Lab Midterm (Labs 1-4)
1/65
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What is a spectrophotometer?
an instrument that passes a wavelength of electromagnetic radiation through a solution and measures the amount of the radiation that the solution absorbs (doesn’t let thru) or transmits (lets thru)
What is the range of the electromagnetic spectrum and their wavelengths from most damaging to least?
gamma ray, x-ray, ultraviolet, visible light (380nm-780nm), infrared, microwaves, radio
In lab 1 (colorimetry intro), which spectrophotometer is used?
visible light/colorimeter (range: violet to red)
What is colorimetry/visible spectrophotometry?
a procedure in which a colorimeter is used to analyze the composition of solutions
What is a sunburn the result of cellularly?
the result of skin cell molecules absorbing the UV radiation from the sun
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative properties?
quantitative depends on the amount of something and qualitative depends on the kind of something
What is transmittance?
relationship where the more concentration the solution, the more light that is absorbed and not allowed thru
What is absorbance (A)?
the relative amount of light of a given wavelength that is absorbed by a solution
What is percent transmittance (%T)?
the fraction of light that enters and passes thru the solution w/o being absorbed
Why calibrate the instrument before absorbing the light of the actual substances?
have to “correct” for light absorption of the one molecule by subtracting everything else (container, solvent, other color-producing reagents)
In lab 1 (colorimetry intro), what is the molecule of absorption interest?
riboflavin: yellow, water-soluble vitamin
What is a blank?
used to calibrate an instrument
In lab 1 (colorimetry intro), what is the blank before recording riboflavin wavelengths?
water
How are absorbance (A) and percent transmittance (%T) related?
reciprocally proportional; A=log(1/T)
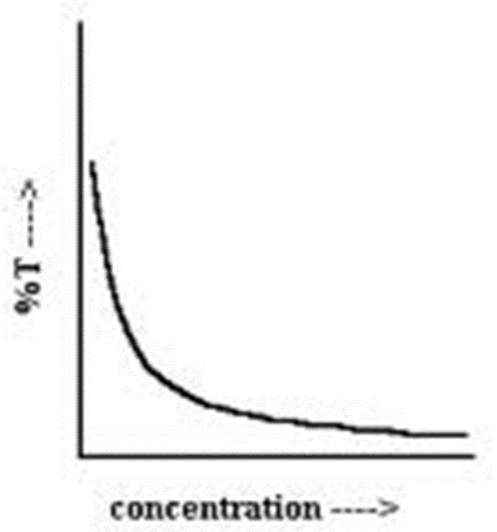
What is riboflavin’s maximum wavelength?
~445nm
How many peaks does riboflavin have? At which wavelengths?
2; ~370nm & ~445nm
Convert mega- (M) to base unit.
1 M = 10^6 base
Convert kilo- (k) to base unit.
1 k = 10³ base
Convert hecto/a- (h) to base unit.
1 h = 10² base
Convert deca- (da) to base unit.
1 da = 10
Convert deci- (d) to base unit.
10^-1 d (0.1 d) = 1 base
Convert centi- (c) to base unit.
1 c = 10^-2 base (0.01 base)
Convert milli- (m) to base unit.
1 m = 10^-3 base (0.001 base)
Convert micro- (µ) to base unit.
1 µ = 10^-6 base (0.000001 base)
Convert nano- (n) to base unit.
1 n = 10^-9 base (0.000000001 base)
Convert pico- (p) to base unit.
1 p = 10^-12 base (0.000000000001 base)
What is the conversion of cups to fluid ounces (fl. oz.)?
1 cup = 8 fl. oz.
What is the conversion of pints (pt.) to cups?
1 pt. = 2 cups
What is the conversion of quarts (qt.) to pints (pt.)?
1 qt. = 2 pt.
What is the conversion of gallons (gal) to quarts (qt.)?
1 gal = 4 qt.
What is the conversion of feet (ft.) to inches (in.)?
1 ft. = 12 in.
What is the conversion of feet (ft.) to yards (yd.)?
3 ft. = 1 yd.
What is the conversion of miles (mi.) to feet (ft.)?
1 mi. = 5280 ft.
What is the conversion of pounds (lbs.) to ounces (oz.)?
1 lb. = 16 oz.
What is the conversion of tons to pounds (lbs.)?
1 ton = 2000 lbs.
What is the conversion of liters (L) to quarts (qt.)?
1 L = 1.06 qt.
What is the conversion of meters (m) to inches (in.)?
1 m = 39.4 in
What is the conversion of pounds (lbs.) to grams (g)?
1 lb. = 453.6 g
In lab 2 (biuret & dilution), what is the molecule of interest?
BSA, bovine serum albumin: an abundant protein in cow blood
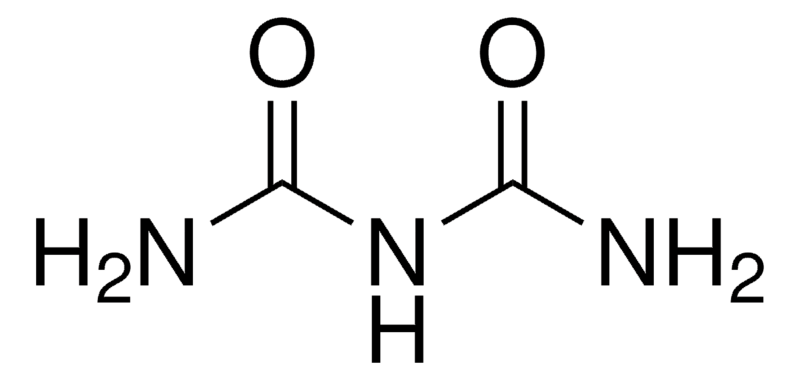
What is biuret? Draw its molecular structure.
small collection of proteins in blood; produces violet color when reacted with CuSO4 and NaOH in aq solutions
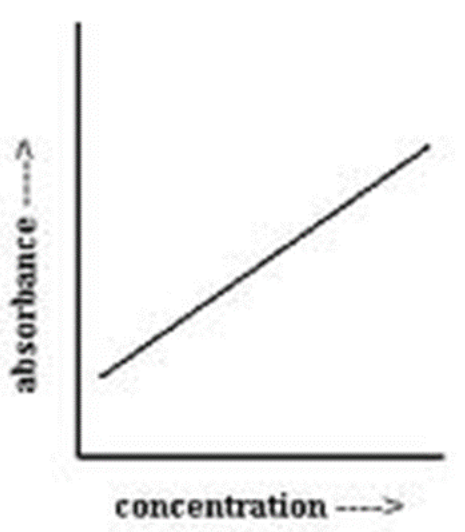
What is the Beer-Lambert law/standard curve?
A=ecl; there exists a concentration range within which there is a direct, linear relationship between solute concentration and absorbance
In lab 2 (biuret & dilution), what is the blank solution for calibration?
KCl and biuret reagent, no albumin since that’s the molecule of interest
How do you title graphs of data?
y-axis (dependent variable) vs. x-axis item (independent variable)
In lab 2 (biuret & dilution), what is the dependent variable (y-axis) and the independent variable (x-axis)?
dependent variable: absorbance
independent variable: solute concentration
Convert 49.5 kg to mg.
49500000 mg = 4.95×10^7 mg
If you dilute 175 mL of a 1.6 M solution of sucrose solution to 1.0 L, determine the new concentration.
C1V1=C2V2
1.0 L —> 1000 mL
(175 mL)(1.6 M)=C2(1000 mL)
C2=0.28 M
If you have 1 mL of a 0.5 M HCl solution and it is diluted by adding 9 mL of H2O, what is the new concentration of your solution expressed as molarity?
C1V2=C2V2
(1 mL)(0.5 M)=C2(1+9 mL)
C2=0.05 M
What is the chemical formula and molecular geometry of methane?
CH4, tetrahedral
What is the chemical formula of ethane?
C2H6
What is diffusion?
the movement of particles (ions or molecules) from areas of high concentration to low concentration
What is passive movement?
diffusion of particles through a selectively permeable membrane
What is dialysis?
type of passive movement with only one solute allowed to pass; selective permeable membrane separate two solutes in the same solution
What is osmosis?
type of passive movement with only water allowed to pass
What are hypertonic solutions?
solutions with much more water absorbed
What are hypotonic solutions?
solutions with much less water; shriveled
What are isotonic solutions?
solutions with a balanced amount of water
Osmotic pressure is a _____ property.
colligative; depends on amount of solute, not the type of solute
_____ bonds hold together the many amino acids of protein.
Peptide
What are isomers?
molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structures/arrangement
There is no _____ _____ at a double bond.
free rotation
What are biological molecules (BIOM)?
molecules that must contain carbon for it’s bonding properties; carbohydrates, fatty acids, fats (triglcerides, triglycerols), phospholipids, steroids, amino acids & proteins
What are alkanes?
made of only methyl function groups (-CH3); hydrophobic, flammable
What are alcohols?
contain hydroxyl functional group (-OH); 1-4 C = hydrophilic (water soluble) and larger alcohols with more methyl groups = hydrophobic
What determines solubility?
having an electronegative charge and h-bonding properties
What are functional groups?
chemical groups that affect molecular function of larger reactions; hydroxyl (OH), carbonyl (C=O), carboxyl (COOH), amine (NH3), methyl (CH3), keytone (end), aldehyde (middle)
What is the difference between cis and trans isomer structures?
cis —> \=/ and trans —> \=\