cell transport
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (hypertonic solution -> hypotonic solution)
osmosis
The movement of water across the cell membrane
(hypotonic -> hypertonic)
osmotic pressure
The force exerted by the water within the animal cell (osmosis)
turgor pressure
The force exerted by the water within the plant cell against the cell wall
plasmolysis
cell membrane shrinking away from cell wall when placed in a hypertonic (high solute concentration) environment, → wilting
crenation
plasmolysis in red blood cells
hypertonic
High solute concentration solution (high solute; low water)
hypotonic
Low solute concentration solution (high water; low solute)
isotonic
Same solute concentration solution
phagocytosis
Cell eating, when the cell membrane engulfs solids/more extensive materials
pinocytosis
Cell drinking, when the cell membrane forms vesicles around liquids
receptor-mediated endocytosis
Receptors on the membrane have to bind to the substance for it to move into the cell.
endocytosis
A type of transport where a cell takes in food/liquid
exocytosis
A type of transport where a cell pushes food/liquid out of the membrane.
solute
being dissolved by solvent
solvent
dissolving solute
concentration
amount/percentage of something in a substance
facilitated diffusion
Transport proteins within the membrane help move molecules across the cell membrane (passive transport)
active transport
Transport that requires ATP energy
passive transport
Transport that does not require ATP energy
semi permeable
When the cell only allows some substances to pass through it but not others.
equilibrium
When molecules are spread evenly throughout an area, an equilibrium is balance, and diffusion stops
contractile vacuole
Organelle within the cell that helps pump out excess water, preventing the cell from over-expanding.
helps w osmosis in plants
homeostasis
Maintaining biological balance, stable
cell membrane
Made up of a phospholipid bilayer, it helps move things in and out of the cell.
sodium/potassium protein pump
carrier protein has space for 3 sodium - phosphate group attaches, carrier changes shape and releases 3 sodium - new shape: can hold 2 potassium - phosphate group releases, carrier back to original shape - releases potassium - repeat
A form of active transport uses ATP
Pumps sodium out of the cell, and potassium into the cell
For every 3 sodium ions out, 2 potassium ions in
Used to set up transporting messages along a nerve cell
protein pump
USES ENERGY (against gradient)
Any protein embedded in the cell membrane that pumps ions and solutes across the membrane.
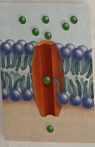
channel proteins
allow substances to pass through the membrane via a channel
Energy NOT required ❌
Very SPECIFIC (each protein transports only 1 kind of molecule)
NO shape change
Ex: Aquaporin moves water molecules faster into the cells
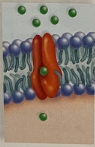
carrier proteins
transport substances by changing shape
Energy IS required ✅ (from ATP - energy storing molecule)
Changes shape & interacts to transport across the membrane
Also SPECIFIC: (each protein transports only 1 type of molecule)
Ex: Sodium & Potassium carrier proteins move sodium and potassium into the cells
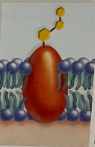
cell recognition proteins
Help antibodies identify which cells are foreign invaders or not by telling them that they are part of the body's self-protein (recognize foreign invaders)
Ex: Glycoproteins in the cell membrane, carbohydrate on top
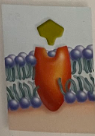
receptor proteins
has a unique shape that allows a specific molecule to dock at it & it transmits a signal to the cell
Ex: insulin receptor proteins in the liver

enzymatic protein
Speed up chemical reactions needed for the cell, substrate -> product
Ex: Membrane enzymes involved in metabolism
junction protein
holds different membranes together & links cells
integral protein
protein embedded through the membrane
peripheral protein
protein on the edge/side of a membrane
function of cholesterol in membrane
keeps cell strong/holds shape
glycolipids
Lipids that attach to carbohydrate chains
glycoproteins
proteins that attach to carbohydrate chains
function of glycolipids/glycoproteins
tells immune system not to attack tissue (cell recognition)
transport proteins
General term for carrier and channel proteins
types of passive transport
Diffusion, facilitated diffusion (channel proteins), osmosis
types of active transport
Na K pumps, endocytosis, exocytosis, carrier proteins
can diffuse through membrane - protein not required
Small gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide), water, non-charged molecules
cannot diffuse through membrane - protein required
Charged molecules + ions, macromolecules, viruses
salt water/onion lab reaction
After the saline solution was added to the onion, the plant cells shrunk because they were placed in a hypertonic solution, extracting water from the cells.
human cells
0.9% salt, 99.1% water
pump/concentrate (generally)
suggest active transport when discussing transport across the cell membrane.
osmosis occurs towards the
hypertonic solution (low water)
simple diffusion
type of passive transport: substances don’t need transport protein, can diffuse through membrane
why does osmosis flow towards hypertonic solutions?
to reach the equilibrium, to balance water
why do you get dehydrated when consuming salt?
The salt you consume (hypertonic) attracts the water from the body cells (hypotonic) to that salt, resulting in dehydration of your body.