Chapter 14 Special Topics
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Pharmacology
The study of the sources and uses of chemicals and how they may interact with the human body to treat diseases. Pharmacy is the practice of preparing and dispensing medications.
the study of the origin, characteristics, and effects of drugs. Drugs are obtained from many different sources. Some drugs, such as vitamins, are found naturally in the foods we eat. Others, such as hormones, are obtained from animals. Penicillin and some other antibiotics are developed from mold, which is a fungus. Plants have long since been used for medicinal healing purposes and continue to be a source of many of today’s modern medicines. Many drugs (such as those used in chemotherapy) are synthetic, meaning they are developed by artificial means in a laboratory.
Drug Names
The chemical name describes the chemical formula or molecular structure of a particular drug.
For example, the chemical name for ibuprofen (an over-the-counter pain medication) is 2-p-isobutylphenyl propionic acid.
ibuprofen in our example, is the generic name (or nonproprietary name) and is recognized and accepted as the official name for a drug.
Brand name: motrin, advil, nuprin
prescription drug
can only be ordered by licensed healthcare practitioners such as physicians, dentists, nurse practitioners, or physician assistants
A prescription is the written explanation to the pharmacist regarding the name of the medication, the dosage, and the directions for use.
Rx: name and size of medication
sig: instructions for label (amount, when, how)
disp: number to dispense
over-the-counter drug
A drug that does not require a prescription
How to read a prescription
Refer to Figure 14-1 for an example of a prescription. In this sample, the prescribed drug (Rx) is Tagamet (a medication to reduce stomach acid) in the 800 milligram (mg) size. The instructions on the label are to say (Sig) to take 1 (1˙) by mouth (po) three times a day (tid). The pharmacist is to dispense (disp) 30 tablets (#30). The prescription concludes by informing the pharmacist to refill the prescription two times and another medication may be substituted. Each prescription must contain the date, physician’s name, address, and Drug Enforcement Administration number as well as the patient’s name and date of birth. The physician must also sign their name at the bottom of the prescription. A blank prescription cannot be handed to a patient.

route of administration
The method by which a drug is introduced into the body
Abbreviations Prescriptions
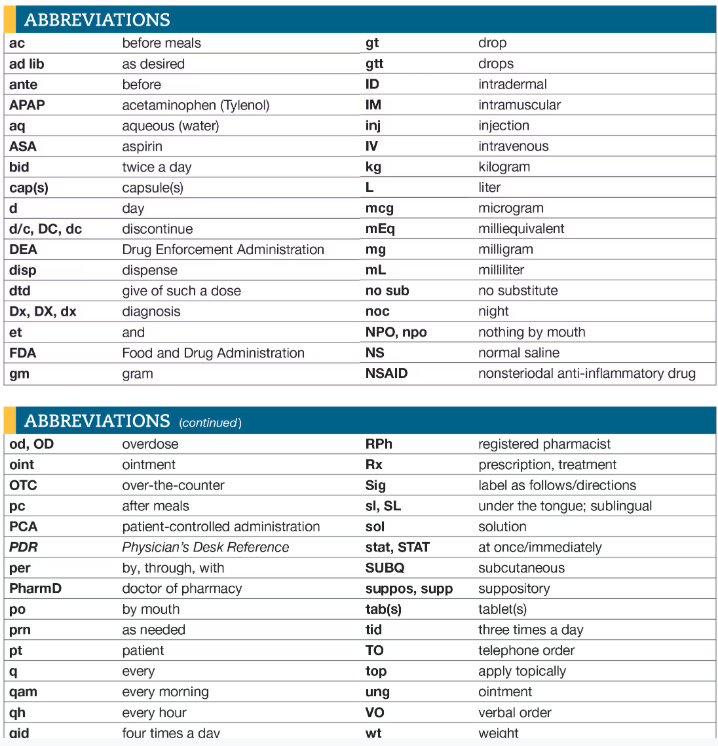
Abbreviations for Eyes and Ears

Example Prescription with Abbreviations

Mental Health