MSK UE & Gait
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
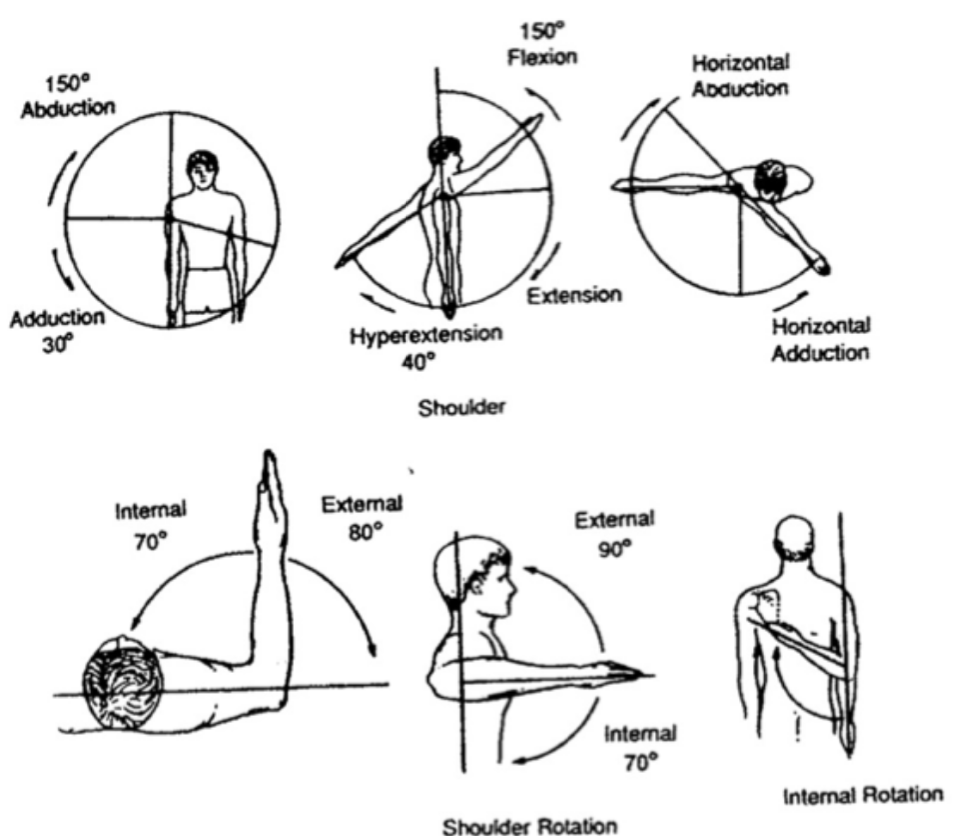
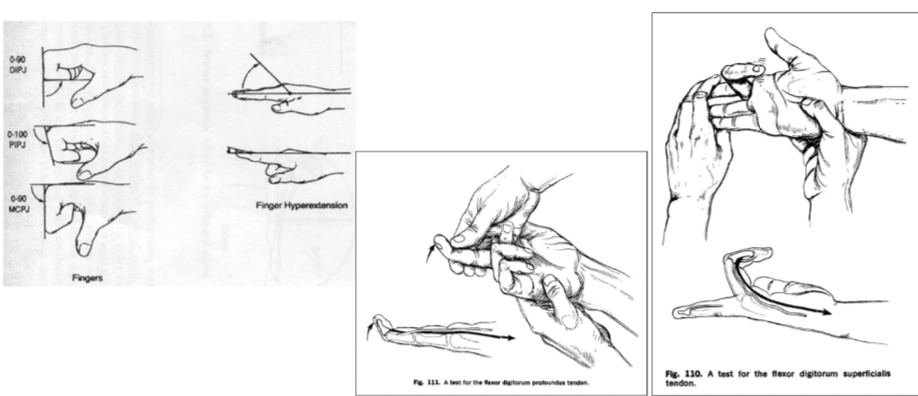
ROM of Shoulder
Flexion (1500)
Extension (400)
Internal rotation (700)
External rotation (800)
ABduction (1500)
ADduction (300)
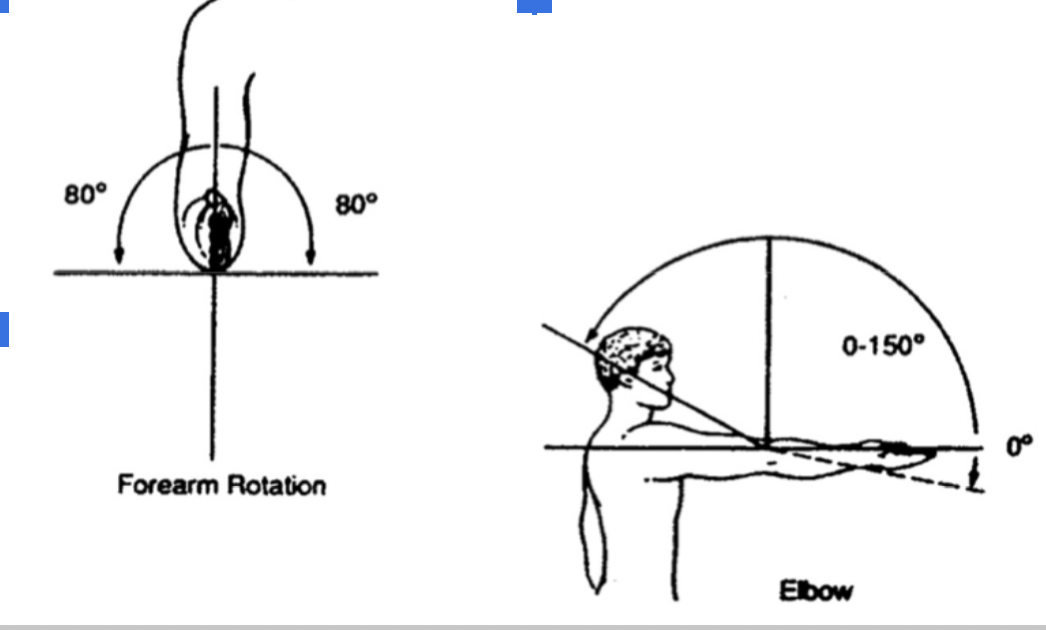
ROM of elbow
Flexion (1500)
Extension (0-50)
Pronation (800)
Supination (800)
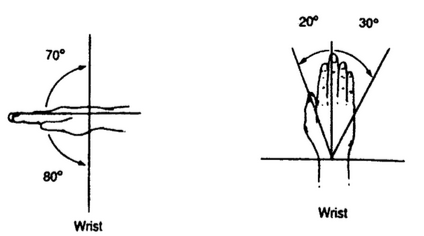
ROM of wrist
Flexion (800)
Extension (700)
Radial deviation (200)
Ulnar deviation (300)
ROM of fingers
ADduction
ABduction
Thumb and small finger opposition
Bony structures and soft tissues of shoulder for palpation
Bony structures (clavicle, scapula, humerus)
Joints/articulation: acromioclavicular joint
Soft tissue
Tendons
muscles
rotator cuff
bursae
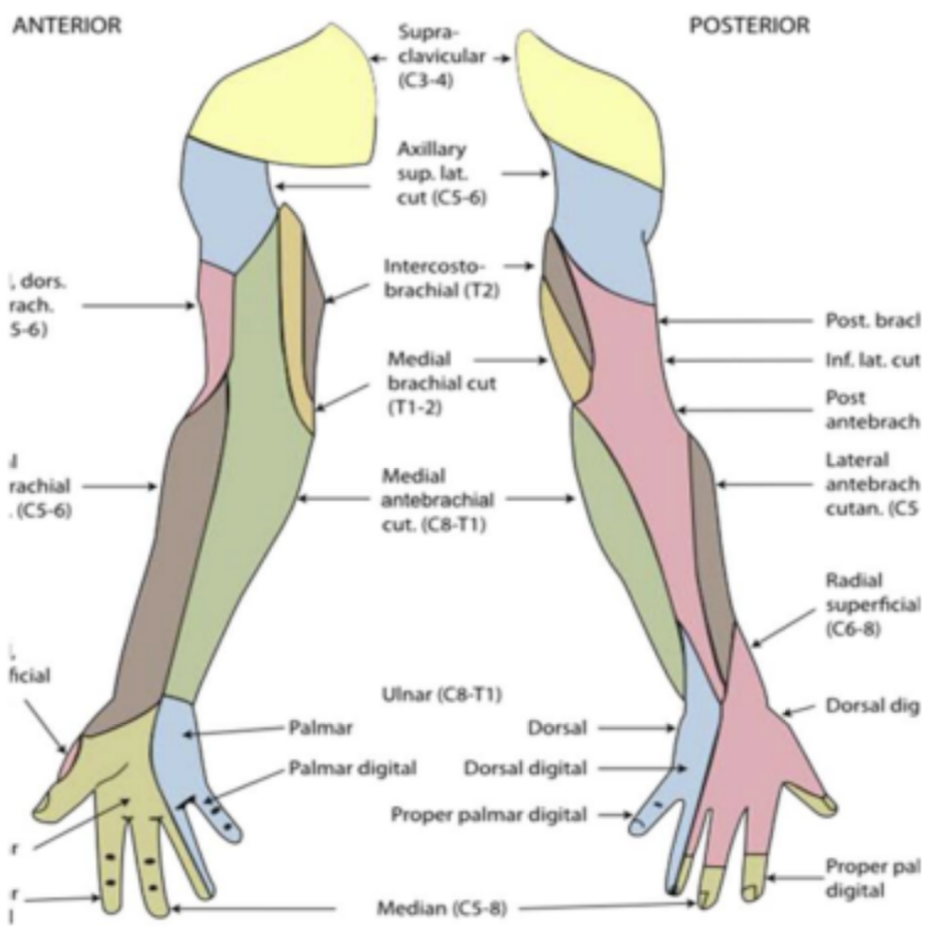
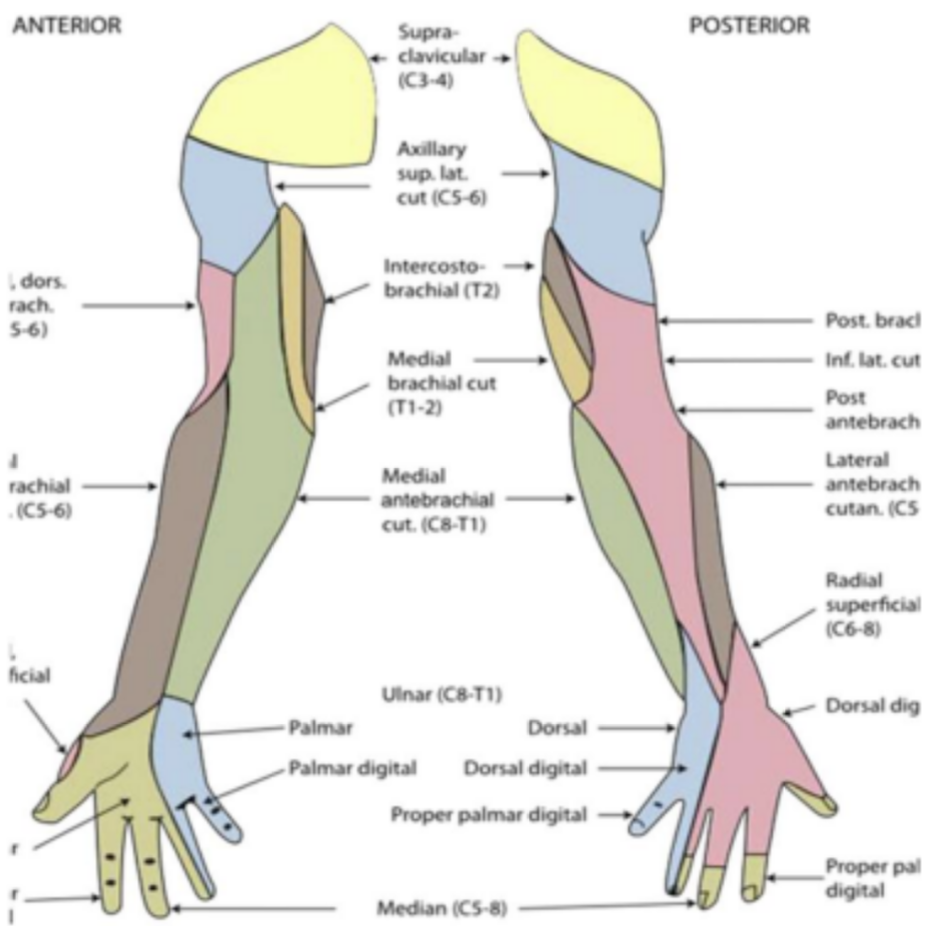
Sensation testing for shoulder
supraclavicular nerve (C3-C4)
axillary nerve (C5-C6)
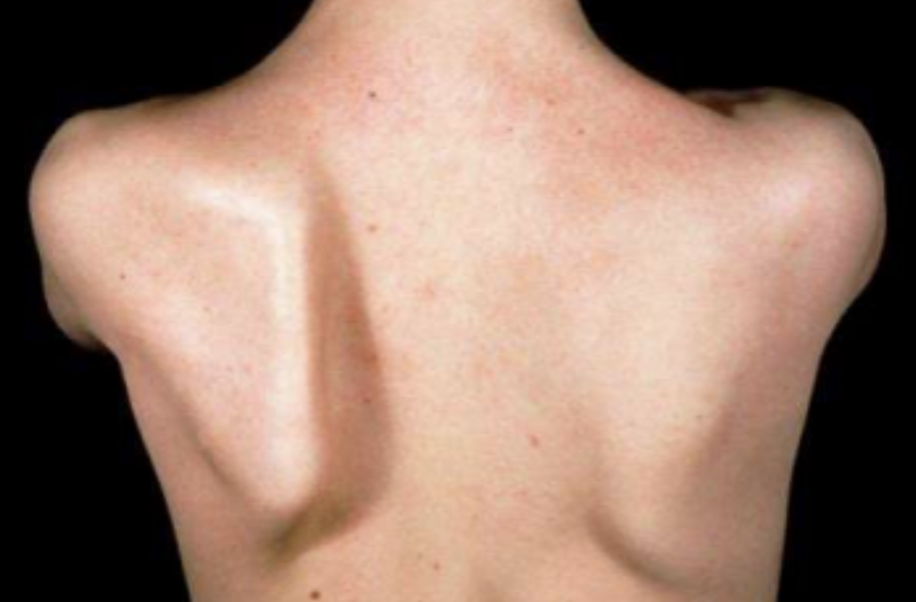
Scapular winging
Identify underlying neuromuscular pathology of serratus anterior
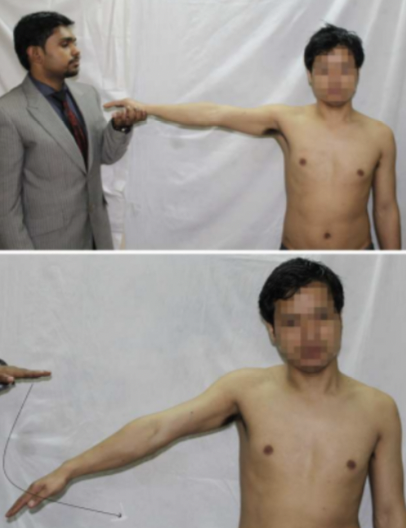
Drop arm test
Identify rotator cuff (supraspinatus) tear
Hawkins test
Identify possible subacromial impingement syndrome
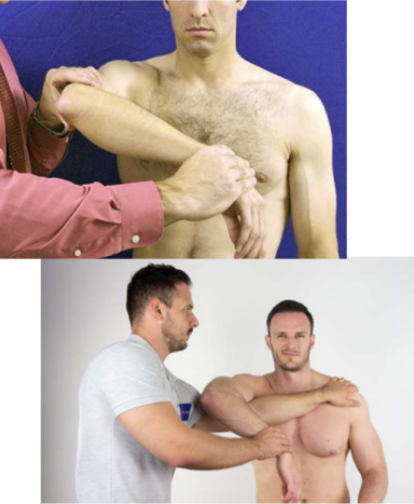
Neer test
Identify possible subacromial impingement syndrome
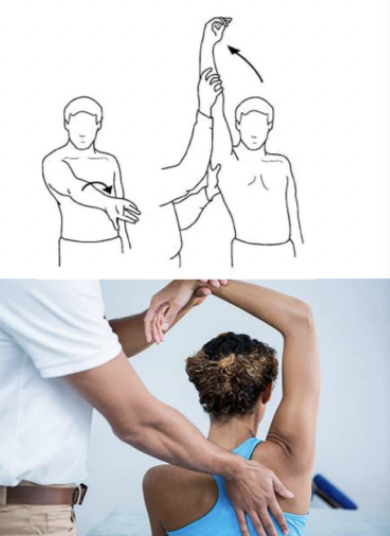
Yergason test
Evaluate for biceps tendonitis or SLAP tear
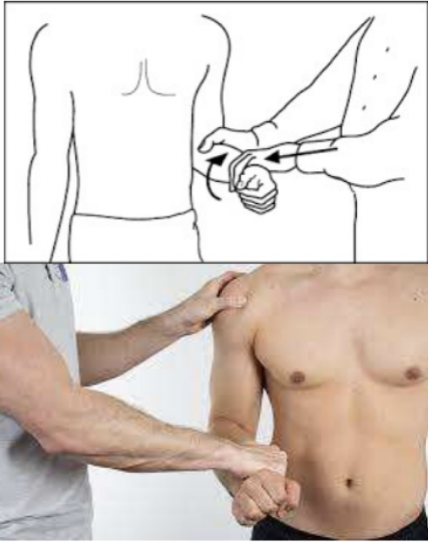
Apprehension test
Tests for Anterior Shoulder Instability
Testing for chronic or ongoing shoulder dislocation
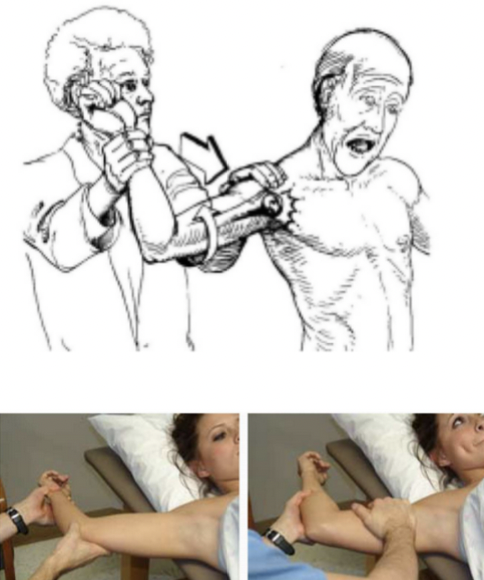
Sensation testing for elbow
Sensation
Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve (C5- C6)
Branch of musculocutaneous nerve
Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve (C8- T1)
Posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve (C5- C6)
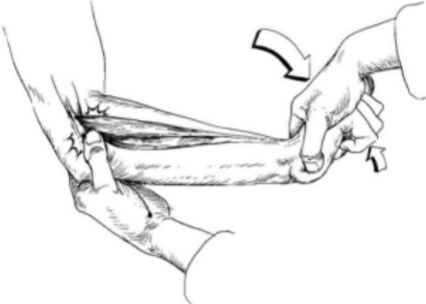
Tennis elbow test
Lateral epicondylitis
Positive test is pain at the lateral epicondyle.
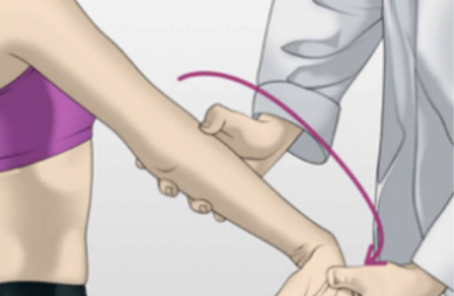
Golfer’s elbow test
medial epicondylitis
Positive test is pain at the medial epicondyle
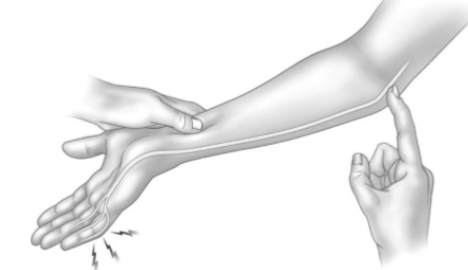
Tinel sign: elbow
Cubital tunnel syndrome (ulnar nerve irritation)
Positive sign is a tingling sensation in the pinky and ring finger
Sensation of wrist, hand & fingers
C6 – test at thumb web space dorsal side of hand
C7 – test at long finger pad tip
C8 – test at little finger pad tip
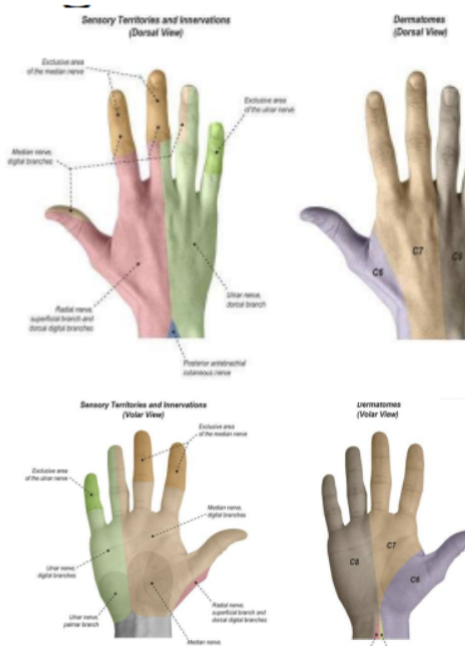
Tinel sign: wrist
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Positive sign is a tingling sensation in the distribution of the median nerve
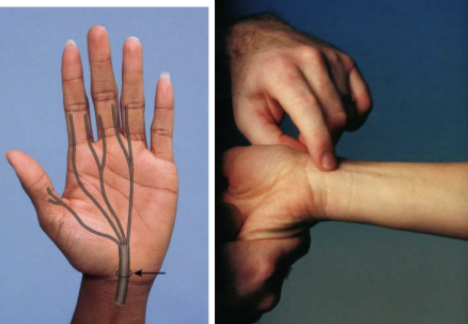
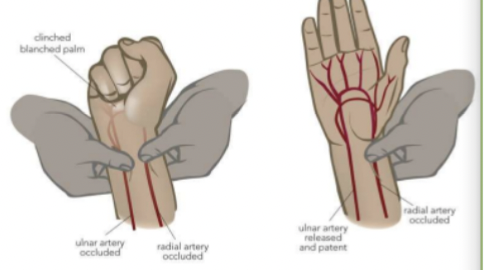
Allen test
Done prior to arterial line/ABG (arterial blood gas) to confirm collateral circulation
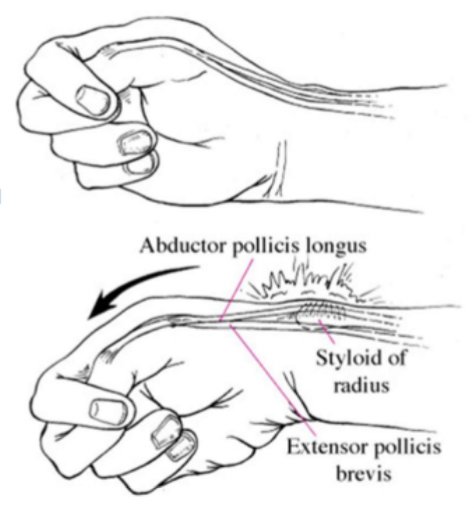
Finkelstein test
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Maneuver designed to elicit pain from the 1st dorsal compartment
Phalen’s test
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
tingling/pain in median nerve distribution
A positive test is tingling and/or pain in the median nerve distribution
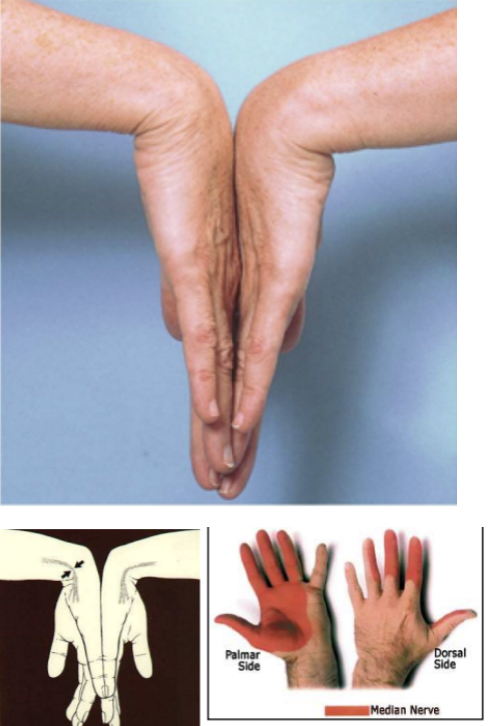
Adson test
Musculoskeletal disorder: Thoracic outlet syndrome
Deep tendon reflexes of upper extremity
Bicep (C5, C6)
Brachioradialis (C5, C6)
Triceps (C6, C7)
Long finger flexors (C8, T1)
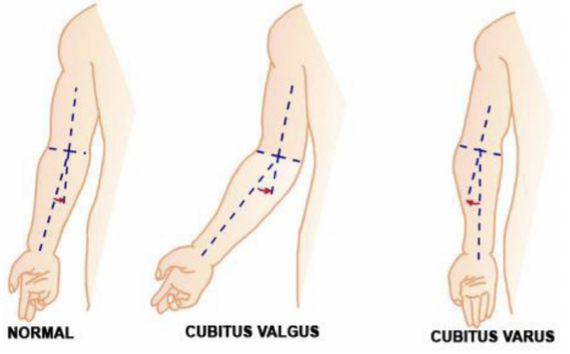
Carrying angle of the elbow
When arms are held out at your sides and your palms are facing forward, forearm and hands should normally point about 5 to 15 degrees away from your body
Primary extensors
Latissimus dorsi
teres major
posterior portion of the deltoid
Latissimus dorsi
Innervation: thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8)
primary extensor & aDductor
Teres major
Innervation: lower subscapular nerve (C5, C6)
Posterior portion of the deltoid
Innervation: axillary nerve (C5, C6)
Primary flexors
Anterior portion of deltoid
Coracobrachialis
Anterior portion of the deltoid
Innervation: axillary nerve (C5)
Coracobrachialis
Innervation: musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6)
ABductors
Middle portion of the deltoid
Suprasinatus
Middle portion of the deltoid
Innervation: axillary nerve (C5, C6)
Supraspinatus
Innervation: suprascapular nerve (C5, C6)
ADductors
Pectoralis major
Latissimus dorsi
Pectoralis major
Innervation: medial and lateral anterior thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C8, T1)
Shoulder sensation testing
Supraclavicular nerve (C3-C4) and axillary nerve (C5-C6)
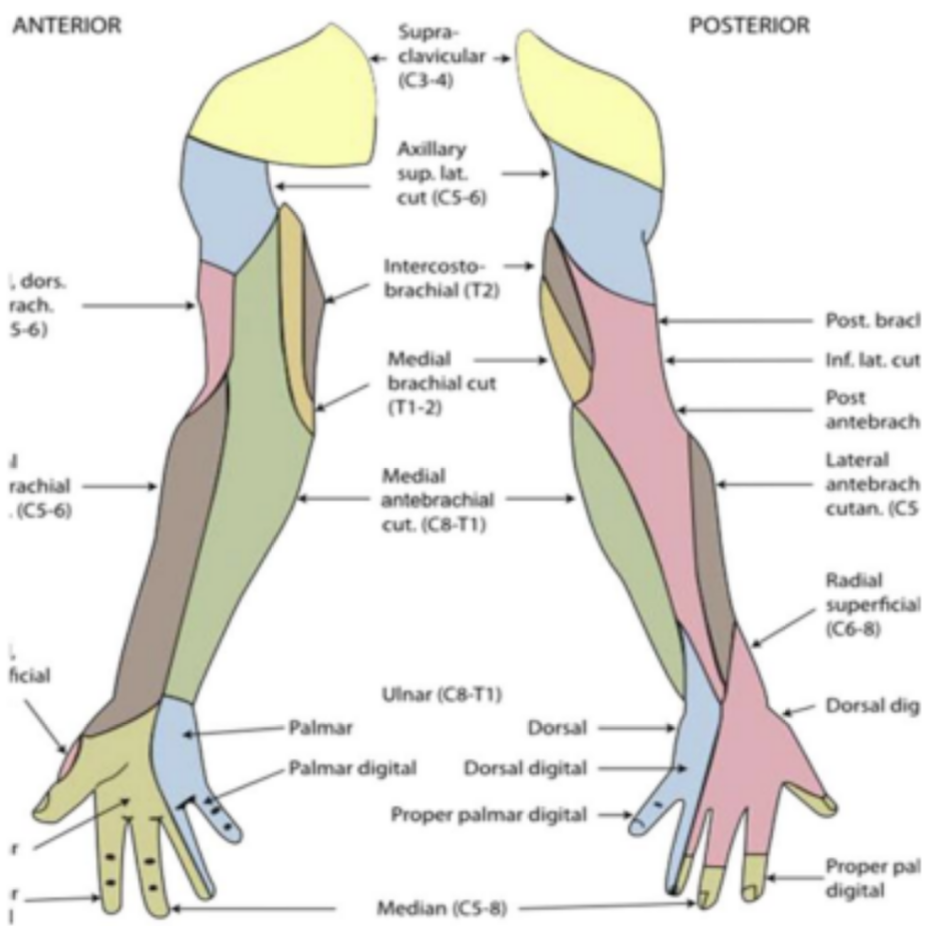
Elbow sensation testing
Lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve (C5-C6)
Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve (C8-T1)
Posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve (C5-C6)
Biceps reflex (C5-C6)
Triceps reflex (C6-C7)
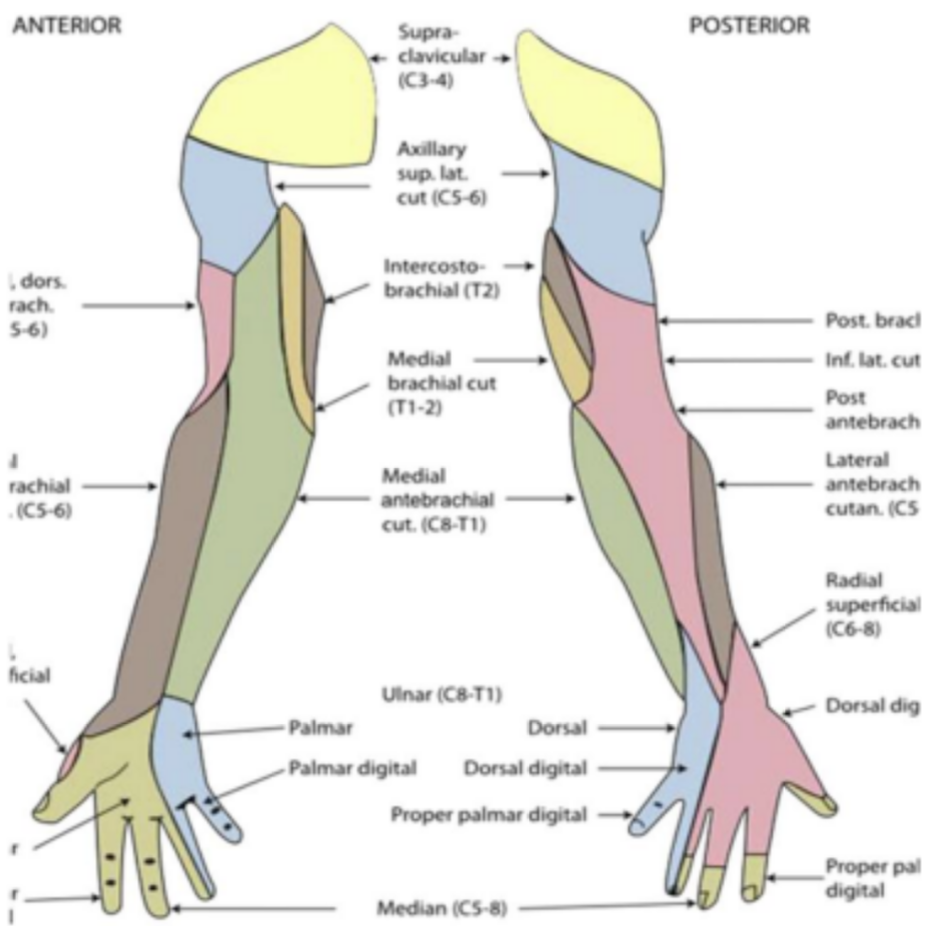
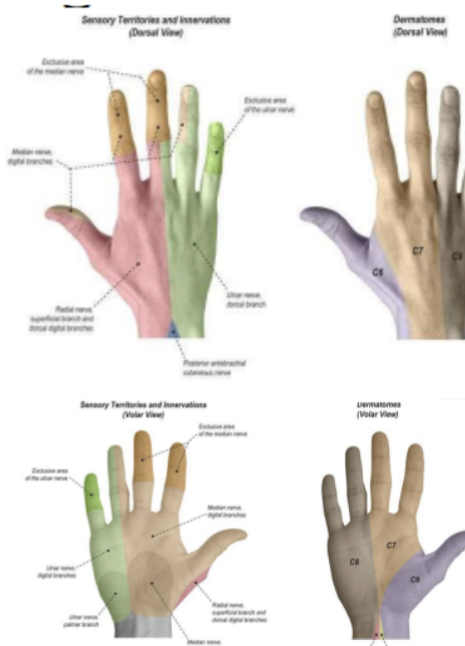
Wrist, hand, fingers sensation
Thumb web space dorsal side of hand (C6)
Long finger pad tip (C7)
Little finger pad tip (C8)
Brachioradialis reflex (C6)
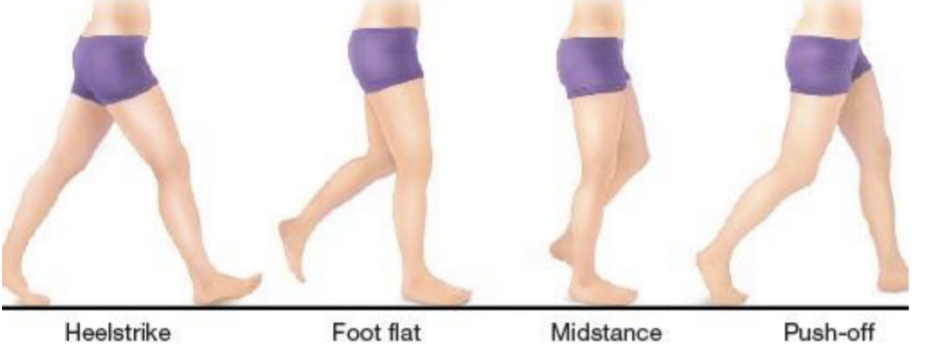
Stance phase
60% of normal cycle = Foot strike, foot flat, mid-stance, toe off
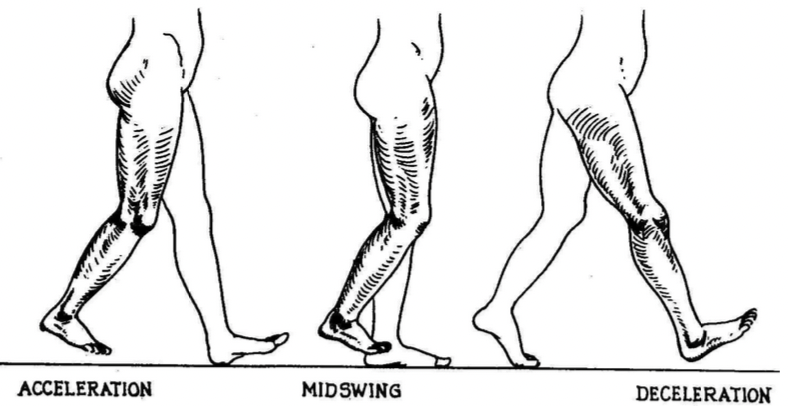
Swing phase
40% of normal cycle = acceleration, mid-swing, deceleration
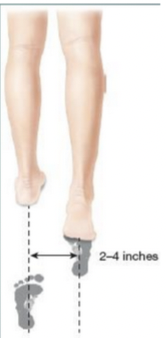
Gait Width and Step Length
Observe patient’s gait width - how far apart the feet are as steps are taken
Normal width is approx. 2-4 inches
Wide-based waddling gaits
Observe step length with each step
Normal length is approx 15 inches
Short-shuffling gaits
Gait abnormalities
abnormal posture
decreased or otherwise altered speed of ambulation
disordered balance
tripping, stumbling or frequent falls
Spastic hemiparesis
stiffness and weakness on one side, awkward and jerky gait
Spastic diplegia
cerebral palsy, causes muscle stiffness in both legs (hypertonia)
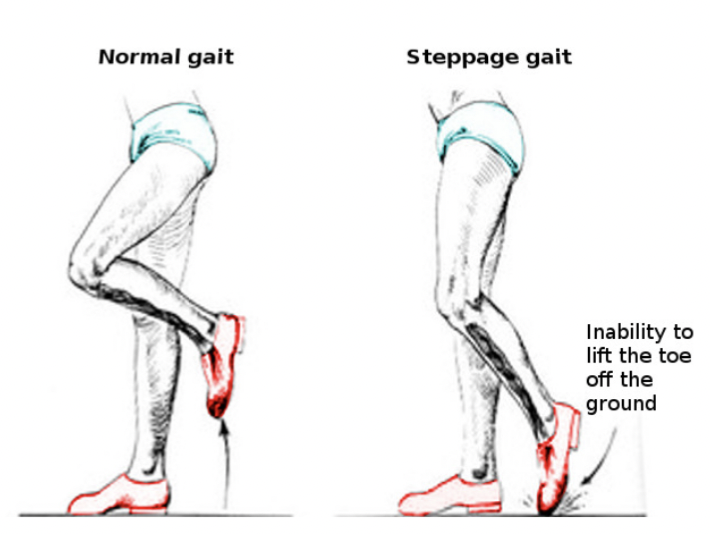
Steppage/ drop foot
walking with a high step, hard to lift food (looks like they’re climbing stairs), foot slaps ground with each step
Ataxia- cerebellar/ sensory
coordination issue, causes increased step width, wide base, and irregularity of steps (slower and shorter strides)

Dystonia
leg and foot points downward and inward, toe curling, involuntary muscle contractions, which causes slow movements and muscle cramps
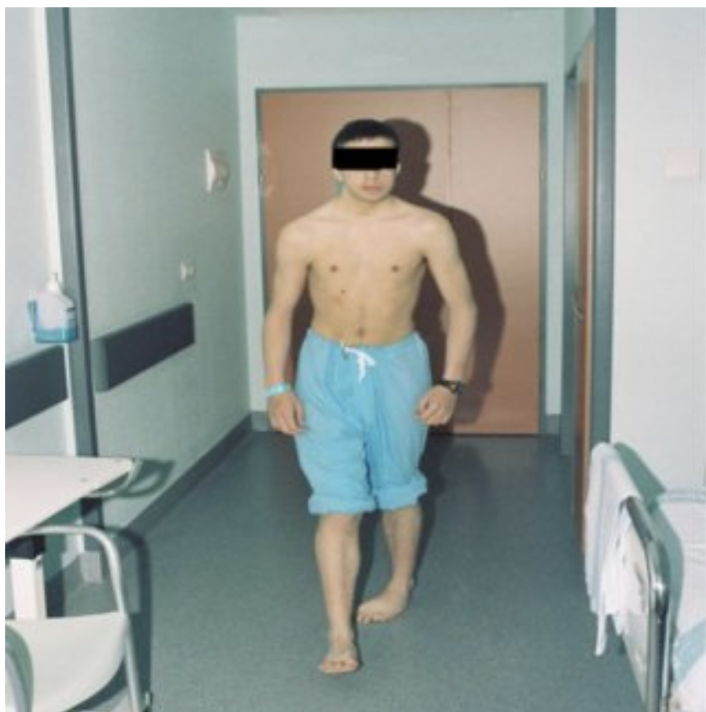
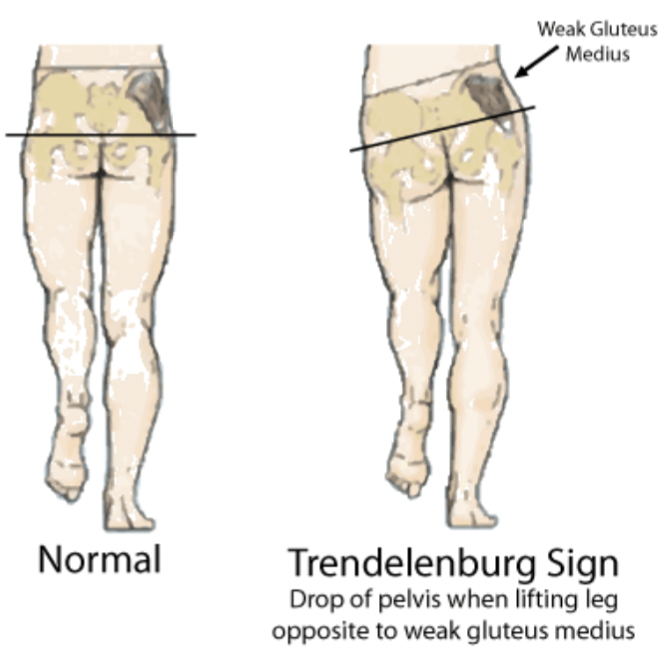
Abductor lurch (Trendelenburg)
uneven pelvic tilt when walking, one gluteus medius muscle significantly weaker and causes whole pelvis to tilt down on opposite
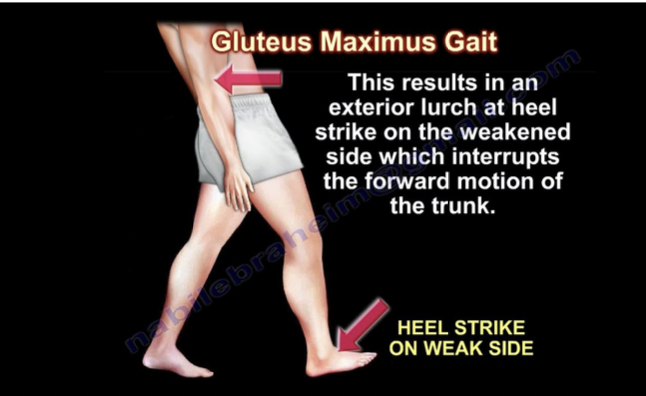
Extensor lurch
uneven pelvic tilt, person appears to be leaning backwards while walking (center of gravity off), weakness on gluteus maximus, heel strikes ground on weaker side
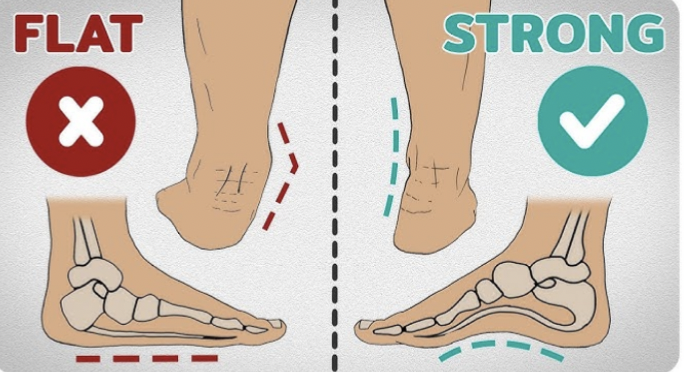
Flat foot
Overpronation (feet rolling inward excessively), feet pointing outward, can over stain muscles involved in foot arch support
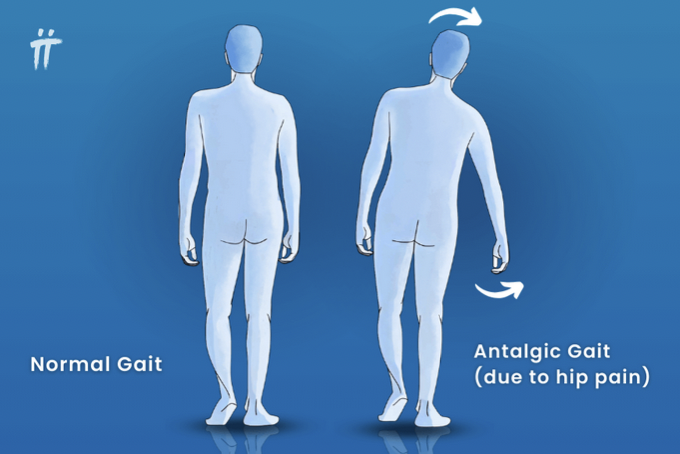
Antalgic
Caused by pain, person is trying to take the weight off the painful side, not put pressure on hurting foot/leg (ex. limp due to injury, arthritis, etc.)