Genetics Exam FINAL
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
DNA synthesis is also known as:
Replication
RNA Synthesis is also known as:
Transcription
Protein synthesis is also known as:
Translation
The site/signal for initiation of DNA synthesis:
Origin
The site/signal for initiation of RNA synthesis:
Promoter
The site/signal for initiation of Protein synthesis:
Ribosome binding site (RBS)
The protein synthesis is terminated:
At the UAA codon
RNA synthesis is often terminated:
Before a stem-loop structure
The direction of DNA and RNA synthesis is:
From 5' to 3'
The direction of protein synthesis is:
Amino terminus to Carboxyl terminus
“AGGAGG”
Consensus Shine-Delgarno sequence (part of RBS)
“AUG”
Methionine or start codon
“UAA”
Stop codon
“UAG”
Stop codon
“TATATT”
Consensus - -10 region of E.coli sigma 70 promoter
In an aminoacyl-tRNA the link between the amino acid and the tRNA is best described as an:
Ester bond
In an aminoacyl-tRNA the link between is the amino acid and the tRNA often occurs between:
COOH terminus of amino acid and 3’ end of tRNA
DNA from Leu+ bacteria is mixed with leu-bacteria. The bacteria are then plated on minimal media (with no Leucine).
Selection
Mutagenized bacteria are plated on rich media and then replica-plated to minimal media. Colonies that grow on rich media, but not on minimal media, are picked.
Screen
Phage are irradiated with UV light
Mutagenesis
Original DNA sequence: a b c d e f g
Classify the following arrangement:
a b c l m d e f g
Insertion
Original DNA sequence: a b c d e f g
Classify the following arrangement:
a b c d e c d e f g
Duplication
Original DNA sequence: a b c d e f g
Classify the following arrangement:
a b c f g
Deletion
Original DNA sequence: a b c d e f g
Classify the following arrangement:
a b e’ d’ c’ f g
Inversion
The change of A to G is:
A transition
The change of A to C is:
A transversion
A substitution of Leucine for Valine in the protein product:
a missense mutation
An alteration of an Arginine codon for a stop codon:
a nonsense mutation
The alteration of an Alanine codon for another Alanine codon:
A silent mutation
Could be caused by a two base-pair insertion:
Frameshift mutation
The genetic makeup of an organism:
Genotype
The physical and behavioral characteristics of an organism:
Phenotype
Applies, typically, to a gamete:
Haploid
Applies, typically, to a zygote, an embryo or an adult:
Diploid
Applies to the bacterium with a duplication:
Diploid
Might be used to construct a genetic map:
Recombination test
Might be used to determine whether two mutations affected the same gene:
Complementation test
Might be used to increase the frequency of mutations:
Mutagen
Might be used to isolate rare mutants from a larger population:
Selection
Might be used to characterize a single mutation:
Test of dominance (aka complementation by wildtype)
How F plasmid moves horizontally from cell to cell:
Conjugation
How bacteriophage P1 moves horizontally from cell to cell:
Transduction
Involves naked DNA:
Transformation or natural transformation
Involves a protein tube or “sex pilus”:
Conjugation
Involves degradation of one strand of DNA:
Conjugation
Involves rolling circle replication:
Conjugation
Involves an “Origin of Transfer”:
Conjugation
Is commonly used to introduce a plasmid into E.coli:
Transformation
Was discovered by Griffith in 1928:
Transformation or natural transformation
Involves phage particles that don’t contain phage DNA:
Transduction
What is the relationship between LacZ and glucose:
Enzyme and product
What is the relationship between Adenylate cyclase and cAMP:
Enzyme and product
What is the relationship between LacI and Allo-lactose:
Repressor and Inducer
What is the relationship between TrpR and Tryptophan:
Repressor and Corepressor
What is the relationship between CAP and cAMP:
Activator and Coactivator
What is the regulatory pattern of Lac operon in E. coli:
Negative Feedback Loop
What is the regulatory pattern of the Trp operon in E. coli:
Negative Feedback Loop
What is the regulatory pattern of the SOS regulon in E. coli:
None of the above
What is the regulatory pattern of the sporulation in Bacillus subtilis:
Cascade
What is the regulatory pattern of the gene expression in Bacteriophage T4:
Cascade
Transposon:
May be mutagenic
Prions:
Transmissible agent that contains no nucleic acid
Conjugal Plasmid:
Involves a direct cell to cell bridge or contact
Viroid:
Transsmissible agent that contains no protein
Homing endouclease:
Inteins or introns
Alkane
CH4
Alcohol
CH3CH2OH
Aldehyde
CH3CHO
Carboxylic Acid
CH3COOH
Amine
CH3CH2NH2
Ethylamine
CH3CH2NH2
Ethanol
CH3CH2OH
Ethanal
CH3CHO
Ethanoic Acid (aka Acetic Acid)
CH3COOH
Ethane
CH4
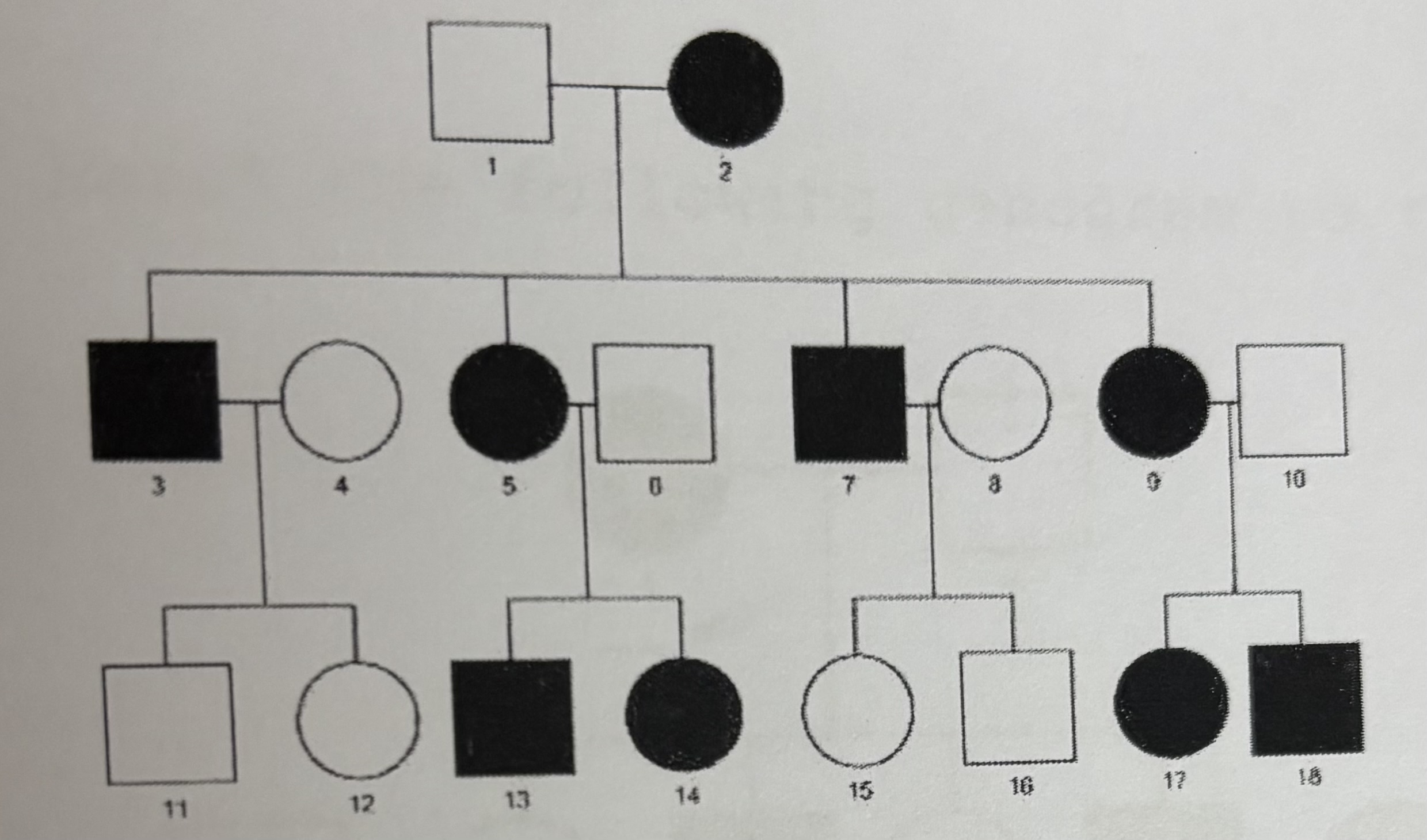
Autosomal Dominant
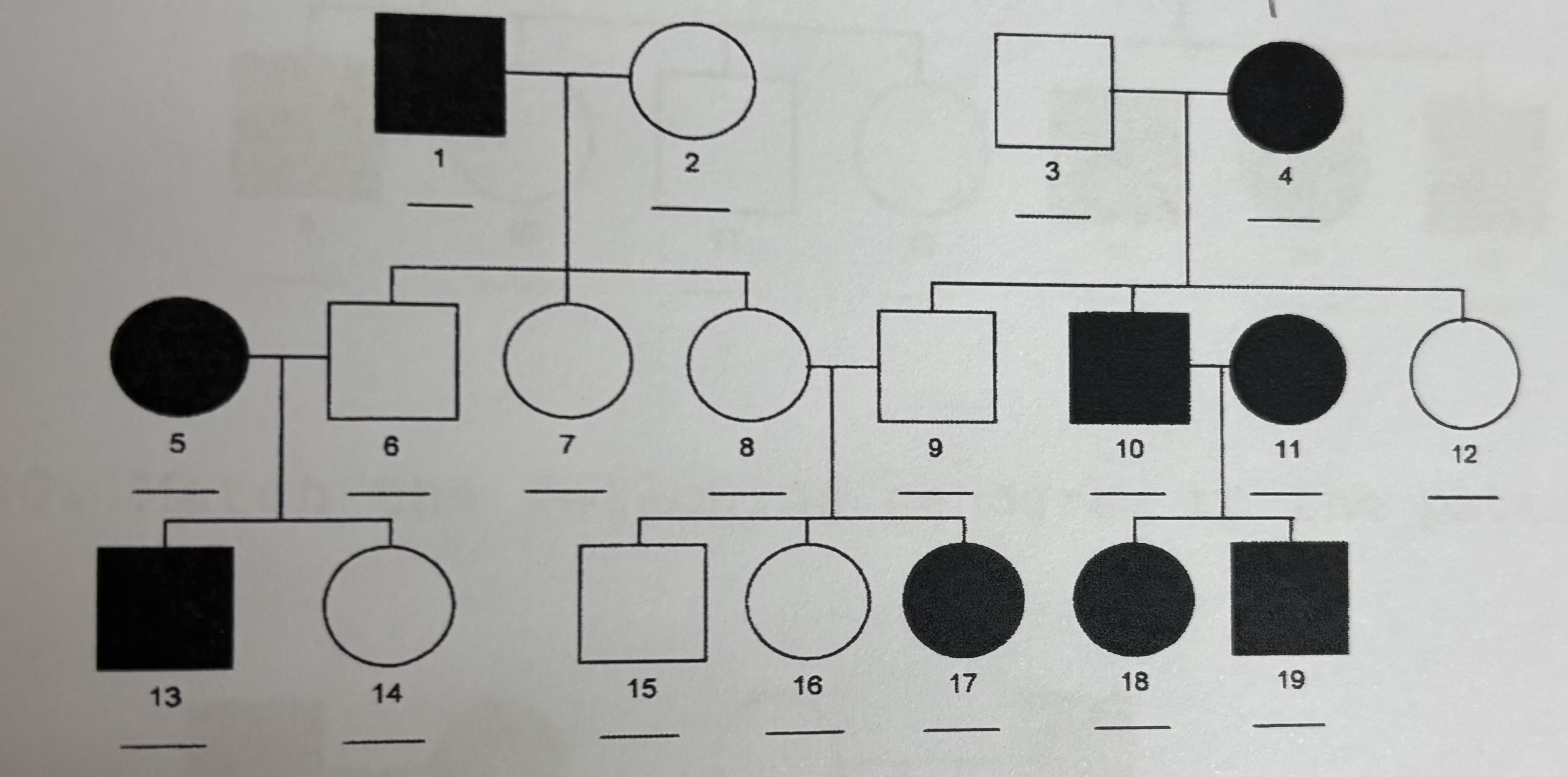
Autosomal Recessive
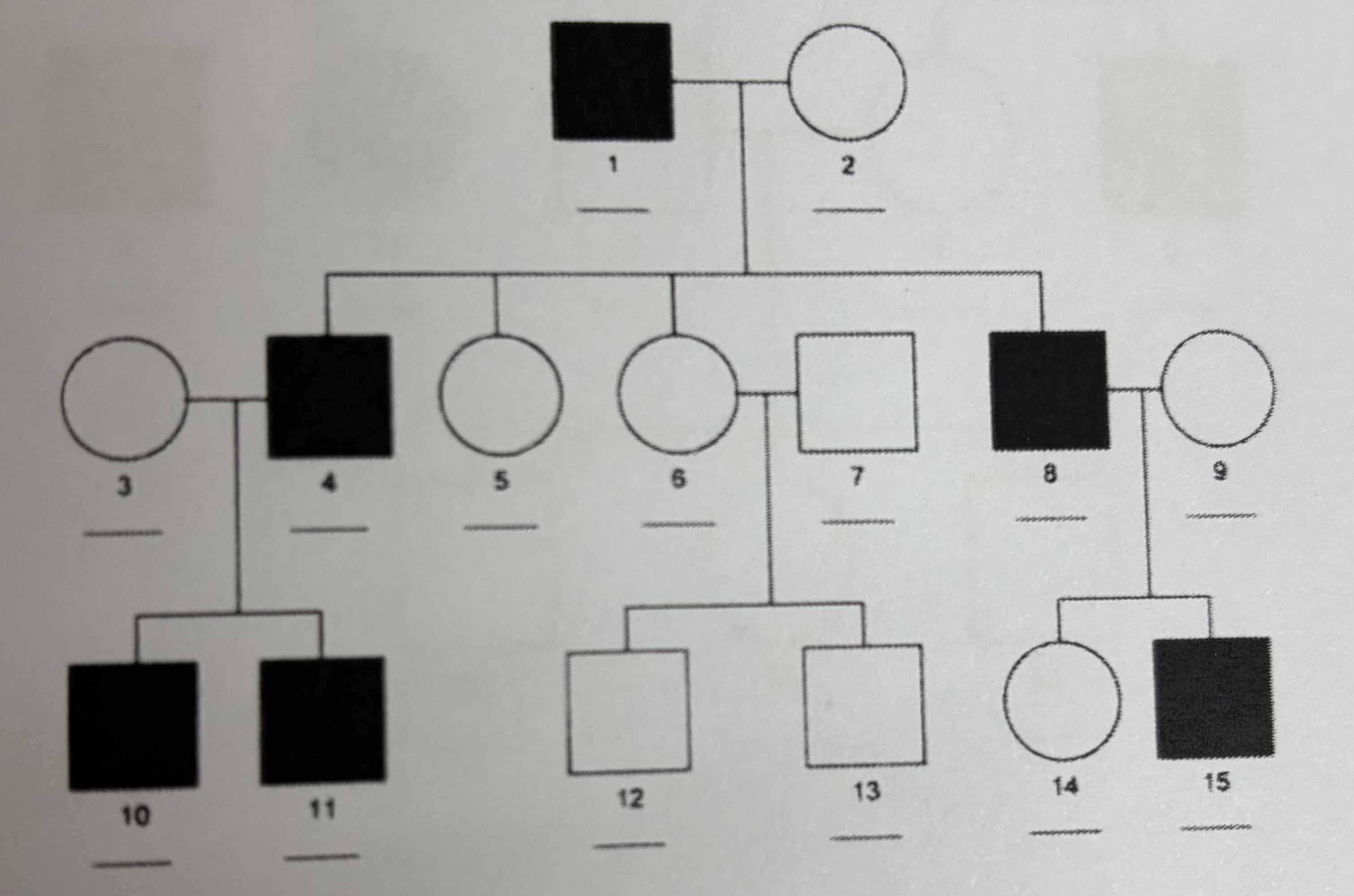
X-linked
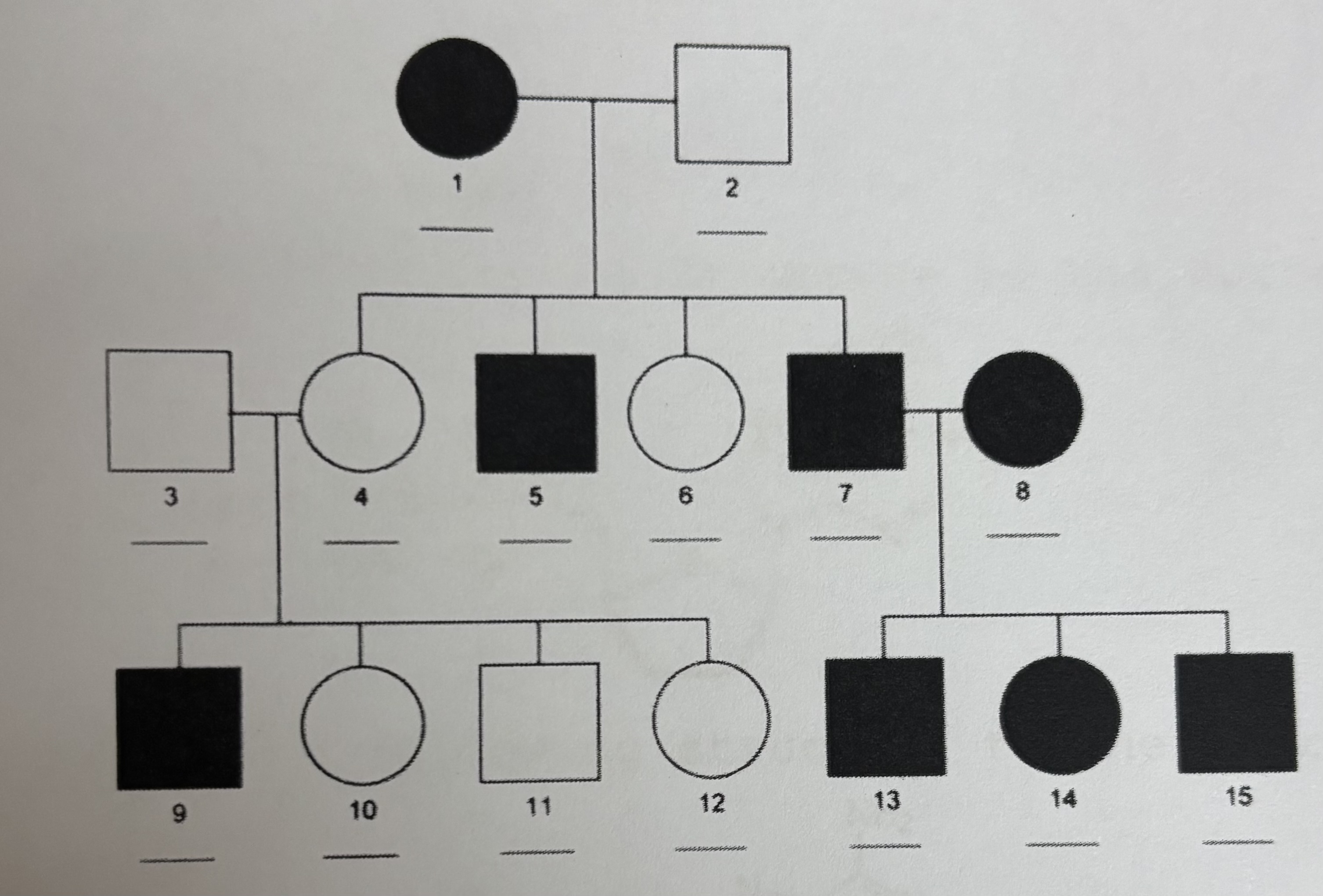
Autosomal Dominant
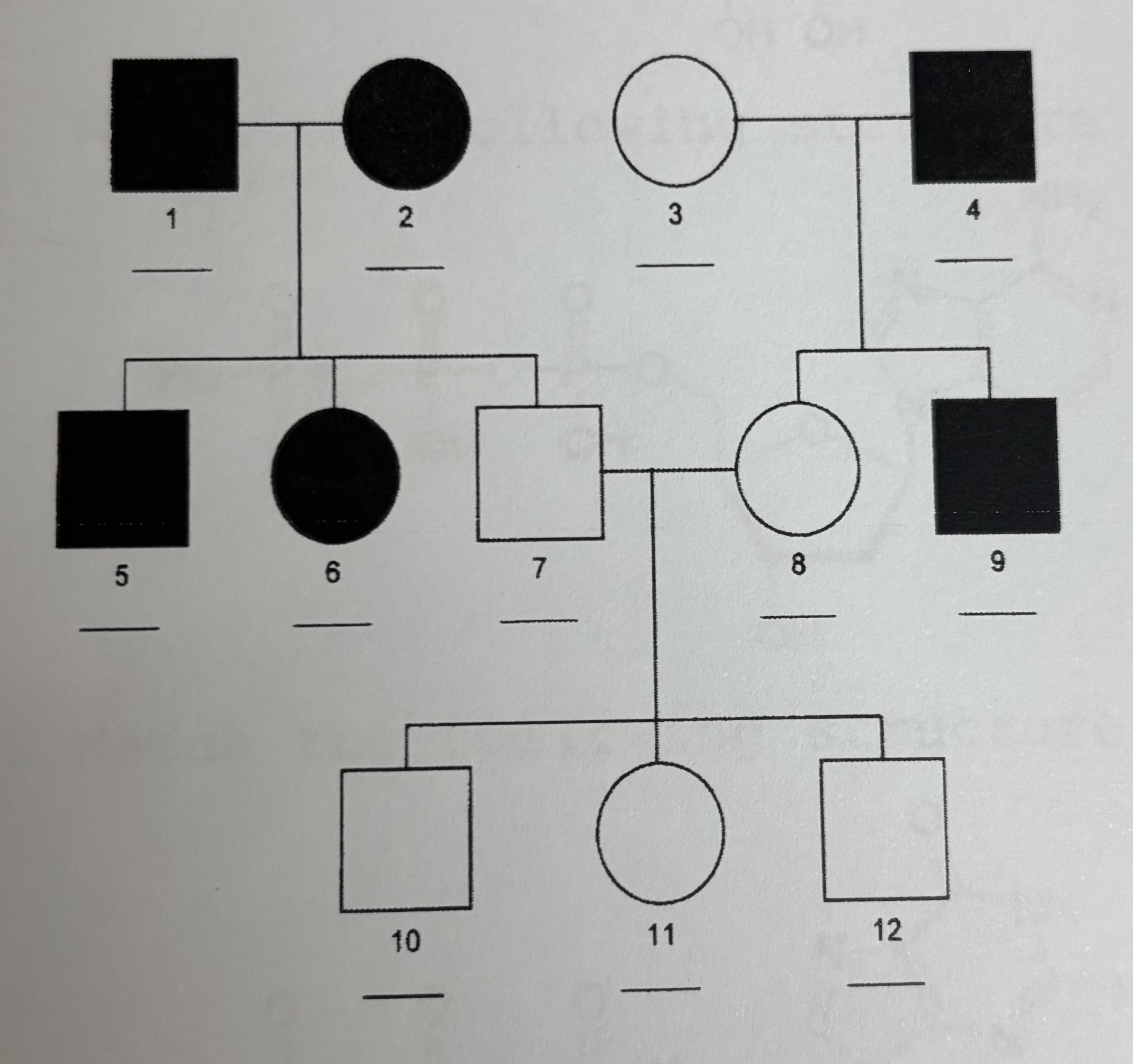
X-Linked
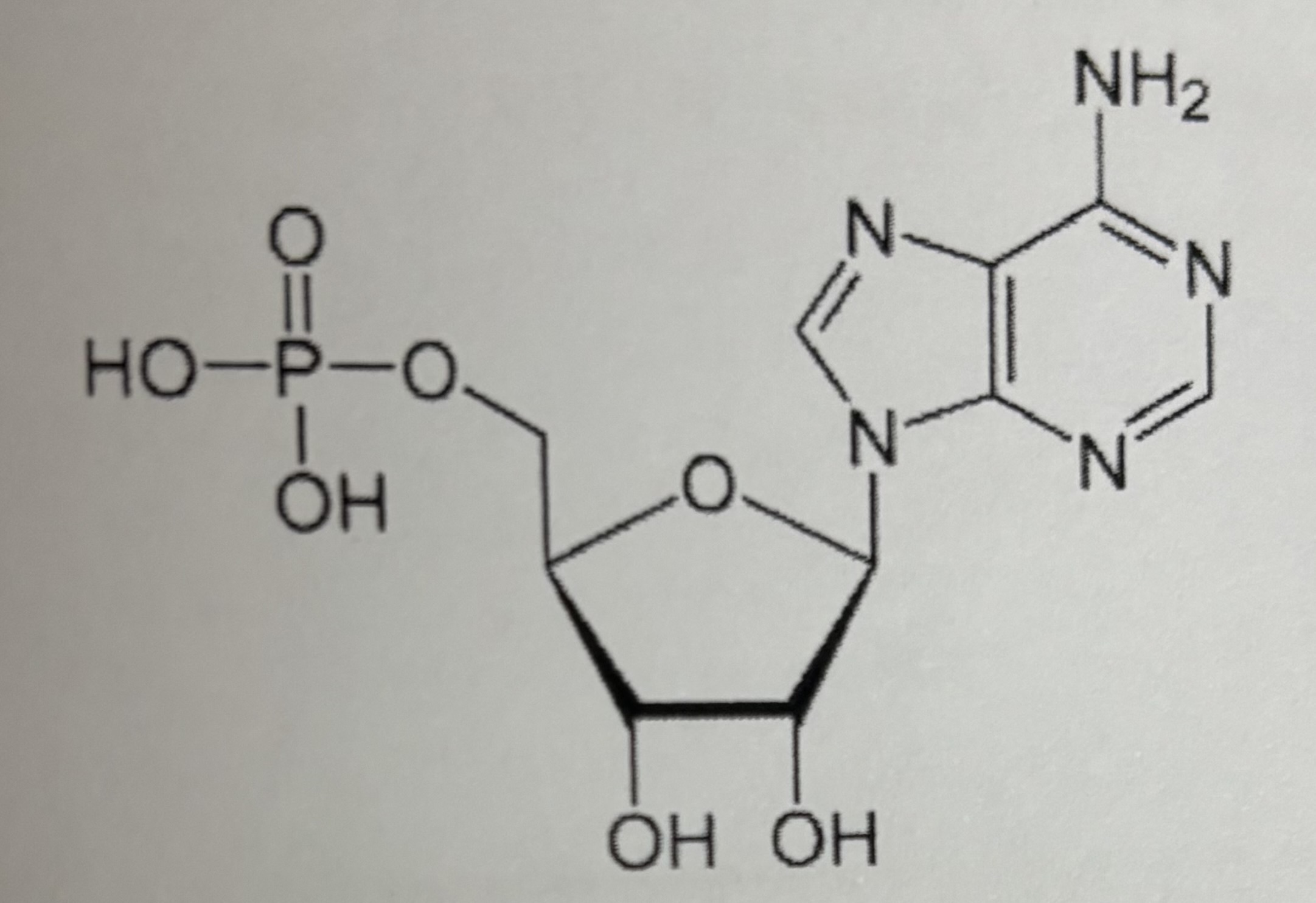
AMP (adenosine monophosphate)
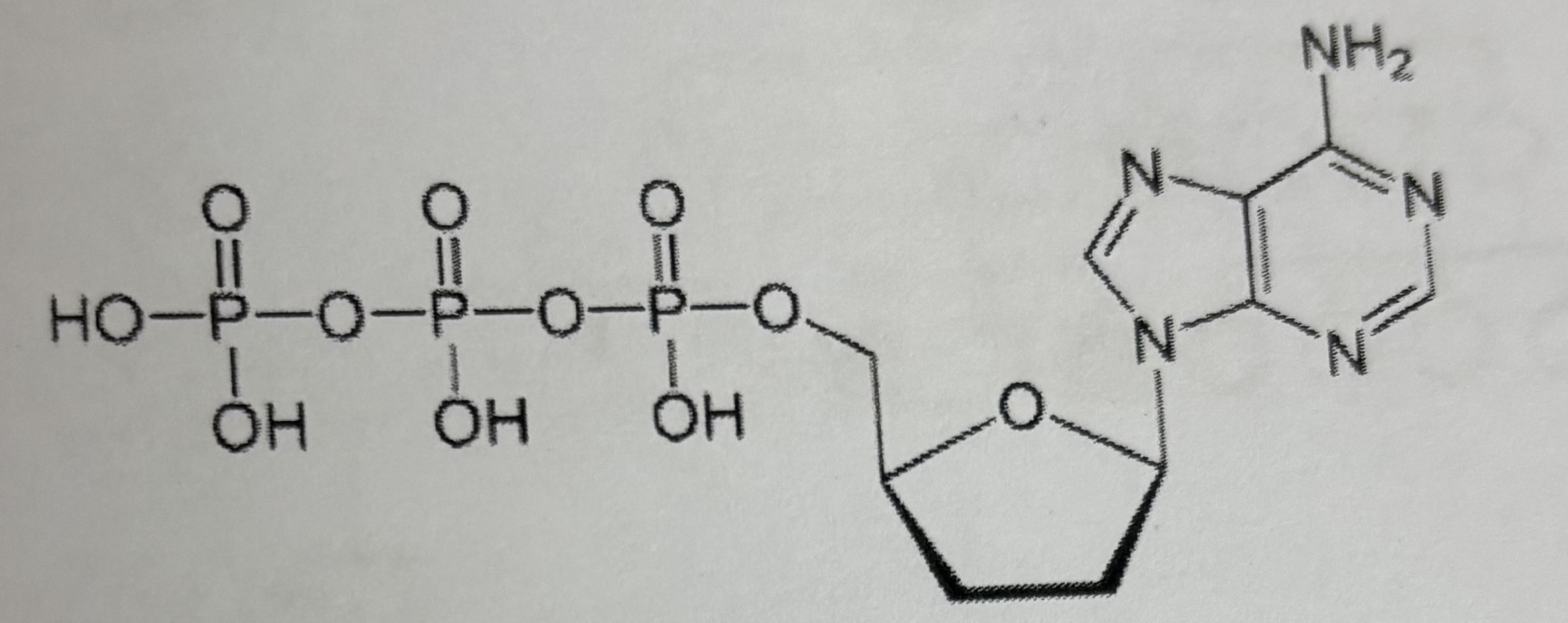
dATP (2’ deoxy adenosine monophosphate)
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
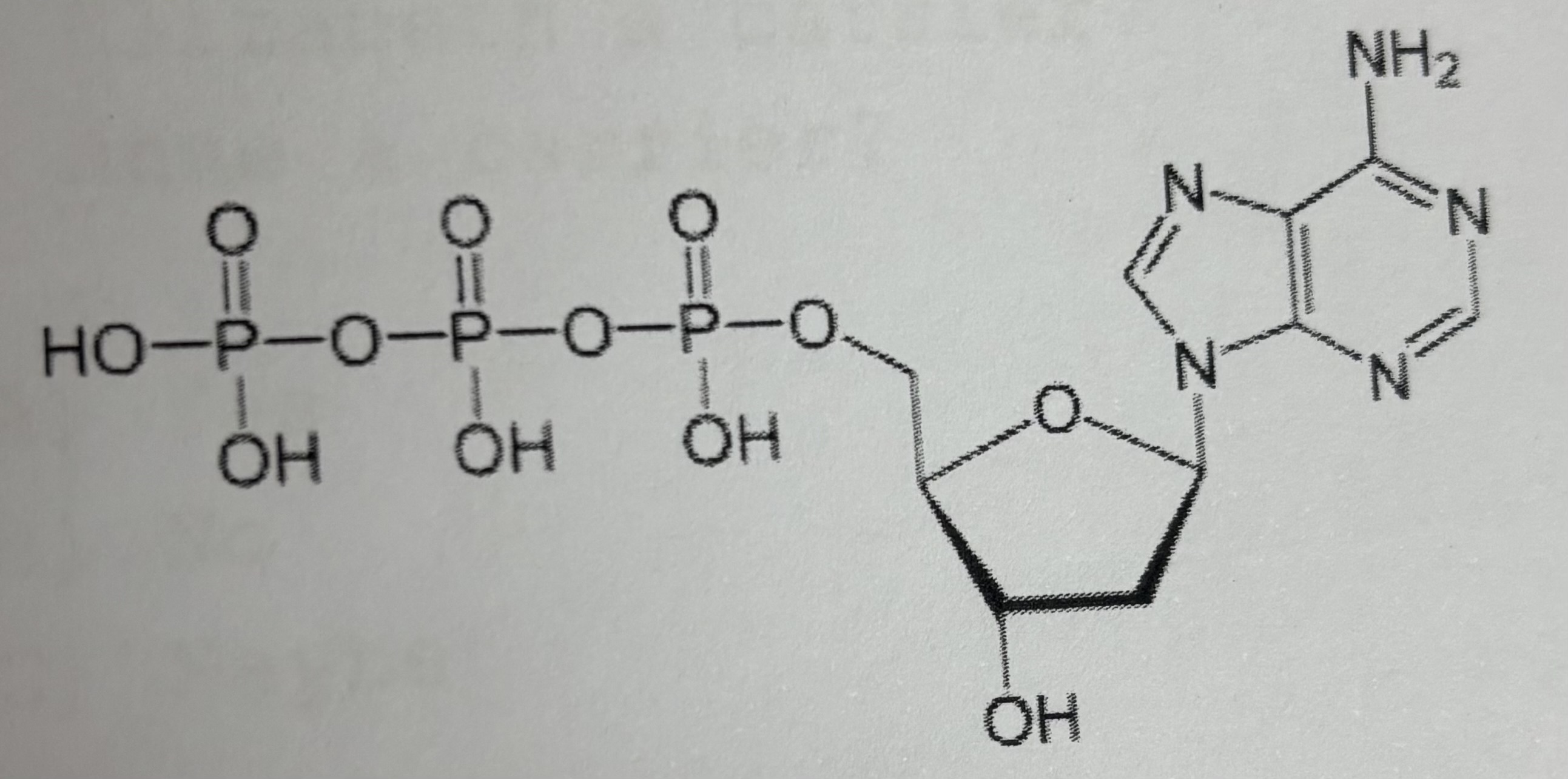
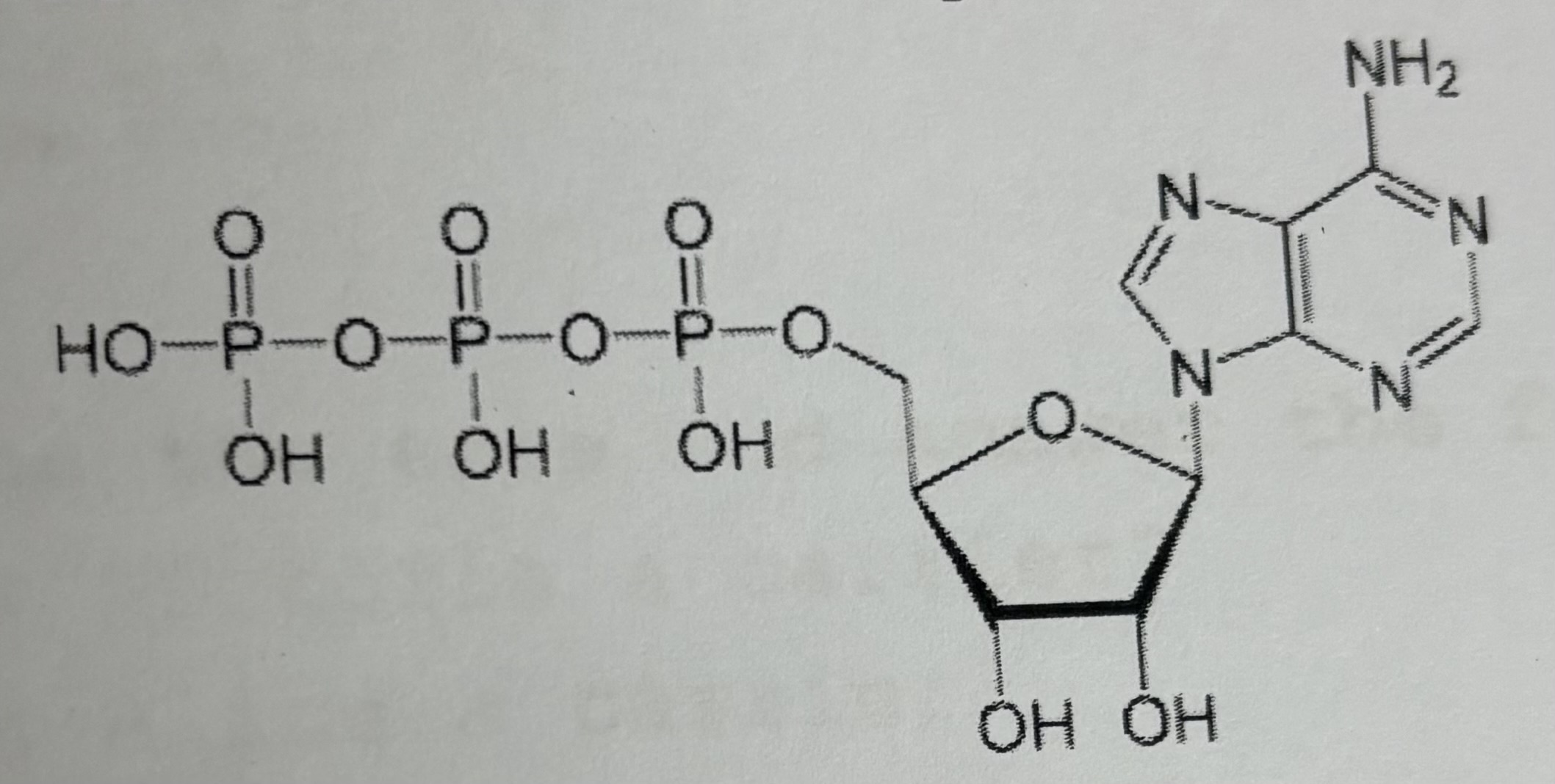
ddATP (2’, 3’ dideoxy adenosine triphosphate)
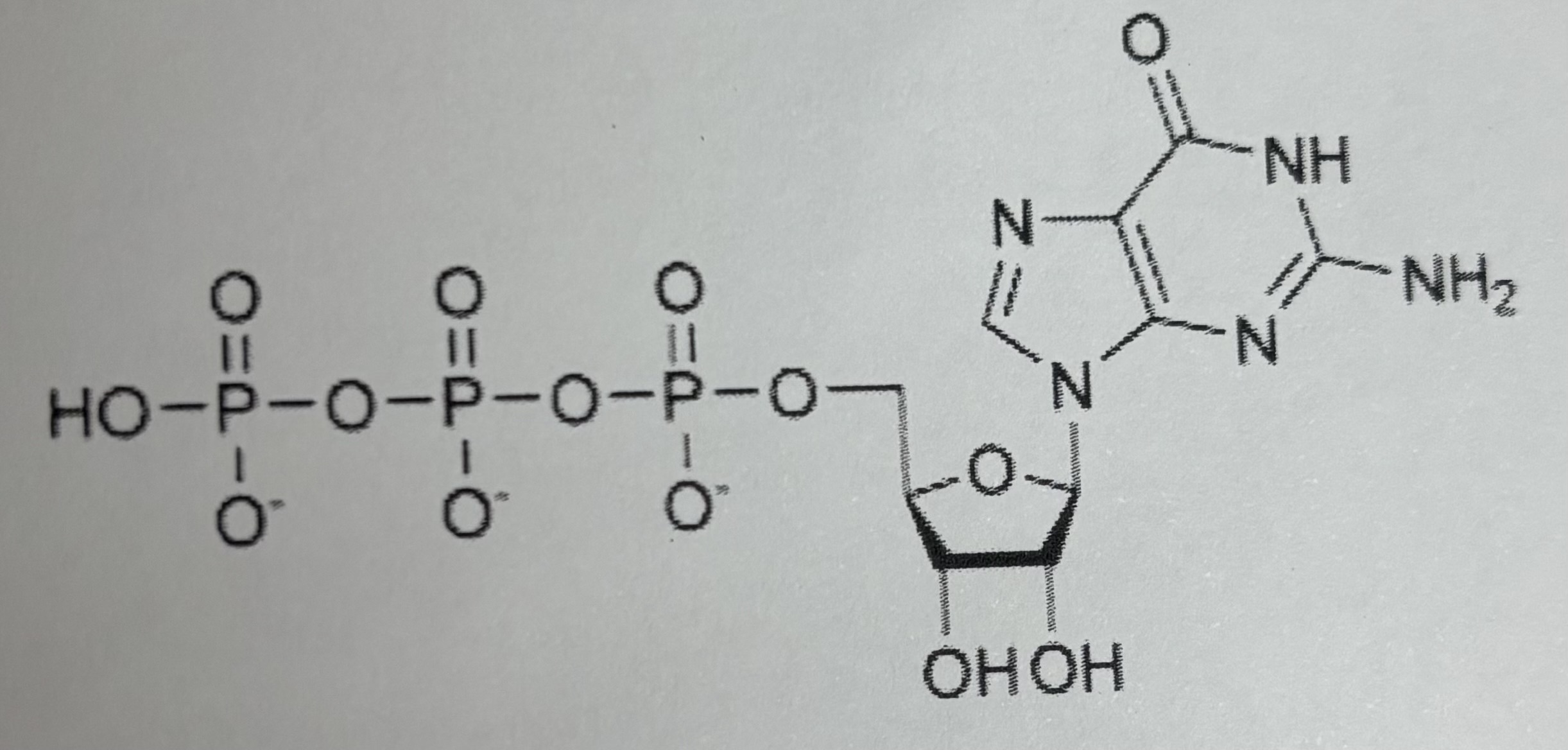
GTP (Guanosine triphosphate)
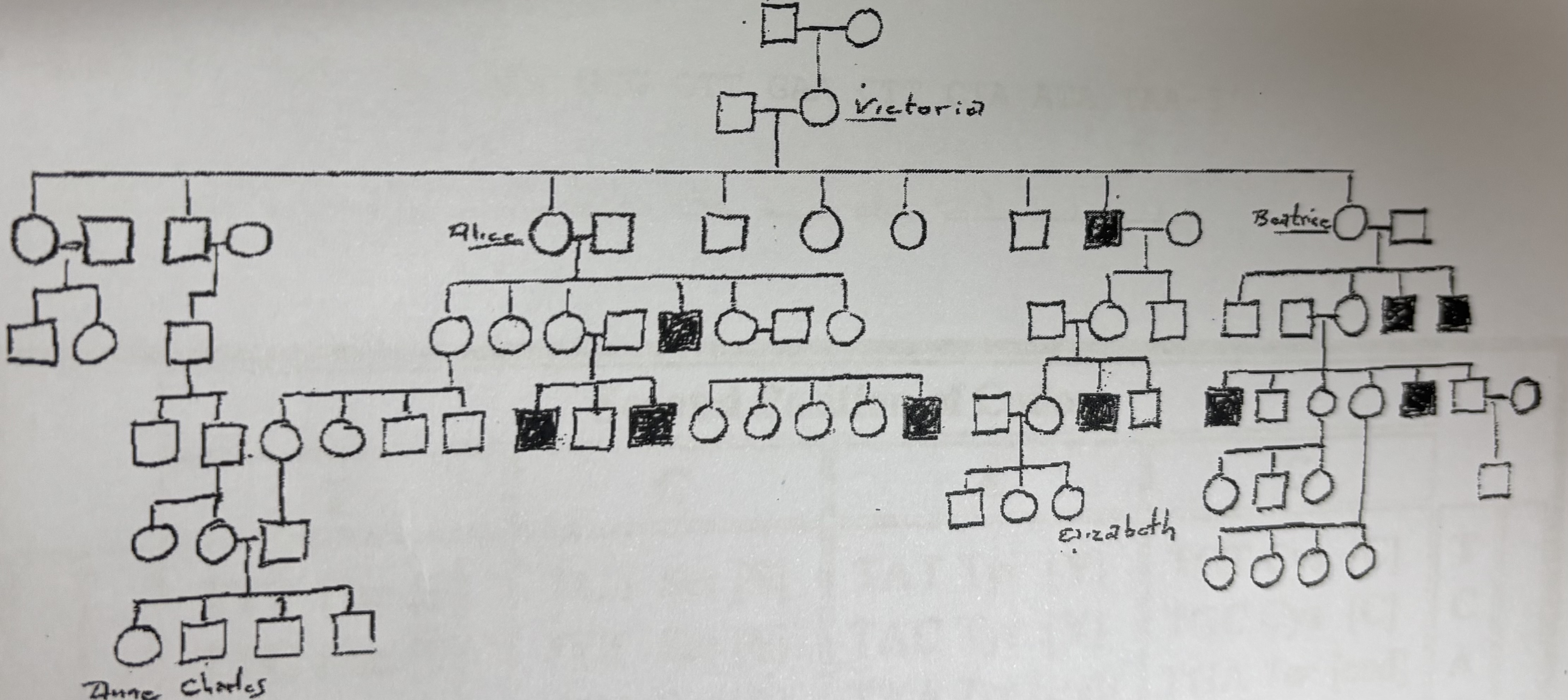
Is Victoria a carrier?
Yes
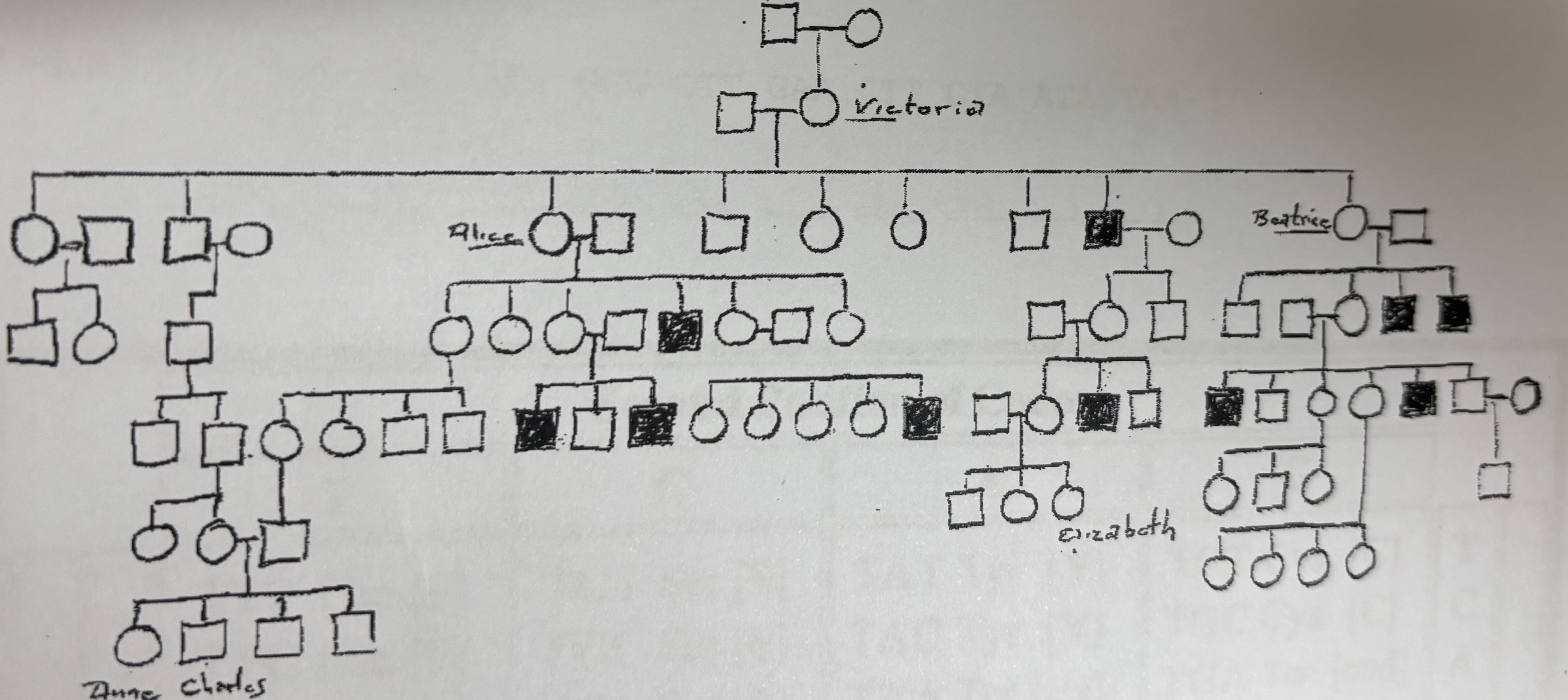
Is Alice a carrier?
Yes
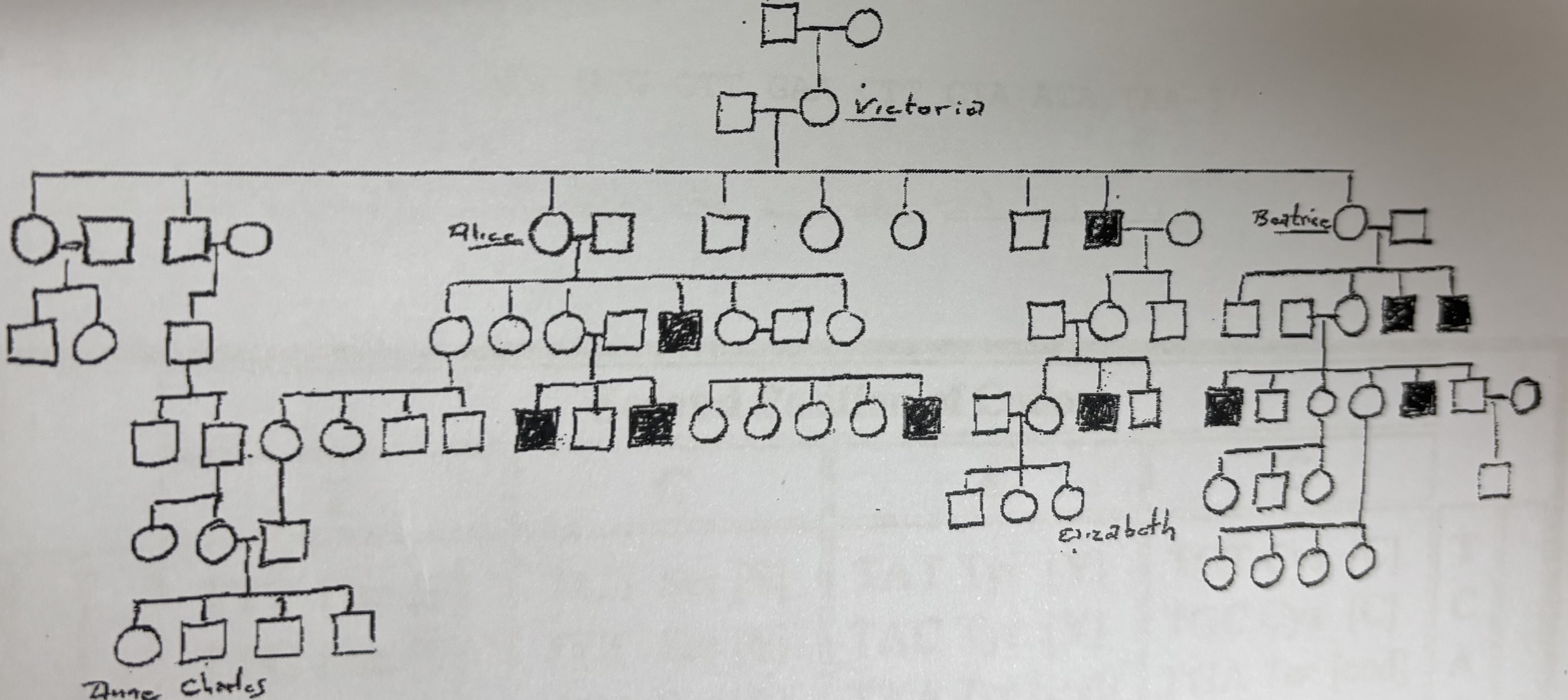
Is Beatrice a carrier?
Yes
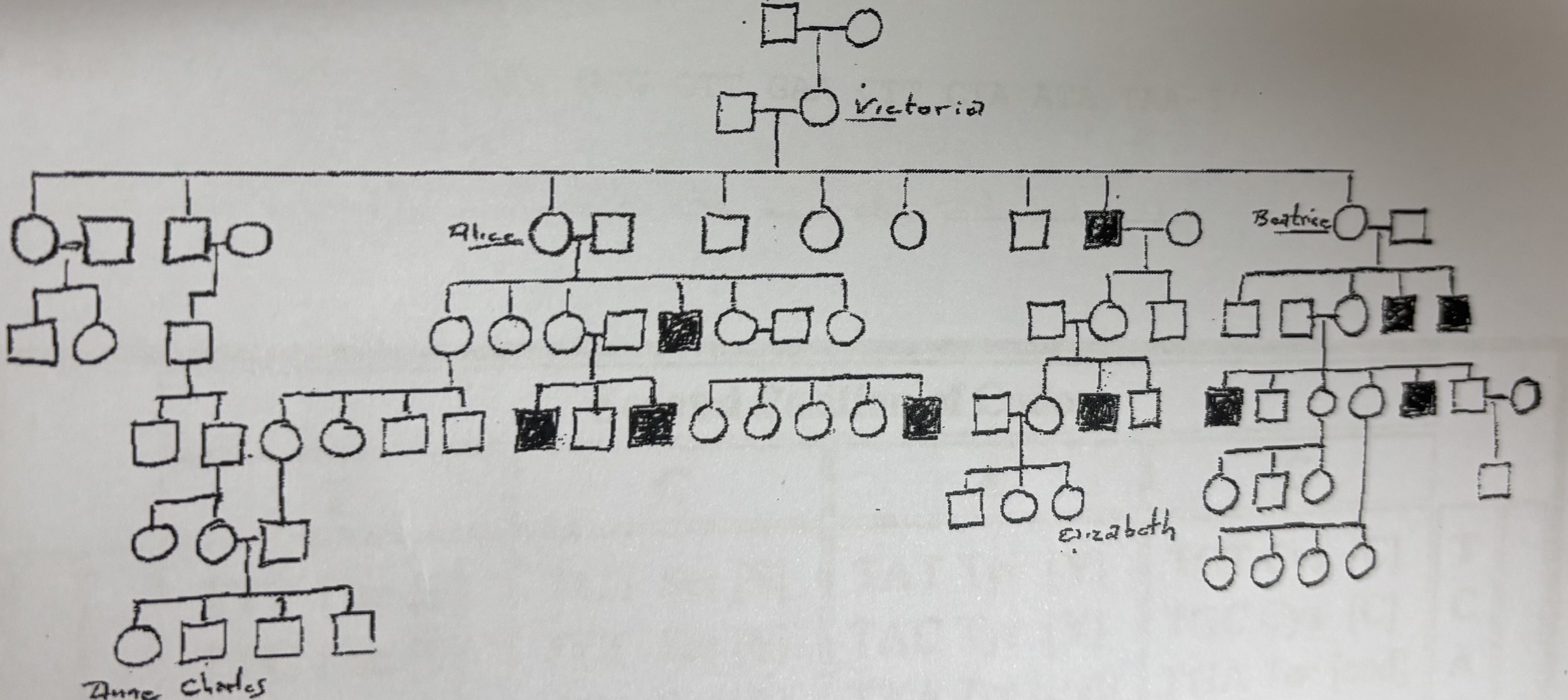
Is Elizabeth a carrier?
Maybe
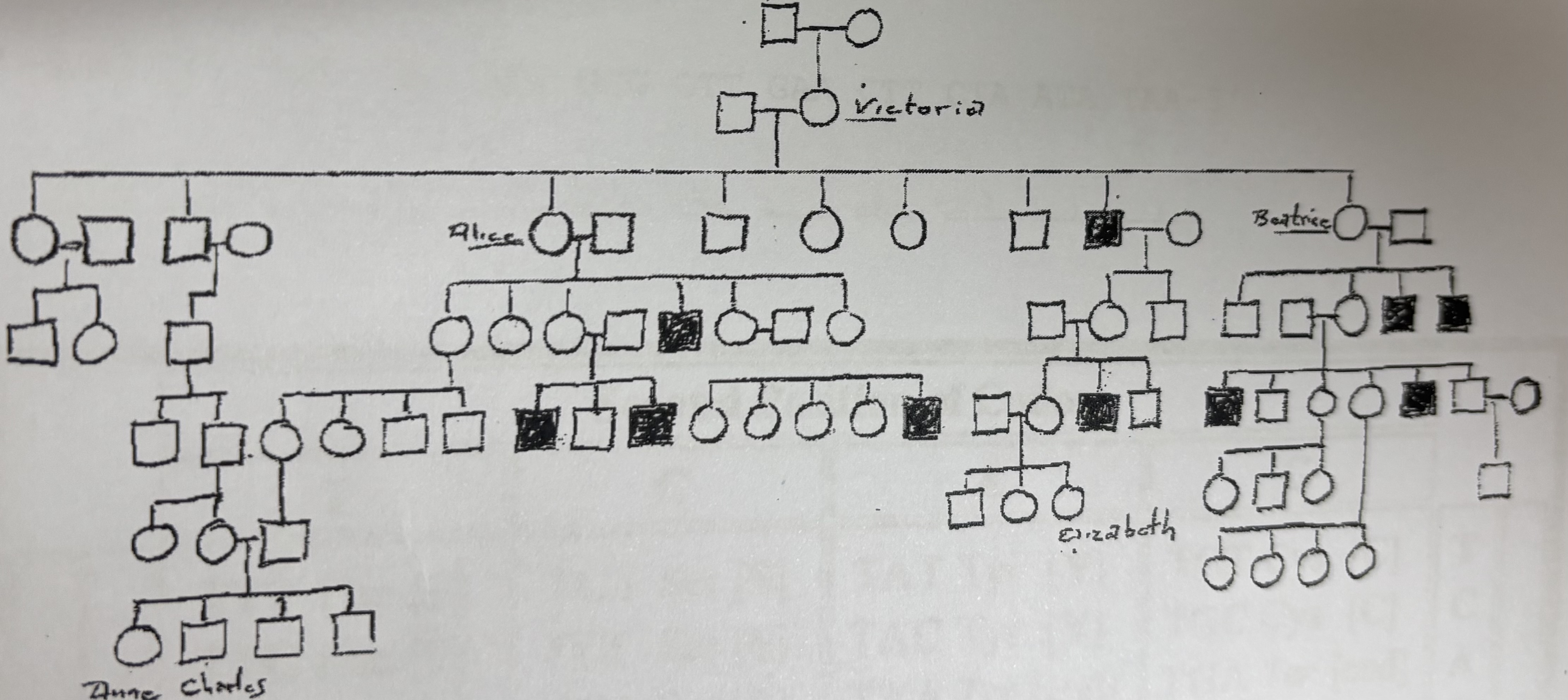
Is Anne a carrier?
No