Earth as they are used and reused.
What happens to gases in the ocean?
They equilibrate with the atmosphere and can be recycled through biological processes.
What is the stoichiometry of nutrients in the ocean?
In the ocean, the ratio of carbon to nitrogen to phosphorus is approximately 106:16:1.
What is the impact of organic decomposition below the photic zone?
It creates an oxygen minimum zone, affecting the survival of marine organisms.
What is the role of bacteria in nutrient recycling?
Breaks down organic matter and recycle nutrients for use by other organisms.
What is the significance of nutrient cycles in ecosystems?
They ensure the availability of essential nutrients for life and support biological productivity.
What role does carbon dioxide play in Earth's atmosphere?
Carbon dioxide is a key component that has varied significantly over Earth's prehistoric past, affecting climate.
How did carbon dioxide and water vapor enter Earth's atmosphere?
They likely entered through outgassing from the Earth's interior during volcanic eruptions.
What was the composition of Earth's early atmosphere?
It is believed to have been rich in carbon dioxide (95%), with minimal water vapor (0.03%) and negligible oxygen.
What is the significance of the Faint Young Sun Paradox?
It questions why Earth wasn't colder despite the Sun being 30% less bright when it formed, suggesting higher early carbon dioxide levels kept the planet warmer.
What major event led to a decrease in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels?
The rise of efficient photosynthesis, which converts CO2 into organic matter and oxygen.
What is the estimated residence time of CO2 in the ocean-atmosphere system?
Approximately 300,000 years.
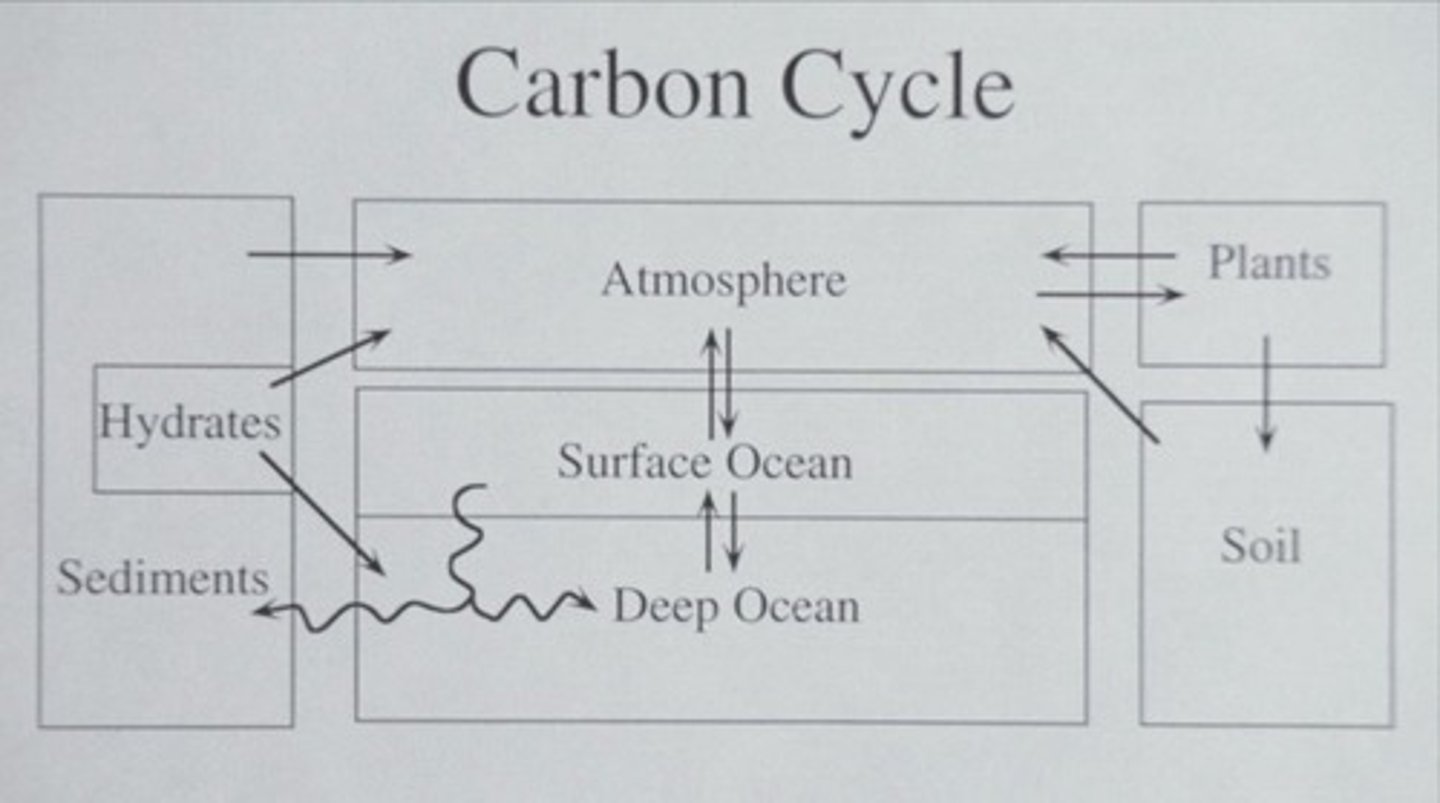
What processes are involved in the long-term carbon cycle?
Physical processes include volcanic activity and weathering, while biological processes involve photosynthesis and respiration.
What are the major sources of atmospheric CO2?
Large igneous provinces (LIPs) and mid-ocean ridge volcanism.
What are the major sinks for atmospheric CO2?
Chemical weathering and biological processes like photosynthesis.
How do plate configurations affect climate?
Continents near poles or shielding them from warm ocean currents can lead to high-latitude glaciations.
What evidence indicates that CO2 levels have varied significantly over time?
Geological evidence and sedimentary proxies show fluctuations in atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
What is the relationship between glaciations and CO2 levels?
Glaciations correlate with low CO2 levels in the atmosphere.
What is the estimated atmospheric CO2 concentration today?
Approximately 350 ppm.
What is the atmospheric composition of Venus?
About 96% CO2, 3% N2, and a surface temperature of 460°C.
What is the atmospheric composition of Mars?
Less than 0.1% CO2, 3% N2, and a surface temperature of -63°C.
What is the impact of temperature on dissolved gases in water?
Warmer water holds less dissolved gas.
What is the carbon cycle's short-term recycling time?
Less than 80 years.
What are the carbon reservoir estimates for the atmosphere?
Approximately 100 moles C/m2.
What is the carbon reservoir in living plants?
About 50 moles C/m2.
What is the carbon reservoir in sediments?
Approximately 4,000,000 moles C/m2.
What is the significance of chemical weathering in the carbon cycle?
It acts as a temperature moderator and provides negative feedback in the climate system.
What happens to CO2 levels during ice ages?
CO2 levels tend to decrease during ice ages.
What is a major factor in the long-term stability of Earth's climate?
Negative feedbacks that stabilize the geosystem.
How does volcanic activity contribute to atmospheric CO2?
Volcanic eruptions release CO2 into the atmosphere, contributing to greenhouse gas levels.
What is the primary greenhouse gas discussed in relation to climate change?
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
How does the temperature of ocean water affect CO2 levels?
Colder ocean water can hold more gases, leading to lower atmospheric CO2 during glacial periods.
What is the Biological Pump?
A process that increases biological primary productivity to reduce greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere.
What challenges exist in increasing biological productivity on land?
Population growth, urbanization, and agriculture make it difficult.
What hypothesis suggests that adding iron to oceans can enhance biological productivity?
The Martin Hypothesis.
What are the two main effects of rising CO2 levels?
Global warming and ocean acidification.
What chemical reaction describes ocean acidification?
CO2 + H2O -> H+ + HCO3
What does the geological record indicate about high atmospheric CO2 concentrations?
They are normally associated with warmer planetary temperatures.
What is a significant challenge in determining the cause-and-effect relationship between greenhouse gas concentrations and temperature changes?
Lack of detailed climate records for pre-Holocene times.
What do climate models suggest about the relationship between greenhouse gas concentrations and temperature changes?
Temperature changes likely lag behind increases in greenhouse gas concentrations.
What is the long-term carbon cycle?
It contrasts carbon storage during sedimentation/burial with outgassing at volcanoes and chemical weathering of rocks.
What is the short-term carbon cycle influenced by?
Variations in biological productivity versus burial.
How have human activities affected the short-term carbon cycle?
By significantly modifying it and adding CO2 to the atmosphere through the use of fossil fuels.
What are the two types of carbon cycles discussed?
Long-term carbon cycle and short-term carbon cycle.
What characterizes an Icehouse world?
A climate state with low atmospheric CO2 levels and colder temperatures.
What characterizes a Greenhouse world?
A climate state with high atmospheric CO2 levels and warmer temperatures.
What is the significance of the Little Ice Age and Medieval Warm Period in climate studies?
They are examples of climate variability that occurred without significant changes in greenhouse gas concentrations.
What percentage of fossil fuel CO2 is estimated to remain in the atmosphere?
50%.
What percentage of fossil fuel CO2 is estimated to be absorbed by the oceans?
25%.
What is the unknown fate of fossil fuel CO2 estimated to be?
25%, likely absorbed by the biosphere.
Sea salt is an example of what?
Nutrients.
Where will the concentration of nutrients be lowest?
Ocean surface.
Where are nutrients incorporated into autotrophs?
During photosynthesis.
Energy loss is a factor in what?
Nutrient cycles.