Atomic Theory Timeline: From Democritus to Modern Electron Cloud Models
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Who was the first philosopher to propose the idea of indivisible matter?
Democritus, who named the smallest piece of matter 'atomos'.
What did Aristotle believe about the composition of matter?
He believed all matter was made of four elements: fire, air, water, and earth.
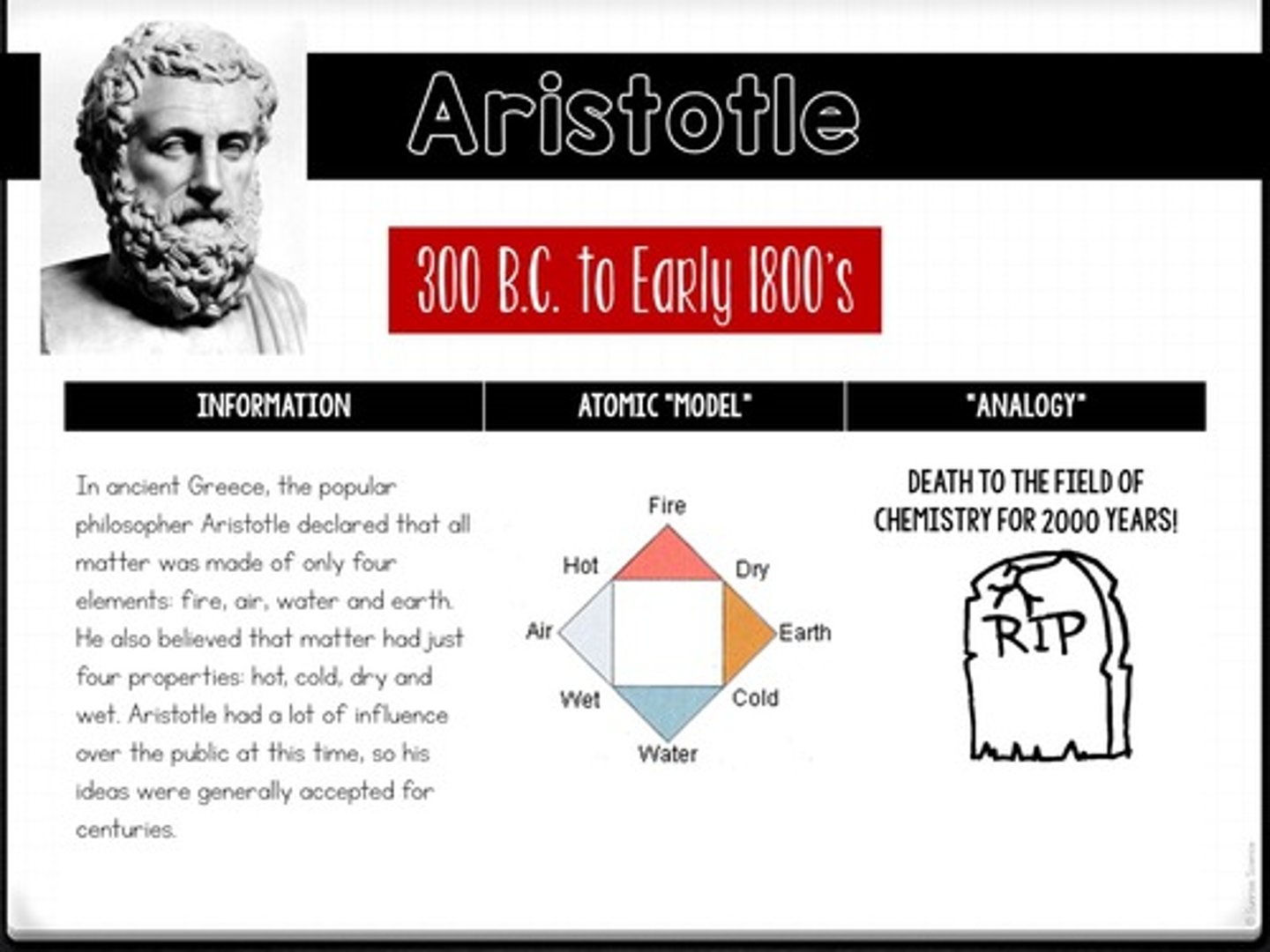
What was the impact of Aristotle's ideas on the field of chemistry?
His ideas dominated for centuries, leading to a 'death' of chemistry for 2000 years.
What did John Dalton contribute to atomic theory in 1803?
He formulated the first atomic theory since Aristotle, stating that all matter is made of atoms that are indivisible and indestructible.
What analogy did Dalton use to describe his atomic model?
He used the billiard ball analogy, suggesting that atoms are solid and indivisible.

What significant discovery did J.J. Thomson make in 1897?
He discovered the electron, a negatively charged particle within the atom.
What was Thomson's atomic model called?
The 'plum pudding' model, where electrons are scattered in a positively charged substance.
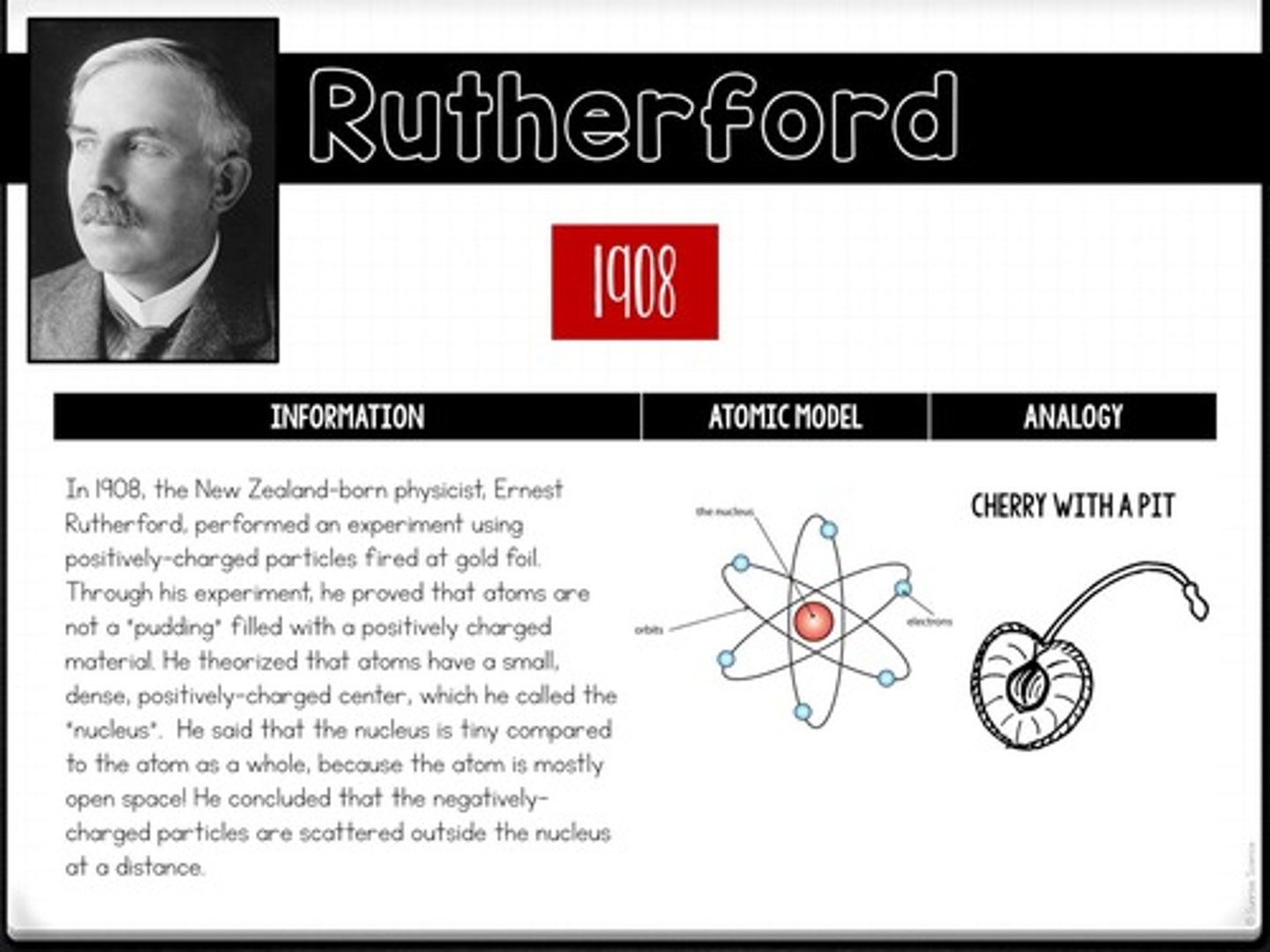
What experiment did Ernest Rutherford conduct in 1908, and what did it reveal?
He fired positively charged particles at gold foil, proving that atoms have a small, dense nucleus.
What analogy did Rutherford use to describe his atomic model?
He compared the atom to a cherry with a pit, where the pit represents the nucleus.
What was Niels Bohr's contribution to atomic theory in 1913?
He proposed that electrons move in definite orbits around the nucleus, similar to planets around the sun.
What analogy did Bohr use for his atomic model?
The solar system analogy, where orbits represent energy levels of electrons.
What does the Modern Cloud Theory state about electron movement?
Electrons move at high speeds in an electron cloud around the nucleus, not in fixed orbits.
Who were some of the key scientists involved in the development of Modern Cloud Theory?
Schrodinger, Heisenberg, Einstein, and many others.
What analogy is used to describe the Modern Cloud Theory?
The cotton ball analogy, representing the electron cloud surrounding the nucleus.

What did Democritus believe about the divisibility of matter?
He believed matter could be divided until reaching the smallest indivisible piece.
How did Dalton's theory differ from Aristotle's view of atoms?
Dalton proposed that atoms of different elements are distinct, while Aristotle believed in four elements.
What was the significance of Rutherford's discovery about the atom's structure?
He showed that atoms are mostly open space with a dense nucleus, challenging previous models.
What was the main focus of Bohr's atomic model?
The arrangement and movement of electrons in specific orbits around the nucleus.
How did the understanding of atomic structure evolve from Dalton to Modern Cloud Theory?
It progressed from solid, indivisible atoms to a complex model with electrons in a cloud.
What role did technology play in the development of atomic theory?
New technologies allowed for advancements in understanding atomic structure over time.
What was the general public's perception of Aristotle's ideas during his time?
His ideas were widely accepted due to his influence, despite being incorrect.
What is the main difference between Bohr's and Modern Cloud Theory's view of electron locations?
Bohr's model has fixed orbits, while Modern Cloud Theory describes electrons in a probabilistic cloud.
What was the impact of Thomson's discovery on the understanding of atomic structure?
It introduced the concept that atoms are made of smaller particles, leading to further developments in atomic theory.