AP Environmental Science Unit 8: Aquatic and Terrestrial Pollution
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
point source
a discharge of pollutants from a specific location
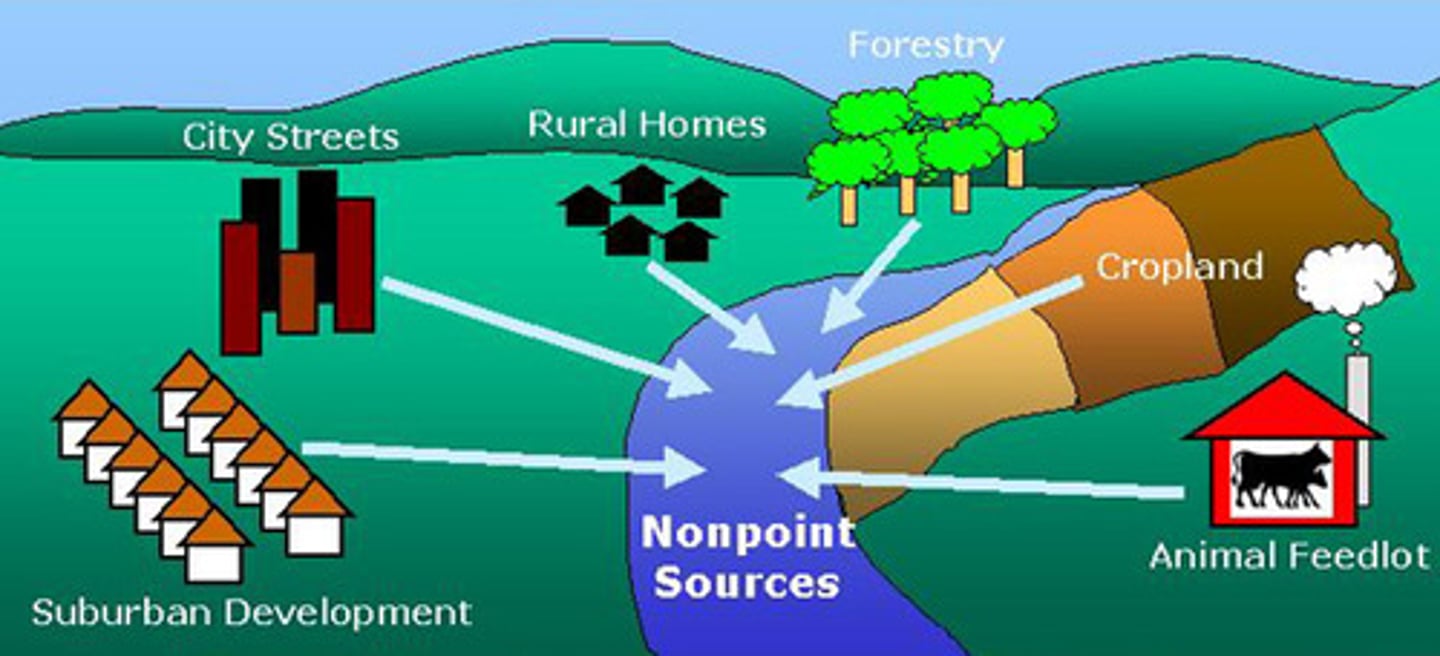
nonpoint source
a diffuse area that produces pollution
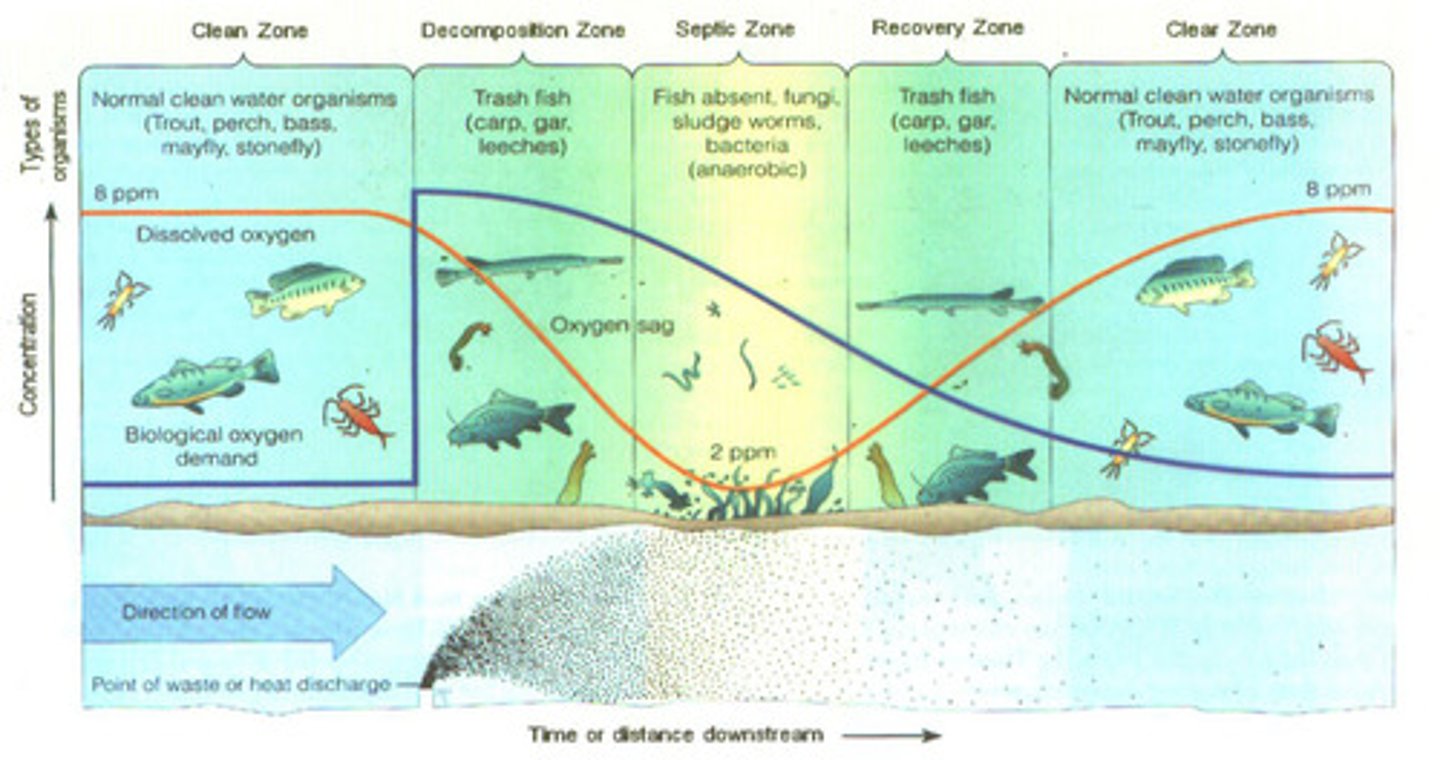
biochemical oxygen demand
the amount of oxygen a quantity of water uses over a period of time at specific temperatures
Eutrophication
A process by which nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in a body of water, leading to increased growth of organisms such as algae or cyanobacteria.
algal bloom
The rapid growth of a population of algae
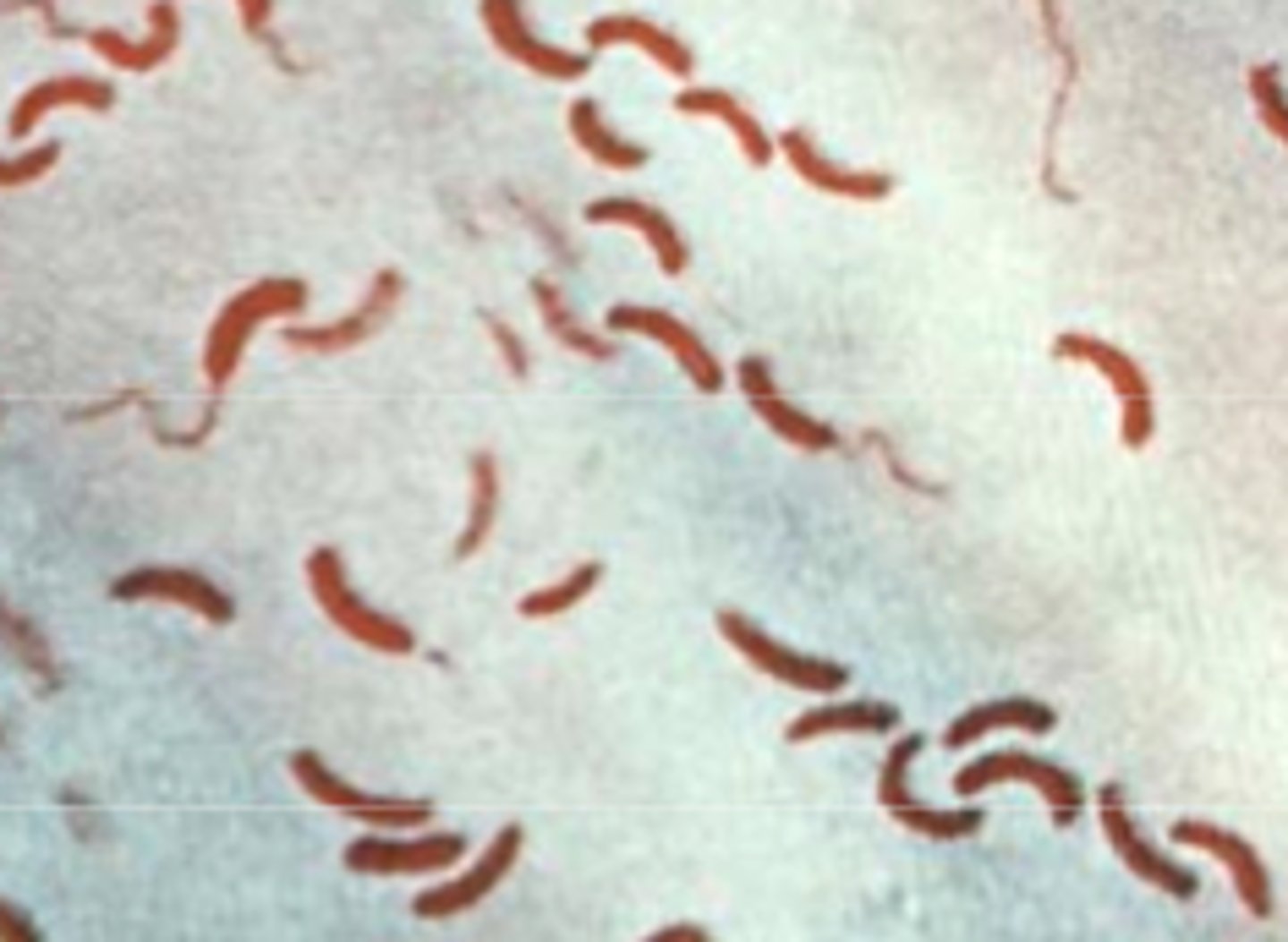
fecal coliform
a group of microorganisms in the human intestines that can serve as an indicator species for potentially harmful microorganisms associated with contamination by sewage
septic system
A relatively small and simple sewage treatment system, made up of a septic tank and a leach field, often used for homes in rural areas
acid deposition
Sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides, emitted by burning fossil fuels, enter the atmosphere-where they combine with oxygen and water to form sulfuric acid and nitric acid-and return to Earth's surface
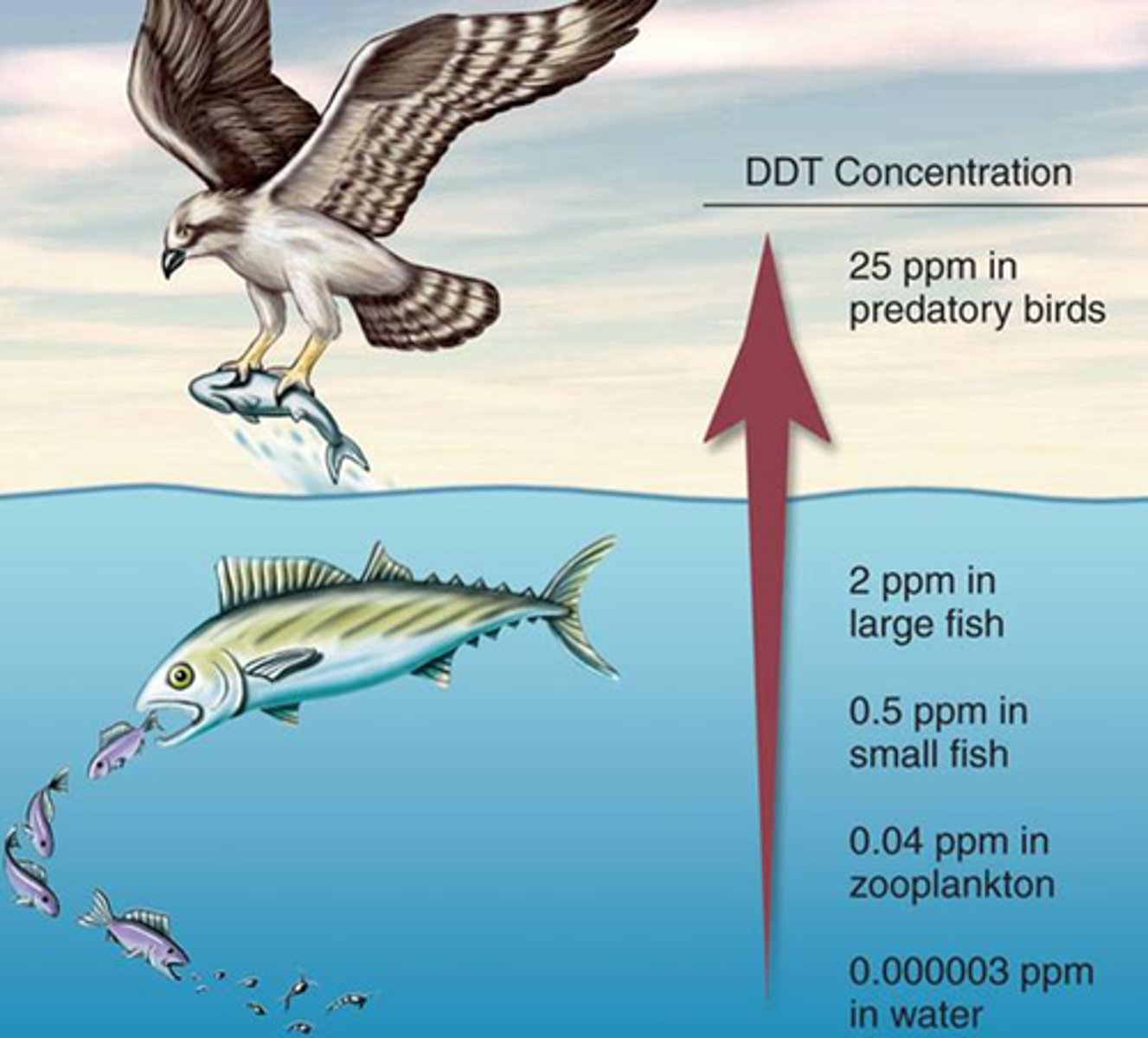
Bioaccumulation
The accumulation of a substance, such as a toxic chemical, in various tissues of a living organism.
Biomagnification
the concentration of toxins in an organism as a result of its ingesting other plants or animals in which the toxins are more widely disbursed.
Bubonic Plague
Also called the Black Death was a deadly disease that spread through Europe and killed one out of every three people

Cholera
an acute intestinal infection caused by ingestion of contaminated water or food
Composting
a process that allows the organic material in solid waste to be decomposed and reintroduced into the soil, often as fertilizer.

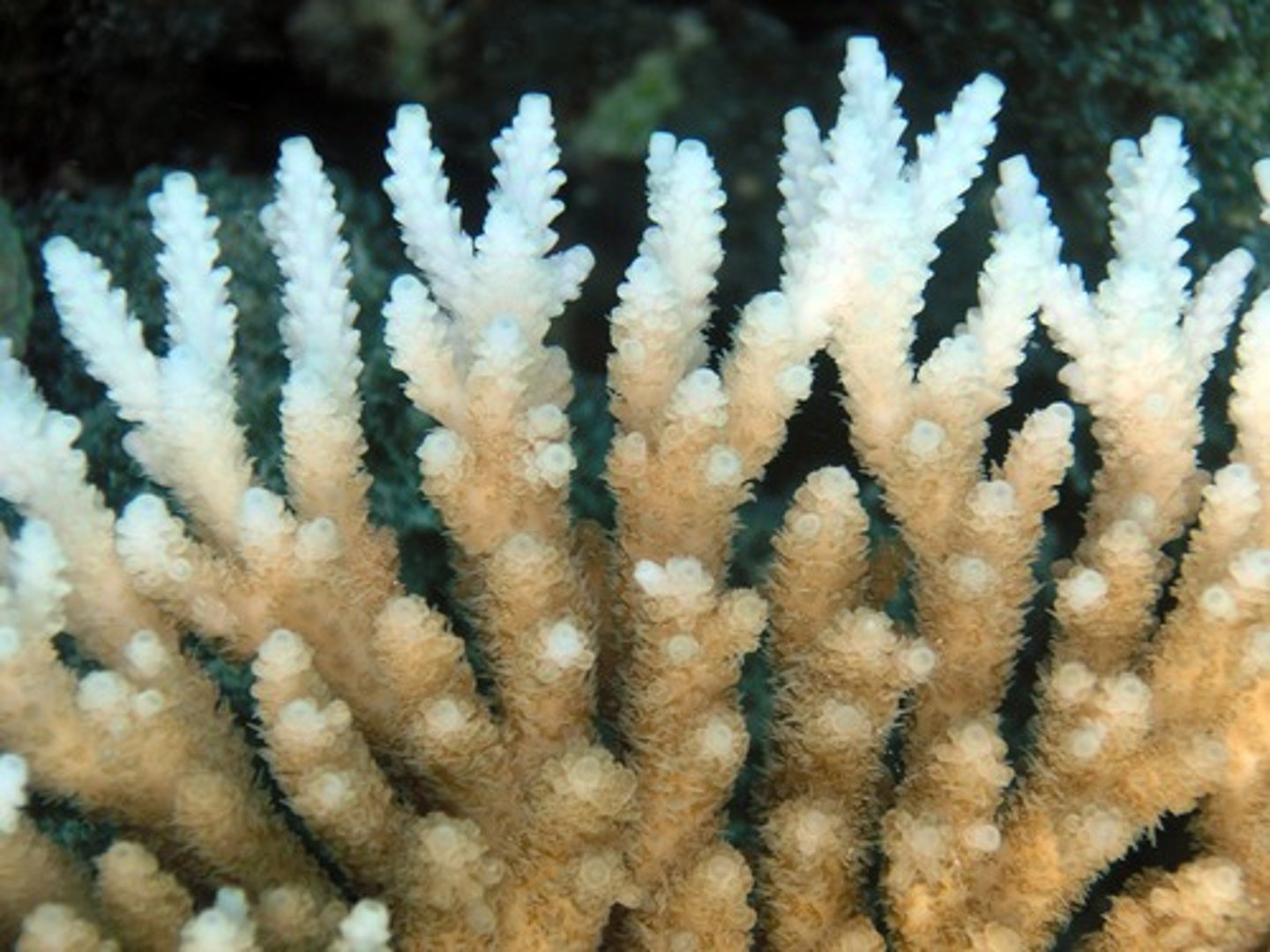
coral bleaching
A phenomenon in which algae inside corals die, causing the corals to turn white.

dead zone
In a body of water, an area with extremely low oxygen concentration and very little life
Decomposition
the state or process of rotting; decay.
dispersant
a chemical used in oil spill cleanup that thins and dissolves the thick crude
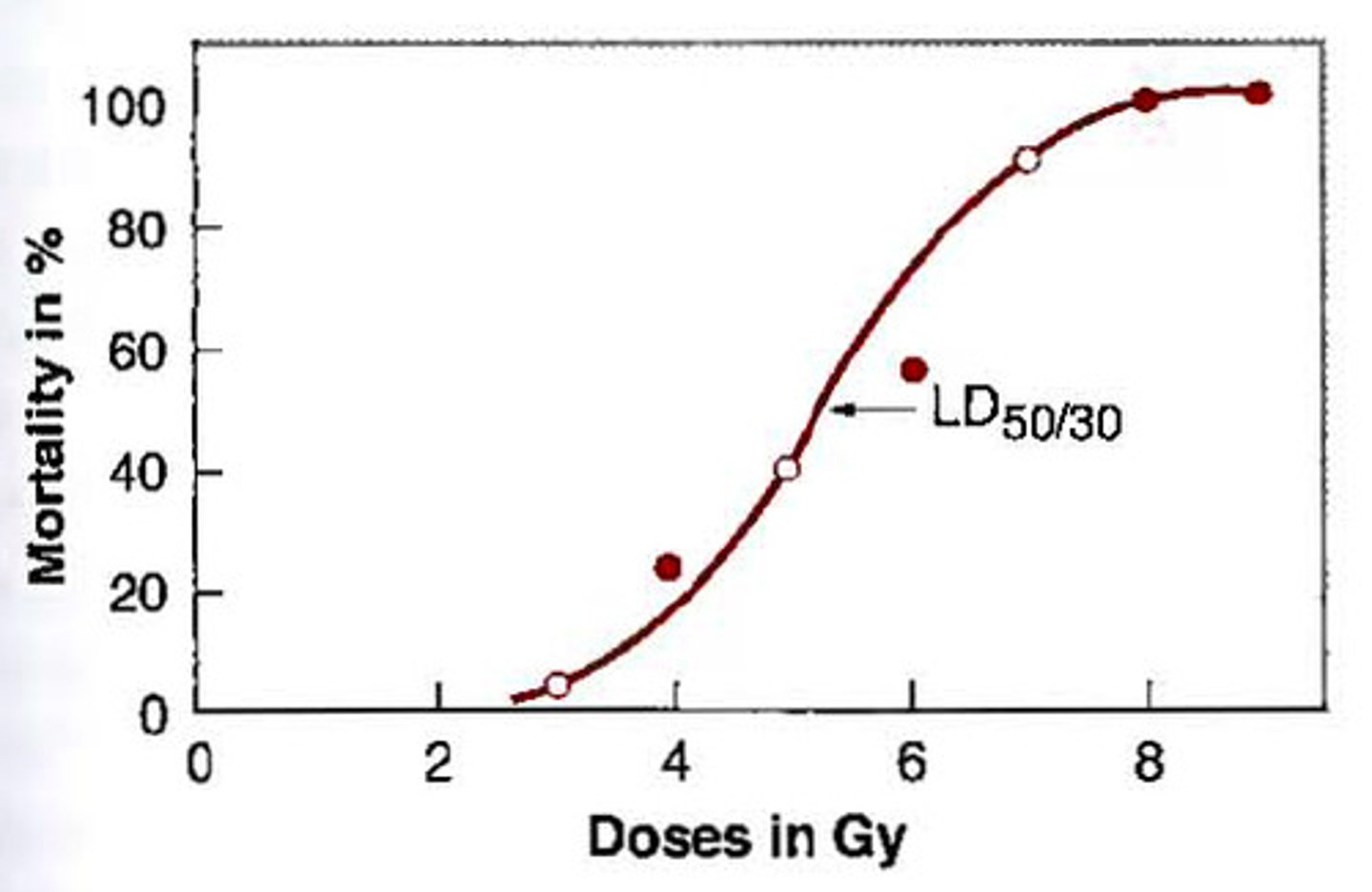
dose-response curve
Plot of data showing effects of various doses of a toxic agent on a group of test organisms.
LD50
the amount of a chemical that kills 50% of the animals in a test population
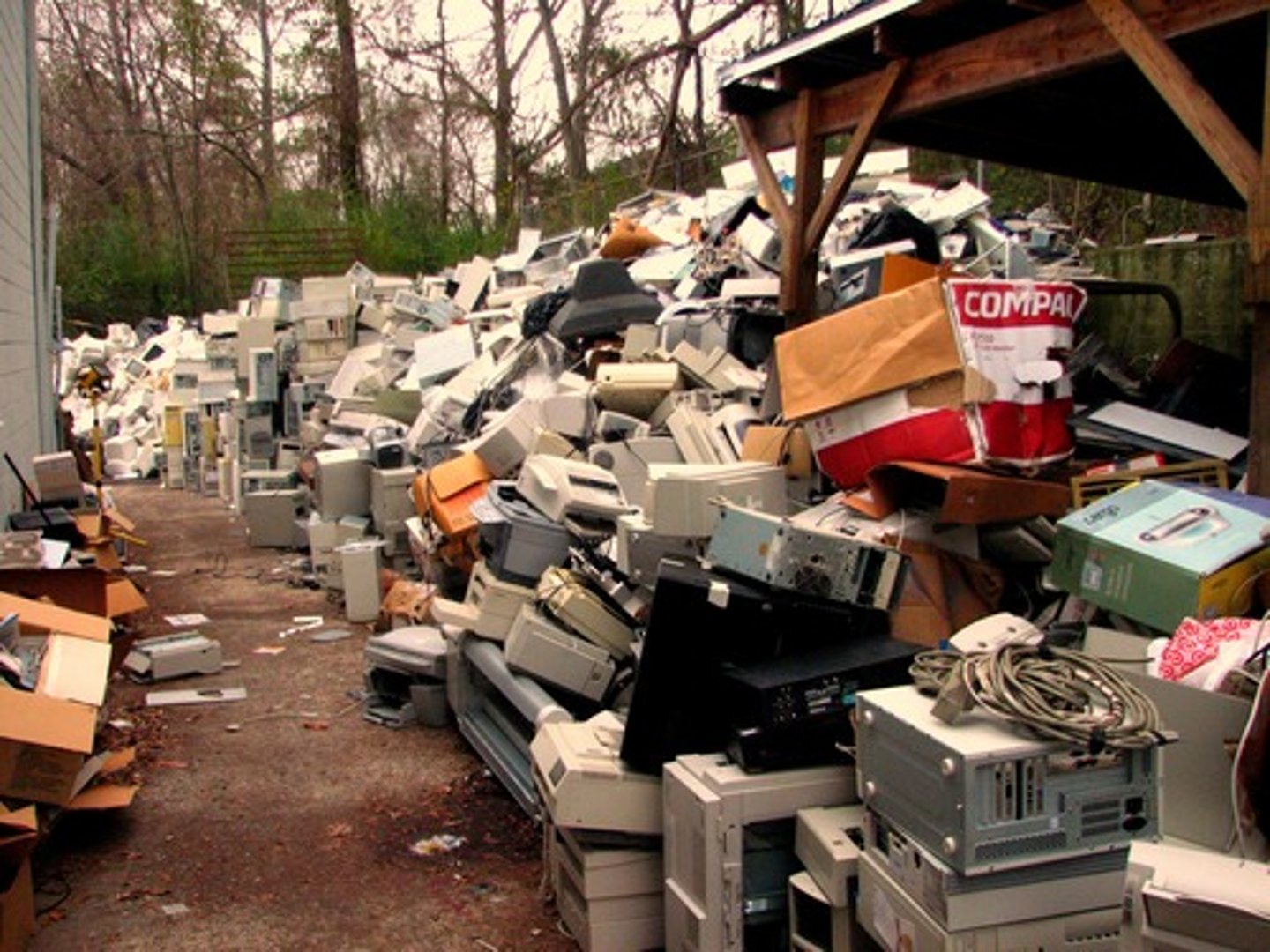
e-waste
discarded electronic equipment such as computers, cell phones, television sets, etc.

endocrine disruptors
chemicals that interfere with the normal functioning of hormones in an animal's body

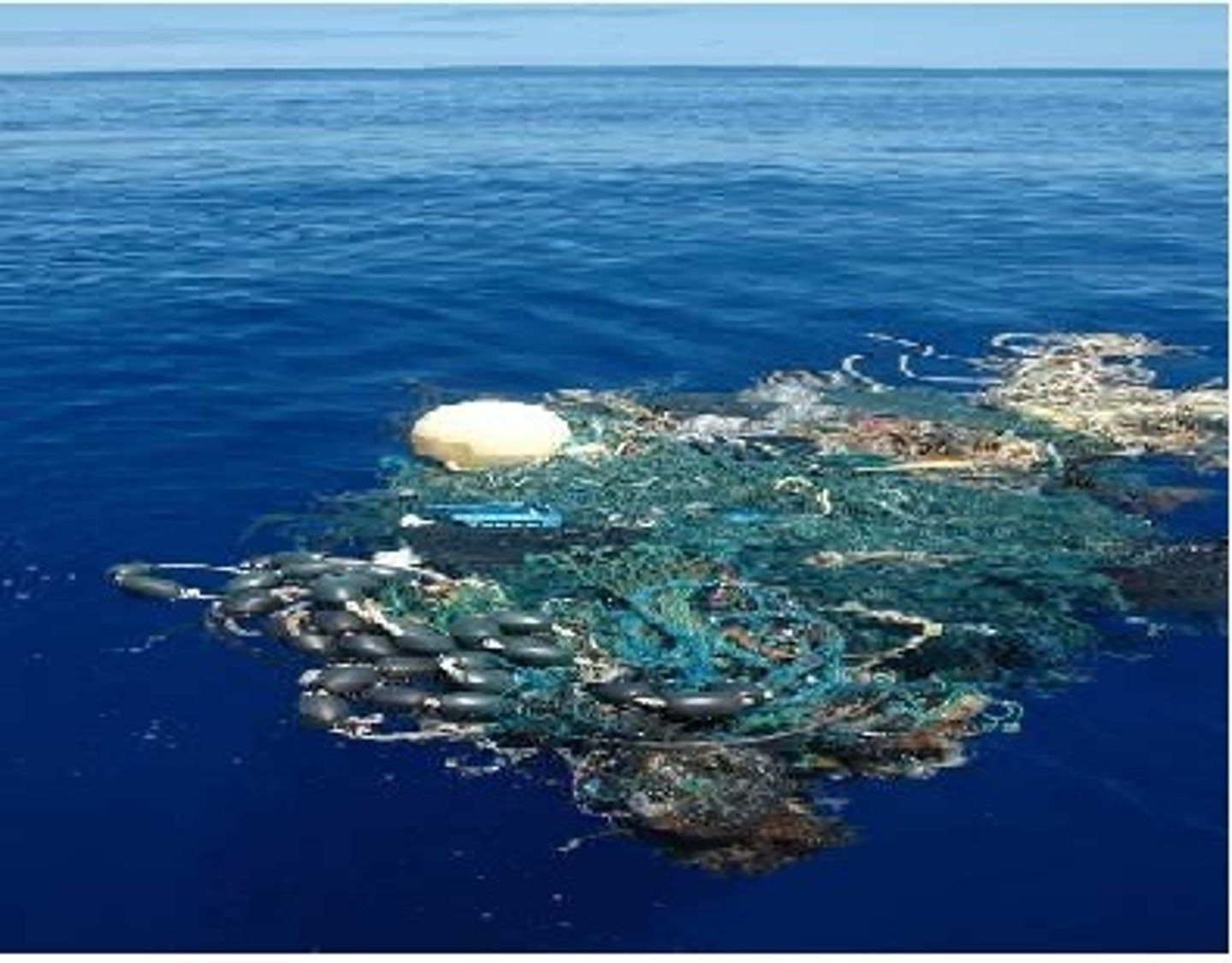
Great Pacific Garbage Patch
a gyre of marine debris particles in the central North Pacific Ocean discovered between 1985 and 1988.

Hypoxic
low oxygen
Incineration
The process of burning waste materials to reduce volume and mass, sometimes to generate electricity or heat
indicator species
Species that serve as early warnings that a community or ecosystem is being degraded.
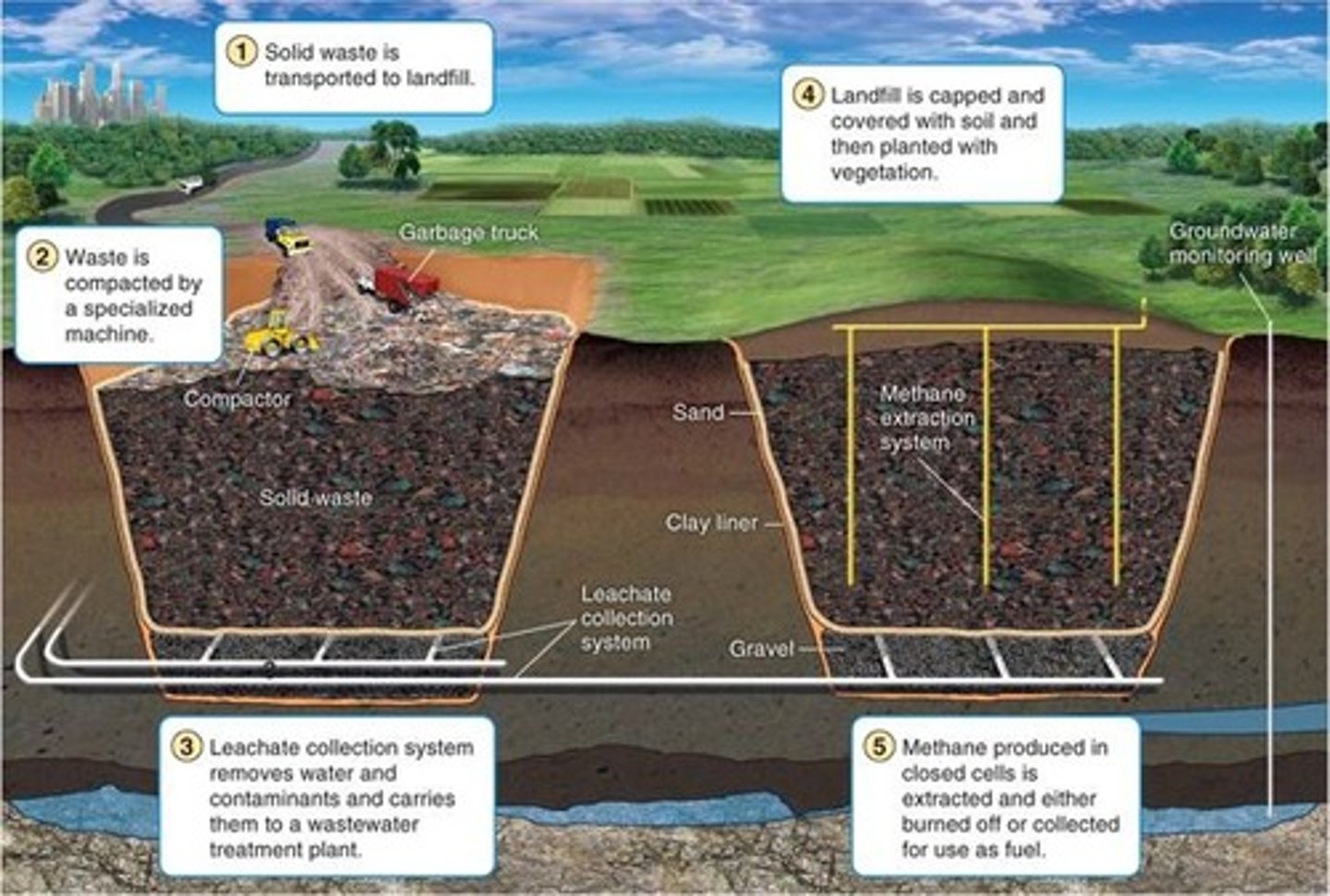
landfill
The disposal of refuse and other waste material by burying it and covering it over with soil
leach field
a component of a septic system, made up of underground pipes laid out below the surface of the ground
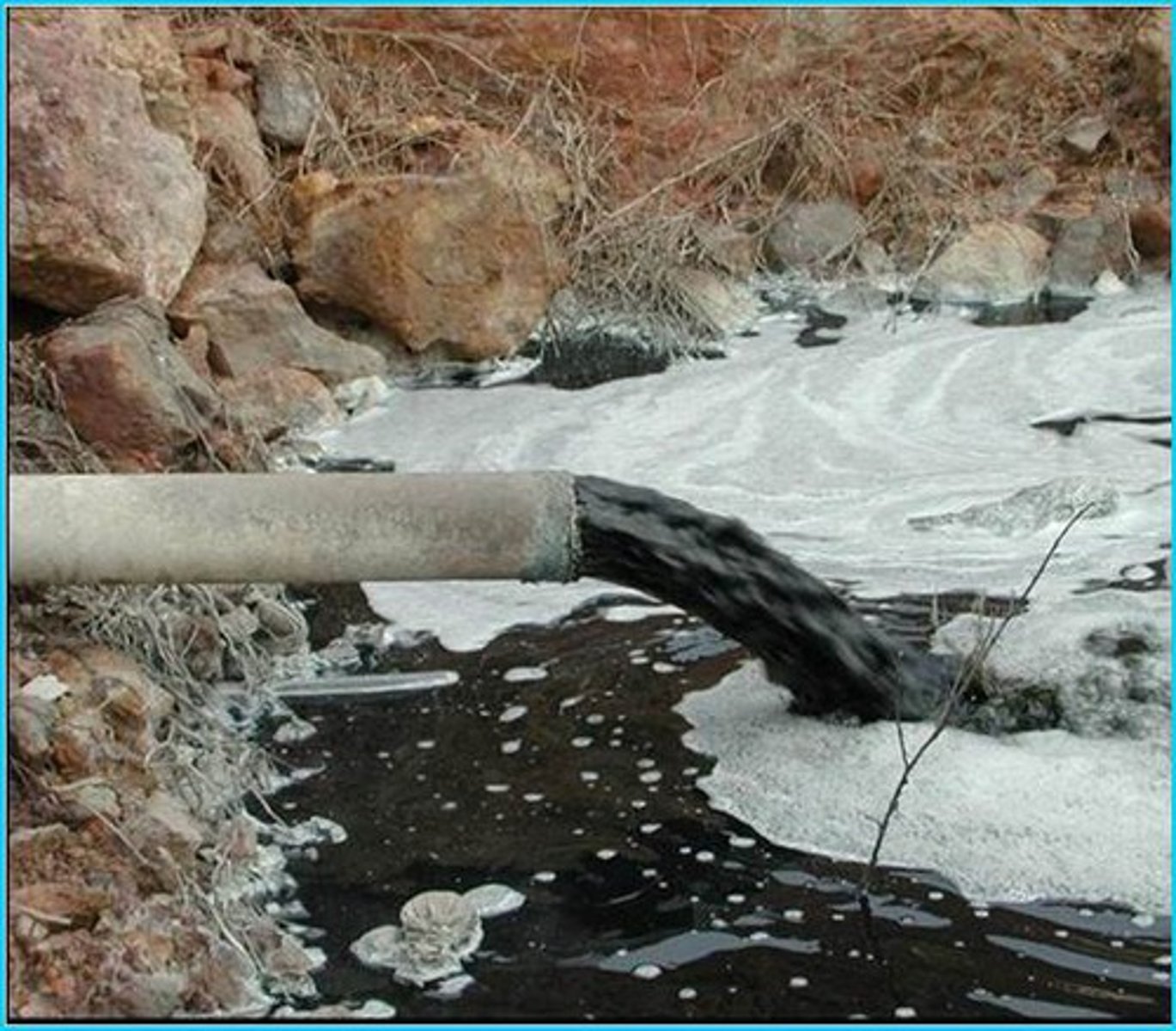
Leachate
polluted liquid produced by water passing through buried wastes in a landfill

Malaria
A disease caused by mosquitoes implanting parasites in the blood.
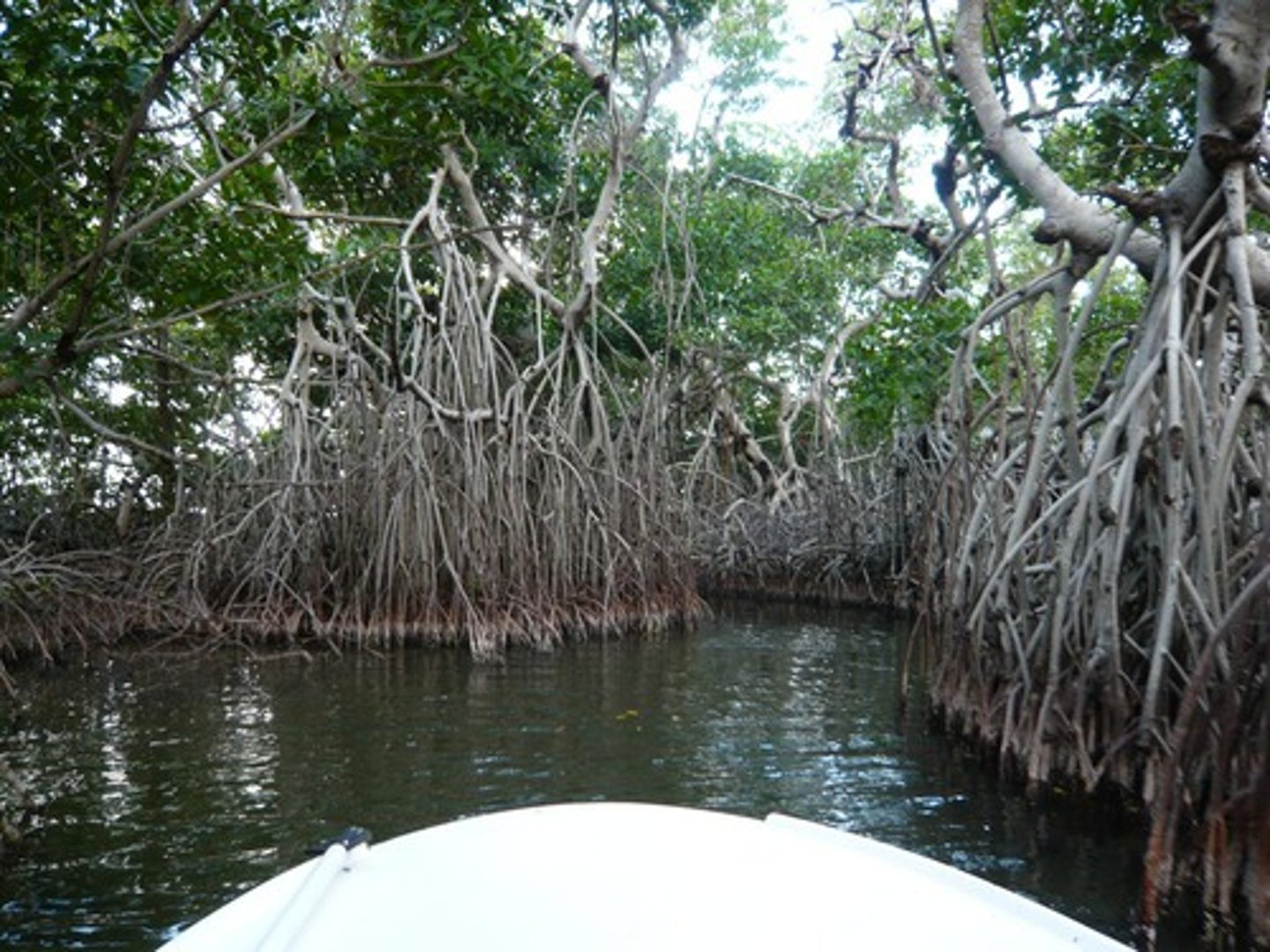
Mangroves
tropical trees that grow along coasts and help maintain the health of coastal environments

Manure lagoon
Human-made pond lined with rubber built to handle large quantities of manure produced by livestock.
Maximum contaminant level (MCL)
The standard for safe drinking water established by the EPA under the Safe Drinking Water Act
mesothelioma
Rare malignant tumor arising in the pleura and associated with asbestos exposure.
Methylmercury
highly toxic heavy metal that biomagnifies in aquatic ecosystems and contaminates humans largely through eating of [shell]fish; damages the central nervous system (esp. children/embryos) and leads to impaired coordination and sense of touch/taste/sight.
Oligotrophic
a condition of a lake or other body of water characterized by low nutrients, low productivity, and high oxygen levels in the water column.
Pathogen
An organism that causes disease
perceived obsolescence
continually changing consumer concepts of acceptable styles to encourage more and earlier buying
persistant organic pollutants (POPs)
compound with carbon in it that resists photochemical, biological and chemical degradation
planned obsolescence
the practice of modifying products so those that have already been sold become obsolete before they actually need replacement
PCBs
synthetic chemicals containing chlorine that are used in the manufacture of plastics and other industrial products, become stored in the tissue of animals, and also persist in the environment
primary treatment
when physically treated sewage water is passed into a settling tank, where suspended solids settle out as sludge; chemically treated polymers may be added to help the suspended solids separate and settle out.
range of tolerance
the limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate
recycling
the act of processing used or abandoned materials for use in creating new products

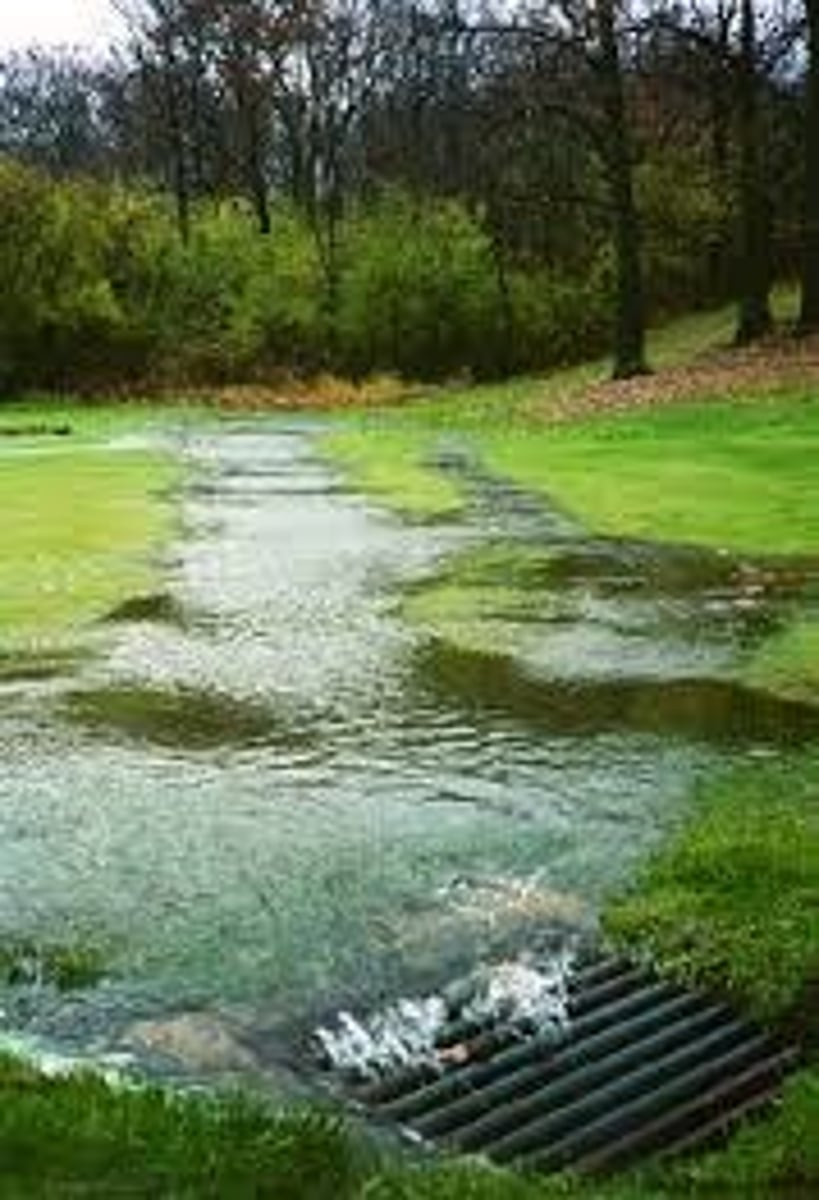
Runoff
water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground

Safe Drinking Water Act
(SDWA, 1974) set maximum contaminant levels for pollutants in drinking water that may have adverse effects on human health
sanitary landfill
A place to deposit solid waste, where a layer of earth is bulldozed over garbage each day to reduce emissions of gases and odors from the decaying trash, to minimize fires, and to discourage vermin.
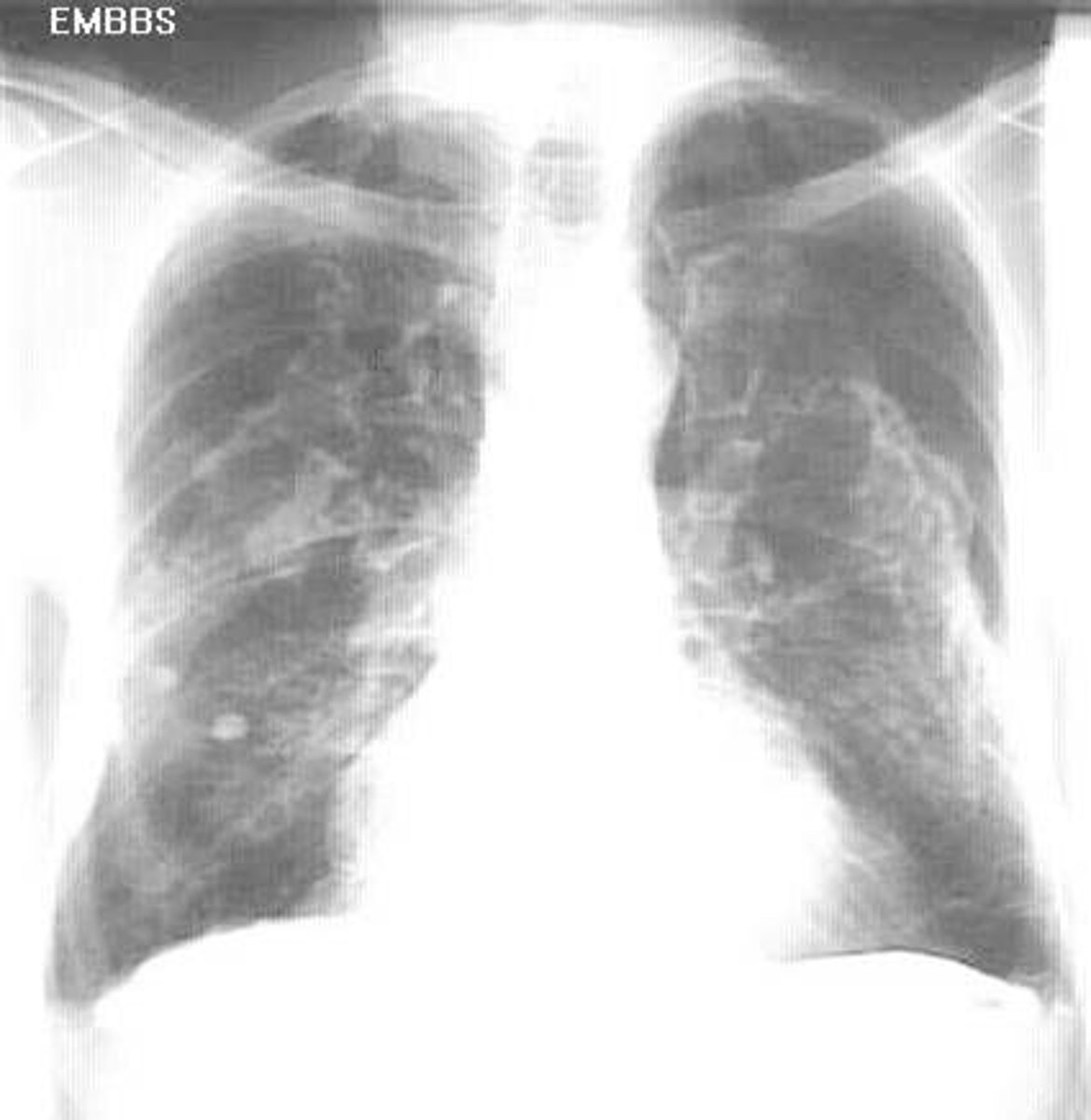
SARS
severe acute respiratory syndrome
thermal pollution
a temperature increase in a body of water that is caused by human activity and that has a harmful effect on water quality and on the ability of that body of water to support life
thermal shock
Many species die because a dramatic change in temperature puts them outside their natural range of temps.
Clean Water Act
(CWA, 1972) set maximum permissible amounts of water pollutants that can be discharged into waterways; aims to make surface waters swimmable and fishable
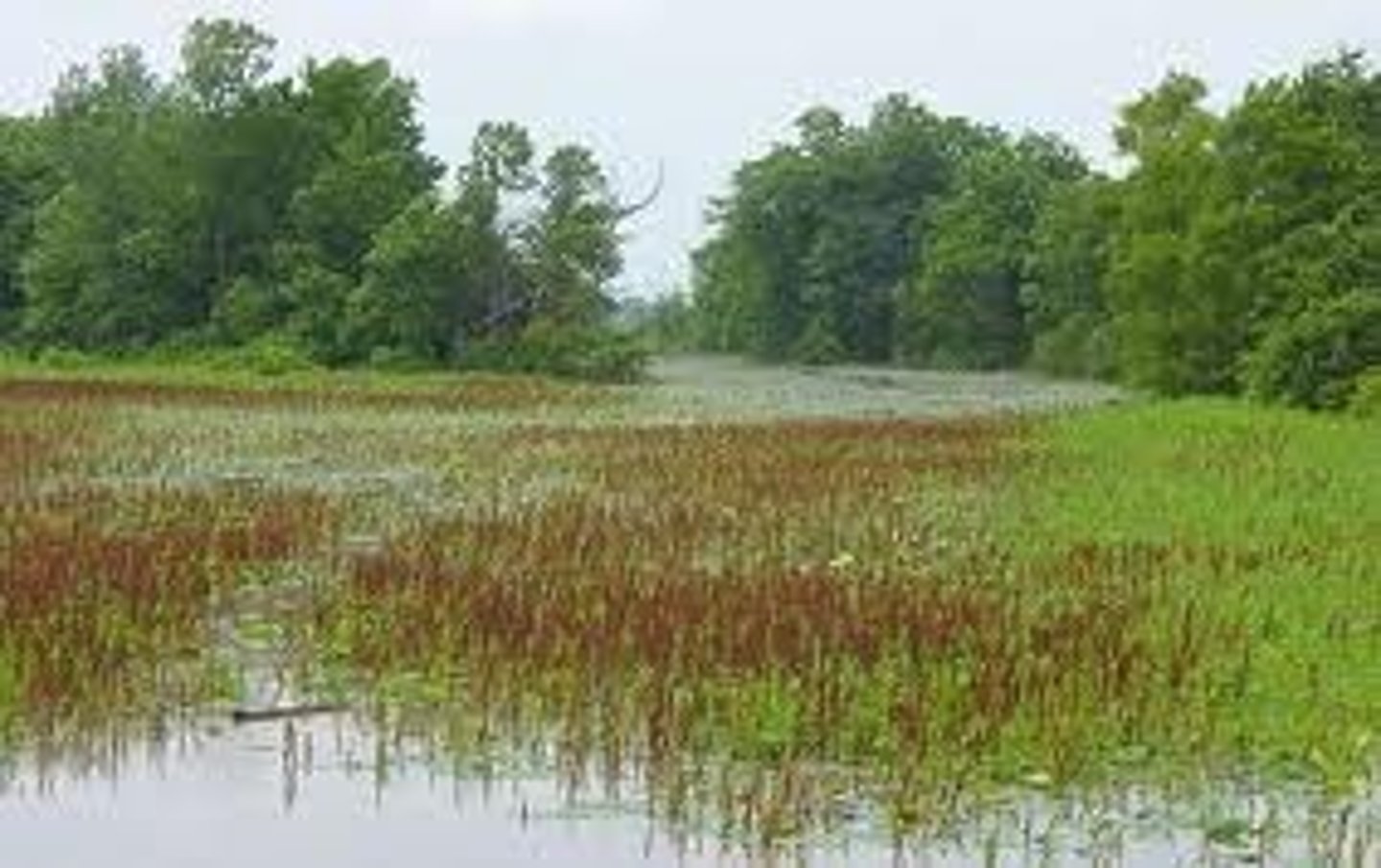
wetland
A land area that is covered with a shallow layer of water during some or all of the year

West Nile Virus
spread to humans by the bite of an infected mosquito