DECA Marketing Exam Studying
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Compiled flashcard set of common questions I get wrong and terms I often forget.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Information system
Combination of software, hardware, and telecommunication networks to collect useful data, especially in an organisation
Ownership investment
Becoming a partial owner of a company or piece of property through the purchase of investments such as stock, real estate properties, bullion
Money market account (MMA)
Interest-bearing account at a bank or credit union
Installment credit
Credit that is granted on condition of its repayment at regular intervals, or installments, over a specified period of time until paid in full
Revolving credit
An open-ended credit account that can be used and paid down repeatedly as long as the account remains open ex. Credit cards
Trade credit
Type of commercial financing in which a customer is allowed to purchase goods or services and pay the supplier at a later scheduled date
Bilateral contract
A contract in which both parties exchange promises to perform
Executed agreement
Agreements that have passed the signature stage and have been approved by all parties involved
Exempt contract
Limits the liability of one party in the case of a breach of contract or contract default
EDI
Electronic Data Interchange
PLU
Price look ups
Commercial bank
Banks for individuals and businesses
Investment bank
Wealth management, help people grow their money, stocks and bonds
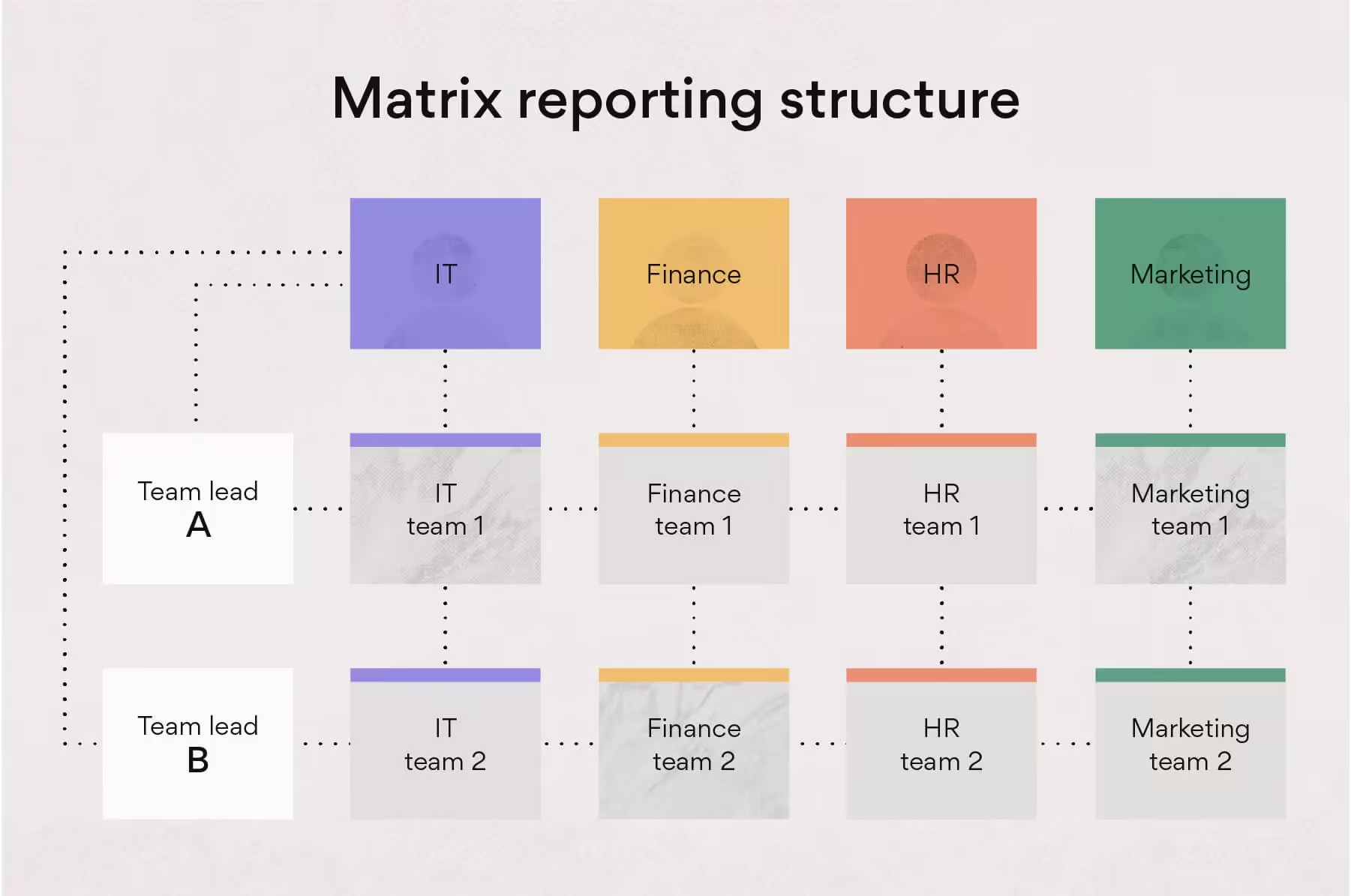
Matrix organizational structure
Model where employees report to multiple managers, blending traditional functional hierarchies with project-based teams, creating a grid-like reporting system for better cross-functional collaboration and flexible resource allocation
Acquired needs theory
States that a person's buying behaviour is influenced by achievement, power, and affiliation
Copy (in an advertisement)
Contains the sales message
Mutual funds
A pool of money managed by a professional Fund Manager. It is a trust that collects money from a number of investors who share a common investment objective and invests the same in equities, bonds, money market instruments and/or other securities
Push money
A direct payment of money offered to the sales force of a reseller by a manufacturer to encourage greater efforts with a particular product or range
The profit and loss statement
A summary of the total income and expense of a business for a period of time
Commodity
Any good or service that is interchangeable with another good or service of the same type with little to no differentiation between producers, such as wheat, oil, or freight services. In marketing, commodities are "price-driven" rather than "brand-driven.”
Snowball sampling
A recruitment technique in which research participants are asked to assist researchers in identifying other potential subjects
Stratified random sampling
A type of sampling method in which the total population is divided into smaller groups or strata to complete the sampling process
Systematic random sampling
Researchers must determine the skip interval. selects every nth member (e.g., every 10th customer) from a population list after a random start, offering a structured, efficient, and representative alternative to simple random sampling
Simple random sampling
Every member of a target population has an equal, non-zero chance of being selected for a survey or study. Subjects are chosen completely at random (e.g., computer-generated random numbers or a lottery method). Ideal for market research, such as surveying a random 100 customers from a database of 10,000 to measure product satisfaction.
SUGGING and FRUGGING
Unethical marketing practices where companies disguise sales or fundraising efforts as legitimate market research to manipulate consumers. "Sugging" stands for Selling Under the Guise of research, while "frugging" stands for Fundraising Under the Guise of research, both of which erode public trust in surveys
Accrual accounting method
A record of revenue or expenses that have been earned or incurred but have not yet been recorded in the company's financial statements
Specialty advertising
Involves giving away gifts in the form of small handy items with the permanent promotional message imprinted on them for the target market
Concurrent engineering
A method of designing and developing products, in which the different stages run simultaneously, rather than consecutively
House of quality matrix
It's focused on providing a clear framework for addressing customer needs, a product planning matrix that is built to show how customer requirements relate directly to the ways and methods companies can use to achieve those requirements.
Lean production
A production methodology focused on eliminating waste, where waste is defined as anything that does not add value for the customer
Pareto Principle
A familiar saying that asserts that 80% of outputs result from 20% of all inputs for any given event. In business, a goal of the 80-20 rule is to identify inputs that are potentially the most productive and make them the priority
Project charter
Official document that authorizes a project, outline of entire project that has gotten approval from all levels of an organization
Tort
Unlawful acts committed against another business that causes monetary loss
When filing a tort against a business, the plaintiff must establish that the defendant
A. violated the doctrine of sovereign immunity
B. damaged property intentionally
C. conspired with a competitor
D. breached the duty of care
D. breached the duty of care
When reordering merchandise, retailers must compare the financial impact of storing inventory against the __________
ordering costs
Direct response marketing
Goal is to encourage an immediate response from consumers in order to quickly generate new leads. The response can be any action such as visiting a website, making a purchase or even just sharing a post on social media
Data mining
Sorting through large data sets to identify patterns, trends, relationships.
Antitrust laws
Regulations that encourage competition by limiting the market power of any particular firm
Infringement
When one of the contracting parties breaches the terms stated in the contract
Type of law violated when a supplier requires intermediaries to enter into tying agreements
Antitrust laws
What type of retirement plan gives employees little control but guarantees a specific amount for employees
A. Defined contributions
B. Defined benefits
C. 401k
D. Social security
B. Defined benefits
Maxton Mart is being pressured by its vendors to pay for inventory it purchased more than 30 days ago. However, Maxton Mart has not received its accounts receivable from customers. What business record have they failed to monitor successfully?
Cash flow
How can a person determine their personal net worth?
Create a personal balance sheet
A 401(k) is an example of a _______
Defined contribution plan
During the 1920s, the US was experiencing a peak in the business cycle. However, the peak ended in 1930s and a long period of bad economic times began that lasted for nearly 10 years. What phase of the business cycle did the US experience in the 1930s?
Contraction
What is a type of non-probability sampling design
Judgement sampling
Analyzing data with Simpson’s Paradox in mind can help account for
A. unconsidered variables or dimensions
B. inconsistencies in data generalization
C. human error
D. incorrect assumptions
A. unconsidered variables or dimensions
When processing survey results, a marketing researcher may decide to discard the questionnaires that contain errors if the number of ____
unsatisfactory results is low
A commission or bonus is an example of a form of _____
compensation
When an agent legally acts in the best interests of her client, the agent is establishing a ________ relationship
Fiduciary
The purpose of depositing large bills in drop boxes upon receipt is to prevent
A. Robbery
B. Fraud
C. Burglary
D. Pilferage
A. Robbery
An author’s new book is an example of a _________
Platform project
A union member is having problems with management, so they should report their problems to the union’s
A. Mediator
B. President
C. Steward
D. Arbitrator
C. Steward
Which of the following is an idea-generation technique that uses programmed thinking?
A. Forced questioning
B. Mind mapping
C. Attribute listing
D. Synectics
C. Attribute listing
Causal research
Structured, quantitative research design used to test hypotheses about cause-and-effect relationships between two or more variables. Used to determine "why" something is happening, rather than just "what" is happening (which is descriptive research)
Exploratory research
Initial investigation into a topic, used when a problem isn't clearly defined, to gain insights, familiarize researchers with the subject, generate hypotheses, and determine the best methods for future, more conclusive studies
Descriptive research
Describes characteristics (e.g., who is buying) without manipulating variables
Wholesaler vs retailer
A wholesaler sells large quantities of goods at lower prices to businesses (B2B), acting as a bulk middleman between manufacturers and retailers, while a retailer sells smaller quantities directly to individual consumers (B2C) at a marked-up price, focusing on the end-user experience with higher per-unit profit margins
When a government regulatory agency accuses a company of running deceptive advertising, the company voluntarily agrees to stop running the ad without admitting guilt. In this situation the remedy used is _____________
A. a cease and desist order
B. a consent order
C. corrective advertising
D. affirmative disclosure
B. A consent order
When assessing risks associated with an upcoming event, event organizations should acquire input from all levels of management and
A. financial consultants
B. public relations agencies
C. local personnel inspectors
D. vertical staff members
D. vertical staff members
Which of the following is a good reason a business would remove a product from its product mix and replace it with another?
A. the product has become a collectible
B. the product has become a fast seller
C. the company wants to increase its market share
D. the company wants to expand its product line
D. the company wants to expand its product line
Convenience products
Inexpensive product that requires a minimum amount of effort on the part of the consumer in order to select and purchase it. Ex. bread, soft drinks, pain reliever, and coffee. They also include headphones, power cords, and other items that are easily misplaced. Focus on availability, brand recognition, and extensive distribution. If the product is not available when, where, and in a form the consumer desires, the convenience product will fail.
Shopping products
Consumers want to be able to compare products categorized as shopping products. Shopping products are usually more expensive and are purchased occasionally. The consumer is more likely to compare a number of options to assess quality, cost, and features.
Specialty products
So unique that it’s worth it to go to great lengths to find and purchase them. Almost without exception, price is not the principle factor affecting the sales of specialty goods. Ex. some consumers feel a strong attachment to their hair stylist or barber.
Unsought products
Products the consumer never plans or hopes to buy. These are either products that the customer is unaware of or products the consumer hopes not to need. Ex. pest control services and funeral plots.