Chapter 12 - Plant Kingdom
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What are characteristics of ALL plants?
multicellular
plastids
cell walls
What are a plant’s organs?
stems, roots, and leaves
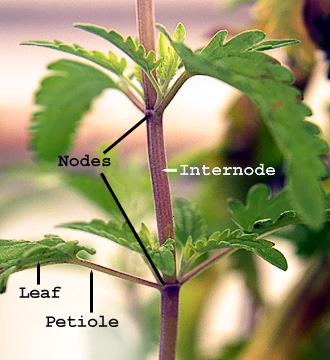
node
A region on a stem where a lead is or was attached

fibrous root systems
root system that consists or many nearly EQUAL-sized roots

lateral root system
the maximum linear distance (one-sided) from the stem of an individual plant reached by its roots.
opposite leaf arrangement
TWO leaves are attached at a node
What is composed in an annual growth ring?
xylem, phloem and the epidermis
xylem
the plant tissue that carries water from the roots to the leaves
What to nonvascular plants contain?
chloroplasts, epidermal cells and plastids
2 main groups of seed plants
gymnosperms and angiosperms
What do angiosperms produce?
fruit
What is the MINIMUM number of leaflets a leaf must have to be a compound leaf?
two
Why can’t nonvascular plants produce seeds?
They need the lowest amount of light for photosynthesis, so overall they are short and lack a vascular system to conduct water and nutrients. And they tend to survive in rather humid places on land and use spores for reproduction. So, instead of producing seeds to reproduce, they use spores.
gymnosperm examples
pine, spruce, cycad, ginko
cellulose
component of plant cell walls
turgor tressure
caused by the presence of water inside plant cells
plastid
a chloroplast, for example
xylem
made primarily of long, hallow cells that transport water
phloem
conducts sugar solution
vascular bundles
arrangements of xylem and phloem in leaves and nonwoody plants
fiber (or fibers)
the type of cell that can be used to make rope or cloth
epidermis
the outermost tissue of leaves, young roots, and young stems
cuticle
a waxy substance secreted by the epidermis
bark
the region of the outside of the xylem in a tree trunk
cork
produced by the cork cambium
vascular
the term for plants that have water-conduciting tissue
rhizoid
the rootlike anchoring structure of mosses
byrophytes
the plant group that contain the true mosses
hornwort
another nonvascular plant besides the mosses and liveworts
frond
a fern leaf
crosier
an immature, coiled fern leaf also known as a fiddlehead
horsetail
a plant which has silica in its cell walls
gynmosperms
the plant group having seeds that re not completley covered
angiosperms
the plant group known as the flowering plants
What branches at the nodes?
a leaf or leaves
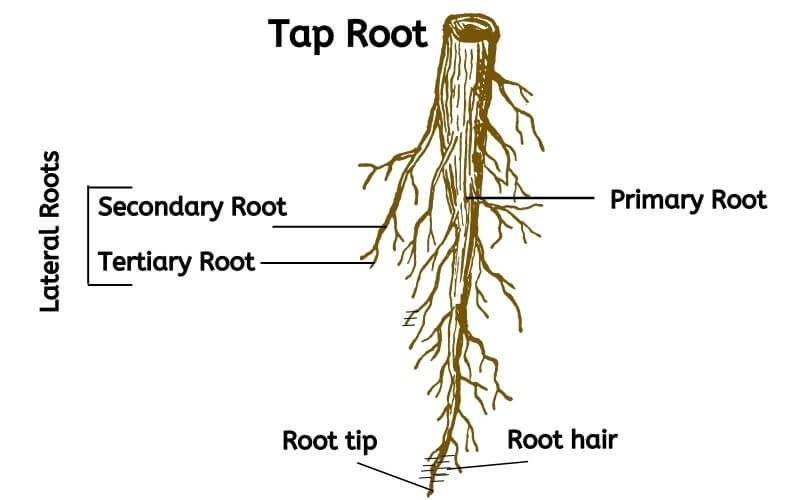
primary root system
The early roots in young plants that consist of taproots, basal roots, and lateral roots. Secondary roots are the side branches of the primary roots.
petiole
the structure that attaches the leaf blade to the node
How do ferns produce?
The male structures release sperm that swim through the film of water of the moist habitat to fertilize the egg in the female structure.
morphology
the shape or form of an organism
anatomy
the bodily structure of an organism
taproot system
one or a few main roots that are thicker and longer than the other roots of the plant
woody stems
stems are the hard and not very flexible
herbaceous stem
the softer and more flexible type of stem
blade
the flat, green part of a leaf
compound leaf
a leaf blade looks like it has several indidual leaves
leaflet
each of the smaller pieces of the blade
veins
water and sugar conducting tissues
parallel venation
leaves that have larger veins that are parallel to each other
palmate ventation
veins on leaves that branch away from the base of the leaf
pinnate venation
leaves with one main vein extending the length of the leaf with smaller veins branching away from it along its entire length
alternate arrangement
a leaf arrangement that has only one leaf attached at a node
opposite arrangement
a leaf arrangement where TWO leaves are at each node
whorled arrangement
a leaf arrangement where two OR MORE leaves are at each node
2 characteristics of plant cells that are important to a plant’s survival
cell walls and pastids
What are cell walls largely made of?
cellulose
chloroplast
an organelle that can convert the sun’s light info food by photosynthesis
photosynthesis
a process by which plants make food
cholorophyll
a pigment that captures light energy
heartwood
old xylem
sapwood
the younger xylem that still carries water
vascular plants
palnts that have vascular tissue
nonvascular plants
plants that not have vascular tissue
The 3 main plant categories that you can put plants into
nonvascular plants
seedless vascular plants
seed vascular plants (or simply seed plants)
sphagnum
peat moss; it is usually used by gardeners as a soil conditioner
Examples of nonvascular plants
liverworts and hornworts
seedless vascular plants
Plants that rely on water more than the seed-producing plants. They require water for the transportation of certain cells involved in sexual reproduction.
fronds
fern leaves
seed plants
Plants that don’t rely on water for sexual reproduction. They reproduce by seeds rather than spores.
fruit
a protective covering for angiosperm plants